 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Python commonly used standard libraries and third-party libraries 2-sys module
Python commonly used standard libraries and third-party libraries 2-sys module
Python commonly used standard libraries and third-party libraries 2-sys module
1. Introduction to the sys module
The os module introduced earlier is mainly for the operating system, while the sys module in this article is mainly for the Python interpreter.
The sys module is a module that comes with Python. It is an interface for interacting with the Python interpreter. The sys module provides many functions and variables to deal with different parts of the Python runtime environment.
2. Common methods of sys module
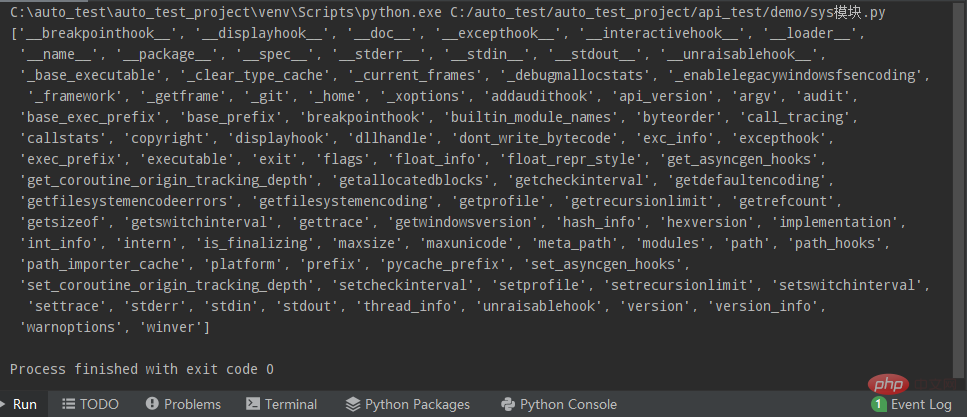
You can check which methods are included in the sys module through the dir() method:
import sys print(dir(sys))
1.sys.argv - Get command line parameters
sys.argv is used to transfer parameters from outside the program to the program, and it can obtain the command line parameter list. The argv list contains all parameters passed to the script:
- sys.argv[0]: represents the program itself
- sys.argv[1]: represents the first parameter of the program
- sys.argv[2]: Indicates the second parameter of the program
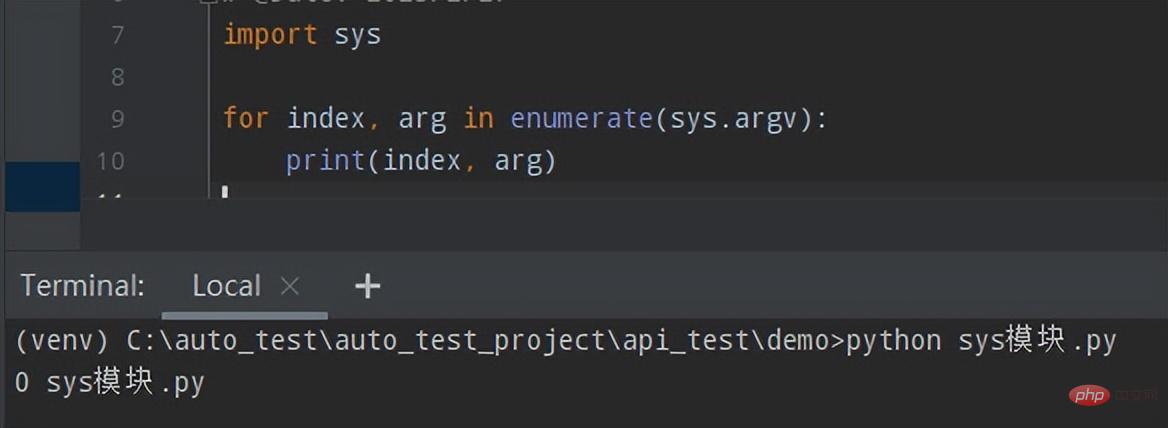
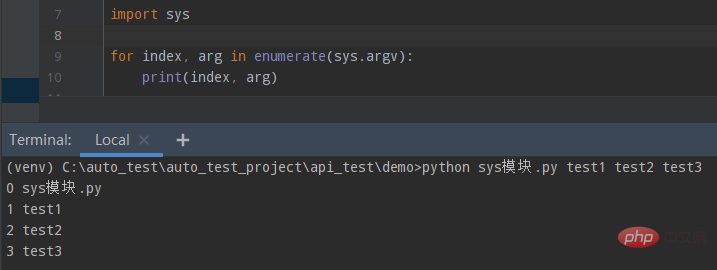
import sys for index, arg in enumerate(sys.argv): print(index, arg)
