 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 ViP3D: End-to-end visual trajectory prediction through 3D agent query
ViP3D: End-to-end visual trajectory prediction through 3D agent query
ViP3D: End-to-end visual trajectory prediction through 3D agent query
arXiv paper "ViP3D: End-to-end Visual Trajectory Prediction via 3D Agent Queries", uploaded on August 2, 22, Tsinghua University, Shanghai (Yao) Qizhi Research Institute, CMU, Fudan, Li Auto and MIT, etc. joint work.

Existing autonomous driving pipelines separate the perception module from the prediction module. The two modules communicate through manually selected features such as agent boxes and trajectories as interfaces. Due to this separation, the prediction module receives only partial information from the perception module. Worse, errors from the perception module can propagate and accumulate, adversely affecting prediction results.
This work proposes ViP3D, a visual trajectory prediction pipeline that uses the rich information of the original video to predict the future trajectory of the agent in the scene. ViP3D uses sparse agent query throughout the pipeline, making it fully differentiable and interpretable. In addition, a new evaluation index for the end-to-end visual trajectory prediction task is proposed, End-to-end Prediction Accuracy (EPA, End-to-end Prediction Accuracy), which comprehensively considers perception and prediction accuracy. At the same time, the predicted trajectory and the ground truth trajectory are scored.
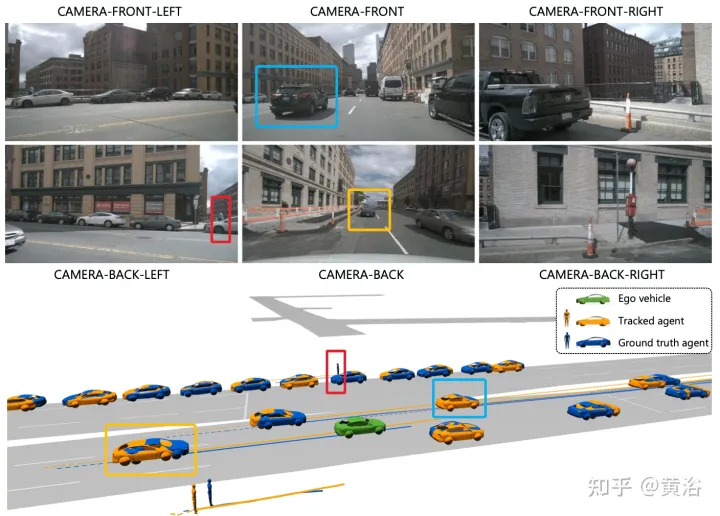
The picture shows the comparison between the traditional multi-step cascade pipeline and ViP3D: the traditional pipeline involves multiple non-differentiable modules, such as detection, tracking and prediction; ViP3D takes multi-view video as input, in an end-to-end manner Generate predicted trajectories that effectively utilize visual information, such as vehicle turn signals.
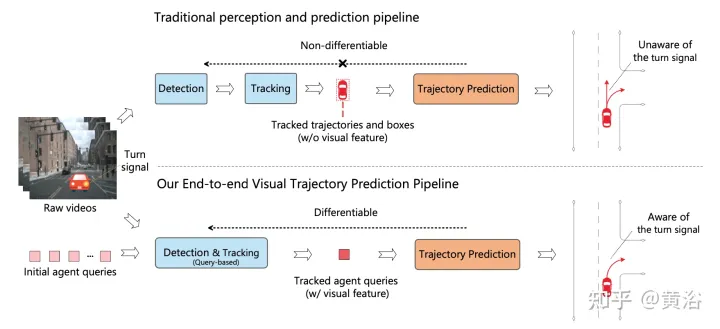
ViP3D aims to solve the trajectory prediction problem of original videos in an end-to-end manner. Specifically, given a multi-view video and a high-definition map, ViP3D predicts the future trajectories of all agents in the scene.
