 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 Using one line of code to greatly improve the effect of zero-shot learning methods, Nanjing University of Technology & Oxford propose a plug-and-play classifier module
Using one line of code to greatly improve the effect of zero-shot learning methods, Nanjing University of Technology & Oxford propose a plug-and-play classifier module
Using one line of code to greatly improve the effect of zero-shot learning methods, Nanjing University of Technology & Oxford propose a plug-and-play classifier module
Zero-shot learning (Zero-Shot Learning) focuses on classifying categories that have not appeared during the training process. Zero-shot learning based on semantic description is implemented through pre-defined high-order semantic information for each category. Knowledge transfer from seen class to unseen class. Traditional zero-shot learning only needs to identify unseen classes in the test phase, while generalized zero-shot learning (GZSL) needs to identify both visible and unseen classes. Its evaluation indicators are the average accuracy of visible classes and the average accuracy of unseen classes. Harmonic average of accuracy.
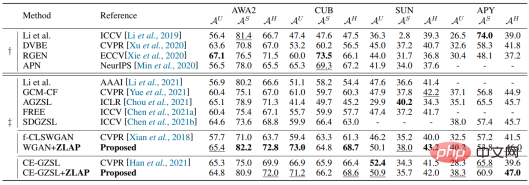
A common zero-shot learning strategy is to use visible class samples and semantics to train a conditional generation model from semantic space to visual sample space, and then generate unseen classes with the help of unseen class semantics pseudo-samples, and finally use visible class samples and unseen class pseudo-samples to train the classification network. However, learning a good mapping relationship between two modalities (semantic modality and visual modality) usually requires a large number of samples (refer to CLIP), which cannot be achieved in traditional zero-shot learning environments. Therefore, the visual sample distribution generated using unseen class semantics usually deviates from the real sample distribution, which means the following two points: 1. The unseen class accuracy obtained by this method is limited. 2. When the average number of pseudo-samples generated per class for unseen classes is equivalent to the average number of samples for each class for visible classes, there is a large difference between the accuracy of unseen classes and the accuracy of visible classes, as shown in Table 1 below.
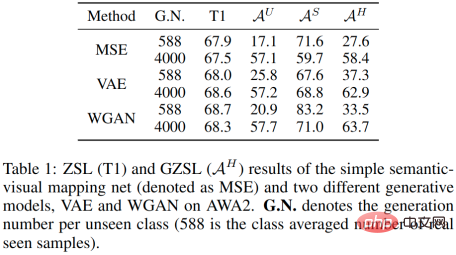
#We found that even if we only learn the mapping of semantics to category center points, we can also map unseen class semantics Copying a single sample point multiple times and then participating in classifier training can also achieve an effect close to using a generative model. This means that the unseen pseudo-sample features generated by the generative model are relatively homogeneous to the classifier.
Previous methods usually cater to GZSL evaluation metrics by generating a large number of unseen class pseudo-samples (although a large number of samples is not helpful for unseen class inter-class discrimination) ). However, this re-sampling strategy has been proven in the field of long-tail learning to cause the classifier to overfit on some features, which is pseudo-unseen that deviates from the real sample. class characteristics. This situation is not conducive to the identification of real samples of seen and unseen classes. So, can we abandon this resampling strategy and instead use the offset and homogeneity of generating pseudo-samples of unseen classes (or the class imbalance between seen classes and unseen classes) as inductive bias? What about classifier learning?
Based on this, weproposed a plug-and-play classifier module that can improve generative zero-shot learning by just modifying one line of code. The effect of the method. Only 10 pseudo-samples are generated per unseen class to achieve SOTA level. Compared with other generative zero-sample methods, the new method has a huge advantage in computational complexity. Research members are from Nanjing University of Science and Technology and Oxford University.

- Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.11822
- Code: https://github.com/cdb342/IJCAI-2022-ZLA
This article uses the consistent training and testing goals as a guide to derive the variational lower bound of the generalized zero-shot learning evaluation index. The classifier modeled in this way can avoid using the re-adoption strategy and prevent the classifier from overfitting on the generated pseudo samples and adversely affecting the recognition of real samples. The proposed method can make the embedding-based classifier effective in the generative method framework and reduce the classifier's dependence on the quality of generated pseudo samples.
