 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 shocked! After 70,000 hours of training, OpenAI's model learned to plan wood in 'Minecraft”
shocked! After 70,000 hours of training, OpenAI's model learned to plan wood in 'Minecraft”
shocked! After 70,000 hours of training, OpenAI's model learned to plan wood in 'Minecraft”
Recently, OpenAI, which seems to have left GPT behind, has started a new life.
After training on massive unlabeled videos and a little bit of labeled data, the AI finally learned how to make a diamond pickaxe in Minecraft.
The entire process takes a hardcore player at least 20 minutes to complete, and requires a total of 24,000 operations.
This thing seems simple, but it is very difficult for AI.
A 7-year-old child can learn it after watching it for 10 minutes
#For the simplest wooden pickaxe, let human players learn the process from scratch Not too difficult.
One nerd can teach the next one in less than 3 minutes with a single video.
The demonstration video is 2 minutes and 52 seconds long
However, Diamond Making a pickaxe is much more complicated.
But even so, a 7-year-old child only needs to watch a ten-minute demonstration video to learn it.
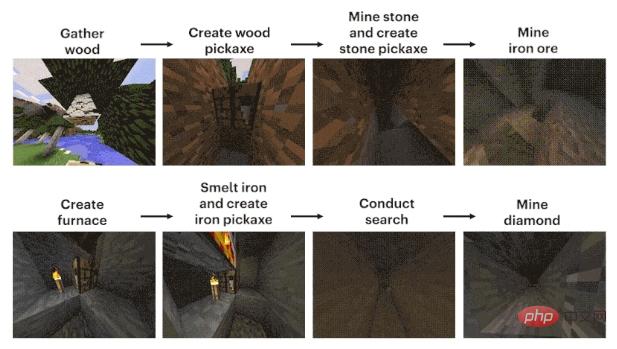
The difficulty of this mission is mainly how to dig the diamond mine.
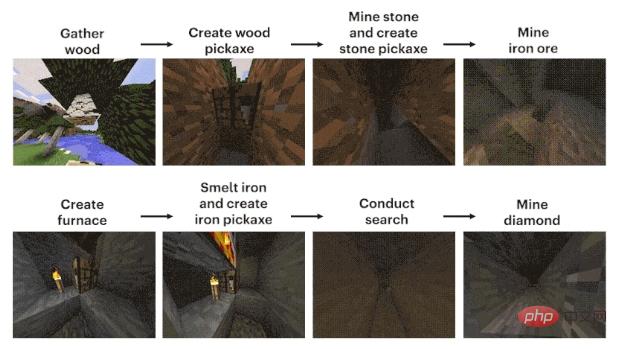
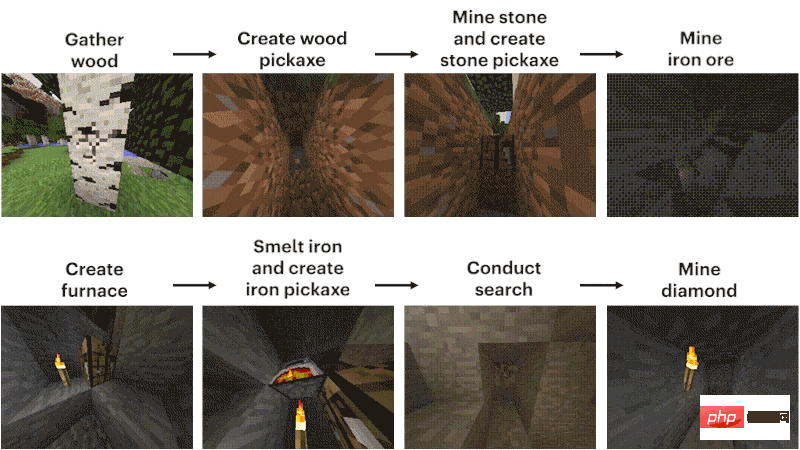
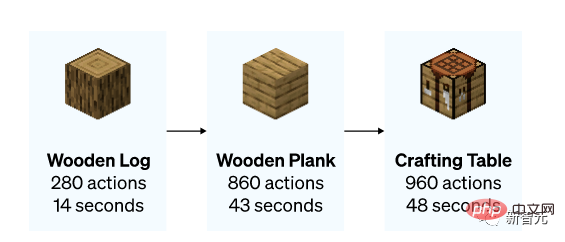
The process can be roughly summarized into 12 steps: first, plan out the pixel block "wood" with bare hands, then synthesize wood blocks from the logs, make wooden sticks from the wooden blocks, and make workshop equipment from the wooden sticks Bench, workbench to make wooden pickaxe, wooden pickaxe to knock stones, stones and sticks to make stone pickaxe, stone pickaxe to make furnace, furnace to process iron ore, iron ore to melt and cast iron ingot, iron ingot to make iron pickaxe, iron pickaxe to Dig diamonds.