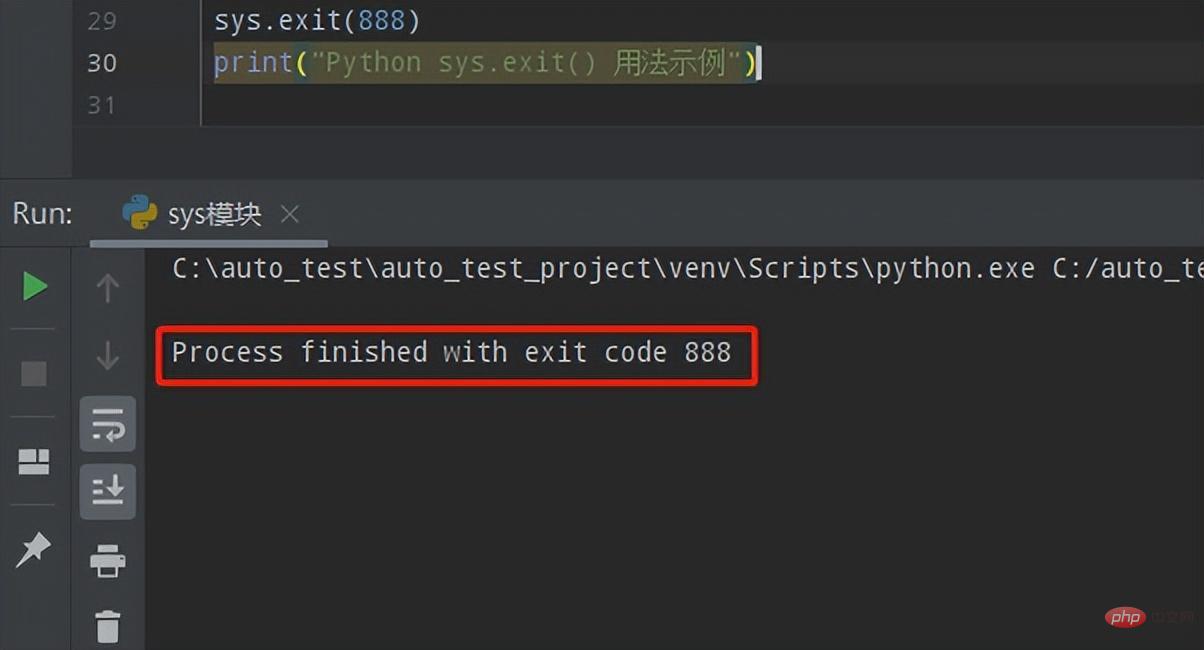
Execute this script file on the Python command line (without any parameters), and obtain the second parameter One element is the script itself. The print result is:
Execute this script file (with parameters) on the Python command line, and the first element obtained is the script itself. The rest are passed parameters. The printing result is:
- When n is 0: normal exit When n is not equal to 0, abnormal exit will trigger SystemExit Exception
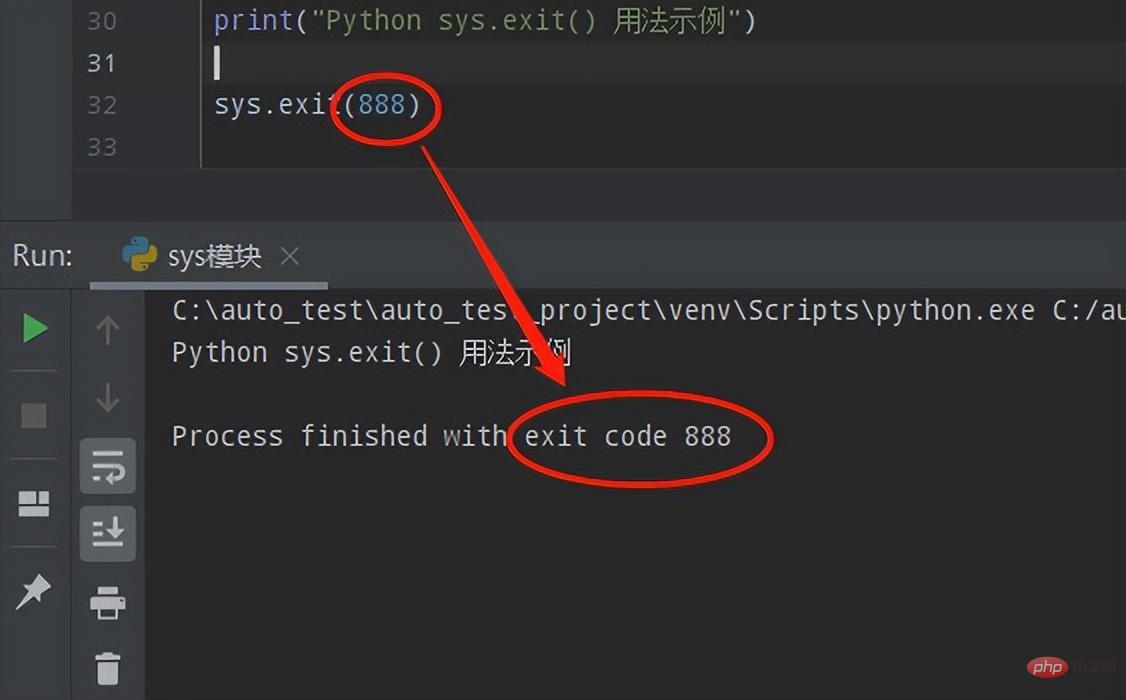
# sys.exit()用法示例
def exit_function(value):
print("sys.exit()捕获到的value是%s" % value)
sys.exit(0)
print("start sys")
try:
sys.exit(888)
except SystemExit as value:
exit_function(value=value)
print("end sys")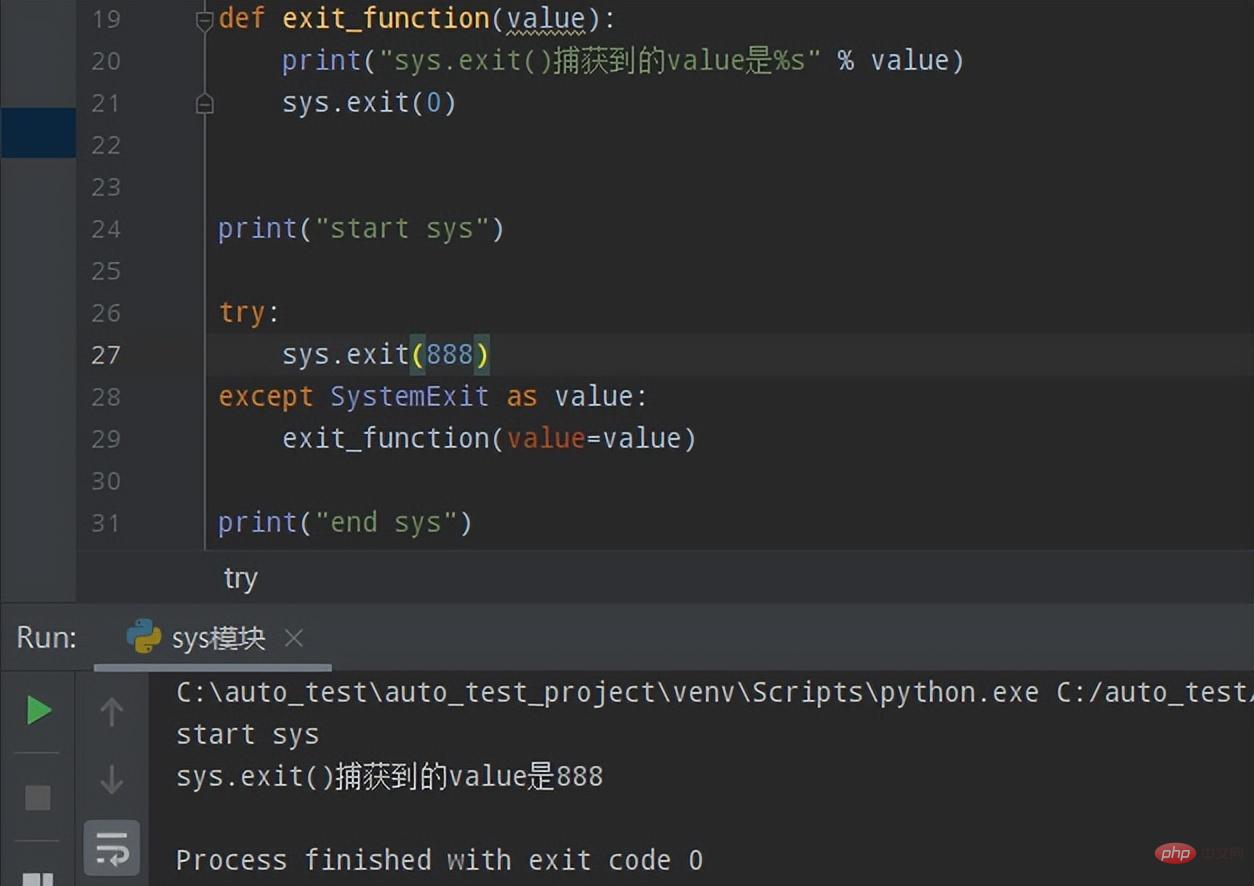
- The program first Execute print("start sys")Then execute the try statement, call sys.exit(888)Then capture the system exception, the value of the captured SystemExit exception is 888Finally call the exit_function function and pass the value 888 to the exit_function function In the exit_function function, execute the statement, print the captured value value, and finally call sys.exit(0) to exit the program
上个示例的执行结果可以看到在exit_function函数中调用sys.exit(0),此时程序就会退出,不会再执行print("end sys"),而当在exit_function函数中注释掉sys.exit(0),则会继续执行最后的代码print("end sys"),即:程序中途不退出,如下所示:
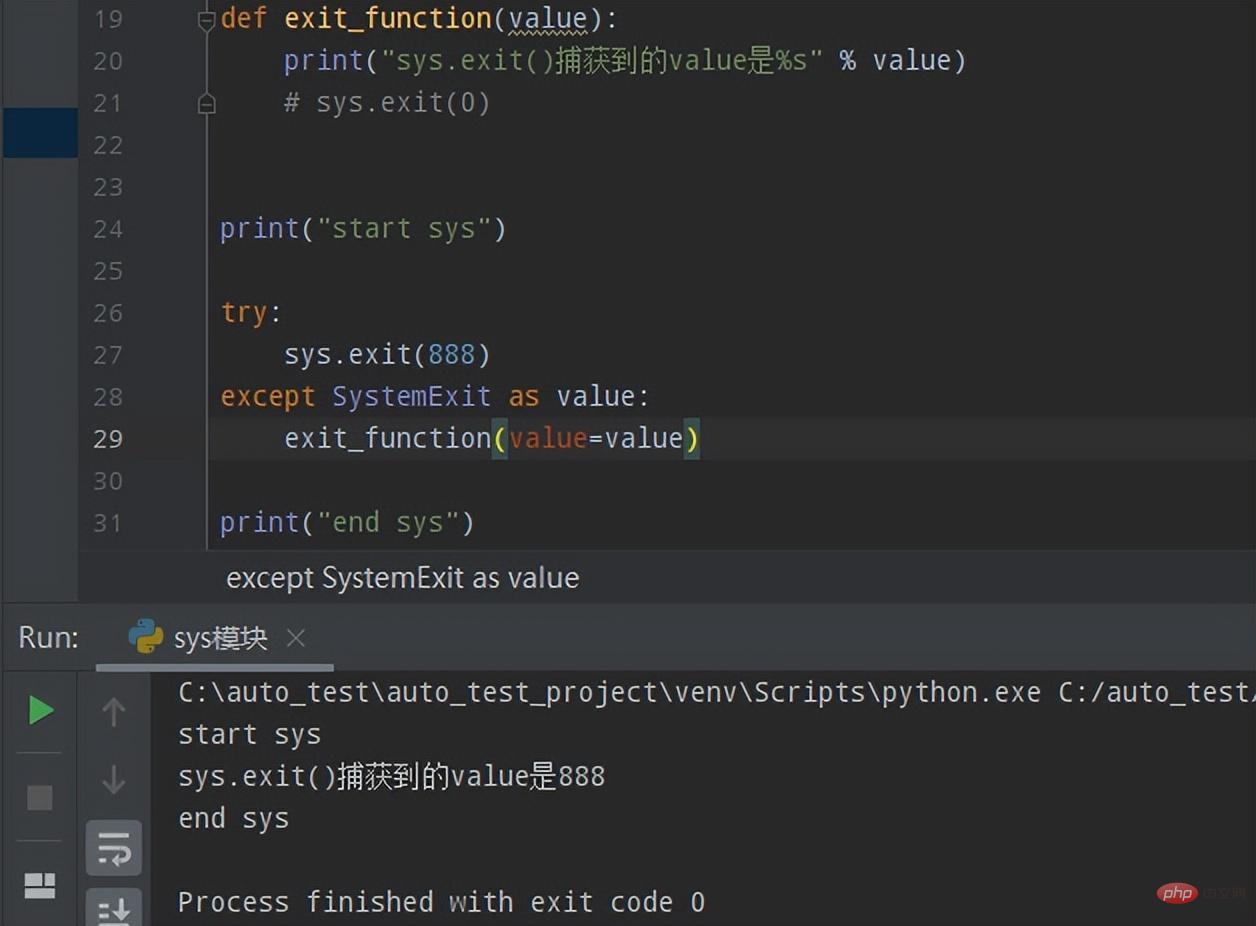
3.sys.platform-获取当前Python运行平台
基本用法
print(sys.platform)
Windows下运行:
