 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 A new paradigm for text and image editing, a single model enables multi-text guided image editing
A new paradigm for text and image editing, a single model enables multi-text guided image editing
A new paradigm for text and image editing, a single model enables multi-text guided image editing
Brief Overview of the Paper
#Research related to image editing using text is very hot, and many recent studies are based on denoising diffusion models to improve However, few scholars continue to pay attention to GAN-related research. This article is based on the classic StyleGAN and CLIP and proposes a semantic modulation module, so that only a single model is needed for different texts to perform text-image editing.
This article first uses the existing encoder to convert the image to be edited into the latent code w in the W^ semantic space of StyleGAN, and then uses the proposed semantic modulation module to encode the latent code Perform adaptive modulation. The semantic modulation module includes semantic alignment and semantic injection modules. It first aligns the semantics between the text encoding and the latent encoding of GAN through the attention mechanism, and then injects the text information into the aligned latent encoding to ensure that the Cain encoding owns the text. Information thereby achieving the ability to edit images using text.
Different from the classic StyleCLIP model, our model does not need to train a separate model for each text. One model can respond to multiple texts to effectively edit images, so we The model becomes FFCLIP-Free Form Text-Driven Image Manipulation. At the same time, our model has achieved very good results on the classic church, face and car data sets.

- ##Paper address: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2210.07883.pdf
- Github address: https://github.com/KumapowerLIU/FFCLIP
Recently, free text prompts describing user intent have been used to edit the StyleGAN latent space for image editing operations [1, 2]. Taking as input a sentence (e.g., ‘Blue’) or a phrase (e.g., ‘Man aged 10’), these methods edit the described image attributes accordingly by modulating the latent encoding in the StyleGAN latent space.
Precise text-image editing relies on an accurate latent mapping between StyleGAN’s visual semantic space and CLIP’s textual semantic space. For example, when the text prompt is "surprise", we first identify its related semantic subspace (i.e. "expression", because surprise belongs to the attribute of expression) in the visual semantic space. After finding the semantic subspace corresponding to the text, the text will tell us the direction in which the latent encoding changes, from the current expression to the surprise expression. Pioneering studies such as TediGAN [1] and StyleCLIP [2] empirically predefined which latent visual subspace corresponds to the target textual hint embedding (i.e., specific attribute selection in TediGAN and grouping mapping in StyleCLIP). This empirical recognition constrains that given a text prompt, they must train a corresponding editing model.
Different text cues require different models to modulate the latent codes in the latent visual subspace of StyleGAN. Although the global orientation method in StyleCLIP does not employ such a process, parameter adjustments and editing orientations are manually predefined. For this reason, we have reason to explore how to automatically find the implicit visual semantic subspace through explicit text, so that a single model can handle multiple texts.
In this paper, we propose FFCLIP-Free Form CLIP, which can automatically find the corresponding visual subspace for different texts. FFCLIP consists of several semantic modulation modules that take as input the latent encoding w^ and the text encoding e in the StyleGAN latent space W^.
The semantic modulation module consists of a semantic alignment module and a semantic injection module. The semantic alignment module takes the text encoding e as the query and the latent encoding w as the key and value. Then we calculate cross-attention in the position and channel dimensions respectively, resulting in two attention maps. Then we use linear transformation to transform the current visual space into the subspace corresponding to the text, where the linear transformation parameters (i.e., translation and scaling parameters) are calculated based on these two attention maps. Through this alignment, we can automatically find the corresponding visual subspace for each text. Finally, the semantic injection module [3] modifies the latent code in the subspace by following another linear transformation.
From an FFCLIP perspective, [1, 2] neutron space empirical selection is a special form of our linear transformation in the semantic alignment module. Their group selection operation is similar to the binary values of our scaling parameters to indicate the usage of each position dimension of w. On the other hand, we observe that the semantics of W^ space are still entangled, and empirical design cannot find an accurate mapping between the latent space of StyleGAN and the textual semantic space of CLIP. Instead, the scaling parameter in our semantic alignment module adaptively modifies the latent code w to map different textual cue embeddings. The alignment is then further improved via our translation parameters. We evaluate our method on benchmark datasets and compare FFCLIP with state-of-the-art methods. The results show that FFCLIP is able to generate more reasonable content while conveying user intent.
