 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 Could the job applicant be a fake? Impostor uses deepfake to steal identity to apply for remote work, FBI: can recognize when speaking
Could the job applicant be a fake? Impostor uses deepfake to steal identity to apply for remote work, FBI: can recognize when speaking
Could the job applicant be a fake? Impostor uses deepfake to steal identity to apply for remote work, FBI: can recognize when speaking

Produced by Big Data Digest
Author: Caleb
Online work is gradually officially entering our lives.
According to statistics from data company Emsi Burning Glass, at the beginning of 2020, of the 163,000 job openings in New York City, only 6,700 allowed online work, accounting for 4% of the total number of positions; but by last year In December, among the 243,000 recruitment positions in the city, the number of online jobs increased to 25,800, accounting for 10.6% of the total number of positions.
But as the saying goes, people’s hearts are separated by the belly, not to mention that there is an extra layer of screens between them. No one can guarantee that the Neso incident will not happen again.
No, according to recent FBI investigations, more and more people are stealing other people's personal identity information and using deepfakes to apply for remote jobs. It is precisely because deepfake technology uses artificial intelligence or machine learning to generate content such as images, videos, or audios that it is difficult to distinguish it from real materials.


For example, according to foreign media reports, a scammer has been working remotely with the help of deepfake in an attempt to gain access to IT jobs and access their customer or financial data, as well as corporate IT data and professional information, etc.
Coincidentally, according to reports from other companies, some job seekers’ personal information belongs to another person entirely.
Videos and voices are all faked. Is it difficult to see through them?
On June 28, the FBI Cybercrime Complaint Center stated in a public consultation that the number of complaints about people being impersonated for job applications has increased recently. Scammers have been using deepfake technology and personally identifiable information stolen from victims to trick employers into hiring them for remote or work-from-home jobs.
These jobs involve IT, computer programming, database and software-related positions.

The identity disguise implemented by deepfake is often difficult to distinguish between authenticity and fraud, and scammers can steal valuable information from within the company. details, and conduct other identity fraud schemes.
Even according to federal law enforcement agencies, during the investigation, they also discovered that the interviewer’s voice used in the online interview had also been forged by deepfake.
It is unclear how many people have successfully joined the company using this method and how many of them have been reported.
It is not completely impossible to identify deepfake. The FBI says there is a way for employers to detect deepfakes. In their daily work, employees still need to video chat with their employers from time to time to report on work progress, etc. When they speak, that is when their flaws are revealed.
"In front of the camera, if the movements and lip movements of the person being interviewed cannot be fully synchronized with the voice", "such as a sudden cough, sneeze or other auditory behavior and visual presentation "The content is inconsistent", that is often the key to seeing through deepfake.

But it’s not that easy to see through deepfake, especially if you don’t pay special attention. According to a recent report by Carnegie Mellon University researchers, the accuracy of artificial intelligence designed to detect doctored videos could range from 30% to 97%. Humans have ways of detecting fake videos, especially once they Trained to see certain visual glitches, such as abnormal shadows or problematic skin texture.
How deepfake is used depends on the person
Whether deepfake is used well or not, is it used on the "edge" , but also depends on the person.
In 2021, former Beatle Paul McCartney used deepfake technology to "return to youth". In the MV with Beck, the audience sees a young, flexible McCartney, with no trace of time left on him.