The overall process of ViP3D is shown in the figure: First, the query-based tracker processes multi-view videos from surrounding cameras to obtain the query of the tracked agent with visual features. The visual features in the agent query capture the movement dynamics and visual characteristics of the agents, as well as the relationships between agents. After that, the trajectory predictor takes the query of the tracking agent as input and associates it with the HD map features, and finally outputs the predicted trajectory.
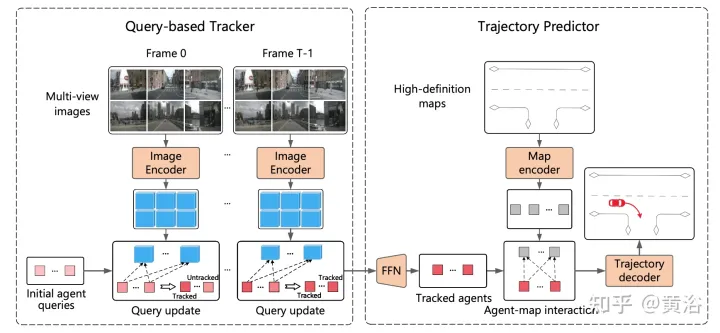
# Query-based tracker extracts visual features from the raw video of the surrounding camera. Specifically, for each frame, image features are extracted according to DETR3D. For time domain feature aggregation, a query-based tracker is designed according to MOTR ("Motr: End-to-end multiple-object tracking with transformer". arXiv 2105.03247, 2021), including two key steps :query feature update and query supervision. The agent query will be updated over time to model the movement dynamics of the agent.
Most existing trajectory prediction methods can be divided into three parts: agent encoding, map encoding and trajectory decoding. After query-based tracking, the query of the tracked agent is obtained, which can be regarded as the agent characteristics obtained through agent encoding. Therefore, the remaining tasks are map encoding and trajectory decoding.
Represent prediction and true value agents as unordered sets Sˆ and S respectively, where each agent is represented by the agent coordinates of the current time step and K possible future trajectories. For each agent type c, calculate the prediction accuracy between Scˆ and Sc. Define the cost between the prediction agent and the truth agent as:

The EPA between Scˆ and Sc is defined as:

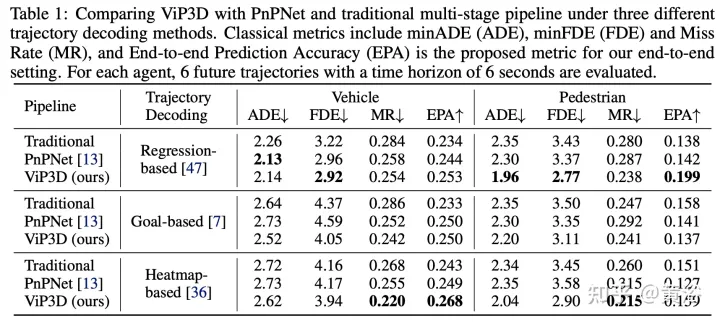
The experimental results are as follows:
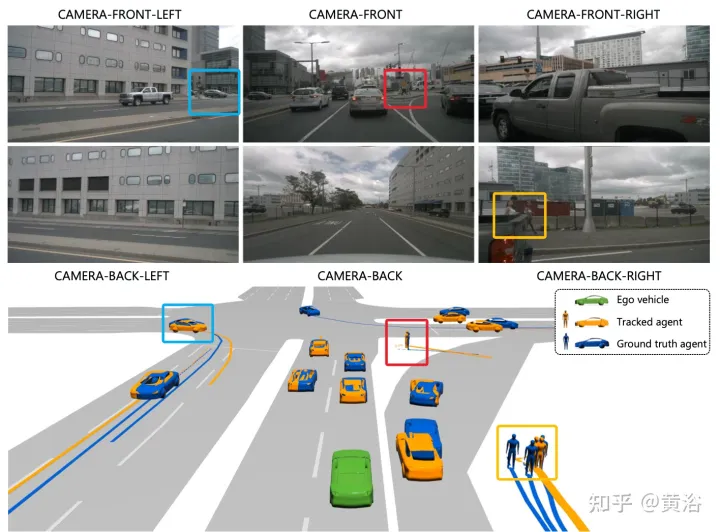
The above is the detailed content of ViP3D: End-to-end visual trajectory prediction through 3D agent query. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Why is Gaussian Splatting so popular in autonomous driving that NeRF is starting to be abandoned?
