 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 Multiple drones collaborate to 3D print a house, and the research appears on the cover of Nature
Multiple drones collaborate to 3D print a house, and the research appears on the cover of Nature
Multiple drones collaborate to 3D print a house, and the research appears on the cover of Nature
We can often see bees, ants and other animals busy building nests. After natural selection, their work efficiency is astonishingly high
The ability of these animals to divide and cooperate has been "passed on" to drones. A study from Imperial College London tells us Showing the future direction, like this:

Drone 3D dusting:

This research result appeared on the cover of "Nature" on Wednesday.

##Paper address: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-04988-4
To demonstrate the capabilities of the drones, the researchers used foam and a special lightweight cement material to build structures ranging in height from 0.18 meters to 2.05 meters. The error compared to the original blueprint was less than 5mm.

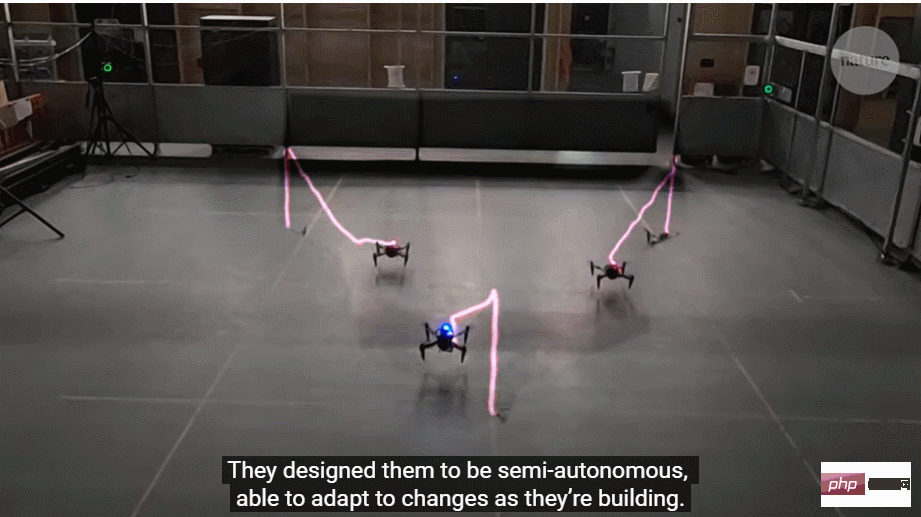
To prove that the system could handle more complex drone formations, the team created a light-trace time-lapse using lights on the drones sequence, simulating the creation of a tall dome-like structure.
. 
Mirko Kovac, the leader of the research and director of the Aerial Robotics Laboratory at Imperial College London, said: This method could be used to build buildings in the Arctic or even Mars, or to help repair normally expensive Scaffolding for high-rise buildings.
However, the technology is currently subject to some limitations, as drones are difficult to carry heavy loads, require regular charging, and still require human supervision. However, the researchers say they hope to alleviate some of these issues by automatically charging the drones during research projects.
How is drone 3D printing implemented? In this regard, researchers have constructed a sophisticated system.
Research IntroductionTo improve productivity and safety, robot-based construction technologies have been proposed for the assembly of building components and free-form continuous additives Manufacturing (AM, additive manufacturing). Compared to assembly-based methods, free-form continuous AM enables the flexible production of geometrically variable designs with high efficiency and low cost. However, these large systems need to be connected to a power source, are inconvenient for inspection, maintenance, and repair, and are difficult to manufacture in harsh environments.
As an alternative to large individual robot systems, small mobile robots can offer greater flexibility and scalability. However, research into using robot formations for construction is still in the early exploratory stages of development. In addition, the current operating height of multi-robots is limited and cannot operate beyond a certain range. The figure below shows a comparison between SOTA robotic platforms developed for AM in the construction industry.