Now, the pressure is on the AI side.
Coincidentally, CMU, OpenAI, DeepMind, Microsoft Research and other institutions have launched a related competition-MineRL since 2019.
Contestants need to develop an artificial intelligence agent that can "create tools independently from scratch and automatically find and mine diamond mines". The winning conditions are also very simple - the fastest one wins. .
How is the result?
After the first MineRL competition, "a 7-year-old child learned it after watching a 10-minute video, but the AI still couldn't figure it out after 8 million steps." However, it was published in Nature magazine.
Although there is a lot of data, I can’t use it
As a sandbox construction game, “Minecraft” is highly open to player strategies and in-game virtual environments. It is particularly suitable as a testing ground and touchstone for various AI model learning and decision-making capabilities.
And as a "national-level" game, it is easy to find videos related to "Minecraft" online.
However, whether it is building a tutorial or showing off your own work, to a certain extent it is only the result shown on the screen.
In other words, people watching the video can only know what the up leader did and how he did it, but they have no way of knowing how he did it.
To be more specific, what is shown on the computer screen is only the result, and the operation steps are the up owner’s constant clicking on the keyboard and the constant movement of the mouse. This part is to see less than.
Even this process has been edited, and it is unlikely that anyone would be able to learn it after watching it, let alone AI.
To make matters worse, many players complain that planing wood in the game is boring, too much like doing homework and completing tasks. As a result, after a wave of updates, there are many tools that can be picked up for free... Now, even the data is hard to find.
If OpenAI wants AI to learn to play "Minecraft", it must find a way to put these massive unlabeled video data to use.
Video pre-training model——VPT
So, VPT came into being.


Paper address: https://cdn.openai.com/vpt/Paper.pdf
This thing is new, but it is not complicated. It is a semi-supervised imitation learning method.
First, collect a wave of data to annotate the data of the outsourcers playing games, which includes videos and records of keyboard and mouse operations.
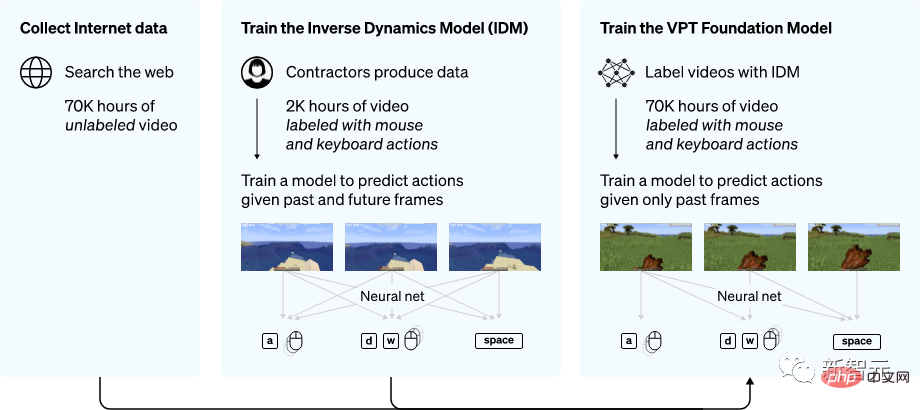
Overview of the VPT method
The researchers then used the data to Using an inverse dynamics model (IDM), we can infer how the keyboard and mouse move during each step in the video.