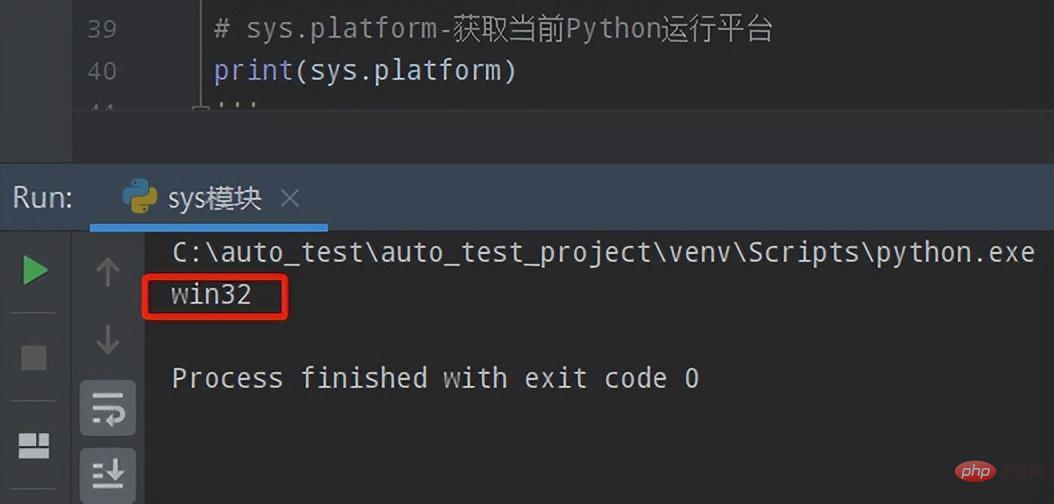
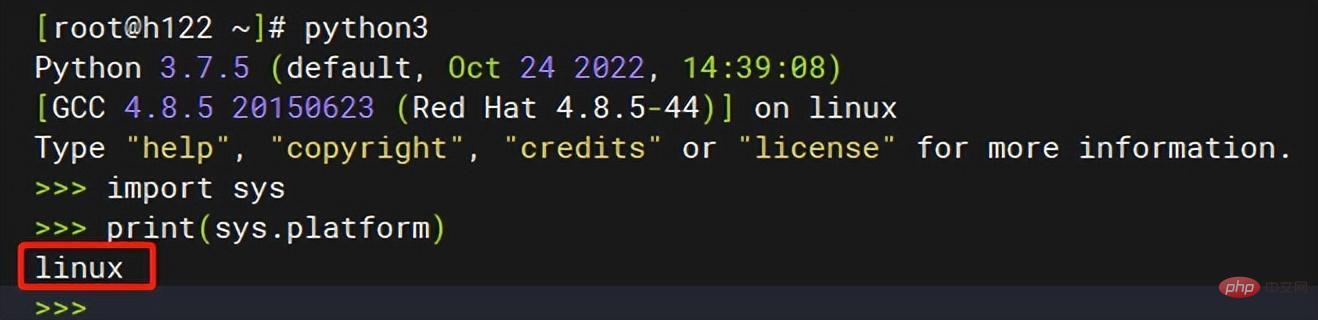
Linux下运行:
除了sys.platform外,通过platform.system()也可以获取到当前系统平台:
Windows下运行:
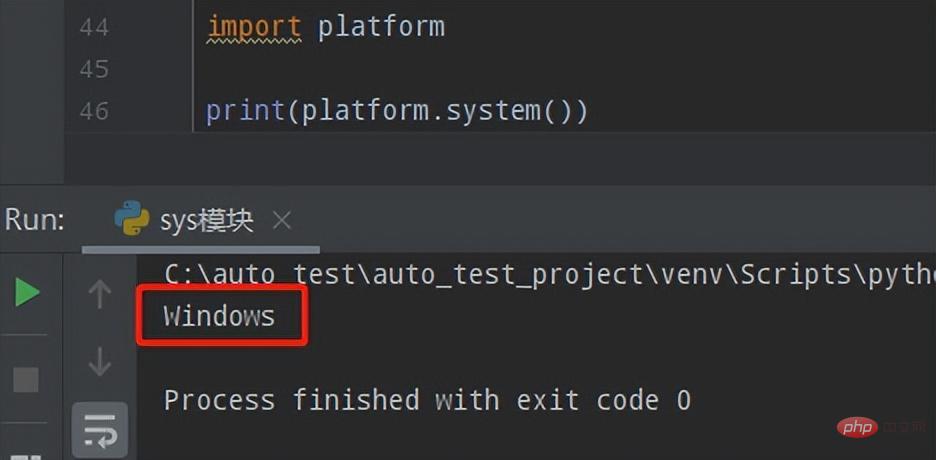
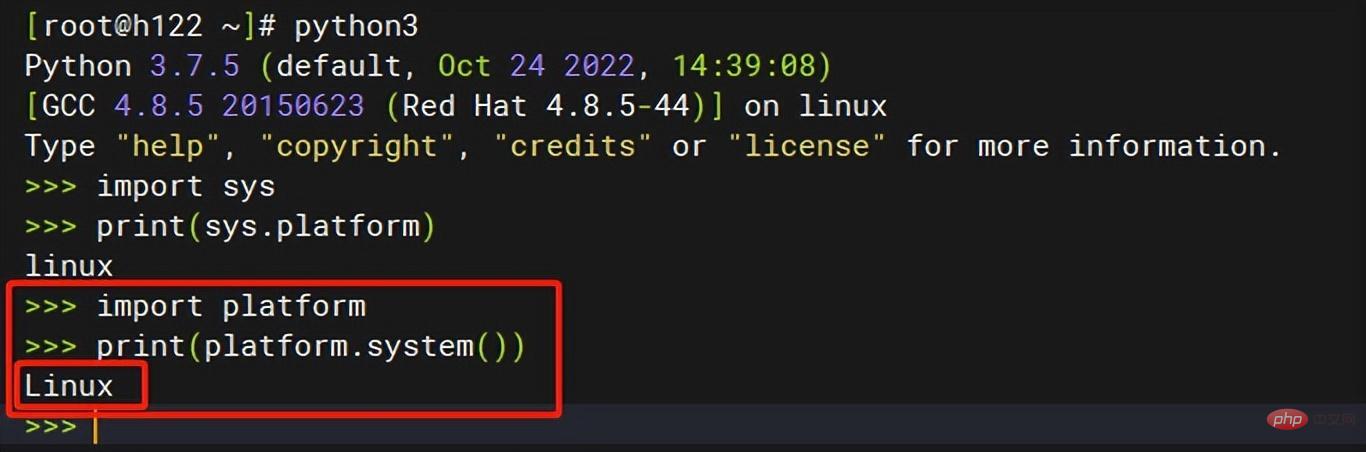
Linux下运行:
适用场景
我们都知道Python是跨平台语言,只要操作系统安装了Python环境,那么同一份Python代码就可以既运行在Linux上,也可以运行在Windows上,亦或是Mac上。
而使用sys.platform或platform.system()获取到当前系统平台名称后,我们就可以针对性地作出不同操作,例如:
linux_content = "111111" windows_content = "222222" # 平台为Linux,执行逻辑1、发送文本1到指定邮件 if platform.system() == "Linux": send_email(linux_content) # 平台为Windows,执行逻辑2、发送文本2到指定邮件 elif platform.system() == "Windows": send_email(windows_content)
4.sys.path-返回Python相关路径
基本用法
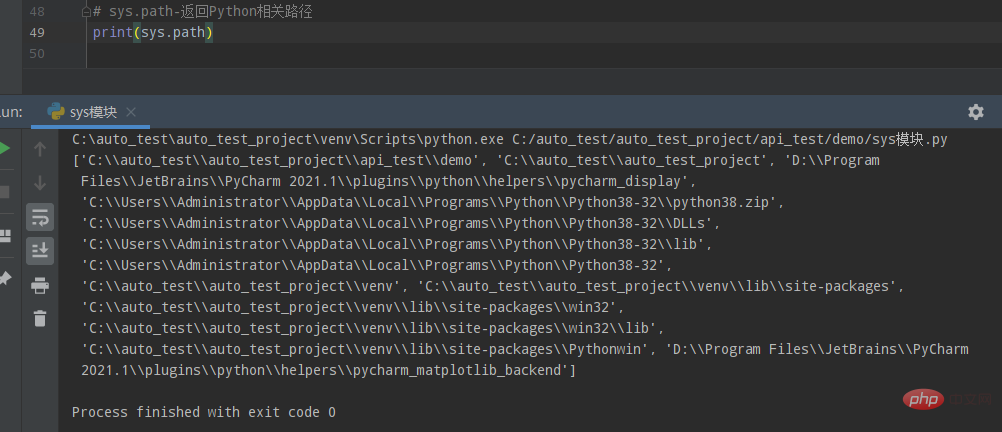
sys.path是Python的搜索模块的路径集,供Python从中查找模块,返回一个list。
print(sys.path)
适用场景
如果是在IDE中执行Python程序,编译器会自动把当前项目的根目录加入到包查找路径中,可以理解为添加到环境变量下,所以直接执行是没有问题的。但是在cmd或是Terminal控制台中直接使用Python相关命令来执行程序,则不会自动将当前项目加入到PYTHONPATH环境变量下,如果涉及到import其他文件夹下的变量就会报类似"ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'xxxx'"这样的错误。
解决方法:通过sys.path.append()方法将当前项目的根目录添加到系统环境变量中:
import sys root_path = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__)) sys.path.append(root_path)
5.sys.stdin与sys.stdout
- Stdin:标准输入
- Stdout:标准输出
- Stderr:错误流
sys.stdin 与 input()
在Python中, input() 等价于 sys.stdin.readline()
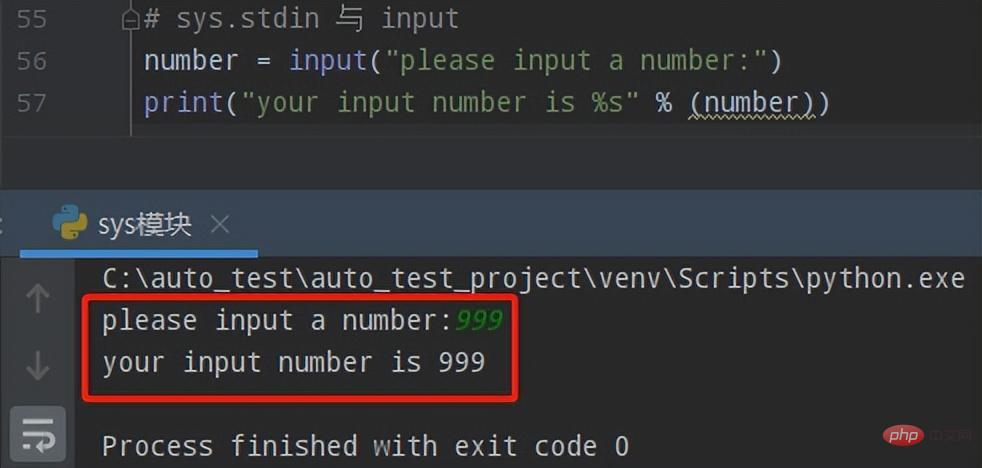
① 先来看看使用input()的实现效果
# sys.stdin 与 input
number = input("please input a number:")
print("your input number is %s" % (number))执行效果如下:
