 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 AI enters archeology! Scientists used deep learning algorithms to discover evidence of human use of fire nearly 1 million years ago, published in PNAS
AI enters archeology! Scientists used deep learning algorithms to discover evidence of human use of fire nearly 1 million years ago, published in PNAS
AI enters archeology! Scientists used deep learning algorithms to discover evidence of human use of fire nearly 1 million years ago, published in PNAS
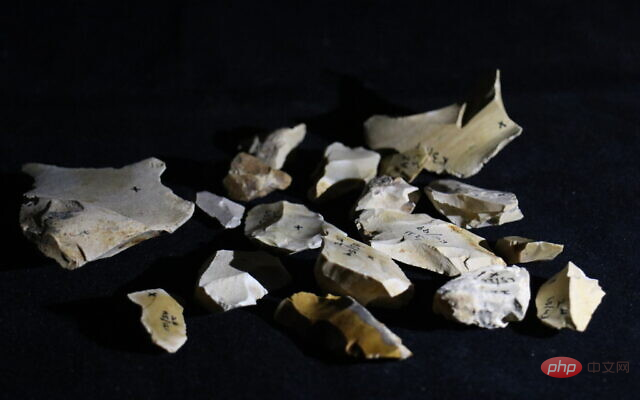

The use of fire was a key factor in the evolution of Homo sapiens. Fire was not only used to create more complex tools, but also made food safer, thus helping to brain development.
To date, only five sites with evidence of fire use dating back 500,000 years have been found worldwide, including Wonderwerk Cave and Swartkrans in South Africa, Chesowanja in Kenya, and Israel Gesher Benot Ya'aqov, Spain's Cueva Negra.
Now, an Israeli research team has used artificial intelligence algorithms to discover a sixth site that shows signs of human use of fire! This study reveals evidence of human use of fire at an Upper Paleolithic site in Israel. The research results have been published in the journal PNAS.

Paper address: https://www.pnas.org/doi/epdf/10.1073/pnas.2123439119
1 AI marches into archeology
Traditional archaeological methods for identifying fire sources at early ancient human sites mainly rely on altered sediments , visual assessment of lithic debris and bones, such as soil reddening, discoloration, warping, cracking, shrinkage, darkening, etc., may underestimate the prevalence of human fire use at the time.
In this study, the author's team developed a spectral "thermometer" based on Raman spectroscopy and deep learning algorithms, used to estimate chert pseudo Thermal exposure of shadows detects extreme temperatures that distort the atomic structure of materials, thus compensating for the possible lack of visual signatures of traces of fire.
Research shows that the Early Paleolithic open-air site (Evron Quarry) in Israel contains the remains of fire-burned animals and rock debris, ranging from 1 million to 800,000 years ago. .


##Caption: From left to right: Filipe Natalio, Ido Azuri, Zane Stepka
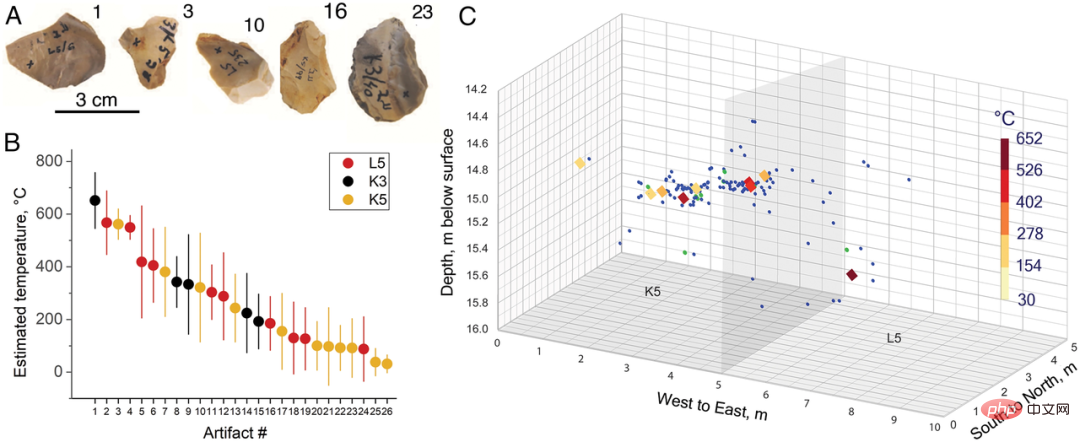
The research team first studied material excavated at Evron Quarry in 1976-1977 and found no obvious visual evidence of heat-related features, such as soil reddening, flint tool discoloration or Cracking, shrinkage or discoloration of animal remains, etc.