FFCLIP
Figure 1 shows our overall framework. FFCLIP first obtains the latent encoding of images and texts through the pre-trained GAN inversion encoder and text encoder. The latent encoding of the image is w in the previously mentioned StyleGAN visual semantic space W^, and the text encoding is e_t . Like StyleCLIP, we use the e4e GAN inversion encoder [4] and the text encoder in CLIP to obtain the corresponding latent encoding respectively. Then we use e_t and w as the input of the modulation module and output the offset Δw of w. Finally, add Δw to the original w and put it into the pre-trained StyleGAN to get the corresponding result.
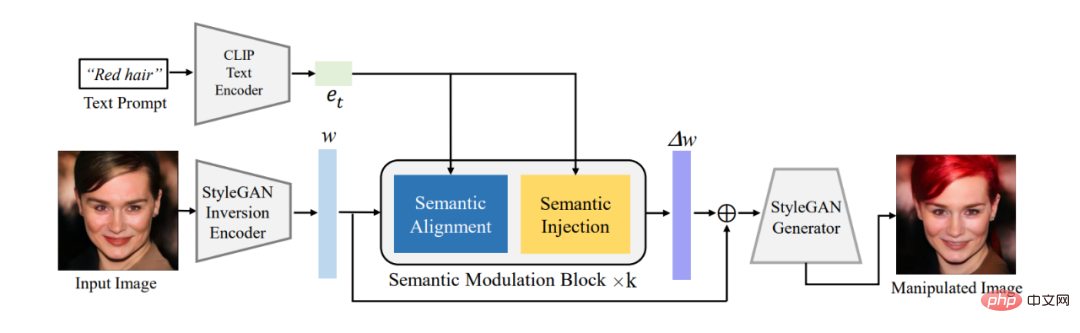
##Figure 1: Overall framework diagram
Figure 2 below is our semantic modulation module. In the semantic alignment module (Semantic Alignment), we can clearly see that we set Δw to Key and Value and set e_t to Query to calculate two attention maps. The sizes of these two attention maps are 18×1 respectively. and 512×512. Then we use the 18×1 attention map as the scaling coefficient S in the linear transformation. Our process of calculating the attention map is as follows:
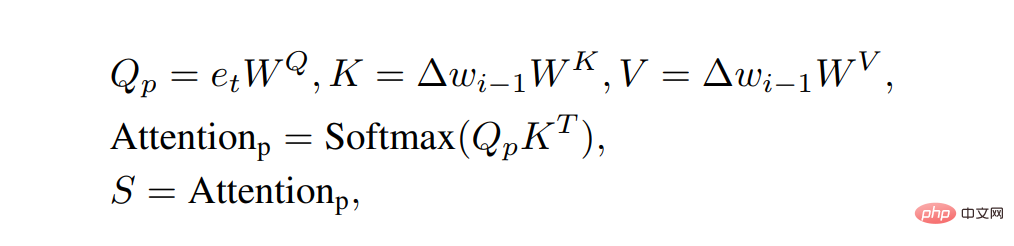
At the same time, we After multiplying the 512×512 attention map by Value, the translation coefficient T in the explicit transformation is obtained through the Pooling operation. Our process of calculating the attention map is as follows:
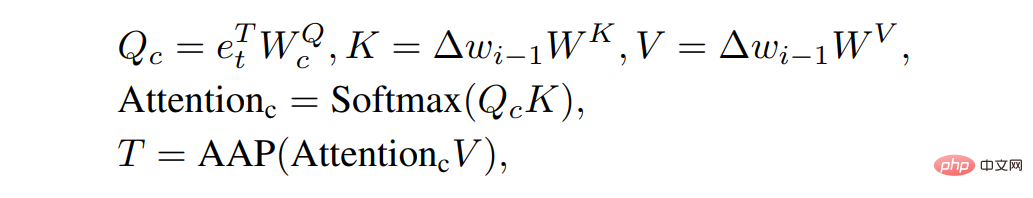
After we have the translation and scaling coefficients, we can find the phase for the current text e_t through linear transformation For the corresponding visual subspace, the calculation steps are as follows:
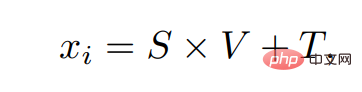
Midterm x_i is the output result of our i-th semantic modulation module. Since the size of Δw is 18×512, the attention maps of 18×1 and 512×512 are calculated in the two dimensions of position and channel of Δw respectively. This operation is similar to Dual Attention [5].