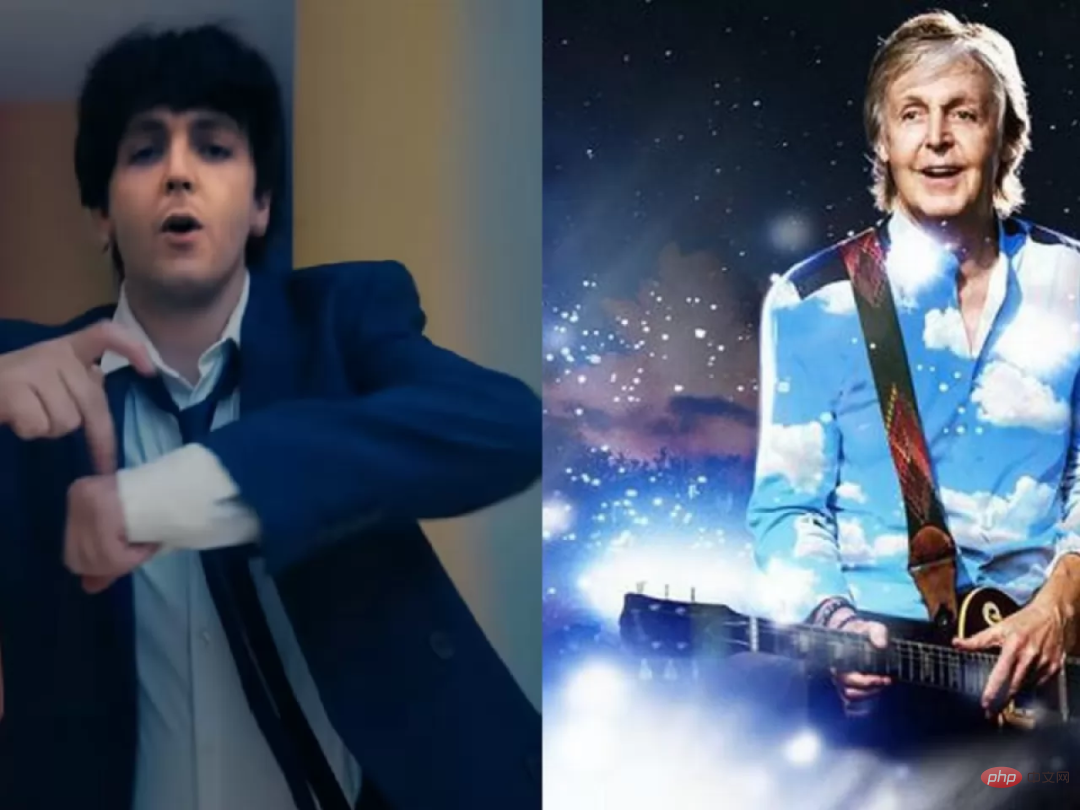

Musk was also deepfake last month.
In this video of TED Chairman "Chris Anderson" interviewing Musk, Musk said that a cryptocurrency trading platform called BitVex was created by himself and promised that within three months, any crypto Currency deposits earn 30% daily returns.


#deepfake also does good things sometimes.
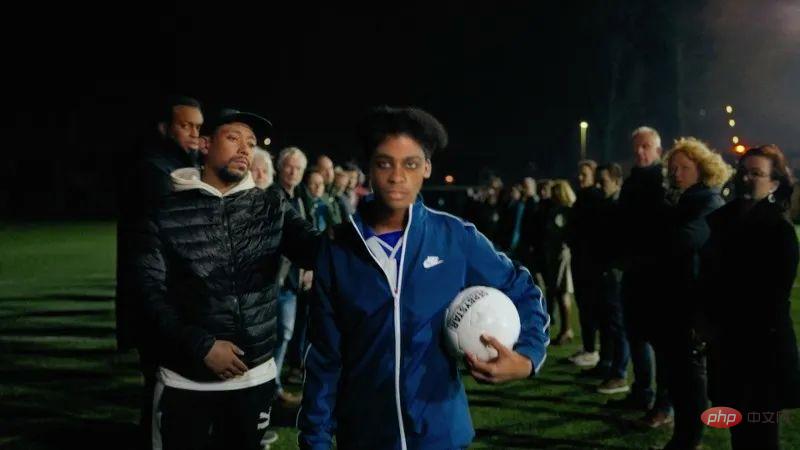
Recently, in a case that reopened the investigation in the Netherlands, in order to find out the truth about 13-year-old Sedar Soares who was shot and killed while throwing snowballs with his friends, with the permission of Sedar Soares’ family Next, the police used deepfake to create a video of Sedar Soares to collect clues from the public and find witnesses. In the minute-long video, images of Soares' life appear as he greets the camera and picks up a football. The day after the video was released, Rotterdam police spokesperson Lillian van Duijvenbode said: "The fact that we have received dozens of tips is very positive."

