Machine Learning Decision Tree Practical Exercise
Translator | Zhu Xianzhong
##Reviewer | Sun Shujuan
Decision tree in machine learningModern machine learning algorithms are changing our daily lives. For example, large language models like BERT are powering Google search, and GPT-3 is powering many high-level language applications.
On the other hand, building complex machine learning algorithms is much easier today than ever before. However, no matter how complex a machine learning algorithm may be, they all fall into one of the following learning categories:
- Supervised learning
- Unsupervised learning
- Semi-supervised learning
- Reinforcement learning
In fact, Decision trees are one of the oldest supervised machine learning algorithms and can solve a wide range of real-world problems. Research shows that the earliest invention of the decision tree algorithm can be traced back to 1963.
Next, let’s delve into the details of this algorithm and see why this type of algorithm is still so popular today.
What is a decision tree?The decision tree algorithm is a popular supervised machine learning algorithm because of its relatively simple method of processing complex data sets. Decision trees get their name from their similarity to the structure of a tree; a tree structure consists of several components such as roots, branches, and leaves in the form of nodes and edges. They are used for decision analysis, much like an if-else based decision flow chart, where decisions will produce the desired predictions. Decision trees can learn these if-else decision rules to split the data set and finally generate a tree-like data model.
Decision trees have been used in the prediction of discrete results for classification problems and the prediction of continuous numerical results for regression problems. Over the years scientists have developed many different algorithms such as CART, C4.5 and ensemble algorithms such as random forests and gradient boosted trees.
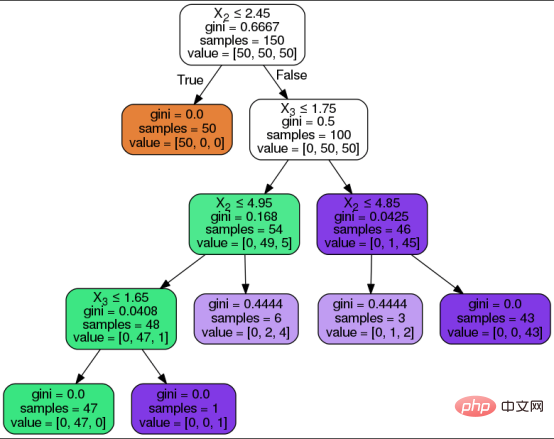
The goal of the decision tree algorithm is to predict the outcome of the input data set. The tree data set is divided into three forms: attributes, attribute values, and types to be predicted. As with any supervised learning algorithm, the data set is divided into two types: training set and test set. Among them, the training set defines the decision rules that the algorithm learns and applies to the test set.
Before we gather together the steps of the decision tree algorithm, let us first understand the components of the decision tree:
- Root Node: It is the starting node at the top of the decision tree and contains all attribute values. The root node is divided into decision nodes based on the decision rules learned by the algorithm.
- Branches: Branches are connectors between nodes that correspond to attribute values. In binary splitting, the branches represent true and false paths.
- Decision Node/Internal Node: Internal node is the decision node between the root node and leaf node, corresponding to the decision rule and its answer path. Nodes represent questions, and branches show paths to relevant answers based on those questions.
- Leaf nodes: Leaf nodes are terminal nodes that represent target predictions. These nodes will not be split further.
The following is a visual representation of a decision tree and its above components, the decision tree algorithm goes through the following steps to arrive at the desired prediction:
- The algorithm starts from the root node with all attribute values.
- The root node is divided into decision nodes based on the decision rules learned by the algorithm from the training set.
- Pass internal decision nodes through branches/edges based on the question and its answer path.
- Continue the previous steps until you reach a leaf node or all attributes are used.
In order to select the best attribute on each node, one of the following two attribute selection metrics will be used for splitting:
- Gini coefficient(Gini index)Measurement of Gini impurity (Gini Impurity) to indicate the likelihood that the algorithm will misclassify a random class label.
- Information gainMeasures the improvement in entropy after segmentation to avoid predicting class 50/ 50 split. Entropy is a mathematical measure of the impurity in a given data sample. The chaotic state in the decision tree is represented by a partition close to 50/50 . Flower classification case using decision tree algorithm
A brief explanation about the data set
The data set for this tutorial is an iris data set. This dataset is already built into the Scikit open source library, so developers do not need to load it externally. The dataset includes a total of four iris attributes and corresponding attribute values, which will be input into the model to predict one of three types of iris flowers.
- Attributes/Features in the dataset: sepal length, sepal width, petal length, petal width.
- Predicted labels/flower types in the dataset: Setosis, Versicolor, Virginica.