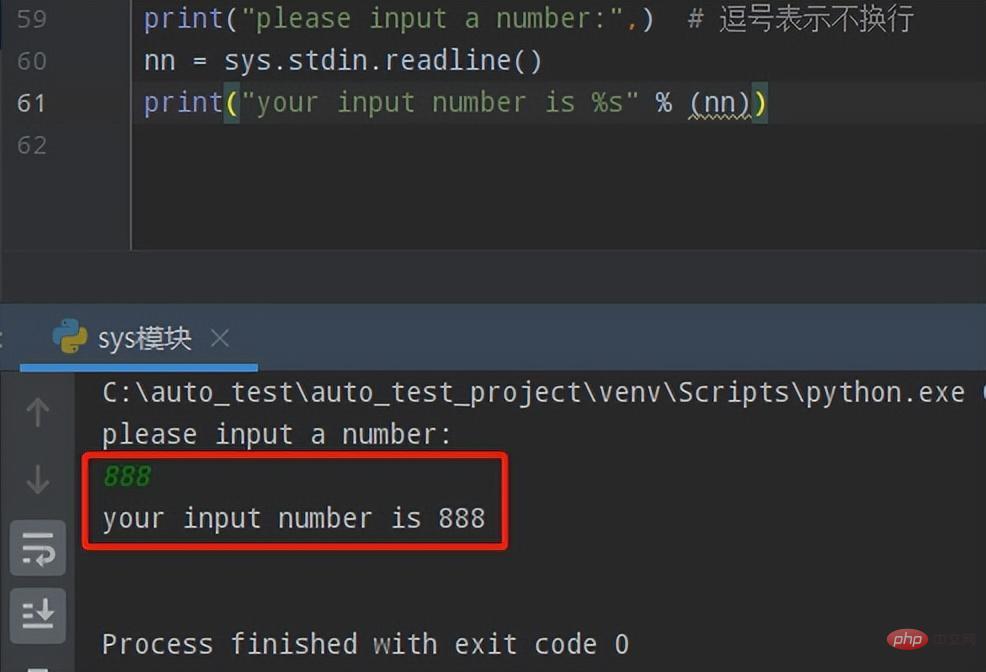
② 再来看看使用sys.stdin.readline()的实现效果
print("please input a number:",)# 逗号表示不换行
nn = sys.stdin.readline()
print("your input number is %s" % (nn))执行效果如下:
sys.stdout 与 print()
在Python中, print() 等价于 sys.stdout.readline()
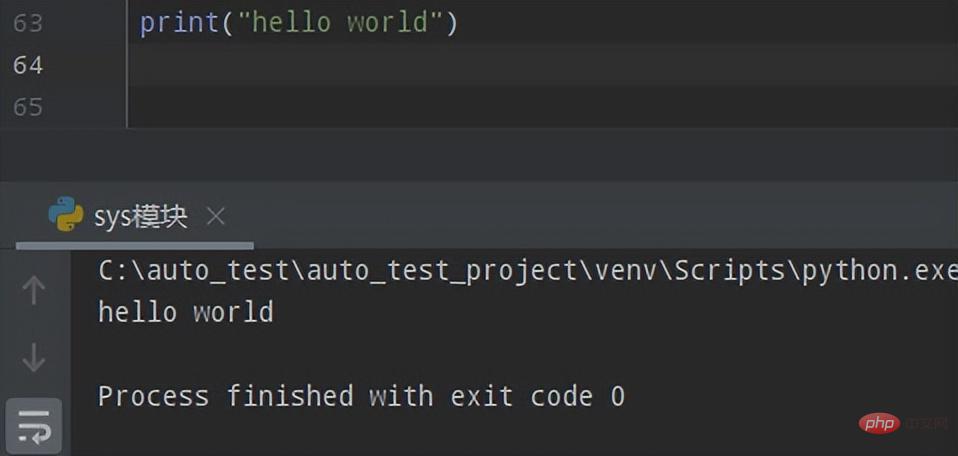
① 先来看看使用print()的实现效果
# sys.stdout 与 print
print("hello world")执行效果如下:
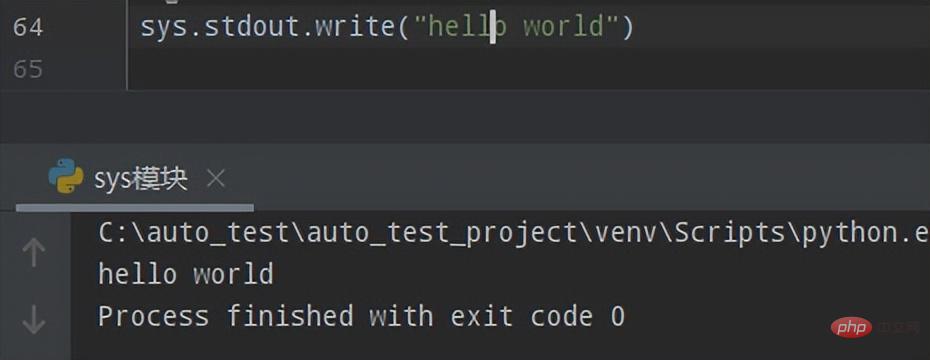
② 再来看看使用sys.stdin.write()的实现效果
sys.stdout.write("hello world")执行效果如下:
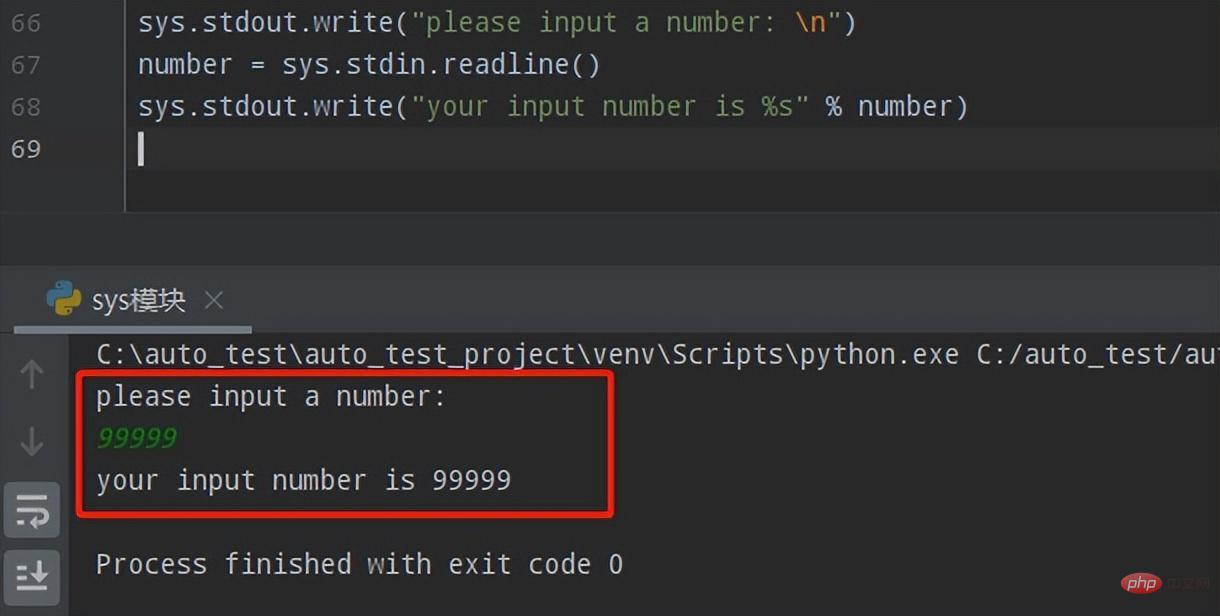
所以综上所述,input()+print() 结合的代码语句即可使用sys.stdin.readline()+sys.stdin.write()代替,如下:
sys.stdout.write("please input a number: n")
number = sys.stdin.readline()
sys.stdout.write("your input number is %s" % number)执行效果如下:
6 Other uses of the .sys module
- sys.version: Get the Python interpreter version
- sys.exc_info(): Return the exception information triplet
- sys.getdefaultencoding(): Get the current encoding of the system, the default is utf-8
- sys.setdefaultencoding(): Set the default encoding of the system
- sys.getfilesystemencoding(): Get the file system Use the encoding method, the default is utf-8
- sys.modules: Return all imported modules in the current Python environment in the form of a dictionary
- sys.copyright: The current Python copyright information
- sys.getrefcount(object): Returns the number of references to the object
- sys.getrecursionlimit(): Returns the maximum recursion depth of Python, the default is 1000