In this way, the entire task becomes much simpler, and only a lot less data is needed to achieve the goal.
After completing IDM with a small amount of outsourced data, you can use IDM to label a larger unlabeled data set.
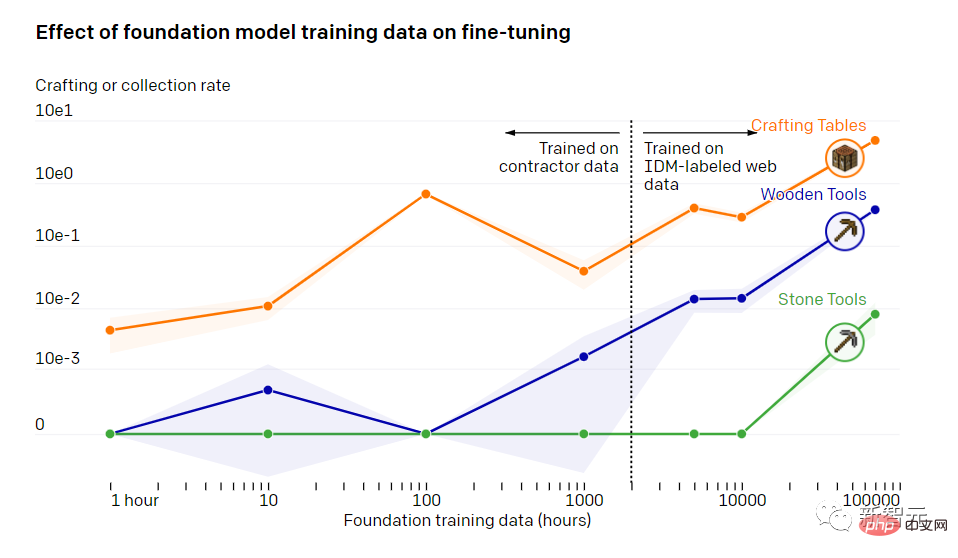
The impact of basic model training data on fine-tuning
In training After 70,000 hours, OpenAI's behavioral cloning model can achieve various tasks that other models cannot.
The model learned how to chop down trees and collect wood, how to use wood to make wooden strips, and how to use wooden strips to make tables. This set of things requires a relatively skilled player to operate for less than 50 seconds.
In addition to making a table, the model can also swim, hunt, and eat.
There is even a cool operation of "running, jumping and building", that is, placing a brick or wood block under your feet when jumping, and you can build a pillar while jumping. This is a required course for hardcore players.
Making a table (0 shot)

##Hunting (0 shot)

##"Running and jumping" simple version (0 shot)
In order to allow the model to complete some more precise tasks, the data set is generally fine-tuned to a smaller size and distinguishes small directions.OpenAI did a study that showed how well a model trained with VPT can adapt to downstream data sets after fine-tuning.
The researchers invited people to play "Minecraft" for 10 minutes and build a house using basic materials. They hope that in this way they can enhance the model's ability to perform some early-game tasks, such as building a workbench.
After fine-tuning the data set, the researchers not only found that the model was more efficient at performing initial tasks, but also found that the model itself understood how to make a piece of wood respectively. A workbench made of stone, and a tool table made of stone.
Sometimes, researchers can see models building crude shelters, searching villages, and looting boxes.
