 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 AI writes its own code to allow the agent to evolve! OpenAI's large model tastes like 'human thought”
AI writes its own code to allow the agent to evolve! OpenAI's large model tastes like 'human thought”
AI writes its own code to allow the agent to evolve! OpenAI's large model tastes like 'human thought”
Make trouble!
The AI "looked" at how humans submitted updates (commits) on GitHub, and then imitated human programmers to modify the code...
In the end, the AI was successfully "trained" An intelligent robot was born:
No kidding, this kind of scary thing actually happened in a recent study released by OpenAI …
Originally, what researchers wanted to solve was a genetic programming (GP) problem—making an intelligent robot learn to move.
(GP is a special field in evolutionary computing. It is mainly aimed at automatically building programs to solve problems independently.)
But OpenAI takes a different approach and uses its own large-scale language model (LLM) ) was put in, and the result was a big "never expected".
In the past, in the process of intelligent agent evolution, human researchers needed to participate in making some detailed adjustments and determining the direction of evolution, so that the intelligent agent could develop in a good direction.
Now, all these tasks are taken care of by the big model. You can learn, write your own code, and "tune" yourself:
This As soon as Joel Lehman, the author of the paper, was exposed on the Internet, it instantly attracted a lot of attention from netizens:
After reading it, a programmer netizen said, "I can't keep up ( The pace of technology) development has:
Even OpenAI itself said in research:
Bridges the gap between evolutionary algorithms operating at the level of human thought.
So how did AI accomplish this "magical" thing?
Take a look at GitHub, AI types the code by itself
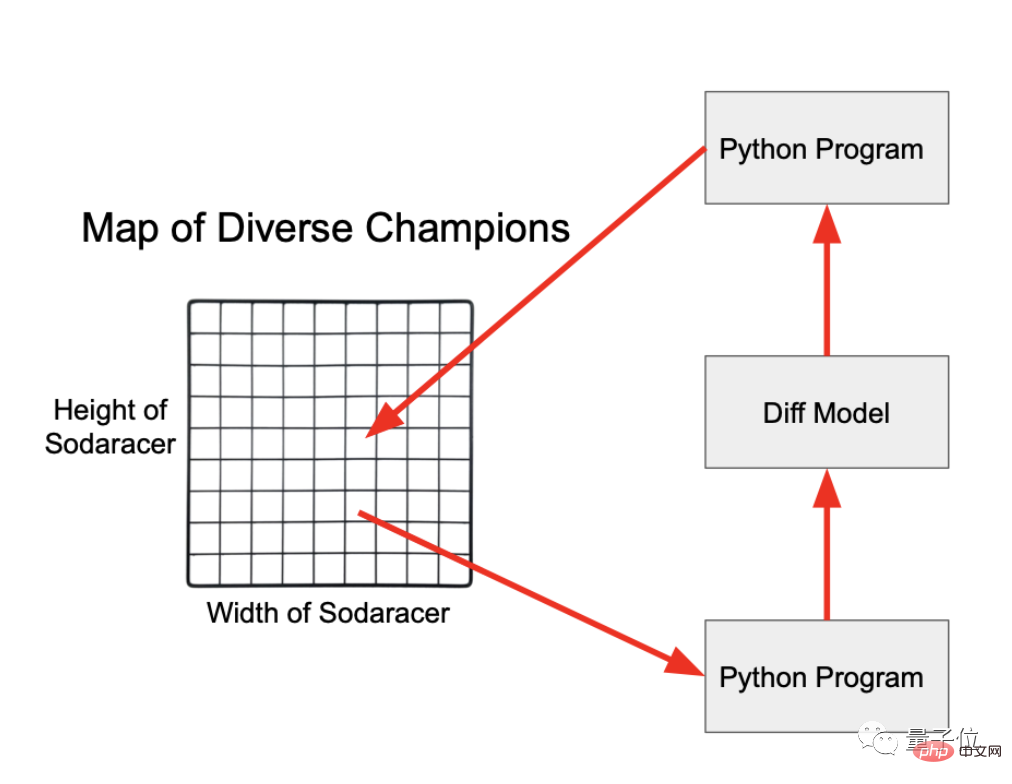
Designing movable robots in a virtual environment is a very popular project in genetic algorithm research.