Import library
First, import the library required to implement the decision tree through the following piece of code.import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
data_set = load_iris()
print('Iris plant classes to predict: ', data_set.target_names)
print('Four features of iris plant: ', data_set.feature_names)
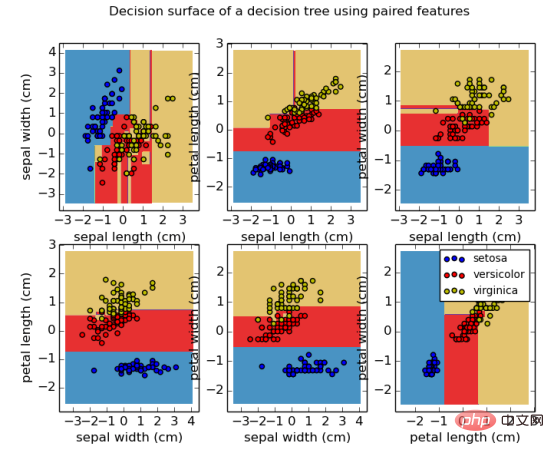 Separating attributes and tags
Separating attributes and tags
#提取花的特性和类型信息
X_att = data_set.data
y_label = data_set.target
print('数据集中总的样本数:', X_att.shape[0])
data_view=pd.DataFrame({
'sepal length':X_att[:,0],
'sepal width':X_att[:,1],
'petal length':X_att[:,2],
'petal width':X_att[:,3],
'species':y_label
})
data_view.head()
#数据集拆分为训练集和测试集两部分
X_att_train, X_att_test, y_label_train, y_label_test = train_test_split(X_att, y_label, random_state = 42, test_size = 0.25)
by using the DecisionTreeClassifier function Classification modelto implement a decision tree, classification standard is set to "entropy"Way. This standard enables to set the attribute selection metric to (Information gain). The code then matches the model to our training set of attributes and labels. 下面的代码负责计算并打印决策树分类模型在训练集和测试集上的准确性。为了计算准确度分数,我们使用了predict函数。测试结果是:训练集和测试集的准确率分别为100%和94.7%。 当今社会,机器学习决策树在许多行业的决策过程中都得到广泛应用。其中,决策树的最常见应用首先是在金融和营销部门,例如可用于如下一些子领域: 作为本文决策树主题讨论的总结,我们有充分的理由安全地假设:决策树的可解释性仍然很受欢迎。决策树之所以容易理解,是因为它们可以被人类以可视化方式展现并便于解释。因此,它们是解决机器学习问题的直观方法,同时也能够确保结果是可解释的。机器学习中的可解释性是我们过去讨论过的一个小话题,它也与即将到来的人工智能伦理主题存在密切联系。 与任何其他机器学习算法一样,决策树自然也可以加以改进,以避免过度拟合和出现过于偏向于优势预测类别。剪枝和ensembling技术是克服决策树算法缺点方案最常采用的方法。决策树尽管存在这些缺点,但仍然是决策分析算法的基础,并将在机器学习领域始终保持重要位置。 朱先忠,51CTO社区编辑,51CTO专家博客、讲师,潍坊一所高校计算机教师,自由编程界老兵一枚。 原文标题:An Introduction to Decision Trees for Machine Learning,作者:Stylianos Kampakis#应用决策树分类器
clf_dt = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion = 'entropy')
clf_dt.fit(X_att_train, y_label_train)
计算模型精度
print('Training data accuracy: ', accuracy_score(y_true=y_label_train, y_pred=clf_dt.predict(X_att_train)))
print('Test data accuracy: ', accuracy_score(y_true=y_label_test, y_pred=clf_dt.predict(X_att_test)))真实世界中的决策树应用程序
如何改进决策树?
译者介绍
The above is the detailed content of Machine Learning Decision Tree Practical Exercise. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 15 recommended open source free image annotation tools
Mar 28, 2024 pm 01:21 PM
15 recommended open source free image annotation tools
Mar 28, 2024 pm 01:21 PM
Image annotation is the process of associating labels or descriptive information with images to give deeper meaning and explanation to the image content. This process is critical to machine learning, which helps train vision models to more accurately identify individual elements in images. By adding annotations to images, the computer can understand the semantics and context behind the images, thereby improving the ability to understand and analyze the image content. Image annotation has a wide range of applications, covering many fields, such as computer vision, natural language processing, and graph vision models. It has a wide range of applications, such as assisting vehicles in identifying obstacles on the road, and helping in the detection and diagnosis of diseases through medical image recognition. . This article mainly recommends some better open source and free image annotation tools. 1.Makesens
 This article will take you to understand SHAP: model explanation for machine learning
Jun 01, 2024 am 10:58 AM
This article will take you to understand SHAP: model explanation for machine learning
Jun 01, 2024 am 10:58 AM
In the fields of machine learning and data science, model interpretability has always been a focus of researchers and practitioners. With the widespread application of complex models such as deep learning and ensemble methods, understanding the model's decision-making process has become particularly important. Explainable AI|XAI helps build trust and confidence in machine learning models by increasing the transparency of the model. Improving model transparency can be achieved through methods such as the widespread use of multiple complex models, as well as the decision-making processes used to explain the models. These methods include feature importance analysis, model prediction interval estimation, local interpretability algorithms, etc. Feature importance analysis can explain the decision-making process of a model by evaluating the degree of influence of the model on the input features. Model prediction interval estimate
 Transparent! An in-depth analysis of the principles of major machine learning models!
