
The epidemic has accelerated the progress of artificial intelligence (AI) in remote patient care. More and more doctors are using digital patient monitoring to track health data, identify abnormalities, and provide treatments that no longer need to be done face-to-face. Additionally, emergency departments are adopting remote monitoring solutions so some patients can leave the hospital faster. These transformative technologies are leading to better treatments for patients and lowering healthcare costs.

The application cases of artificial intelligence in the medical field are constantly increasing, mainly due to various algorithms Continuous learning and training make technology smarter and patient experience improved.
Most applications of artificial intelligence in the medical field use "augmented intelligence", which brings together the output of algorithms to provide clinicians with "where to look" when obtaining analysis results. direction, and also plays an important quality control role in the process of providing services. Augmented intelligence focuses on the auxiliary role of technology and aims to enhance human intelligence rather than replace it.
Consumer electronics companies such as Apple are using artificial intelligence to help individuals maintain awareness of their health. Some wrist-worn devices with heart rate monitoring capabilities can notify users when their heart rate is abnormal and can provide relevant information to share with their doctors. Doctors are also expanding their ability to monitor patients remotely by running FDA-approved technology on artificial intelligence engines. For example, Current Health’s solutions provide predictive vital sign monitoring and alerts for health deterioration, among other features.
Many different companies in the field of medical-grade non-hospital cardiac monitoring are actively deploying artificial intelligence for ECG recording and arrhythmia detection. Leveraging artificial intelligence can improve patient outcomes better than traditional techniques such as rule-based or traditional machine learning algorithms (used in Holter monitors). Less sophisticated algorithms often don't provide a high enough diagnostic yield that doctors can't reach a firm diagnosis without repeated monitoring. Devices using artificial intelligence not only bring personalized medicine closer to reality, but also further expand the ability of health systems to serve populations in challenging situations, such as in remote areas or in places where clinic visits may not be possible. Provide services under the circumstances.
In addition to being beneficial to patients, artificial intelligence can also free doctors from back-office tasks of an administrative nature, such as screening and management work on large data sets, allowing them to focus on using their clinical skills to care for patients.
Artificial intelligence can recognize patterns that humans cannot. For example, the heart beats about 1.5 million times on average in two weeks, and doctors may have to find a certain six-second period to make clinical judgments. Finding something clinically meaningful is like looking for a needle in a haystack, and AI can ensure greater accuracy at scale.
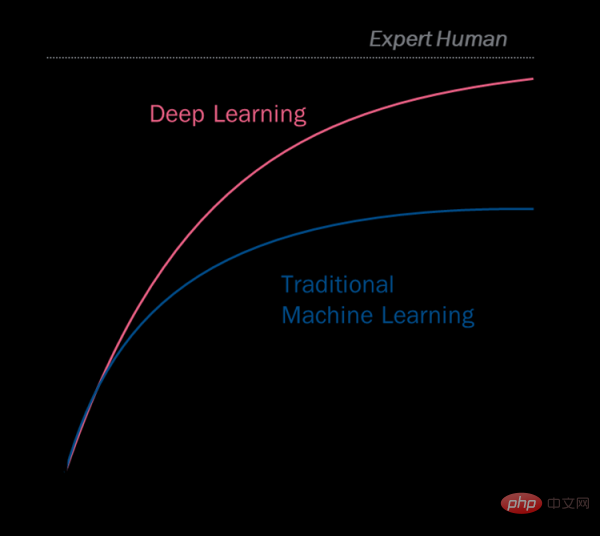
To achieve this level of reliability, vendors, data science teams and AI need clean data and lots of it. This massive data expansion requires sophisticated analytics, which can be achieved using machine learning and deep learning algorithms. Over the past decade, deep learning, a subset of machine learning, has reached a point where it matches human performance in developing algorithms in several scientific fields. Unlike more traditional machine learning methods, which predict results based on features collected by humans, deep learning algorithms use artificial neural network predictions and therefore have the advantage of automatically learning relevant features from raw data. As a result, deep learning algorithms can leverage large amounts of annotated instance data and significant computing power to build complex models and be able to predict the correct outcome for new inputs with very high accuracy.
The deployment of machine learning and deep learning methods into healthcare is subject to strict oversight by the FDA and requires 510(K) clearance. Obtaining a 510(k) clearance indicates that the use of related technical equipment is safe and effective. As the pace of algorithmic innovation and data volume creation continues to accelerate, regulators have introduced frameworks that harmonize best practices and regulatory requirements while allowing devices to continue to improve at a faster pace than in the past. Work in this area obviously includes the following two documents. The FDA released the "Action Plan for Medical Devices Based on Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning Software" in January 2021, and subsequently released the "Good Practices for Medical Device Development: Guiding Principles", which are in collaboration with Health Canada and British Drugs Developed jointly with the Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA).
Using advanced algorithms and large amounts of data, deep learning has achieved expert-level and human-level performance in many applications.
Artificial intelligence has great potential in the medical field, and we have only just begun. Last year, the Biden administration created an AI task force with the goal of making it easier to access government data and expand access to critical resources and educational tools to continue spurring AI innovation. The move builds on the 2020 bill, which included a five-year budget of $250 million.
With a nationwide focus on AI innovation and funding on the rise, the next frontier for AI and wearables will be the expanded use of predictive capabilities: the insights paradigm will shift from clinical retrospective reporting to the future risk profile of the situation. In healthcare, the key will be deciding which patient groups to monitor and when by identifying and analyzing health risks, in addition to ensuring patients receive appropriate preventive care.
Artificial intelligence innovation is transforming healthcare delivery. AI innovations can enhance the patient experience, reduce administrative burden on patients, physicians and care teams, and potentially improve health outcomes. Further investment and technological advancements will undoubtedly revolutionize remote patient care as we know it. Healthcare systems are constantly evolving to meet current and future challenges. And due to the recent COVID-19 pandemic, the momentum for adoption of remote care and use of artificial intelligence is set to continue.
The above is the detailed content of Artificial Intelligence is driving a revolution in remote patient care. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!
 Application of artificial intelligence in life
Application of artificial intelligence in life
 What is the basic concept of artificial intelligence
What is the basic concept of artificial intelligence
 How to install pycharm
How to install pycharm
 How to open an account with u currency
How to open an account with u currency
 The difference between xls and xlsx
The difference between xls and xlsx
 Eou web3 wallet tutorial
Eou web3 wallet tutorial
 Cost-effectiveness analysis of learning python, java and c++
Cost-effectiveness analysis of learning python, java and c++
 Projector mobile phone
Projector mobile phone
 How to use fusioncharts.js
How to use fusioncharts.js