In particular, the Sodarace competition is very popular because it requires a small amount of calculations and facilitates visualization of the process.
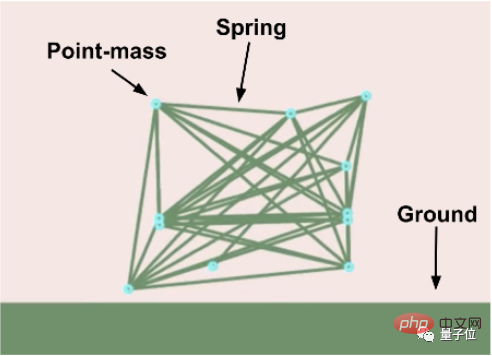
The rules are simple. Robots composed of "joints" and "muscles" race on various terrains.
OpenAI also deliberately rewritten the entire competition program from dedicated genetic coding to a Python version in order to demonstrate the versatility of the new method to modern programming languages.
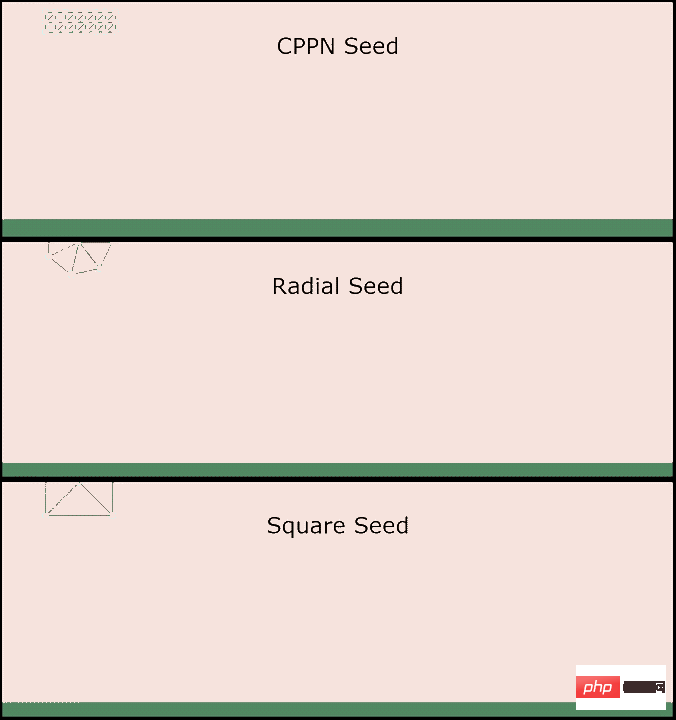
For example, this piece of Python code can be used as the initial seed robot.

After defining the four vertex joints and end joints of a square and connecting them with "muscles", the result is as follows.
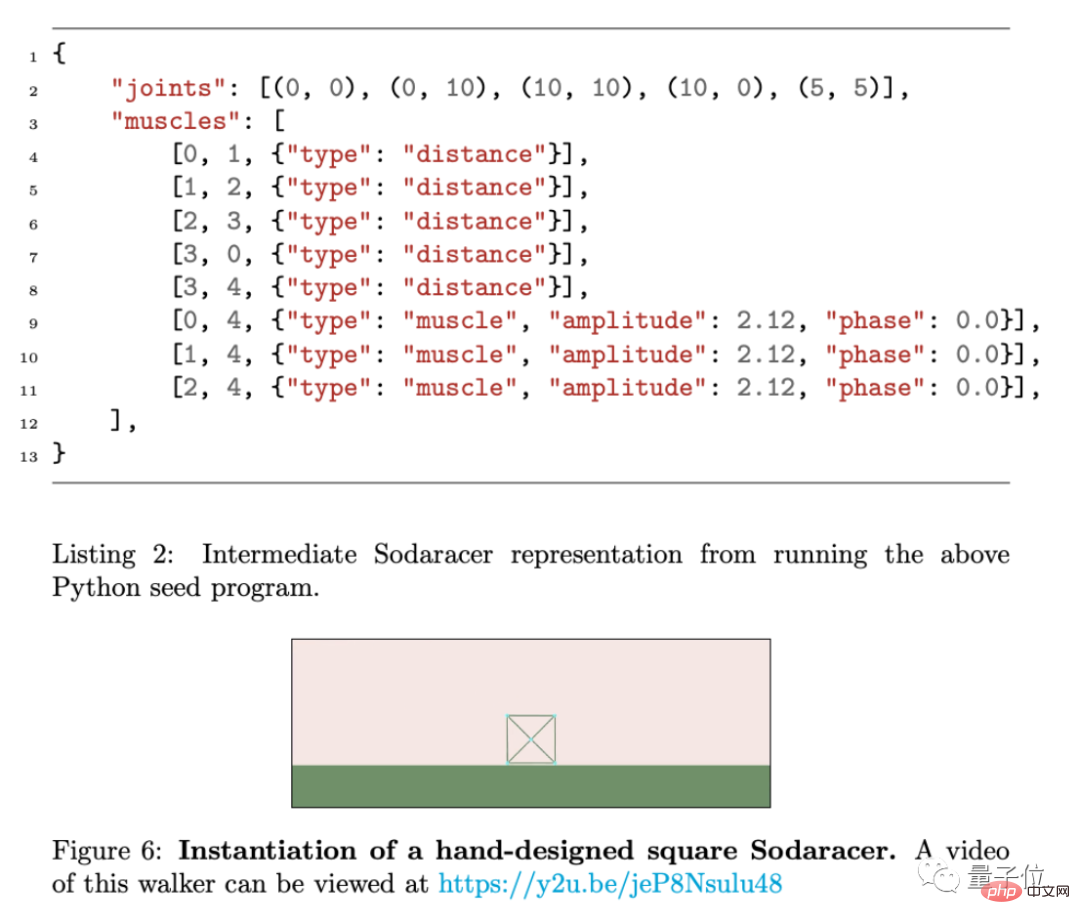
#However, such a square structure cannot move at all. Next, the code needs to be modified by genetic algorithm.
The research team believes that there are still two gaps in efficiency between using traditional genetic algorithms to modify code versus human programmers doing it themselves:
One is that software is becoming more and more complex, and humans can create modules However, the most advanced genetic algorithms currently cannot do this in programming languages used by humans.
The other is that almost all genetic algorithms rely on random mutations, and every time human programmers modify the code, they have a purpose, either to add functionality, to improve efficiency, or to repair it. bug.
So is there a way for AI to learn how humans modify the code?
Yes, the required training data is all stored on GitHub.
Excellent programmers will write a commit description every time they submit code, explaining clearly what has been modified in this submission.
The commit description combined with the diff data comparing the code before and after submission is an excellent learning material for AI.
The researchers screened out some submitted data with clear descriptions and small amounts of modified code to train a GPT-3 architecture AI model.
It is equivalent to letting AI learn from human programmers how to modify a piece of code purposefully.
The model used in this paper does not need to be as large as the 175 billion parameters of the full version of GPT-3, and a maximum of 750 million parameters is enough.
