Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 An article explaining in detail the basic data types of the Python data analysis module Numpy
An article explaining in detail the basic data types of the Python data analysis module Numpy
An article explaining in detail the basic data types of the Python data analysis module Numpy
Introduction to Numpy
NumPy (Numerical Python) is an extension library of the Python language that supports a large number of dimensional array and matrix operations. In addition, it also provides a large number of mathematical function libraries for array operations.
NumPy is a very fast mathematics library, mainly used for array calculations, including:
- A powerful N-dimensional Array object ndarray
- Broadcast function function
- Tool for integrating C/C/Fortran code
- Linear algebra, Fourier transform, random number generation and other functions
- The most important feature of NumPy is its N The dimensional array object ndarray is a collection of a series of data of the same type. The index of the elements in the collection starts with the 0 subscript.
- ndarray object is a multi-dimensional array used to store elements of the same type. Each element in the array
- ndarray has the same storage size area in memory
numpy object creation:
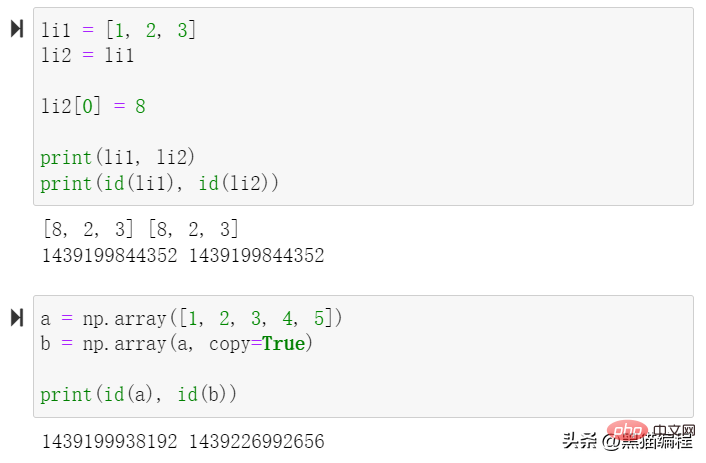
numpy.array(object, dtype = None, copy = True, order = None, subok = False, ndmin = 0)
| ##Name | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| object | array or Nested array | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| dtype | array element Data type, optional | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| copy | Whether the object Need to copy, optional | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| order | Create array The style, C is the row direction, F is the column direction, A is any direction (default) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| subok | Default returns an array consistent with the base class type | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
##ndmin | Specify the minimum dimension of the generated array |
Name | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ##bool_ | ##Boolean data type (True or False) |||||||||||||||||||||||||
##Default integer type ( Similar to long, int32 or int64 in C language) | ##intc | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
The same as the int type of C, usually int32 or int 64 | ##intp | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Integer type used for indexing (similar to C's ssize_t, usually still int32 or int64) | int8 | Bytes (-128 to 127) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
##int16 | Integer (-32768 to 32767) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ##int32 | Integer (-2147483648 to 2147483647) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unsigned integer (0 to 255) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unsigned integer (0 to 65535) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unsigned integer (0 to 4294967295) | ##uint64 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Unsigned integer (0 to 18446744073709551615) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
float_ | ##Abbreviation for float64 type | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
float16 | ##Half-precision floating point number, including: 1 sign bit, 5 exponent bits , 10 mantissa digits | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| float32 | Single precision Floating point number, including: 1 sign bit, 8 exponent bits, 23 mantissa bits | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| float64
| Double precision floating point number, including: 1 sign bit, 11 exponent bits, 52 mantissa bits | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| complex_ | Abbreviation of complex128 type, that is, 128-bit complex number | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| complex64 | Complex number, representing a double 32-bit floating point number (real part and imaginary part) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| complex128 | ##Complex number, representing a double 64-bit floating point number (real part and imaginary part )
字符 | 对应类型 |
b | 布尔型 |
i | (有符号) 整型 |
u | 无符号整型 integer |
f | 浮点型 |
c | 复数浮点型 |
m | timedelta(时间间隔) |
M | datetime(日期时间) |
O | (Python) 对象 |
S, a | (byte-)字符串 |
U | Unicode |
V | 原始数据 (void) |
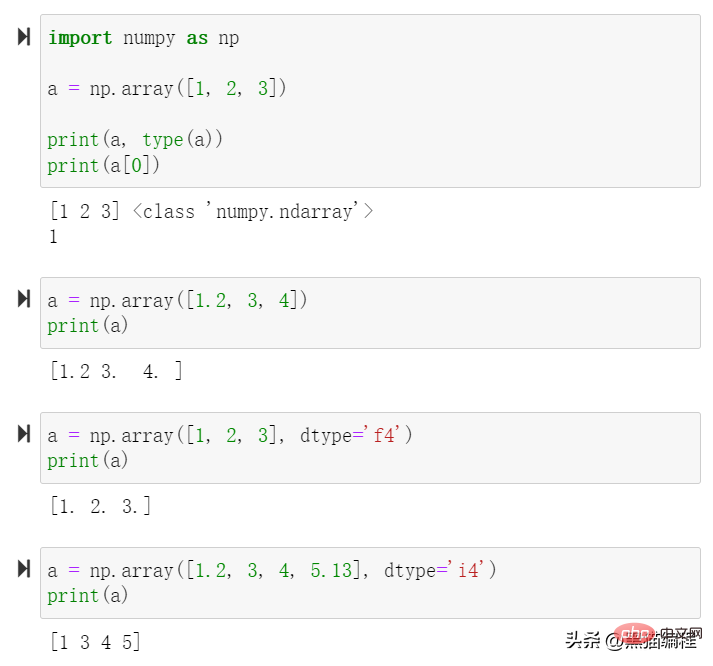
dt = np.dtype(np.int32)
print(dt)
输出:
int32
dt = np.dtype('i4')
print(dt)
输出:
int32
dt = np.dtype([('age', np.int8)])
print(dt)
输出:
[('age', 'i1')]结构化数据类型
student = np.dtype([('name','S20'), ('age','i1'), ('score', 'f4')])