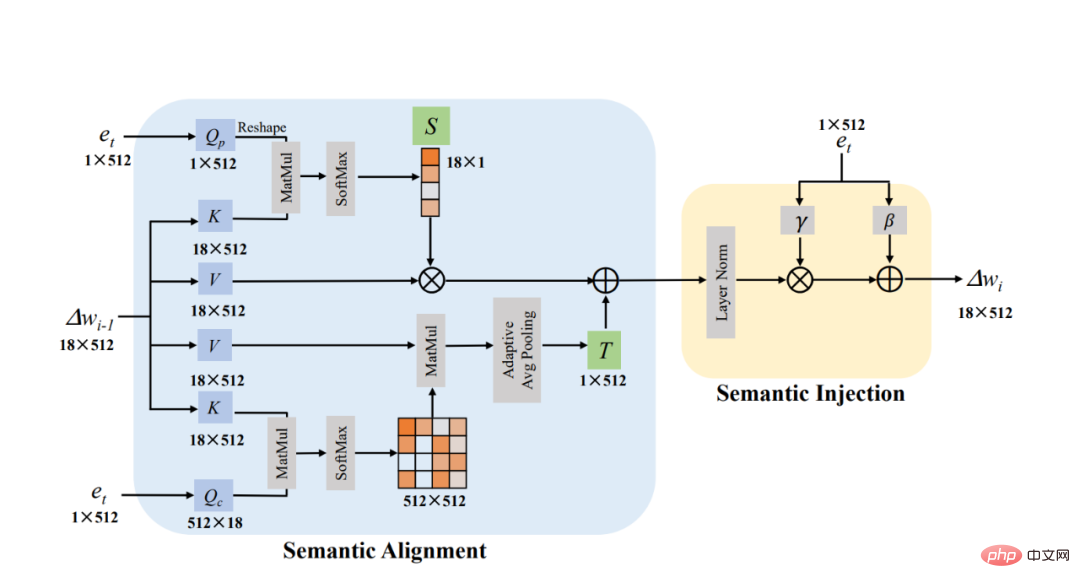
Figure 2: Semantic modulation module
We can obtain the visual subspace corresponding to the text through the above operations. Then we use a method similar to AdaIN to inject text information into this space to obtain the final result. We call this operation the semantic injection module (Semantic Injection). The implementation steps of the entire module are as follows:
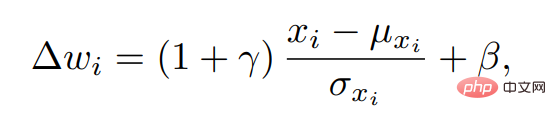
In the end, a total of 4 semantic modulation modules were stacked in our FFCLIP, and finally the final offset Δw was obtained.
Experimental results
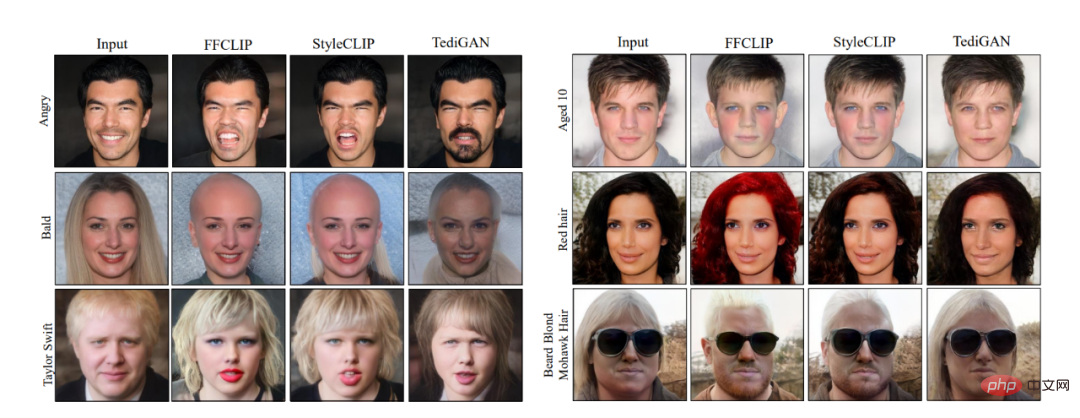
##Figure 3: Visual comparison chart
As shown in Figure 3, we made a visual comparison with StyleCLIP [1], TediGAN [2] and HairCLIP [3]: it can be seen that FFCLIP can better reflect the semantics of the text , and generate more realistic edited images. At the same time, the corresponding numerical comparison results are shown in the table below. Our method can achieve the best results in both objective and subjective values.