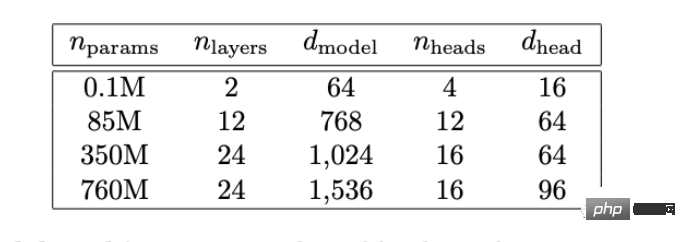
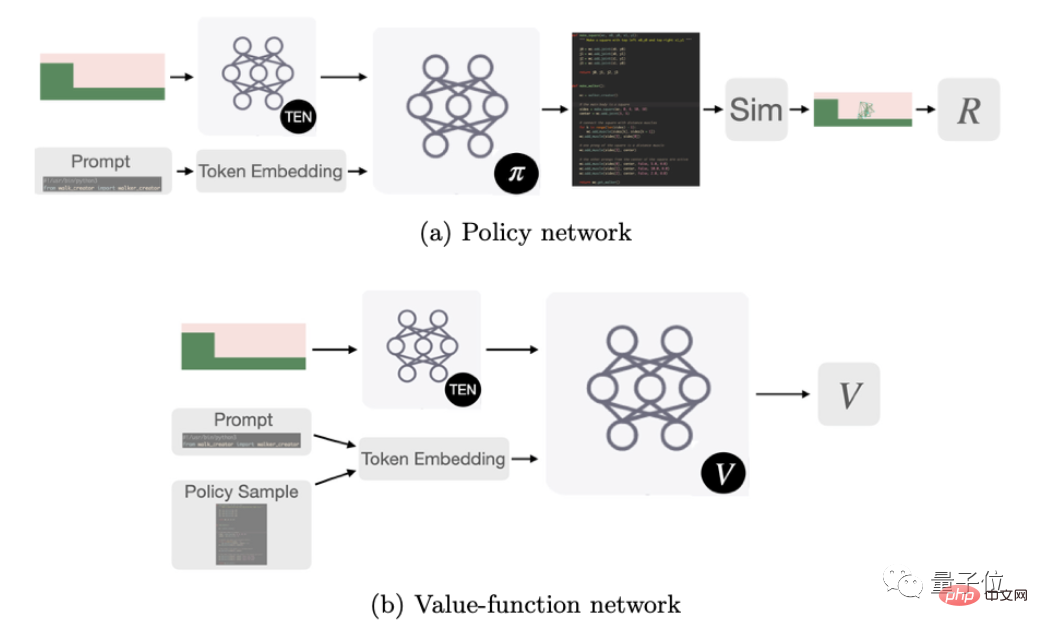
The basic AI model is thus obtained, which will play the role of mutation operator in the genetic algorithm.
The next process of letting AI design a new robot is divided into three steps.
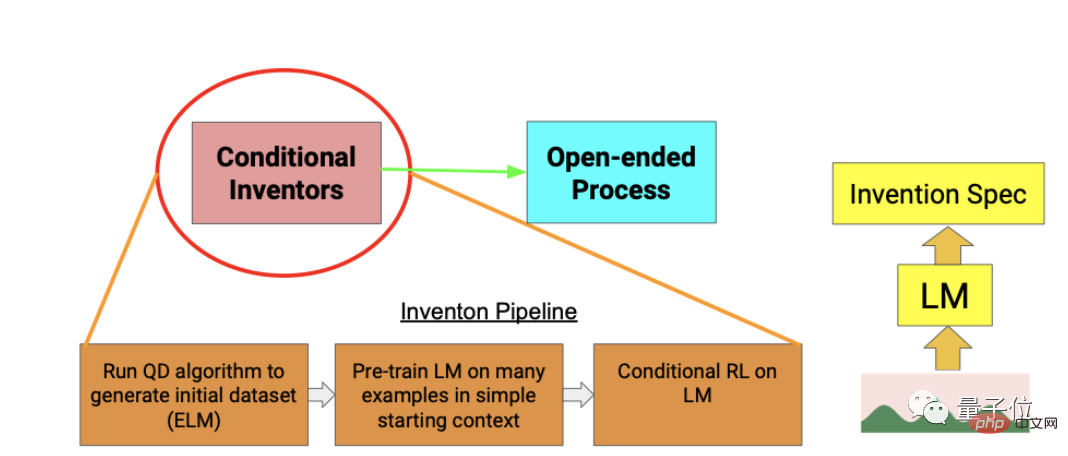
The first step is to use the classic MAP-Elites algorithm to generate an initial set of robots.
This is a QD (Quality Diversity) algorithm that ensures that robots behave differently and are all of high quality.
The second step is to use the initial data generated in the first step for pre-training, so that the AI can first learn to design robots within the training data distribution.