Again, the value orientation of technology depends on the people who use the technology.
Exercise your deepfake recognition ability
As an AI deep learning tool, deepfake can replace the face of a person in a picture. Technology that takes someone else's picture to create a very realistic "fake" video or picture, hence the name "face swapping".
The researchers used the autoencoder neural architecture to make this idea a reality. The basic idea is very simple: train a set of encoders and corresponding decoding neural networks for each face. When coding, the picture of the first person was used. When decoding, a second human decoder is used.
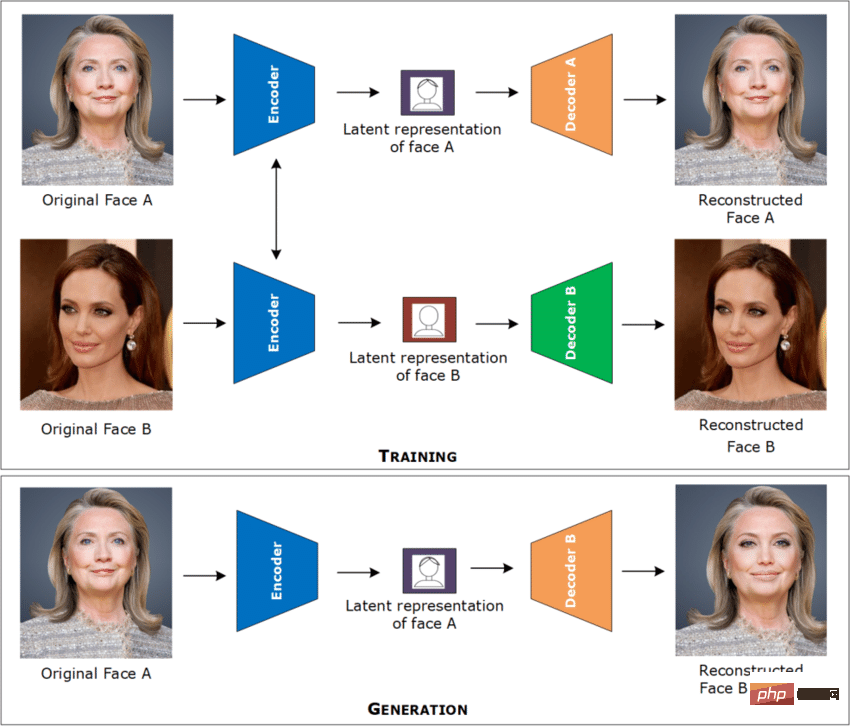
In order to help people better identify deepfake scams, researchers also collected 100,000 deepfakes hosted in Kaggle public competitions videos and 19,154 real videos, a series of neural networks were trained to detect deepfakes.
In general, there is no completely absolute method to help identification, but there are several points worth noting in deepfake:
- Pay attention to the face: High-end DeepFake manipulations are almost all based on the face;
- Pay attention to the cheeks and forehead: Does the skin appear too smooth or too wrinkled? Does skin aging match the aging of hair and eyes? Deepfakes tend to be jarring in some ways;
- Pay attention to the eyes and eyebrows: are the shadows in the right place? Deepfakes often fail to replicate scenes with natural physics completely correctly;
- Watch out for glasses: Is there any glare? Is there too much glare? Does the angle of glare change when a person moves? Once again, DeepFakes often don't fully represent the natural physics of lighting;
- Pay attention to facial hair, or lack thereof: does facial hair look realistic? Deepfake may add or remove beards, sideburns or beards, but such behavior often brings a sense of disobedience;
- Pay attention to moles on the face: Do moles look real;
- Pay attention to blinking: Whether the person blinks enough or too much;
- Pay attention to the size and color of the lips: whether the size and color match the rest of the person's face.