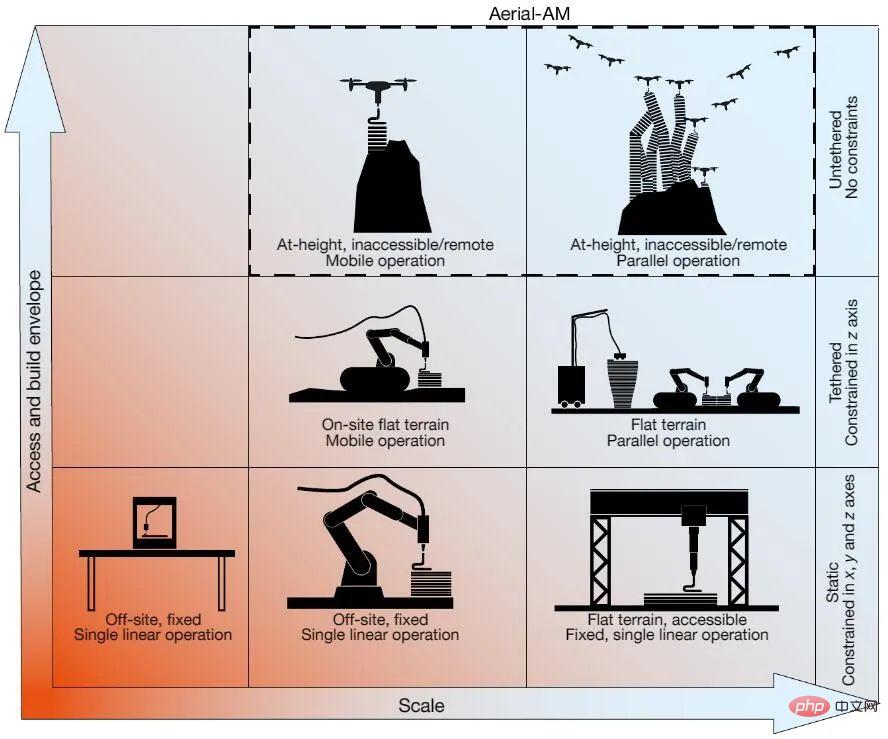
Natural builders have shown greater adaptability when building than current robotic systems and their inherent limitations, with many Do this with the help of fly-in and additive construction methods. For example, a swallow can make 1200 flights between the source of materials and the site of construction to gradually complete the nest. Social insects such as termites and wasps demonstrate a greater degree of adaptability and scalability: Aerial construction by social wasps demonstrated efficient and direct path optimization, easing the need to navigate throughout the construction process.
These natural systems inspire approaches to collective construction using multi-agents that require solving multi-agent coordination problems beyond currently available technologies. In addition to collective interaction methods for multi-robot systems, material design and use and environmental manipulation mechanisms must be integrated and co-developed to enable cooperative construction.
The system proposed by Imperial College is called Aerial-AM, which combines biological cooperation mechanisms with engineering principles and uses multiple drones to achieve it.
The UAV team’s realization of autonomous additive manufacturing requires the parallel development of a number of key technologies, including: 1) Aerial robots capable of high-precision material deposition and print quality, and real-time qualitative assessment ; 2) Aerial robot teams can broadcast their activities to each other and share data wirelessly without interfering with each other; 3) Autonomous navigation and task planning system, combined with printing path strategy to adaptively determine and allocate manufacturing tasks; 4) Design or selection of material planning , specifically a lightweight and printable cement mixture suitable for aerial additive manufacturing methods without the need for formwork or temporary scaffolding.
Aerial-AM uses two types of aerial robotic platforms, called BuildDrone and ScanDrone. The BuildDrone is used to stack physical materials, and the ScanDrone is used to perform augmentation after each layer of material is deposited. Aerial scanning and verification observations. Both robotic platforms are coordinated on their respective workflows via a distributed multi-agent approach. The build cycle includes in-flight print performance characterization of the BuildDrones and ScanDrone, real-time trajectory adaptation and material printing of the BuildDrones, and validation of print results with ScanDrone and human supervisors.
