Five ways to incorporate generative AI into your technology strategy

Generative AI has quickly appeared on the strategic agenda of many products. While far from perfect, the technology has achieved tangible breakthroughs, offering the potential for disruptive change. It even reminds people of the original iPhone in 2007 - although the product itself still has a lot of room for improvement, it marks the arrival of a new era of human-computer interaction.
So, how do technology products adapt to the explosive popularity of generative AI? The following five methods may be worth considering.
1. In-depth understanding of what customers need to do
About 20 years ago, I worked with Clay Christensen of Harvard University on his Jobs to be Done consulting project. The main content was to help a company Technology giants introduce mobile electronics into business processes. The so-called "Jobs to be Done" is a set of query methods developed by Clay. The core is to help people figure out the difference between the jobs at hand and the jobs that must be done. The state of that technology company at the time was very typical: it was attracted by new technologies and wanted to take a risk. Clay's idea is to help the other party sort out the core motivations for change. So we started exploring where mobile electronics would perform better, ultimately identifying a handful of customer types and use cases, and then used Jobs to be Done to sort out how to make the most of the technology and what impact it would have on existing jobs.
But things are different now, and technology transformation is about more than understanding what customers want or splitting activities into tasks. Generative AI can even propose new possibilities that customers themselves have never thought of, thereby completely reshaping the shape of tasks. Therefore, we must maintain this open and rigorous thinking attitude and explore step by step the opportunities for AI to reshape the original business system.
For example, AI can currently help target advertising content to the most appropriate digital media. This is nothing new. Instead of focusing only on how AI can help media planners complete tasks efficiently (such as helping Facebook and Google allocate advertising budgets), it is better to take a step back and explore the possibility of change using the concept of Jobs to be Done. Can generative AI generate the best advertising creative based on different attributes, set appropriate budgets, and model the return on investment of advertising campaigns? This is certainly not simple, but it is feasible. What will be derived from this will be truly unique and highly customized creative digital advertising content.
2. Understand the changing trends of customer preferences
In this rapidly changing new era, it is often very dangerous to base product planning on the present. Considering the changes that generative AI brings to user expectations, such as the subversion of the interaction between humans and machines, perhaps new opportunities lie within. Will future devices still offer menus? Are users willing to search manually in the software? Or will they get used to telling the computer what they want and then waiting for a tailor-made answer?
This change in preference will have a significant impact on the business. Although the degree of disruption is not as direct as pure solutions, the convergence of preferences from all aspects will also influence the future vision. People quickly become accustomed to new forms of software interaction, so it’s a good idea to observe and summarize what industry leaders are exploring. For example, how will companies like Adobe and Shutterstock incorporate generative AI into the experience of their own creative product suites? And what kind of changes in customer expectations will come from functions such as instructing AI through text to create customized images for content?
3. Understand in which aspects the advantages of generative AI will overlap with business
What we want to talk about here is actually a problem with two sides. Specifically, we need to consider both what generative AI can do for us and what we can do for generative AI.
Generative AI has a series of obvious advantages, such as excellent integration, personalization and engagement capabilities. We need to evaluate the impact of these advantages on user experience and even the core functions of the product, and use the power of AI to take it to the next level. For example, could generative AI suggest new actions for users to try that they haven’t done before? Can I preview the possible results of these operations?
On the other hand, we might as well think about how existing systems can help generative AI become better. AI systems rely on data. If everyone uses the same data, there will be no competitive advantage at all. On the contrary, after the introduction of proprietary data, enterprise-level generative AI for thousands of people is the general direction of the future. How can we use our own systems to collect and generate data that can help build competitive advantage? For example, can personalized experiences be better built with proprietary data, or solutions optimized with more precise value-based information? Can existing systems be used to label and classify data to help AI make better use of it? The data war is about to begin, and whoever has the best data will win.
4. Fundamentally re-examine the customer journey and user experience
The huge potential of generative AI is not limited to improving the interaction between customers and software (this is only the initial impact), but ultimately changing this everything. Therefore, we should uphold professional design thinking and be ready to update the original design plan at any time. After accumulating a certain number of existing experience optimization solutions, you can gradually figure out in which direction revolutionary disruption will occur.
To this end, we still have to return to the “must-do work” emphasized by Jobs to be Done. This includes not only the work content itself, but also factors such as motivations and obstacles to adopting new solutions, based on which detailed standard design is made. How can generative AI bring unprecedented capabilities to critical tasks? How can you provide customers with different paths to success on an emotional and functional level? Where can you create your highlight moments?