These eight questions can help people check and identify deepfake.
High-quality deepfake is not easy to identify, but through practice, people can establish an intuition based on the authenticity of deepfake. Just trust the intuition and use appropriate auxiliary verification. .
If you are still worried, you can also take a simple test on this website: https://detectfakes.media.mit.edu/
The above is the detailed content of Could the job applicant be a fake? Impostor uses deepfake to steal identity to apply for remote work, FBI: can recognize when speaking. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1382
1382
 52
52
 YOLO is immortal! YOLOv9 is released: performance and speed SOTA~
Feb 26, 2024 am 11:31 AM
YOLO is immortal! YOLOv9 is released: performance and speed SOTA~
Feb 26, 2024 am 11:31 AM
Today's deep learning methods focus on designing the most suitable objective function so that the model's prediction results are closest to the actual situation. At the same time, a suitable architecture must be designed to obtain sufficient information for prediction. Existing methods ignore the fact that when the input data undergoes layer-by-layer feature extraction and spatial transformation, a large amount of information will be lost. This article will delve into important issues when transmitting data through deep networks, namely information bottlenecks and reversible functions. Based on this, the concept of programmable gradient information (PGI) is proposed to cope with the various changes required by deep networks to achieve multi-objectives. PGI can provide complete input information for the target task to calculate the objective function, thereby obtaining reliable gradient information to update network weights. In addition, a new lightweight network framework is designed
 The foundation, frontier and application of GNN
Apr 11, 2023 pm 11:40 PM
The foundation, frontier and application of GNN
Apr 11, 2023 pm 11:40 PM
Graph neural networks (GNN) have made rapid and incredible progress in recent years. Graph neural network, also known as graph deep learning, graph representation learning (graph representation learning) or geometric deep learning, is the fastest growing research topic in the field of machine learning, especially deep learning. The title of this sharing is "Basics, Frontiers and Applications of GNN", which mainly introduces the general content of the comprehensive book "Basics, Frontiers and Applications of Graph Neural Networks" compiled by scholars Wu Lingfei, Cui Peng, Pei Jian and Zhao Liang. . 1. Introduction to graph neural networks 1. Why study graphs? Graphs are a universal language for describing and modeling complex systems. The graph itself is not complicated, it mainly consists of edges and nodes. We can use nodes to represent any object we want to model, and edges to represent two
 An overview of the three mainstream chip architectures for autonomous driving in one article
Apr 12, 2023 pm 12:07 PM
An overview of the three mainstream chip architectures for autonomous driving in one article
Apr 12, 2023 pm 12:07 PM
The current mainstream AI chips are mainly divided into three categories: GPU, FPGA, and ASIC. Both GPU and FPGA are relatively mature chip architectures in the early stage and are general-purpose chips. ASIC is a chip customized for specific AI scenarios. The industry has confirmed that CPUs are not suitable for AI computing, but they are also essential in AI applications. GPU Solution Architecture Comparison between GPU and CPU The CPU follows the von Neumann architecture, the core of which is the storage of programs/data and serial sequential execution. Therefore, the CPU architecture requires a large amount of space to place the storage unit (Cache) and the control unit (Control). In contrast, the computing unit (ALU) only occupies a small part, so the CPU is performing large-scale parallel computing.
 'The owner of Bilibili UP successfully created the world's first redstone-based neural network, which caused a sensation on social media and was praised by Yann LeCun.'
May 07, 2023 pm 10:58 PM
'The owner of Bilibili UP successfully created the world's first redstone-based neural network, which caused a sensation on social media and was praised by Yann LeCun.'