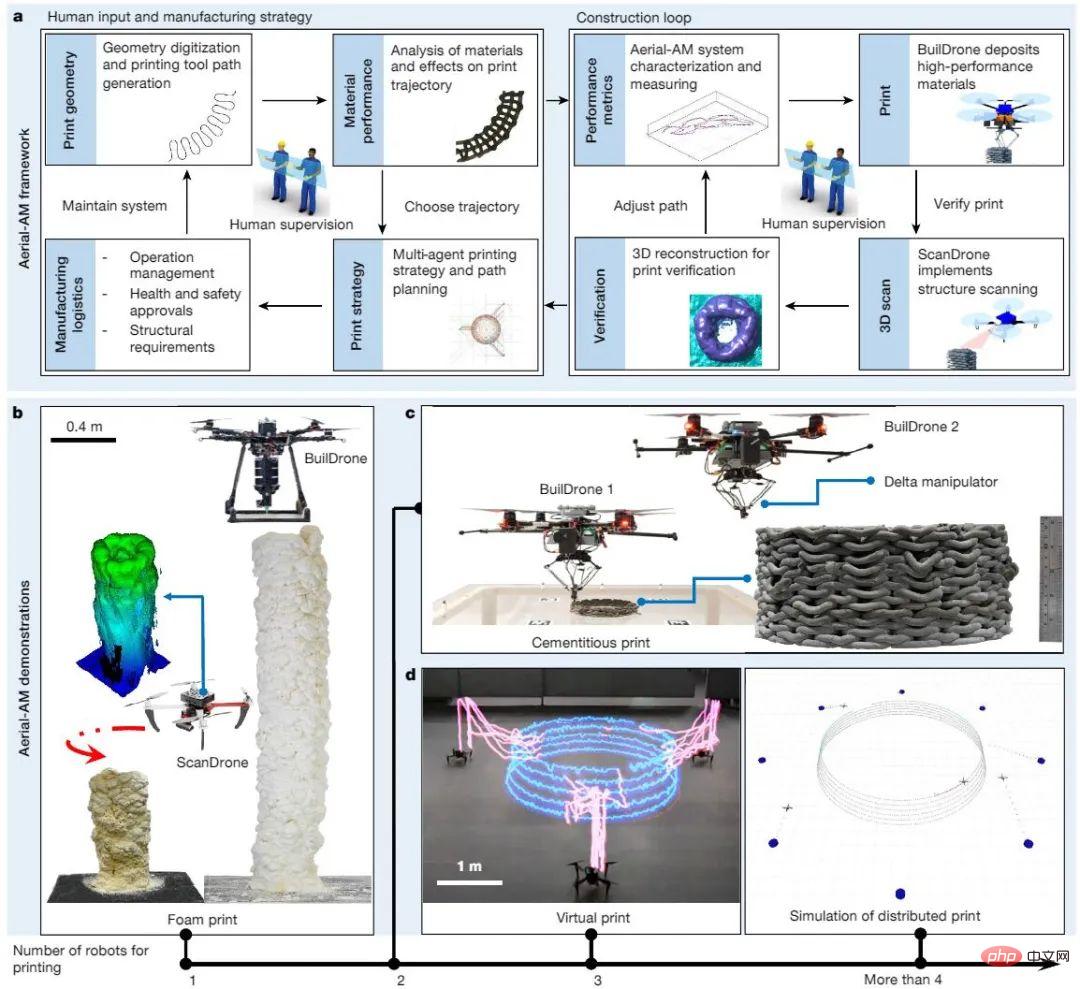
Figure 2. Aerial-AM framework for unconstrained and unbounded AM.
The multi-agent Aerial-AM framework proposed by the new research consists of two loops, running on the slow time scale of planning and the fast time scale of real-time operation, using for manufacturing and progress observation. In a proof-of-concept, researchers used a ScanDrone airborne vision system to perform 3D scans to map progress, building a large cylinder out of expanded foam material.