Method
1. Introducing parameterized prior
We decided to start with the loss function of the classifier. Assuming that the class space has been completed by generated pseudo-samples of unseen classes, the previous classifier is optimized with the goal of maximizing global accuracy:
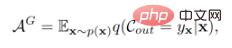

Where  is the global accuracy,
is the global accuracy,  represents the classifier output,
represents the classifier output,  represents the sample distribution,
represents the sample distribution,  is the corresponding label of sample X. The evaluation index of GZSL is:
is the corresponding label of sample X. The evaluation index of GZSL is:
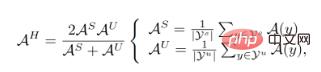

 and
and  Represents visible class and unseen class collections respectively. The inconsistency between training objectives and testing objectives means that previous classifier training strategies did not take into account the differences between seen and unseen classes. Naturally, we try to achieve consistent results between training and testing goals by deriving
Represents visible class and unseen class collections respectively. The inconsistency between training objectives and testing objectives means that previous classifier training strategies did not take into account the differences between seen and unseen classes. Naturally, we try to achieve consistent results between training and testing goals by deriving 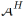 . After derivation, we got its lower bound:
. After derivation, we got its lower bound:
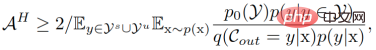
where 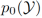 represents the visible class - the unseen class prior, It has nothing to do with the data and is adjusted as a hyperparameter in the experiment.
represents the visible class - the unseen class prior, It has nothing to do with the data and is adjusted as a hyperparameter in the experiment. 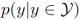 represents the internal prior of the visible class or the unseen class, which is replaced by the frequency of the visible class sample or the uniform distribution during the implementation process. By maximizing the lower bound of
represents the internal prior of the visible class or the unseen class, which is replaced by the frequency of the visible class sample or the uniform distribution during the implementation process. By maximizing the lower bound of 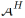 , we obtain the final optimization goal:
, we obtain the final optimization goal:
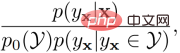
Thus, our classification The modeling objectives have undergone the following changes compared to the previous ones:
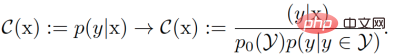
Fitting the posterior probability by using cross-entropy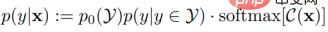 , we get the classifier loss as:
, we get the classifier loss as:
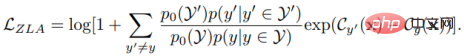
This is similar to the logic adjustment (Logit Adjustment) in long-tail learning, so we call it zero-sample logic adjustment (ZLA). So far, we have implemented the introduction of parameterized priors to implant the category imbalance between seen classes and unseen classes as inductive bias into classifier training, and only need to add additional bias terms to the original logits in the code implementation. can achieve the above effects.

#2. Introducing semantic prior
So far, the core of zero-sample migration is semantic prior. ) only plays a role in the training generator and pseudo-sample generation stages. The identification of unseen classes depends entirely on the quality of the generated unseen class pseudo-samples. Obviously, if semantic priors can be introduced in the classifier training stage, it will help to identify unseen classes. In the field of zero-shot learning, there is a class of embedding-based methods that can achieve this function. However, this type of method is similar to the knowledge learned by the generative model, that is, the connection between semantics and vision (semantic-visual link), which led to the direct introduction of the previous generative framework (refer to the paper f-CLSWGAN) based on The embedded classifier cannot achieve better results than the original (unless the classifier itself has better zero-shot performance). Through the ZLA strategy proposed in this paper, we are able to change the role that the generated pseudo-samples of unseen classes play in classifier training. From the original provision of invisible class information to the current adjustment of the decision boundary between invisible classes and visible classes, we can introduce semantic priors in the classifier training stage. Specifically, we use a prototype learning method to map the semantics of each category into a visual prototype (i.e., classifier weight), and then model the adjusted posterior probability as the cosine similarity between the sample and the visual prototype. Degree (cosine similarity), that is,
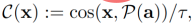
where 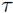 is the temperature coefficient. In the testing phase, samples are predicted to correspond to the category of the visual prototype with the greatest cosine similarity.
is the temperature coefficient. In the testing phase, samples are predicted to correspond to the category of the visual prototype with the greatest cosine similarity.