Jan 17, 2024 pm 02:57 PM
Why is Gaussian Splatting so popular in autonomous driving that NeRF is starting to be abandoned?
Jan 17, 2024 pm 02:57 PM
Written above & the author’s personal understanding Three-dimensional Gaussiansplatting (3DGS) is a transformative technology that has emerged in the fields of explicit radiation fields and computer graphics in recent years. This innovative method is characterized by the use of millions of 3D Gaussians, which is very different from the neural radiation field (NeRF) method, which mainly uses an implicit coordinate-based model to map spatial coordinates to pixel values. With its explicit scene representation and differentiable rendering algorithms, 3DGS not only guarantees real-time rendering capabilities, but also introduces an unprecedented level of control and scene editing. This positions 3DGS as a potential game-changer for next-generation 3D reconstruction and representation. To this end, we provide a systematic overview of the latest developments and concerns in the field of 3DGS for the first time.
 CLIP-BEVFormer: Explicitly supervise the BEVFormer structure to improve long-tail detection performance
Mar 26, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
CLIP-BEVFormer: Explicitly supervise the BEVFormer structure to improve long-tail detection performance
Mar 26, 2024 pm 12:41 PM
Written above & the author’s personal understanding: At present, in the entire autonomous driving system, the perception module plays a vital role. The autonomous vehicle driving on the road can only obtain accurate perception results through the perception module. The downstream regulation and control module in the autonomous driving system makes timely and correct judgments and behavioral decisions. Currently, cars with autonomous driving functions are usually equipped with a variety of data information sensors including surround-view camera sensors, lidar sensors, and millimeter-wave radar sensors to collect information in different modalities to achieve accurate perception tasks. The BEV perception algorithm based on pure vision is favored by the industry because of its low hardware cost and easy deployment, and its output results can be easily applied to various downstream tasks.
 The facial features are flying around, opening the mouth, staring, and raising eyebrows, AI can imitate them perfectly, making it impossible to prevent video scams
Dec 14, 2023 pm 11:30 PM
The facial features are flying around, opening the mouth, staring, and raising eyebrows, AI can imitate them perfectly, making it impossible to prevent video scams
Dec 14, 2023 pm 11:30 PM
With such a powerful AI imitation ability, it is really impossible to prevent it. It is completely impossible to prevent it. Has the development of AI reached this level now? Your front foot makes your facial features fly, and on your back foot, the exact same expression is reproduced. Staring, raising eyebrows, pouting, no matter how exaggerated the expression is, it is all imitated perfectly. Increase the difficulty, raise the eyebrows higher, open the eyes wider, and even the mouth shape is crooked, and the virtual character avatar can perfectly reproduce the expression. When you adjust the parameters on the left, the virtual avatar on the right will also change its movements accordingly to give a close-up of the mouth and eyes. The imitation cannot be said to be exactly the same, but the expression is exactly the same (far right). The research comes from institutions such as the Technical University of Munich, which proposes GaussianAvatars, which
 Choose camera or lidar? A recent review on achieving robust 3D object detection
Jan 26, 2024 am 11:18 AM
Choose camera or lidar? A recent review on achieving robust 3D object detection
Jan 26, 2024 am 11:18 AM
0.Written in front&& Personal understanding that autonomous driving systems rely on advanced perception, decision-making and control technologies, by using various sensors (such as cameras, lidar, radar, etc.) to perceive the surrounding environment, and using algorithms and models for real-time analysis and decision-making. This enables vehicles to recognize road signs, detect and track other vehicles, predict pedestrian behavior, etc., thereby safely operating and adapting to complex traffic environments. This technology is currently attracting widespread attention and is considered an important development area in the future of transportation. one. But what makes autonomous driving difficult is figuring out how to make the car understand what's going on around it. This requires that the three-dimensional object detection algorithm in the autonomous driving system can accurately perceive and describe objects in the surrounding environment, including their locations,