Apr 12, 2024 pm 05:55 PM
Transparent! An in-depth analysis of the principles of major machine learning models!
Apr 12, 2024 pm 05:55 PM
In layman’s terms, a machine learning model is a mathematical function that maps input data to a predicted output. More specifically, a machine learning model is a mathematical function that adjusts model parameters by learning from training data to minimize the error between the predicted output and the true label. There are many models in machine learning, such as logistic regression models, decision tree models, support vector machine models, etc. Each model has its applicable data types and problem types. At the same time, there are many commonalities between different models, or there is a hidden path for model evolution. Taking the connectionist perceptron as an example, by increasing the number of hidden layers of the perceptron, we can transform it into a deep neural network. If a kernel function is added to the perceptron, it can be converted into an SVM. this one
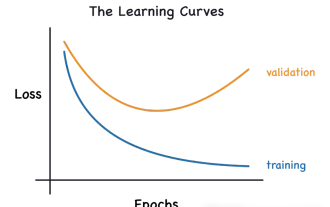 Identify overfitting and underfitting through learning curves
Apr 29, 2024 pm 06:50 PM
Identify overfitting and underfitting through learning curves
Apr 29, 2024 pm 06:50 PM
This article will introduce how to effectively identify overfitting and underfitting in machine learning models through learning curves. Underfitting and overfitting 1. Overfitting If a model is overtrained on the data so that it learns noise from it, then the model is said to be overfitting. An overfitted model learns every example so perfectly that it will misclassify an unseen/new example. For an overfitted model, we will get a perfect/near-perfect training set score and a terrible validation set/test score. Slightly modified: "Cause of overfitting: Use a complex model to solve a simple problem and extract noise from the data. Because a small data set as a training set may not represent the correct representation of all data." 2. Underfitting Heru
 The evolution of artificial intelligence in space exploration and human settlement engineering
Apr 29, 2024 pm 03:25 PM
The evolution of artificial intelligence in space exploration and human settlement engineering
Apr 29, 2024 pm 03:25 PM
In the 1950s, artificial intelligence (AI) was born. That's when researchers discovered that machines could perform human-like tasks, such as thinking. Later, in the 1960s, the U.S. Department of Defense funded artificial intelligence and established laboratories for further development. Researchers are finding applications for artificial intelligence in many areas, such as space exploration and survival in extreme environments. Space exploration is the study of the universe, which covers the entire universe beyond the earth. Space is classified as an extreme environment because its conditions are different from those on Earth. To survive in space, many factors must be considered and precautions must be taken. Scientists and researchers believe that exploring space and understanding the current state of everything can help understand how the universe works and prepare for potential environmental crises
 Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Common challenges faced by machine learning algorithms in C++ include memory management, multi-threading, performance optimization, and maintainability. Solutions include using smart pointers, modern threading libraries, SIMD instructions and third-party libraries, as well as following coding style guidelines and using automation tools. Practical cases show how to use the Eigen library to implement linear regression algorithms, effectively manage memory and use high-performance matrix operations.
 Explainable AI: Explaining complex AI/ML models
Jun 03, 2024 pm 10:08 PM
Explainable AI: Explaining complex AI/ML models
Jun 03, 2024 pm 10:08 PM
Translator | Reviewed by Li Rui | Chonglou Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) models are becoming increasingly complex today, and the output produced by these models is a black box – unable to be explained to stakeholders. Explainable AI (XAI) aims to solve this problem by enabling stakeholders to understand how these models work, ensuring they understand how these models actually make decisions, and ensuring transparency in AI systems, Trust and accountability to address this issue. This article explores various explainable artificial intelligence (XAI) techniques to illustrate their underlying principles. Several reasons why explainable AI is crucial Trust and transparency: For AI systems to be widely accepted and trusted, users need to understand how decisions are made
 Five schools of machine learning you don't know about
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Five schools of machine learning you don't know about
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Machine learning is an important branch of artificial intelligence that gives computers the ability to learn from data and improve their capabilities without being explicitly programmed. Machine learning has a wide range of applications in various fields, from image recognition and natural language processing to recommendation systems and fraud detection, and it is changing the way we live. There are many different methods and theories in the field of machine learning, among which the five most influential methods are called the "Five Schools of Machine Learning". The five major schools are the symbolic school, the connectionist school, the evolutionary school, the Bayesian school and the analogy school. 1. Symbolism, also known as symbolism, emphasizes the use of symbols for logical reasoning and expression of knowledge. This school of thought believes that learning is a process of reverse deduction, through existing