Experiment
We combine the proposed classifier with the basic WGAN to generate 10 samples in each unseen class The effect is comparable to SoTAs. In addition, we inserted it into the more advanced CE-GZSL method to improve the initial effect without changing other parameters (including the number of generated samples).
In ablation experiments, we compared a generation-based prototype learner with a pure prototype learner. We found that the last ReLU layer is critical to the success of a pure prototype learner because zeroing out negative numbers increases the similarity of the category prototype to unseen class features (unseen class features are also ReLU activated). However, setting some values to zero also limits the expression of the prototype, which is not conducive to further recognition performance. Using pseudo-unseen class samples to compensate for unseen class information can not only achieve higher performance when using RuLU, but also achieve further performance transcendence without a ReLU layer.
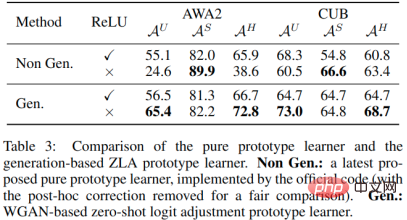
In another ablation study, we compared a prototype learner to an initial classifier. The results show that the prototype learner has no advantage over the initial classifier when generating a large number of unseen class samples. When using the ZLA technology proposed in this article, the prototype learner shows its superiority. As mentioned before, this is because both the prototype learner and the generative model are learning semantic-visual connections, so the semantic information is difficult to fully utilize. ZLA enables the generated unseen class samples to adjust the decision boundary instead of just providing unseen class information, thereby activating the prototype learner.
The above is the detailed content of Using one line of code to greatly improve the effect of zero-shot learning methods, Nanjing University of Technology & Oxford propose a plug-and-play classifier module. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1384
1384
 52
52
 This article will take you to understand SHAP: model explanation for machine learning
Jun 01, 2024 am 10:58 AM
This article will take you to understand SHAP: model explanation for machine learning
Jun 01, 2024 am 10:58 AM
In the fields of machine learning and data science, model interpretability has always been a focus of researchers and practitioners. With the widespread application of complex models such as deep learning and ensemble methods, understanding the model's decision-making process has become particularly important. Explainable AI|XAI helps build trust and confidence in machine learning models by increasing the transparency of the model. Improving model transparency can be achieved through methods such as the widespread use of multiple complex models, as well as the decision-making processes used to explain the models. These methods include feature importance analysis, model prediction interval estimation, local interpretability algorithms, etc. Feature importance analysis can explain the decision-making process of a model by evaluating the degree of influence of the model on the input features. Model prediction interval estimate
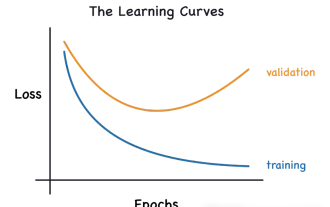 Identify overfitting and underfitting through learning curves
Apr 29, 2024 pm 06:50 PM
Identify overfitting and underfitting through learning curves
Apr 29, 2024 pm 06:50 PM
This article will introduce how to effectively identify overfitting and underfitting in machine learning models through learning curves. Underfitting and overfitting 1. Overfitting If a model is overtrained on the data so that it learns noise from it, then the model is said to be overfitting. An overfitted model learns every example so perfectly that it will misclassify an unseen/new example. For an overfitted model, we will get a perfect/near-perfect training set score and a terrible validation set/test score. Slightly modified: "Cause of overfitting: Use a complex model to solve a simple problem and extract noise from the data. Because a small data set as a training set may not represent the correct representation of all data." 2. Underfitting Heru
 Transparent! An in-depth analysis of the principles of major machine learning models!
Apr 12, 2024 pm 05:55 PM
Transparent! An in-depth analysis of the principles of major machine learning models!