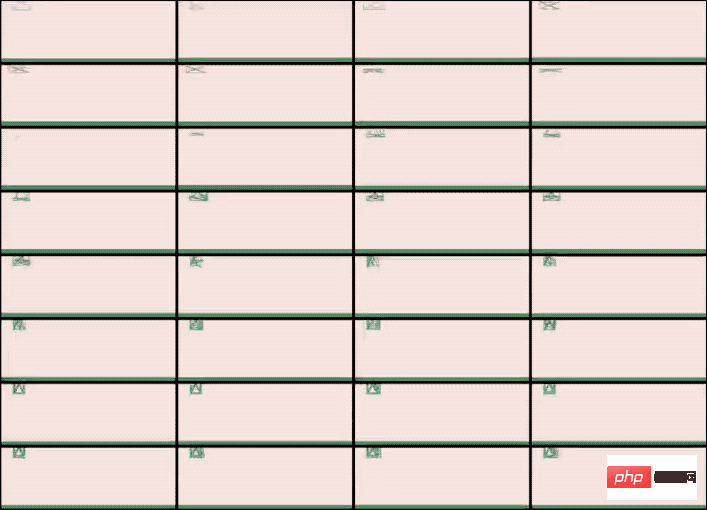
That’s the animated picture at the beginning that shocked everyone on the Internet, showing how AI transforms an immovable “block” into a mobile robot with alternating bouncing legs step by step.
The third step is to fine-tune the reinforcement learning algorithm so that the AI can generate robots that can adapt to the environment according to different terrain conditions.
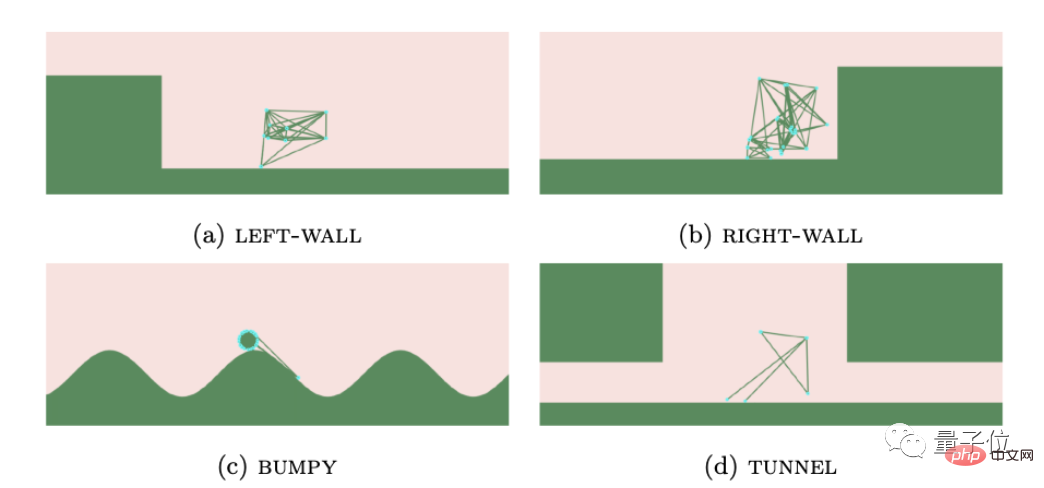
In the end, the researchers selected robots that evolved from the first three seeds to demonstrate the effects.
It can be seen that their structure and movement methods are completely different.

Netizens exclaimed “the thinking is so clear”
Once this study was announced, it can be said that it caused thousands of waves with one stone.
Many netizens are amazed by this novel way of combining "large model evolution algorithm":

Researchers who have done related work also said , I never thought that I could use a large model to learn mutations in the form of diffs:
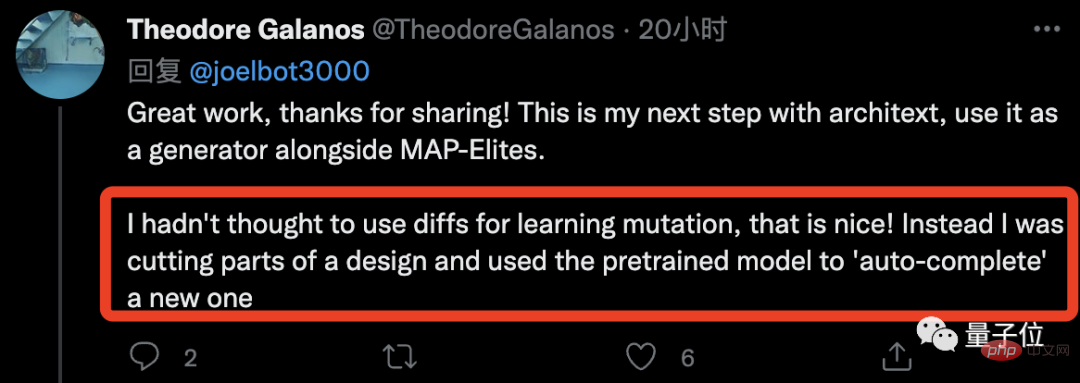
In addition to the discussion of the research model and itself, some netizens also added this Picture:

Emmm...it’s a bit like that.