5. Re-evaluate competitive strategy
Although proprietary data can help us maintain a certain advantage in the AI competition, it cannot last long. Considering that AI may increase the efficiency of code writing and debugging to unprecedented levels, market competition is expected to continue to heat up. So what does all this mean for our product strategy?
Competitive pressure will come from all aspects. We need to carefully consider all feasible innovation vehicles, such as whether we can provide AI-assisted professional services to ensure that customers can succeed with our products and that the solutions can be closely integrated with the way customers do business. In addition, you should also consider how to build a complementary product ecosystem that is difficult for competitors to match. The addition of generative AI will not only change the intensity of market competition, but also change the specific face of sustainable business advantages.
The emergence of generative AI has accelerated the emergence of many people on the eve of the birth of the Internet. Yes, but the difference this time is that everything will change faster. As the AI revolution takes root rapidly, you may wish to make planning adjustments to your product strategy in advance through the above five methods.
The above is the detailed content of Five ways to incorporate generative AI into your technology strategy. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 Chinese mathematician Terence Tao leads the White House Generative AI Working Group, and Li Feifei will speak at the group
May 25, 2023 am 10:36 AM
Chinese mathematician Terence Tao leads the White House Generative AI Working Group, and Li Feifei will speak at the group
May 25, 2023 am 10:36 AM
The Generative AI Working Group established by the President's Council of Advisors on Science and Technology is designed to help assess key opportunities and risks in the field of artificial intelligence and provide advice to the President on ensuring that these technologies are developed and deployed as fairly, safely, and responsibly as possible. AMD CEO Lisa Su and Google Cloud Chief Information Security Officer Phil Venables are also members of the working group. Chinese-American mathematician and Fields Medal winner Terence Tao. On May 13, local time, Chinese-American mathematician and Fields Medal winner Terence Tao announced that he and physicist Laura Greene will co-lead the Generative Artificial Intelligence Working Group of the U.S. Presidential Council of Advisors on Science and Technology (PCAST) .
 From 'human + RPA' to 'human + generative AI + RPA', how does LLM affect RPA human-computer interaction?
Jun 05, 2023 pm 12:30 PM
From 'human + RPA' to 'human + generative AI + RPA', how does LLM affect RPA human-computer interaction?
Jun 05, 2023 pm 12:30 PM
Image source@visualchinesewen|Wang Jiwei From "human + RPA" to "human + generative AI + RPA", how does LLM affect RPA human-computer interaction? From another perspective, how does LLM affect RPA from the perspective of human-computer interaction? RPA, which affects human-computer interaction in program development and process automation, will now also be changed by LLM? How does LLM affect human-computer interaction? How does generative AI change RPA human-computer interaction? Learn more about it in one article: The era of large models is coming, and generative AI based on LLM is rapidly transforming RPA human-computer interaction; generative AI redefines human-computer interaction, and LLM is affecting the changes in RPA software architecture. If you ask what contribution RPA has to program development and automation, one of the answers is that it has changed human-computer interaction (HCI, h
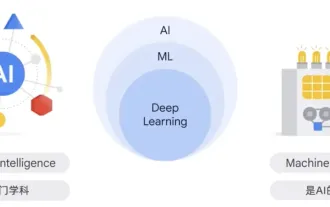 Why is generative AI sought after by various industries?
Mar 30, 2024 pm 07:36 PM
Why is generative AI sought after by various industries?
Mar 30, 2024 pm 07:36 PM
Generative AI is a type of human artificial intelligence technology that can generate various types of content, including text, images, audio and synthetic data. So what is artificial intelligence? What is the difference between artificial intelligence and machine learning? Artificial intelligence is the discipline, a branch of computer science, that studies the creation of intelligent agents, which are systems that can reason, learn, and perform actions autonomously. At its core, artificial intelligence is concerned with the theories and methods of building machines that think and act like humans. Within this discipline, machine learning ML is a field of artificial intelligence. It is a program or system that trains a model based on input data. The trained model can make useful predictions from new or unseen data derived from the unified data on which the model was trained.