Apr 12, 2024 pm 05:55 PM
In layman’s terms, a machine learning model is a mathematical function that maps input data to a predicted output. More specifically, a machine learning model is a mathematical function that adjusts model parameters by learning from training data to minimize the error between the predicted output and the true label. There are many models in machine learning, such as logistic regression models, decision tree models, support vector machine models, etc. Each model has its applicable data types and problem types. At the same time, there are many commonalities between different models, or there is a hidden path for model evolution. Taking the connectionist perceptron as an example, by increasing the number of hidden layers of the perceptron, we can transform it into a deep neural network. If a kernel function is added to the perceptron, it can be converted into an SVM. this one
 The evolution of artificial intelligence in space exploration and human settlement engineering
Apr 29, 2024 pm 03:25 PM
The evolution of artificial intelligence in space exploration and human settlement engineering
Apr 29, 2024 pm 03:25 PM
In the 1950s, artificial intelligence (AI) was born. That's when researchers discovered that machines could perform human-like tasks, such as thinking. Later, in the 1960s, the U.S. Department of Defense funded artificial intelligence and established laboratories for further development. Researchers are finding applications for artificial intelligence in many areas, such as space exploration and survival in extreme environments. Space exploration is the study of the universe, which covers the entire universe beyond the earth. Space is classified as an extreme environment because its conditions are different from those on Earth. To survive in space, many factors must be considered and precautions must be taken. Scientists and researchers believe that exploring space and understanding the current state of everything can help understand how the universe works and prepare for potential environmental crises
 Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Common challenges faced by machine learning algorithms in C++ include memory management, multi-threading, performance optimization, and maintainability. Solutions include using smart pointers, modern threading libraries, SIMD instructions and third-party libraries, as well as following coding style guidelines and using automation tools. Practical cases show how to use the Eigen library to implement linear regression algorithms, effectively manage memory and use high-performance matrix operations.
 Five schools of machine learning you don't know about
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Five schools of machine learning you don't know about
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Machine learning is an important branch of artificial intelligence that gives computers the ability to learn from data and improve their capabilities without being explicitly programmed. Machine learning has a wide range of applications in various fields, from image recognition and natural language processing to recommendation systems and fraud detection, and it is changing the way we live. There are many different methods and theories in the field of machine learning, among which the five most influential methods are called the "Five Schools of Machine Learning". The five major schools are the symbolic school, the connectionist school, the evolutionary school, the Bayesian school and the analogy school. 1. Symbolism, also known as symbolism, emphasizes the use of symbols for logical reasoning and expression of knowledge. This school of thought believes that learning is a process of reverse deduction, through existing
 Explainable AI: Explaining complex AI/ML models
Jun 03, 2024 pm 10:08 PM
Explainable AI: Explaining complex AI/ML models
Jun 03, 2024 pm 10:08 PM
Translator | Reviewed by Li Rui | Chonglou Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) models are becoming increasingly complex today, and the output produced by these models is a black box – unable to be explained to stakeholders. Explainable AI (XAI) aims to solve this problem by enabling stakeholders to understand how these models work, ensuring they understand how these models actually make decisions, and ensuring transparency in AI systems, Trust and accountability to address this issue. This article explores various explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) techniques to illustrate their underlying principles. Several reasons why explainable AI is crucial Trust and transparency: For AI systems to be widely accepted and trusted, users need to understand how decisions are made
 Is Flash Attention stable? Meta and Harvard found that their model weight deviations fluctuated by orders of magnitude
May 30, 2024 pm 01:24 PM
Is Flash Attention stable? Meta and Harvard found that their model weight deviations fluctuated by orders of magnitude
May 30, 2024 pm 01:24 PM
MetaFAIR teamed up with Harvard to provide a new research framework for optimizing the data bias generated when large-scale machine learning is performed. It is known that the training of large language models often takes months and uses hundreds or even thousands of GPUs. Taking the LLaMA270B model as an example, its training requires a total of 1,720,320 GPU hours. Training large models presents unique systemic challenges due to the scale and complexity of these workloads. Recently, many institutions have reported instability in the training process when training SOTA generative AI models. They usually appear in the form of loss spikes. For example, Google's PaLM model experienced up to 20 loss spikes during the training process. Numerical bias is the root cause of this training inaccuracy,