Team Introduction
The team members of this research are all from OpenAI.
The first author of the paper is Joel Lehman, a machine learning scientist. Its areas of focus include artificial intelligence security, reinforcement learning and open search algorithms.

At the same time, Joel Lehman previously co-wrote a scientific book "Why Greatness Cannot Be Planned: The Secret of Objectiveness" based on his thoughts on the development of artificial intelligence:

As for the next step of this research, Joel Lehman himself said:
There is another important question, which is the extent to which the model can be applied to other environments.
The efficacy of mutations in GP can now be greatly improved by ELM, which will inspire a wide range of new applications and research directions.
So has this research also given you new inspiration?
Reference link:
[1]https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.08896
[2]https://twitter. com/joelbot3000/status/1538770905119150080?s=21&t=l8AASYjgC6RAEEimcQaFog
The above is the detailed content of AI writes its own code to allow the agent to evolve! OpenAI's large model tastes like 'human thought”. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to solve the problem of third-party interface returning 403 in Node.js environment?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
How to solve the problem of third-party interface returning 403 in Node.js environment?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
Solve the problem of third-party interface returning 403 in Node.js environment. When we use Node.js to call third-party interfaces, we sometimes encounter an error of 403 from the interface returning 403...
 In Laravel, how to deal with the situation where verification codes are failed to be sent by email?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
In Laravel, how to deal with the situation where verification codes are failed to be sent by email?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
The method of handling Laravel's email failure to send verification code is to use Laravel...
 How to automatically set permissions of unixsocket after system restart?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
How to automatically set permissions of unixsocket after system restart?
Mar 31, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
How to automatically set the permissions of unixsocket after the system restarts. Every time the system restarts, we need to execute the following command to modify the permissions of unixsocket: sudo...
 How to implement sorting and add rankings in PHP two-dimensional arrays?
Apr 01, 2025 am 07:00 AM
How to implement sorting and add rankings in PHP two-dimensional arrays?
Apr 01, 2025 am 07:00 AM
Detailed explanation of PHP two-dimensional array sorting and ranking implementation This article will explain in detail how to sort a PHP two-dimensional array and use each sub-array according to the sorting results...
 Why does an error occur when installing an extension using PECL in a Docker environment? How to solve it?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:06 PM
Why does an error occur when installing an extension using PECL in a Docker environment? How to solve it?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 03:06 PM
Causes and solutions for errors when using PECL to install extensions in Docker environment When using Docker environment, we often encounter some headaches...
 Ouyi okex global website official website login entrance 2025
Mar 31, 2025 pm 03:45 PM
Ouyi okex global website official website login entrance 2025
Mar 31, 2025 pm 03:45 PM
Ouyi OKX (formerly OKEx) Global Station is a world-leading digital asset service platform founded in 2017 and headquartered in Malta. It has tens of millions of users. The platform provides transactions of more than 150 currencies and has formulated a strict currency audit mechanism and market monitoring and progress tracking mechanism. Supports transactions of more than 20 mainstream legal currencies and cryptocurrencies such as the US dollar, euro, and pound.
 How does PHP implement AES encryption and decryption consistent with Java?
Apr 01, 2025 am 07:15 AM
How does PHP implement AES encryption and decryption consistent with Java?
Apr 01, 2025 am 07:15 AM
How to implement AES encryption and decryption with Java...
 How to get the return code when email sending fails in Laravel?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 02:45 PM
How to get the return code when email sending fails in Laravel?
Apr 01, 2025 pm 02:45 PM
Method for obtaining the return code when Laravel email sending fails. When using Laravel to develop applications, you often encounter situations where you need to send verification codes. And in reality...