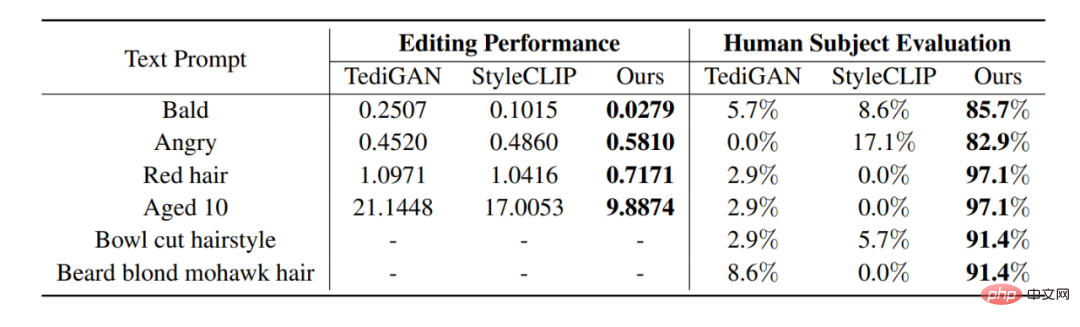
Table 1: Numerical comparison
At the same time, our method also shows very good robustness. FFCLIP has not seen word combinations during training but uses single words for training. However, in testing, it can perform image processing based on the semantics of word groups very well. Edit, the visual effect is shown in Figure 4.
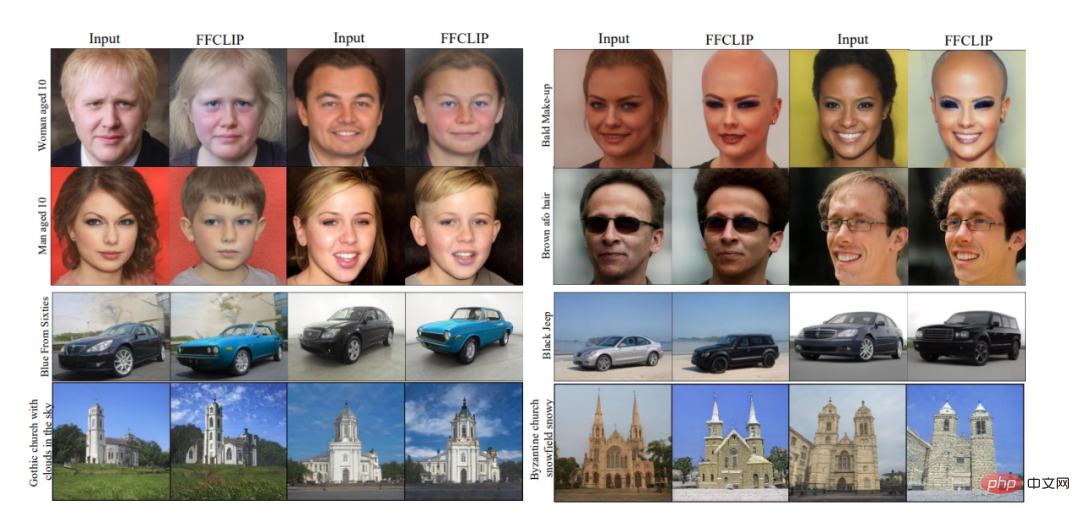
##Figure 4: Phrase editing
For more experimental results and ablation experiments, please see the original text.Summary
In this paper we propose FFCLIP, a new method for efficient image editing that can target different texts but only requires a single model. The motivation of this article is that existing methods match the current text and the semantic subspace of GAN based on existing experience, so an editing model can only handle one text prompt. We improve latent mapping through alignment and injected semantic modulation. It facilitates one editing model to handle multiple text prompts. Experiments on multiple datasets demonstrate that our FFCLIP effectively produces semantically relevant and visually realistic results.The above is the detailed content of A new paradigm for text and image editing, a single model enables multi-text guided image editing. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 The world's most powerful open source MoE model is here, with Chinese capabilities comparable to GPT-4, and the price is only nearly one percent of GPT-4-Turbo
May 07, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
The world's most powerful open source MoE model is here, with Chinese capabilities comparable to GPT-4, and the price is only nearly one percent of GPT-4-Turbo
May 07, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
Imagine an artificial intelligence model that not only has the ability to surpass traditional computing, but also achieves more efficient performance at a lower cost. This is not science fiction, DeepSeek-V2[1], the world’s most powerful open source MoE model is here. DeepSeek-V2 is a powerful mixture of experts (MoE) language model with the characteristics of economical training and efficient inference. It consists of 236B parameters, 21B of which are used to activate each marker. Compared with DeepSeek67B, DeepSeek-V2 has stronger performance, while saving 42.5% of training costs, reducing KV cache by 93.3%, and increasing the maximum generation throughput to 5.76 times. DeepSeek is a company exploring general artificial intelligence
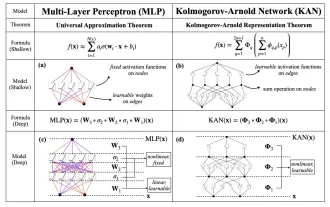 KAN, which replaces MLP, has been extended to convolution by open source projects
Jun 01, 2024 pm 10:03 PM
KAN, which replaces MLP, has been extended to convolution by open source projects
Jun 01, 2024 pm 10:03 PM