 Say goodbye to design software to generate renderings in one sentence, generative AI subverts the field of decoration and decoration, with 28 popular tools
Jun 10, 2023 pm 03:33 PM
Say goodbye to design software to generate renderings in one sentence, generative AI subverts the field of decoration and decoration, with 28 popular tools
Jun 10, 2023 pm 03:33 PM
▲This picture was generated by AI. Kujiale, Sanweijia, Dongyi Risheng, etc. have already taken action. The decoration and decoration industry chain has introduced AIGC on a large scale. What are the applications of generative AI in the field of decoration and decoration? What impact does it have on designers? One article to understand and say goodbye to various design software to generate renderings in one sentence. Generative AI is subverting the field of decoration and decoration. Using artificial intelligence to enhance capabilities improves design efficiency. Generative AI is revolutionizing the decoration and decoration industry. What impact does generative AI have on the decoration and decoration industry? What are the future development trends? One article to understand how LLM is revolutionizing decoration and decoration. These 28 popular generative AI decoration design tools are worth trying. Article/Wang Jiwei In the field of decoration and decoration, there has been a lot of news related to AIGC recently. Collov launches generative AI-powered design tool Col
 Watch: What is the potential of applying generative AI to network automation?
Aug 17, 2023 pm 07:57 PM
Watch: What is the potential of applying generative AI to network automation?
Aug 17, 2023 pm 07:57 PM
Generative artificial intelligence (GenAI) is expected to become a compelling technology trend by 2023, bringing important applications to businesses and individuals, including education, according to a new report from market research firm Omdia. In the telecom space, use cases for GenAI are mainly focused on delivering personalized marketing content or supporting more sophisticated virtual assistants to enhance customer experience. Although the application of generative AI in network operations is not obvious, EnterpriseWeb has developed an interesting concept. Validation, demonstrating the potential of generative AI in the field, the capabilities and limitations of generative AI in network automation One of the early applications of generative AI in network operations was the use of interactive guidance to replace engineering manuals to help install network elements, from
 Which technology giant is behind Haier and Siemens' generative AI innovation?
Nov 21, 2023 am 09:02 AM
Which technology giant is behind Haier and Siemens' generative AI innovation?
Nov 21, 2023 am 09:02 AM
Gu Fan, General Manager of the Strategic Business Development Department of Amazon Cloud Technology Greater China In 2023, large language models and generative AI will "surge" in the global market, not only triggering "an overwhelming" follow-up in the AI and cloud computing industry, but also vigorously Attract manufacturing giants to join the industry. Haier Innovation Design Center created the country's first AIGC industrial design solution, which significantly shortened the design cycle and reduced conceptual design costs. It not only accelerated the overall conceptual design by 83%, but also increased the integrated rendering efficiency by about 90%, effectively solving Problems include high labor costs and low concept output and approval efficiency in the design stage. Siemens China's intelligent knowledge base and intelligent conversational robot "Xiaoyu" based on its own model has natural language processing, knowledge base retrieval, and big language training through data
 Tencent Hunyuan upgrades model matrix, launching 256k long text model on the cloud
Jun 01, 2024 pm 01:46 PM
Tencent Hunyuan upgrades model matrix, launching 256k long text model on the cloud
Jun 01, 2024 pm 01:46 PM
The implementation of large models is accelerating, and "industrial practicality" has become a development consensus. On May 17, 2024, the Tencent Cloud Generative AI Industry Application Summit was held in Beijing, announcing a series of progress in large model development and application products. Tencent's Hunyuan large model capabilities continue to upgrade. Multiple versions of models hunyuan-pro, hunyuan-standard, and hunyuan-lite are open to the public through Tencent Cloud to meet the model needs of enterprise customers and developers in different scenarios, and to implement the most cost-effective model solutions. . Tencent Cloud releases three major tools: knowledge engine for large models, image creation engine, and video creation engine, creating a native tool chain for the era of large models, simplifying data access, model fine-tuning, and application development processes through PaaS services to help enterprises
 Transformative Trend: Generative Artificial Intelligence and Its Impact on Software Development
Feb 26, 2024 pm 10:28 PM
Transformative Trend: Generative Artificial Intelligence and Its Impact on Software Development
Feb 26, 2024 pm 10:28 PM
The rise of artificial intelligence is driving the rapid development of software development. This powerful technology has the potential to revolutionize the way we build software, with far-reaching impacts on every aspect of design, development, testing and deployment. For companies trying to enter the field of dynamic software development, the emergence of generative artificial intelligence technology provides them with unprecedented development opportunities. By incorporating this cutting-edge technology into their development processes, companies can significantly increase production efficiency, shorten product time to market, and launch high-quality software products that stand out in the fiercely competitive digital market. According to a McKinsey report, it is predicted that the generative artificial intelligence market size is expected to reach US$4.4 trillion by 2031. This forecast not only reflects a trend, but also shows the technology and business landscape.