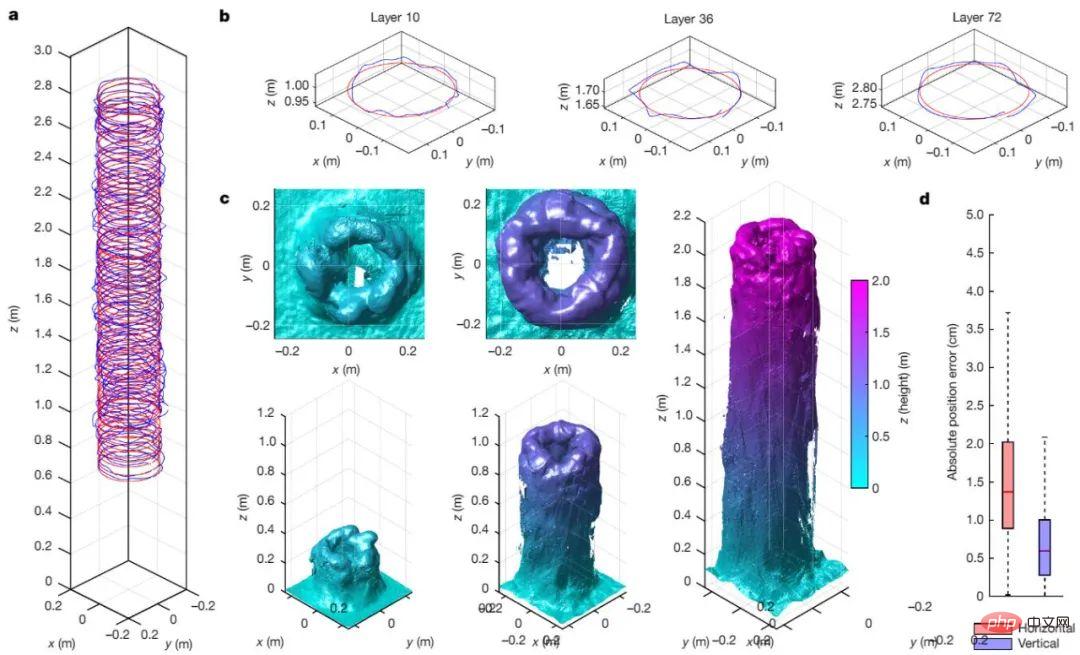
Figure 3. Aerial-AM BuildDrone prints 2.05 m high cylindrical geometry with 72 passes of material deposition, and real-time print evaluation by ScanDrone.
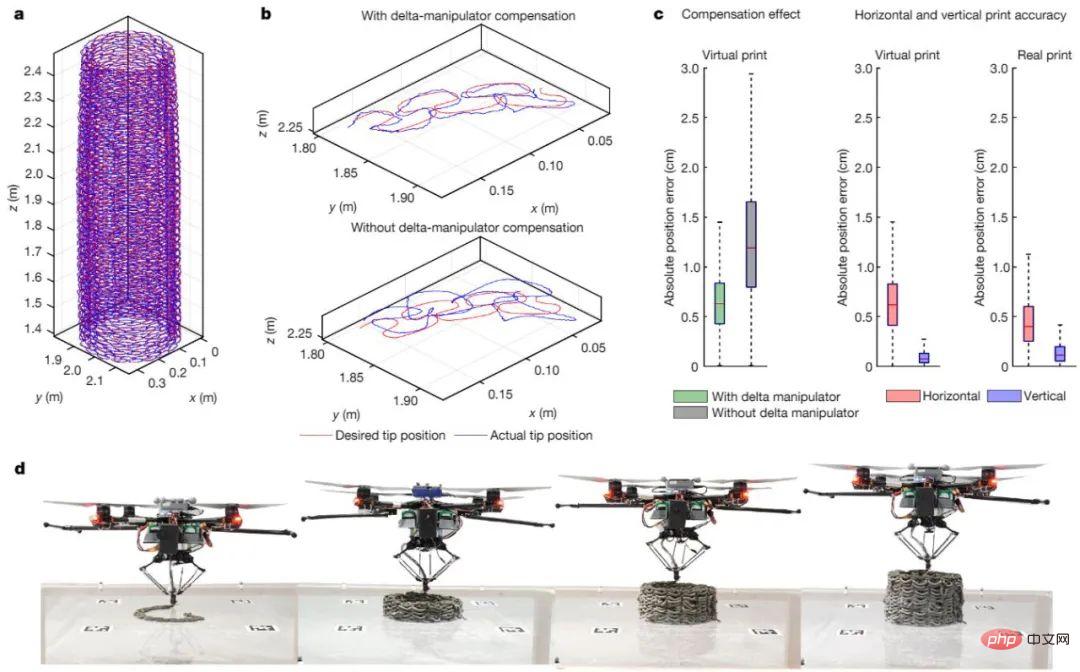
## Figure 4. Two BuildDrones 3D printing thin-walled cylinders using an error-compensated delta robot to deposit cement Material.