Earlier this month, researchers from MIT and other institutions proposed a very promising alternative to MLP - KAN. KAN outperforms MLP in terms of accuracy and interpretability. And it can outperform MLP running with a larger number of parameters with a very small number of parameters. For example, the authors stated that they used KAN to reproduce DeepMind's results with a smaller network and a higher degree of automation. Specifically, DeepMind's MLP has about 300,000 parameters, while KAN only has about 200 parameters. KAN has a strong mathematical foundation like MLP. MLP is based on the universal approximation theorem, while KAN is based on the Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theorem. As shown in the figure below, KAN has
 Hello, electric Atlas! Boston Dynamics robot comes back to life, 180-degree weird moves scare Musk
Apr 18, 2024 pm 07:58 PM
Hello, electric Atlas! Boston Dynamics robot comes back to life, 180-degree weird moves scare Musk
Apr 18, 2024 pm 07:58 PM
Boston Dynamics Atlas officially enters the era of electric robots! Yesterday, the hydraulic Atlas just "tearfully" withdrew from the stage of history. Today, Boston Dynamics announced that the electric Atlas is on the job. It seems that in the field of commercial humanoid robots, Boston Dynamics is determined to compete with Tesla. After the new video was released, it had already been viewed by more than one million people in just ten hours. The old people leave and new roles appear. This is a historical necessity. There is no doubt that this year is the explosive year of humanoid robots. Netizens commented: The advancement of robots has made this year's opening ceremony look like a human, and the degree of freedom is far greater than that of humans. But is this really not a horror movie? At the beginning of the video, Atlas is lying calmly on the ground, seemingly on his back. What follows is jaw-dropping
 AI subverts mathematical research! Fields Medal winner and Chinese-American mathematician led 11 top-ranked papers | Liked by Terence Tao
Apr 09, 2024 am 11:52 AM
AI subverts mathematical research! Fields Medal winner and Chinese-American mathematician led 11 top-ranked papers | Liked by Terence Tao
Apr 09, 2024 am 11:52 AM
AI is indeed changing mathematics. Recently, Tao Zhexuan, who has been paying close attention to this issue, forwarded the latest issue of "Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society" (Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society). Focusing on the topic "Will machines change mathematics?", many mathematicians expressed their opinions. The whole process was full of sparks, hardcore and exciting. The author has a strong lineup, including Fields Medal winner Akshay Venkatesh, Chinese mathematician Zheng Lejun, NYU computer scientist Ernest Davis and many other well-known scholars in the industry. The world of AI has changed dramatically. You know, many of these articles were submitted a year ago.