- sys.getsizeof(object[, default ]): Return the size of the object
- sys.getwindowsversion(): Return the version information of the current windwos system
Summary
The sys module is a module that comes with Python , mainly used for interacting with the Python interpreter. It comes with many methods or attributes, among which:
1.sys.argv is used to transfer parameters from outside the program to the program, and it can obtain the command line parameter list. The argv list contains all parameters passed to the script:
- sys.argv[0]: represents the program itself
- sys.argv[1]: represents the first parameter of the program
- sys.argv[2]: Indicates the second parameter of the program
2.sys.exit(n) is used to exit the program:
- When n is 0: normal exit
- When n is not equal to 0, abnormal exit will cause SystemExit exception
sys.exit(n) often captures SystemExit Used together with exceptions to control whether the program exits midway freely;
3.sys.platform is used to obtain the current Python running platform, similar to platform.system(), and is often used to target different operating systems. Make different operation logic;
4.sys.path is the path set of Python’s search module. Add the root directory of the current project to the system environment variable through the sys.path.append() method. You can use To solve the error report that the module cannot be found;
5. In Python, input() is equivalent to sys.stdin.readline(), and print() is equivalent to sys.stdout.readline().
The above is the detailed content of Python commonly used standard libraries and third-party libraries 2-sys module. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
An application that converts XML directly to PDF cannot be found because they are two fundamentally different formats. XML is used to store data, while PDF is used to display documents. To complete the transformation, you can use programming languages and libraries such as Python and ReportLab to parse XML data and generate PDF documents.
 What is the process of converting XML into images?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
What is the process of converting XML into images?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:24 PM
To convert XML images, you need to determine the XML data structure first, then select a suitable graphical library (such as Python's matplotlib) and method, select a visualization strategy based on the data structure, consider the data volume and image format, perform batch processing or use efficient libraries, and finally save it as PNG, JPEG, or SVG according to the needs.
 Is there a mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:45 PM
Is there a mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:45 PM