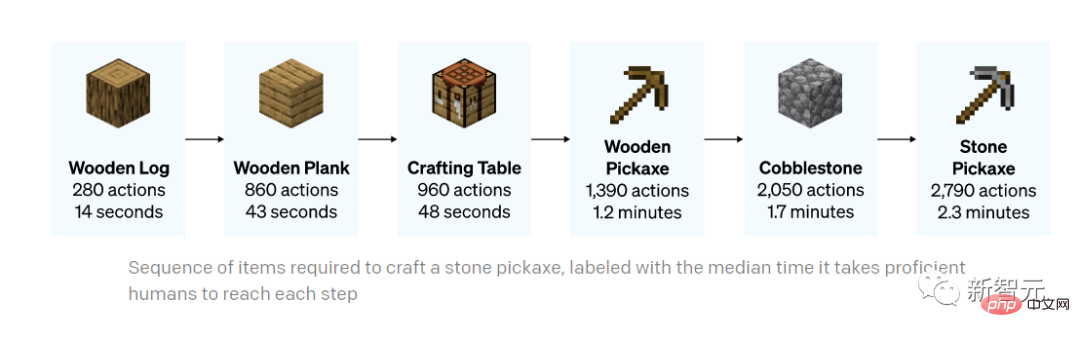
The whole process of making a stone pickaxe (the time marked below is the time it takes for a skilled player to perform the same task)
Making a Stone Pickaxe
Then let’s take a look , how OpenAI experts fine-tuned it.The method they use is reinforcement learning (RL).
Most RL methods address these challenges by stochastically exploring priors, i.e. models are often incentivized to reward random actions through entropy. The VPT model should be a better prior model for RL because simulating human behavior may be more helpful than taking random actions.
The researchers set up the model for the arduous task of collecting a diamond pickaxe, a feature never seen before in Minecraft because the entire task is performed using the native human-machine interface. It will become more difficult.
Crafting a diamond pickaxe requires a long and complex series of subtasks. To make this task tractable, the researchers rewarded the agent for each item in the sequence.
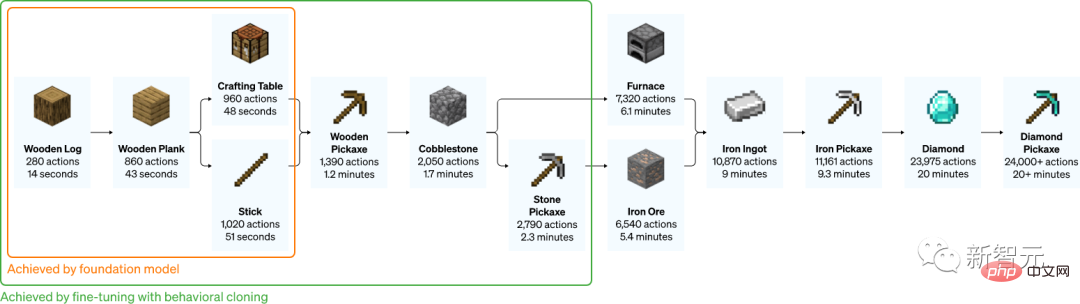
In stark contrast, the VPT model was fine-tuned to not only learn how to craft a diamond pickaxe, but also achieved even human-level success in collecting all items.
This is the first time someone has demonstrated a computer model capable of crafting diamond tools in Minecraft.
The above is the detailed content of shocked! After 70,000 hours of training, OpenAI's model learned to plan wood in 'Minecraft”. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1385
1385
 52
52
 How to check CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
How to check CentOS HDFS configuration
Apr 14, 2025 pm 07:21 PM
Complete Guide to Checking HDFS Configuration in CentOS Systems This article will guide you how to effectively check the configuration and running status of HDFS on CentOS systems. The following steps will help you fully understand the setup and operation of HDFS. Verify Hadoop environment variable: First, make sure the Hadoop environment variable is set correctly. In the terminal, execute the following command to verify that Hadoop is installed and configured correctly: hadoopversion Check HDFS configuration file: The core configuration file of HDFS is located in the /etc/hadoop/conf/ directory, where core-site.xml and hdfs-site.xml are crucial. use
 Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
Centos shutdown command line
Apr 14, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
The CentOS shutdown command is shutdown, and the syntax is shutdown [Options] Time [Information]. Options include: -h Stop the system immediately; -P Turn off the power after shutdown; -r restart; -t Waiting time. Times can be specified as immediate (now), minutes ( minutes), or a specific time (hh:mm). Added information can be displayed in system messages.