 Google is ecstatic: JAX performance surpasses Pytorch and TensorFlow! It may become the fastest choice for GPU inference training
Apr 01, 2024 pm 07:46 PM
Google is ecstatic: JAX performance surpasses Pytorch and TensorFlow! It may become the fastest choice for GPU inference training
Apr 01, 2024 pm 07:46 PM
The performance of JAX, promoted by Google, has surpassed that of Pytorch and TensorFlow in recent benchmark tests, ranking first in 7 indicators. And the test was not done on the TPU with the best JAX performance. Although among developers, Pytorch is still more popular than Tensorflow. But in the future, perhaps more large models will be trained and run based on the JAX platform. Models Recently, the Keras team benchmarked three backends (TensorFlow, JAX, PyTorch) with the native PyTorch implementation and Keras2 with TensorFlow. First, they select a set of mainstream
 Tesla robots work in factories, Musk: The degree of freedom of hands will reach 22 this year!
May 06, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
Tesla robots work in factories, Musk: The degree of freedom of hands will reach 22 this year!
May 06, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
The latest video of Tesla's robot Optimus is released, and it can already work in the factory. At normal speed, it sorts batteries (Tesla's 4680 batteries) like this: The official also released what it looks like at 20x speed - on a small "workstation", picking and picking and picking: This time it is released One of the highlights of the video is that Optimus completes this work in the factory, completely autonomously, without human intervention throughout the process. And from the perspective of Optimus, it can also pick up and place the crooked battery, focusing on automatic error correction: Regarding Optimus's hand, NVIDIA scientist Jim Fan gave a high evaluation: Optimus's hand is the world's five-fingered robot. One of the most dexterous. Its hands are not only tactile
 FisheyeDetNet: the first target detection algorithm based on fisheye camera
Apr 26, 2024 am 11:37 AM
FisheyeDetNet: the first target detection algorithm based on fisheye camera
Apr 26, 2024 am 11:37 AM
Target detection is a relatively mature problem in autonomous driving systems, among which pedestrian detection is one of the earliest algorithms to be deployed. Very comprehensive research has been carried out in most papers. However, distance perception using fisheye cameras for surround view is relatively less studied. Due to large radial distortion, standard bounding box representation is difficult to implement in fisheye cameras. To alleviate the above description, we explore extended bounding box, ellipse, and general polygon designs into polar/angular representations and define an instance segmentation mIOU metric to analyze these representations. The proposed model fisheyeDetNet with polygonal shape outperforms other models and simultaneously achieves 49.5% mAP on the Valeo fisheye camera dataset for autonomous driving
 DualBEV: significantly surpassing BEVFormer and BEVDet4D, open the book!
Mar 21, 2024 pm 05:21 PM
DualBEV: significantly surpassing BEVFormer and BEVDet4D, open the book!
Mar 21, 2024 pm 05:21 PM
This paper explores the problem of accurately detecting objects from different viewing angles (such as perspective and bird's-eye view) in autonomous driving, especially how to effectively transform features from perspective (PV) to bird's-eye view (BEV) space. Transformation is implemented via the Visual Transformation (VT) module. Existing methods are broadly divided into two strategies: 2D to 3D and 3D to 2D conversion. 2D-to-3D methods improve dense 2D features by predicting depth probabilities, but the inherent uncertainty of depth predictions, especially in distant regions, may introduce inaccuracies. While 3D to 2D methods usually use 3D queries to sample 2D features and learn the attention weights of the correspondence between 3D and 2D features through a Transformer, which increases the computational and deployment time.