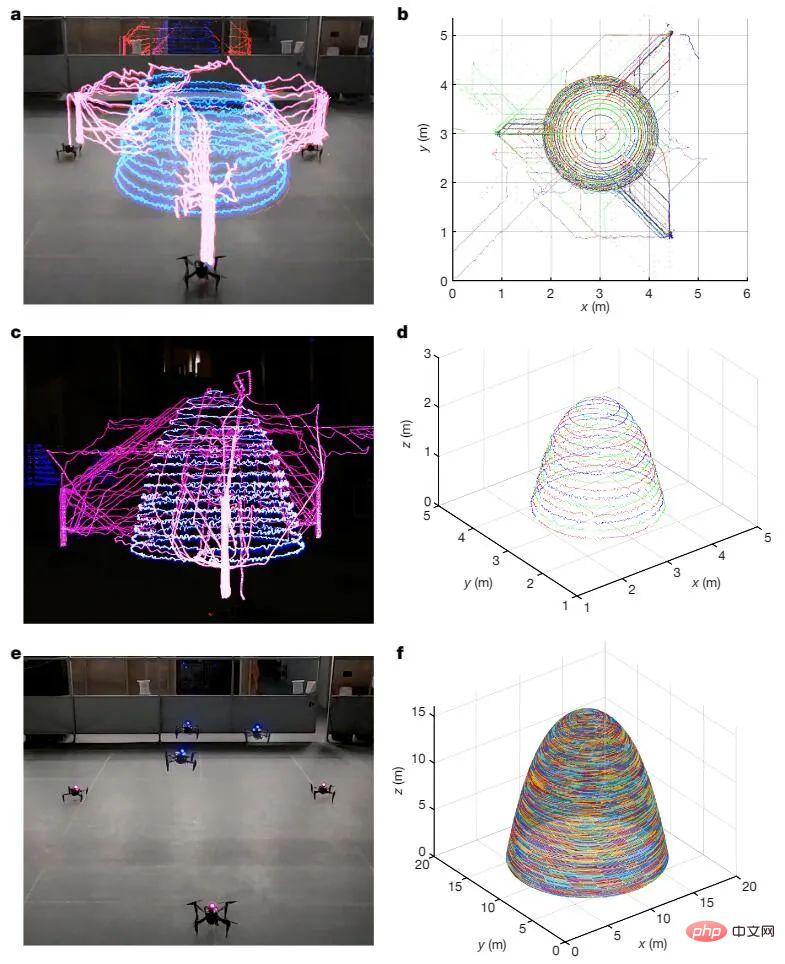
Figure 5. Aerial-AM multi-robot optical track virtual printing dome-shaped rotating surface. a, c are flight trajectories, b, d are top and perspective views. f shows simulation results using 15 robots to print an enlarged version of the geometry with a base diameter of 15 m.
Using BuildDrone’s material deposition and ScanDrone’s real-time qualitative assessment of printed structures, researchers successfully printed cylinders up to 2.05 meters high, demonstrating the Aerial-AM method of manufacturing Ability to handle large geometric objects. Experiments on the fabrication of cementitious thin-walled cylinders demonstrated that the coupling of a self-aligned parallel delta robot with a BuildDrone allows the deposition of material in the lateral and vertical directions with high precision (maximum 5 mm position error), a level well within the limits allowed by UK construction requirements .
Virtual light track AM and simulation results show that the Aerial-AM framework can effectively print a variety of geometries through parallel multi-robot manufacturing while resolving congestion and completing autonomous tasks under abnormal conditions. adapt.
While these experiments successfully demonstrated the feasibility of Aerial-AM, they were only a first step in exploring the potential of using aerial robots for construction. Researchers said that in order to realize 3D printing of houses with drones, significant progress is needed in robotics and materials science, especially in cutting-edge areas such as the deposition of support materials, the solidification of active materials, and task sharing among multiple robots. develop.
As for the UAV itself, in order to bring the research results out of the laboratory, researchers are planning to implement multi-sensor simultaneous positioning and mapping (SLAM) with differential global positioning system (GPS). ) system to provide adequate outdoor positioning.
Once practical, Aerial-AM may provide an alternative way to support housing and critical infrastructure in remote areas.