 What are the backup methods for GitLab on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:33 PM
What are the backup methods for GitLab on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:33 PM
Backup and Recovery Policy of GitLab under CentOS System In order to ensure data security and recoverability, GitLab on CentOS provides a variety of backup methods. This article will introduce several common backup methods, configuration parameters and recovery processes in detail to help you establish a complete GitLab backup and recovery strategy. 1. Manual backup Use the gitlab-rakegitlab:backup:create command to execute manual backup. This command backs up key information such as GitLab repository, database, users, user groups, keys, and permissions. The default backup file is stored in the /var/opt/gitlab/backups directory. You can modify /etc/gitlab
 Centos install mysql
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:09 PM
Centos install mysql
Apr 14, 2025 pm 08:09 PM
Installing MySQL on CentOS involves the following steps: Adding the appropriate MySQL yum source. Execute the yum install mysql-server command to install the MySQL server. Use the mysql_secure_installation command to make security settings, such as setting the root user password. Customize the MySQL configuration file as needed. Tune MySQL parameters and optimize databases for performance.
 How is the GPU support for PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:48 PM
How is the GPU support for PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:48 PM
Enable PyTorch GPU acceleration on CentOS system requires the installation of CUDA, cuDNN and GPU versions of PyTorch. The following steps will guide you through the process: CUDA and cuDNN installation determine CUDA version compatibility: Use the nvidia-smi command to view the CUDA version supported by your NVIDIA graphics card. For example, your MX450 graphics card may support CUDA11.1 or higher. Download and install CUDAToolkit: Visit the official website of NVIDIACUDAToolkit and download and install the corresponding version according to the highest CUDA version supported by your graphics card. Install cuDNN library:
 Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Docker uses Linux kernel features to provide an efficient and isolated application running environment. Its working principle is as follows: 1. The mirror is used as a read-only template, which contains everything you need to run the application; 2. The Union File System (UnionFS) stacks multiple file systems, only storing the differences, saving space and speeding up; 3. The daemon manages the mirrors and containers, and the client uses them for interaction; 4. Namespaces and cgroups implement container isolation and resource limitations; 5. Multiple network modes support container interconnection. Only by understanding these core concepts can you better utilize Docker.
 How to choose a GitLab database in CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:39 PM
How to choose a GitLab database in CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:39 PM
When installing and configuring GitLab on a CentOS system, the choice of database is crucial. GitLab is compatible with multiple databases, but PostgreSQL and MySQL (or MariaDB) are most commonly used. This article analyzes database selection factors and provides detailed installation and configuration steps. Database Selection Guide When choosing a database, you need to consider the following factors: PostgreSQL: GitLab's default database is powerful, has high scalability, supports complex queries and transaction processing, and is suitable for large application scenarios. MySQL/MariaDB: a popular relational database widely used in Web applications, with stable and reliable performance. MongoDB:NoSQL database, specializes in
 How to view GitLab logs under CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:18 PM
How to view GitLab logs under CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:18 PM
A complete guide to viewing GitLab logs under CentOS system This article will guide you how to view various GitLab logs in CentOS system, including main logs, exception logs, and other related logs. Please note that the log file path may vary depending on the GitLab version and installation method. If the following path does not exist, please check the GitLab installation directory and configuration files. 1. View the main GitLab log Use the following command to view the main log file of the GitLabRails application: Command: sudocat/var/log/gitlab/gitlab-rails/production.log This command will display product