 The latest from Oxford University! Mickey: 2D image matching in 3D SOTA! (CVPR\'24)
Apr 23, 2024 pm 01:20 PM
The latest from Oxford University! Mickey: 2D image matching in 3D SOTA! (CVPR\'24)
Apr 23, 2024 pm 01:20 PM
Project link written in front: https://nianticlabs.github.io/mickey/ Given two pictures, the camera pose between them can be estimated by establishing the correspondence between the pictures. Typically, these correspondences are 2D to 2D, and our estimated poses are scale-indeterminate. Some applications, such as instant augmented reality anytime, anywhere, require pose estimation of scale metrics, so they rely on external depth estimators to recover scale. This paper proposes MicKey, a keypoint matching process capable of predicting metric correspondences in 3D camera space. By learning 3D coordinate matching across images, we are able to infer metric relative
 MotionLM: Language modeling technology for multi-agent motion prediction
Oct 13, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
MotionLM: Language modeling technology for multi-agent motion prediction
Oct 13, 2023 pm 12:09 PM
This article is reprinted with permission from the Autonomous Driving Heart public account. Please contact the source for reprinting. Original title: MotionLM: Multi-Agent Motion Forecasting as Language Modeling Paper link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2309.16534.pdf Author affiliation: Waymo Conference: ICCV2023 Paper idea: For autonomous vehicle safety planning, reliably predict the future behavior of road agents is crucial. This study represents continuous trajectories as sequences of discrete motion tokens and treats multi-agent motion prediction as a language modeling task. The model we propose, MotionLM, has the following advantages: First
 Do you know that programmers will be in decline in a few years?
Nov 08, 2023 am 11:17 AM
Do you know that programmers will be in decline in a few years?
Nov 08, 2023 am 11:17 AM
"ComputerWorld" magazine once wrote an article saying that "programming will disappear by 1960" because IBM developed a new language FORTRAN, which allows engineers to write the mathematical formulas they need and then submit them. Give the computer a run, so programming ends. A few years later, we heard a new saying: any business person can use business terms to describe their problems and tell the computer what to do. Using this programming language called COBOL, companies no longer need programmers. . Later, it is said that IBM developed a new programming language called RPG that allows employees to fill in forms and generate reports, so most of the company's programming needs can be completed through it.
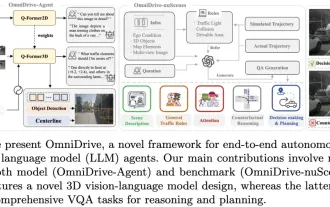 LLM is all done! OmniDrive: Integrating 3D perception and reasoning planning (NVIDIA's latest)
May 09, 2024 pm 04:55 PM
LLM is all done! OmniDrive: Integrating 3D perception and reasoning planning (NVIDIA's latest)
May 09, 2024 pm 04:55 PM
Written above & the author’s personal understanding: This paper is dedicated to solving the key challenges of current multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) in autonomous driving applications, that is, the problem of extending MLLMs from 2D understanding to 3D space. This expansion is particularly important as autonomous vehicles (AVs) need to make accurate decisions about 3D environments. 3D spatial understanding is critical for AVs because it directly impacts the vehicle’s ability to make informed decisions, predict future states, and interact safely with the environment. Current multi-modal large language models (such as LLaVA-1.5) can often only handle lower resolution image inputs (e.g.) due to resolution limitations of the visual encoder, limitations of LLM sequence length. However, autonomous driving applications require