a = np.array([('xm', 10, 98.123456789), ('xh', 8, 99.111111111), ('xl', '9', 100)], dtype=student)
print(a)
输出:
[(b'xm', 10,98.12346 ) (b'xh',8,99.111115) (b'xl',9, 100.)]The above is the detailed content of An article explaining in detail the basic data types of the Python data analysis module Numpy. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1359
1359
 52
52
 What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
There is no built-in sum function in C language, so it needs to be written by yourself. Sum can be achieved by traversing the array and accumulating elements: Loop version: Sum is calculated using for loop and array length. Pointer version: Use pointers to point to array elements, and efficient summing is achieved through self-increment pointers. Dynamically allocate array version: Dynamically allocate arrays and manage memory yourself, ensuring that allocated memory is freed to prevent memory leaks.
 How to convert xml into pictures
Apr 03, 2025 am 07:39 AM
How to convert xml into pictures
Apr 03, 2025 am 07:39 AM
XML can be converted to images by using an XSLT converter or image library. XSLT Converter: Use an XSLT processor and stylesheet to convert XML to images. Image Library: Use libraries such as PIL or ImageMagick to create images from XML data, such as drawing shapes and text.
 Who gets paid more Python or JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:09 AM
Who gets paid more Python or JavaScript?
Apr 04, 2025 am 12:09 AM
There is no absolute salary for Python and JavaScript developers, depending on skills and industry needs. 1. Python may be paid more in data science and machine learning. 2. JavaScript has great demand in front-end and full-stack development, and its salary is also considerable. 3. Influencing factors include experience, geographical location, company size and specific skills.
 How to convert xml to mp3
Apr 03, 2025 am 09:00 AM
How to convert xml to mp3
Apr 03, 2025 am 09:00 AM
The steps to convert XML to MP3 include: Extract audio data from XML: parse the XML file, find the base64 encoding string containing the audio data, and decode it into binary format. Encode the audio data to MP3: Install the MP3 encoder and set the encoding parameters, encode the binary audio data to MP3 format, and save it to a file.
 How to change the format of xml
Apr 03, 2025 am 08:42 AM
How to change the format of xml
Apr 03, 2025 am 08:42 AM
There are several ways to modify XML formats: manually editing with a text editor such as Notepad; automatically formatting with online or desktop XML formatting tools such as XMLbeautifier; define conversion rules using XML conversion tools such as XSLT; or parse and operate using programming languages such as Python. Be careful when modifying and back up the original files.
 Is distinctIdistinguish related?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 10:30 PM
Is distinctIdistinguish related?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 10:30 PM
Although distinct and distinct are related to distinction, they are used differently: distinct (adjective) describes the uniqueness of things themselves and is used to emphasize differences between things; distinct (verb) represents the distinction behavior or ability, and is used to describe the discrimination process. In programming, distinct is often used to represent the uniqueness of elements in a collection, such as deduplication operations; distinct is reflected in the design of algorithms or functions, such as distinguishing odd and even numbers. When optimizing, the distinct operation should select the appropriate algorithm and data structure, while the distinct operation should optimize the distinction between logical efficiency and pay attention to writing clear and readable code.
 Apr 03, 2025 am 08:12 AM
Apr 03, 2025 am 08:12 AM
XML data modification can be done manually or using programming languages and libraries. Manual modifications are suitable for small amounts of modifications to small documents, including adding, modifying, or deleting elements and attributes. For more complex modifications, programming languages and libraries such as Python's xml.dom and Java's javax.xml.parsers, which provide tools for processing XML data. When modifying XML data, ensure its validity, create backups, and follow XML syntax rules, including the correct tags and properties.
 How to convert xml into word
Apr 03, 2025 am 08:15 AM
How to convert xml into word
Apr 03, 2025 am 08:15 AM
There are three ways to convert XML to Word: use Microsoft Word, use an XML converter, or use a programming language.