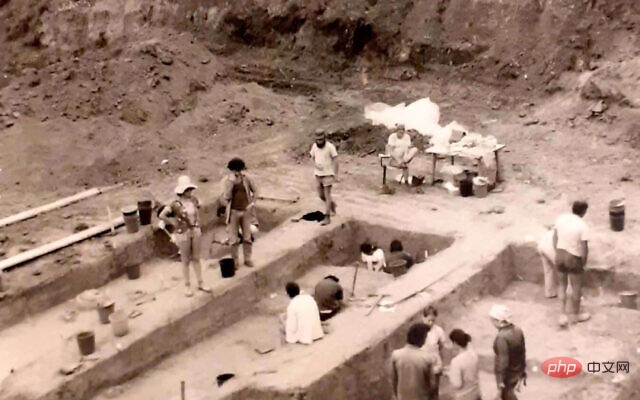

Caption: Archaeological excavation site of Evron Quarry site
Team test Many methods are used, including traditional data analysis methods, machine learning modeling and more advanced deep learning models. Popular deep learning models have specific architectures that outperform other models. The benefit of using AI technology is that it can analyze the chemical composition of materials and use this to estimate their thermal exposure.
AI technology can reliably distinguish whether modern flint has been burned, and can also reveal the temperature at which it burned. The heat of a fire can cause changes in nearby stones, and burning can change bone structure at the atomic level, with corresponding changes in the infrared spectrum.In this study, the team used a deep learning model (a one-dimensional convolutional neural network) to learn the Raman spectral patterns of flint artifacts to estimate the temperature of the stone tools. The model performed better than a fully connected artificial neural network (FC-ANN), being able to reduce the mean absolute error between true and estimated temperatures from 118 °C to 103 °C.
First, the team pre-trained on modern flint collected from different locations in Israel and heated to known temperatures under controlled laboratory conditions. Second, the trained model was applied to an unknown sample (i.e., stone tools collected from the Evron Quarry site). The team used a supervised deep learning approach to correlate Raman spectra with the heating temperature of the chert. This method relies on irreversible thermally induced structural changes in the organic and inorganic components of chert while overcoming its inherent variability. The advantage of using a deep learning model for temperature estimation is that it can approximate any nonlinear decision boundaries between heat and spectral changes due to heat in alpha-quartz, moganite, and D and G band spectral regions. In the picture below, the stone does not visually show any traces of being burned by fire. By using a deep learning model, the ultraviolet Raman spectrum collected from the stone is The thermal exposure was estimated and found that they had been heated to between 200°C and 600°C. This suggests that ancient humans had the ability to control fire rather than just use natural wildfire. Regarding the excavated bones, the research team also experimentally confirmed that they had been burned by fire. Chazan, one of the authors, said: "Without the flint results verified by artificial intelligence, no one would bother to test the thermal exposure of these bones. Condition". This study, however, cannot determine whether the tools at the site were burned by natural or artificial fire. Spatial changes caused by burn marks can be interpreted as evidence of human intervention, as natural fires often cause homogeneous thermal changes throughout the burned area. The authors acknowledge that wildfires and patchy vegetation can also cause uneven temperature distribution across an area, and that temperature is not a reliable distinguishing criterion between using wildfires and artificial fires. But despite this, the estimated temperatures of Stone Age tools and the presence of burned fauna suggest the possibility that fire was used by ancient humans at the site. In the future, the methods used in this study can be extended to other Upper Paleolithic sites, which will have the potential to expand our understanding of the relationship between early hominins and fire. Understand, opening a window into early human life. 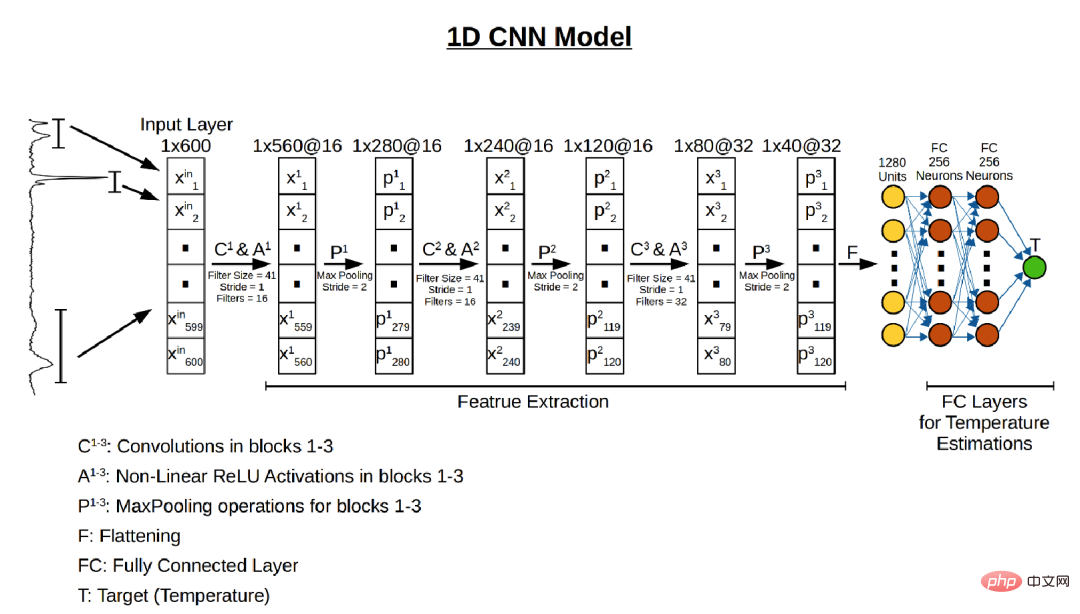
2 Follow-up discussion
The above is the detailed content of AI enters archeology! Scientists used deep learning algorithms to discover evidence of human use of fire nearly 1 million years ago, published in PNAS. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1381
1381
 52
52
 Debian mail server firewall configuration tips
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:42 AM
Debian mail server firewall configuration tips
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:42 AM
Configuring a Debian mail server's firewall is an important step in ensuring server security. The following are several commonly used firewall configuration methods, including the use of iptables and firewalld. Use iptables to configure firewall to install iptables (if not already installed): sudoapt-getupdatesudoapt-getinstalliptablesView current iptables rules: sudoiptables-L configuration