May 07, 2023 pm 10:58 PM
In Minecraft, redstone is a very important item. It is a unique material in the game. Switches, redstone torches, and redstone blocks can provide electricity-like energy to wires or objects. Redstone circuits can be used to build structures for you to control or activate other machinery. They themselves can be designed to respond to manual activation by players, or they can repeatedly output signals or respond to changes caused by non-players, such as creature movement and items. Falling, plant growth, day and night, and more. Therefore, in my world, redstone can control extremely many types of machinery, ranging from simple machinery such as automatic doors, light switches and strobe power supplies, to huge elevators, automatic farms, small game platforms and even in-game machines. built computer. Recently, B station UP main @
 How to solve the problem that Windows Hello face camera cannot be found in win11 facial recognition?
Mar 28, 2024 am 09:21 AM
How to solve the problem that Windows Hello face camera cannot be found in win11 facial recognition?
Mar 28, 2024 am 09:21 AM
When we use the win11 system, we have a function called windowshello face. This function is mainly used for face unlocking. However, many users are asking about the solution for win11 facial recognition and cannot find the windowshello face camera? Let this site carefully introduce to users the solution to the problem that Win11 facial recognition cannot find faces. How to solve the problem of Windows 11 facial recognition not being able to find Windows Shello face camera? Solution 1. Roll back the biometric driver 1. Open the device manager - biometric device - right click on Windows helloface software device properties > driver > roll back the driver
 A drone that can withstand strong winds? Caltech uses 12 minutes of flight data to teach drones to fly in the wind
Apr 09, 2023 pm 11:51 PM
A drone that can withstand strong winds? Caltech uses 12 minutes of flight data to teach drones to fly in the wind
Apr 09, 2023 pm 11:51 PM
When the wind is strong enough to blow the umbrella, the drone is stable, just like this: Flying with the wind is a part of flying in the air. From a large level, when the pilot lands the aircraft, the wind speed may be Bringing challenges to them; on a smaller level, gusty winds can also affect drone flight. Currently, drones either fly under controlled conditions, without wind, or are operated by humans using remote controls. Drones are controlled by researchers to fly in formations in the open sky, but these flights are usually conducted under ideal conditions and environments. However, for drones to autonomously perform necessary but routine tasks, such as delivering packages, they must be able to adapt to wind conditions in real time. To make drones more maneuverable when flying in the wind, a team of engineers from Caltech
 Multi-path, multi-domain, all-inclusive! Google AI releases multi-domain learning general model MDL
May 28, 2023 pm 02:12 PM
Multi-path, multi-domain, all-inclusive! Google AI releases multi-domain learning general model MDL
May 28, 2023 pm 02:12 PM
Deep learning models for vision tasks (such as image classification) are usually trained end-to-end with data from a single visual domain (such as natural images or computer-generated images). Generally, an application that completes vision tasks for multiple domains needs to build multiple models for each separate domain and train them independently. Data is not shared between different domains. During inference, each model will handle a specific domain. input data. Even if they are oriented to different fields, some features of the early layers between these models are similar, so joint training of these models is more efficient. This reduces latency and power consumption, and reduces the memory cost of storing each model parameter. This approach is called multi-domain learning (MDL). In addition, MDL models can also outperform single
 How to solve the problem of facial recognition not working on Apple mobile phone
Mar 08, 2024 pm 06:28 PM
How to solve the problem of facial recognition not working on Apple mobile phone
Mar 08, 2024 pm 06:28 PM
Facial recognition on Apple phones doesn’t work. Users don’t have to worry if they encounter this situation. It’s not necessarily a problem with the device. You can try many methods to solve it. I’ll introduce it to you today. What should I do if the facial recognition on my Apple phone is not working? Solutions: 1. The FaceID function needs to ensure that there are no foreign objects blocking the face and that the face is unobstructed. Check that the front camera is not blocked. 2. Check the ambient lighting environment: When face recognition is performed, it is necessary to maintain sufficient ambient brightness and avoid interference from strong light sources. 3. Reset FaceID: Open the "Face & Password" option in "Settings" and click "Reset Face ID" to reset FaceID. 4. Upgrade the iOS version: If the iOS version running on the device is too old, it may affect Fac due to insufficient stability.