The above is the detailed content of Multiple drones collaborate to 3D print a house, and the research appears on the cover of Nature. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 The Stable Diffusion 3 paper is finally released, and the architectural details are revealed. Will it help to reproduce Sora?
Mar 06, 2024 pm 05:34 PM
The Stable Diffusion 3 paper is finally released, and the architectural details are revealed. Will it help to reproduce Sora?
Mar 06, 2024 pm 05:34 PM
StableDiffusion3’s paper is finally here! This model was released two weeks ago and uses the same DiT (DiffusionTransformer) architecture as Sora. It caused quite a stir once it was released. Compared with the previous version, the quality of the images generated by StableDiffusion3 has been significantly improved. It now supports multi-theme prompts, and the text writing effect has also been improved, and garbled characters no longer appear. StabilityAI pointed out that StableDiffusion3 is a series of models with parameter sizes ranging from 800M to 8B. This parameter range means that the model can be run directly on many portable devices, significantly reducing the use of AI
 Have you really mastered coordinate system conversion? Multi-sensor issues that are inseparable from autonomous driving
Oct 12, 2023 am 11:21 AM
Have you really mastered coordinate system conversion? Multi-sensor issues that are inseparable from autonomous driving
Oct 12, 2023 am 11:21 AM
The first pilot and key article mainly introduces several commonly used coordinate systems in autonomous driving technology, and how to complete the correlation and conversion between them, and finally build a unified environment model. The focus here is to understand the conversion from vehicle to camera rigid body (external parameters), camera to image conversion (internal parameters), and image to pixel unit conversion. The conversion from 3D to 2D will have corresponding distortion, translation, etc. Key points: The vehicle coordinate system and the camera body coordinate system need to be rewritten: the plane coordinate system and the pixel coordinate system. Difficulty: image distortion must be considered. Both de-distortion and distortion addition are compensated on the image plane. 2. Introduction There are four vision systems in total. Coordinate system: pixel plane coordinate system (u, v), image coordinate system (x, y), camera coordinate system () and world coordinate system (). There is a relationship between each coordinate system,
 This article is enough for you to read about autonomous driving and trajectory prediction!
Feb 28, 2024 pm 07:20 PM
This article is enough for you to read about autonomous driving and trajectory prediction!
Feb 28, 2024 pm 07:20 PM
Trajectory prediction plays an important role in autonomous driving. Autonomous driving trajectory prediction refers to predicting the future driving trajectory of the vehicle by analyzing various data during the vehicle's driving process. As the core module of autonomous driving, the quality of trajectory prediction is crucial to downstream planning control. The trajectory prediction task has a rich technology stack and requires familiarity with autonomous driving dynamic/static perception, high-precision maps, lane lines, neural network architecture (CNN&GNN&Transformer) skills, etc. It is very difficult to get started! Many fans hope to get started with trajectory prediction as soon as possible and avoid pitfalls. Today I will take stock of some common problems and introductory learning methods for trajectory prediction! Introductory related knowledge 1. Are the preview papers in order? A: Look at the survey first, p
 DualBEV: significantly surpassing BEVFormer and BEVDet4D, open the book!
Mar 21, 2024 pm 05:21 PM
DualBEV: significantly surpassing BEVFormer and BEVDet4D, open the book!
Mar 21, 2024 pm 05:21 PM
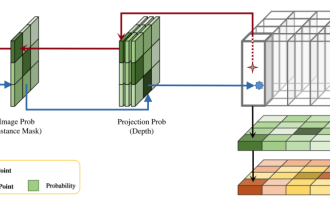
This paper explores the problem of accurately detecting objects from different viewing angles (such as perspective and bird's-eye view) in autonomous driving, especially how to effectively transform features from perspective (PV) to bird's-eye view (BEV) space. Transformation is implemented via the Visual Transformation (VT) module. Existing methods are broadly divided into two strategies: 2D to 3D and 3D to 2D conversion. 2D-to-3D methods improve dense 2D features by predicting depth probabilities, but the inherent uncertainty of depth predictions, especially in distant regions, may introduce inaccuracies. While 3D to 2D methods usually use 3D queries to sample 2D features and learn the attention weights of the correspondence between 3D and 2D features through a Transformer, which increases the computational and deployment time.