 How debian readdir integrates with other tools
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
How debian readdir integrates with other tools
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
The readdir function in the Debian system is a system call used to read directory contents and is often used in C programming. This article will explain how to integrate readdir with other tools to enhance its functionality. Method 1: Combining C language program and pipeline First, write a C program to call the readdir function and output the result: #include#include#include#includeintmain(intargc,char*argv[]){DIR*dir;structdirent*entry;if(argc!=2){
 How to implement file sorting by debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:06 AM
How to implement file sorting by debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:06 AM
In Debian systems, the readdir function is used to read directory contents, but the order in which it returns is not predefined. To sort files in a directory, you need to read all files first, and then sort them using the qsort function. The following code demonstrates how to sort directory files using readdir and qsort in Debian system: #include#include#include#include#include//Custom comparison function, used for qsortintcompare(constvoid*a,constvoid*b){returnstrcmp(*(
 How to perform digital signature verification with Debian OpenSSL
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:09 AM
How to perform digital signature verification with Debian OpenSSL
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:09 AM
Using OpenSSL for digital signature verification on Debian systems, you can follow these steps: Preparation to install OpenSSL: Make sure your Debian system has OpenSSL installed. If not installed, you can use the following command to install it: sudoaptupdatesudoaptininstallopenssl to obtain the public key: digital signature verification requires the signer's public key. Typically, the public key will be provided in the form of a file, such as public_key.pe
 Debian mail server SSL certificate installation method
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:39 AM
Debian mail server SSL certificate installation method
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:39 AM
The steps to install an SSL certificate on the Debian mail server are as follows: 1. Install the OpenSSL toolkit First, make sure that the OpenSSL toolkit is already installed on your system. If not installed, you can use the following command to install: sudoapt-getupdatesudoapt-getinstallopenssl2. Generate private key and certificate request Next, use OpenSSL to generate a 2048-bit RSA private key and a certificate request (CSR): openss
 Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
The CentOS shutdown command is shutdown, and the syntax is shutdown [Options] Time [Information]. Options include: -h Stop the system immediately; -P Turn off the power after shutdown; -r restart; -t Waiting time. Times can be specified as immediate (now), minutes ( minutes), or a specific time (hh:mm). Added information can be displayed in system messages.
 How Debian OpenSSL prevents man-in-the-middle attacks
Apr 13, 2025 am 10:30 AM
How Debian OpenSSL prevents man-in-the-middle attacks
Apr 13, 2025 am 10:30 AM
In Debian systems, OpenSSL is an important library for encryption, decryption and certificate management. To prevent a man-in-the-middle attack (MITM), the following measures can be taken: Use HTTPS: Ensure that all network requests use the HTTPS protocol instead of HTTP. HTTPS uses TLS (Transport Layer Security Protocol) to encrypt communication data to ensure that the data is not stolen or tampered during transmission. Verify server certificate: Manually verify the server certificate on the client to ensure it is trustworthy. The server can be manually verified through the delegate method of URLSession
 How to do Debian Hadoop log management
Apr 13, 2025 am 10:45 AM
How to do Debian Hadoop log management
Apr 13, 2025 am 10:45 AM
Managing Hadoop logs on Debian, you can follow the following steps and best practices: Log Aggregation Enable log aggregation: Set yarn.log-aggregation-enable to true in the yarn-site.xml file to enable log aggregation. Configure log retention policy: Set yarn.log-aggregation.retain-seconds to define the retention time of the log, such as 172800 seconds (2 days). Specify log storage path: via yarn.n