There is no APP that can convert all XML files into PDFs because the XML structure is flexible and diverse. The core of XML to PDF is to convert the data structure into a page layout, which requires parsing XML and generating PDF. Common methods include parsing XML using Python libraries such as ElementTree and generating PDFs using ReportLab library. For complex XML, it may be necessary to use XSLT transformation structures. When optimizing performance, consider using multithreaded or multiprocesses and select the appropriate library.
 How to beautify the XML format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:57 PM
How to beautify the XML format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:57 PM
XML beautification is essentially improving its readability, including reasonable indentation, line breaks and tag organization. The principle is to traverse the XML tree, add indentation according to the level, and handle empty tags and tags containing text. Python's xml.etree.ElementTree library provides a convenient pretty_xml() function that can implement the above beautification process.
 Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
The speed of mobile XML to PDF depends on the following factors: the complexity of XML structure. Mobile hardware configuration conversion method (library, algorithm) code quality optimization methods (select efficient libraries, optimize algorithms, cache data, and utilize multi-threading). Overall, there is no absolute answer and it needs to be optimized according to the specific situation.
 How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
Use most text editors to open XML files; if you need a more intuitive tree display, you can use an XML editor, such as Oxygen XML Editor or XMLSpy; if you process XML data in a program, you need to use a programming language (such as Python) and XML libraries (such as xml.etree.ElementTree) to parse.
 How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
It is impossible to complete XML to PDF conversion directly on your phone with a single application. It is necessary to use cloud services, which can be achieved through two steps: 1. Convert XML to PDF in the cloud, 2. Access or download the converted PDF file on the mobile phone.
 How to convert XML to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to convert XML to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
It is not easy to convert XML to PDF directly on your phone, but it can be achieved with the help of cloud services. It is recommended to use a lightweight mobile app to upload XML files and receive generated PDFs, and convert them with cloud APIs. Cloud APIs use serverless computing services, and choosing the right platform is crucial. Complexity, error handling, security, and optimization strategies need to be considered when handling XML parsing and PDF generation. The entire process requires the front-end app and the back-end API to work together, and it requires some understanding of a variety of technologies.