 The first multi-view autonomous driving scene video generation world model | DrivingDiffusion: New ideas for BEV data and simulation
Oct 23, 2023 am 11:13 AM
The first multi-view autonomous driving scene video generation world model | DrivingDiffusion: New ideas for BEV data and simulation
Oct 23, 2023 am 11:13 AM
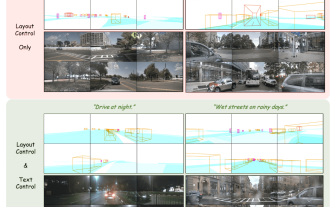
Some of the author’s personal thoughts In the field of autonomous driving, with the development of BEV-based sub-tasks/end-to-end solutions, high-quality multi-view training data and corresponding simulation scene construction have become increasingly important. In response to the pain points of current tasks, "high quality" can be decoupled into three aspects: long-tail scenarios in different dimensions: such as close-range vehicles in obstacle data and precise heading angles during car cutting, as well as lane line data. Scenes such as curves with different curvatures or ramps/mergings/mergings that are difficult to capture. These often rely on large amounts of data collection and complex data mining strategies, which are costly. 3D true value - highly consistent image: Current BEV data acquisition is often affected by errors in sensor installation/calibration, high-precision maps and the reconstruction algorithm itself. this led me to
 AI optimized design, thermal resistance reduced by 2.3C / 100W, Asetek cooperates with Fabric8Labs to launch new cold head
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:59 PM
AI optimized design, thermal resistance reduced by 2.3C / 100W, Asetek cooperates with Fabric8Labs to launch new cold head
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:59 PM
According to news from this website on June 3, water cooling solution provider Asetek announced that it has cooperated with metal 3D printing company Fabric8Labs to launch a new AI-optimized cold head, which will be displayed at the ASUS ROG booth at Computex 2024 Taipei International Computer Show. Compared with previous generations of water cooling solutions, the AI-optimized cold head uses artificial intelligence and ECAM additive manufacturing technology to improve heat dissipation performance in an "unprecedented" way by optimizing fluid dynamics. According to reports, the official used complex AI simulation tools to build the entire cold head structure. The fins are different in design and can only be manufactured using 3D printing processes. This website noticed that compared with Asetek’s eighth-generation solution, the original AI-optimized cold head design can reduce the thermal resistance by 2.3C/1
 GSLAM | A general SLAM architecture and benchmark
Oct 20, 2023 am 11:37 AM
GSLAM | A general SLAM architecture and benchmark
Oct 20, 2023 am 11:37 AM
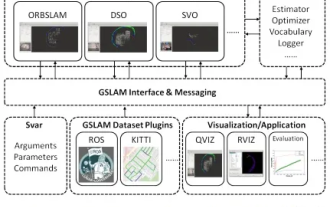
Suddenly discovered a 19-year-old paper GSLAM: A General SLAM Framework and Benchmark open source code: https://github.com/zdzhaoyong/GSLAM Go directly to the full text and feel the quality of this work ~ 1 Abstract SLAM technology has achieved many successes recently and attracted many attracted the attention of high-tech companies. However, how to effectively perform benchmarks on speed, robustness, and portability with interfaces to existing or emerging algorithms remains a problem. In this paper, a new SLAM platform called GSLAM is proposed, which not only provides evaluation capabilities but also provides researchers with a useful way to quickly develop their own SLAM systems.
 'Minecraft' turns into an AI town, and NPC residents role-play like real people
Jan 02, 2024 pm 06:25 PM
'Minecraft' turns into an AI town, and NPC residents role-play like real people
Jan 02, 2024 pm 06:25 PM
Please note that this square man is frowning, thinking about the identities of the "uninvited guests" in front of him. It turned out that she was in a dangerous situation, and once she realized this, she quickly began a mental search to find a strategy to solve the problem. Ultimately, she decided to flee the scene and then seek help as quickly as possible and take immediate action. At the same time, the person on the opposite side was thinking the same thing as her... There was such a scene in "Minecraft" where all the characters were controlled by artificial intelligence. Each of them has a unique identity setting. For example, the girl mentioned before is a 17-year-old but smart and brave courier. They have the ability to remember and think, and live like humans in this small town set in Minecraft. What drives them is a brand new,



