 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 How Artificial Intelligence Can Eliminate Fake News and Bias on the Internet
How Artificial Intelligence Can Eliminate Fake News and Bias on the Internet
How Artificial Intelligence Can Eliminate Fake News and Bias on the Internet
There is always a chance that the information people hear or read is inaccurate, whether it comes from newspapers, magazines, online sources, or broadcasts. Disinformation has been around since the dawn of human culture, but the sheer volume of information we receive from our interconnected online world makes us particularly vulnerable to inadvertently consuming material that is distorted or falsified. People need to understand the complexities of how AI can help solve the problem of fake news and bias.
Consumers are used to having their opinions influenced by what they read, see and hear online, such as through influencer marketing or celebrity endorsements. Opinions have a lot of power whether supported by facts or not, and much fake news relies on stirring up strong emotions. When it comes to people's attention and feelings, it's often necessary to stop and think about whether what we hear or read is accurate.
According to MIT researchersOpen a new window, real news takes six times longer to reach 1,500 people on Twitter than fake news. Furthermore, the chain length (the number of people sharing a social media post) between accurate news and fake news is highly disproportionate. Verifiable news never exceeded 10, but false news increased to 19. This is partly due to malicious actors using bot swarms to spread incorrect information.
Disinformation now affects people, governments and businesses around the world. In today's expanding digital information economy, discovering and separating so-called "fake news" is a major task. However, improvements in artificial intelligence (AI) may make it easier for online information users to distinguish reality from fiction.
Here’s a look at how artificial intelligence can be used to stop the spread of misinformation and make the internet a more balanced news source.
What’s the place of artificial intelligence in article evaluation?
By using advanced algorithms to find and reach people who may be susceptible to absorbing information, legitimate companies use artificial intelligence to locate and target a piece of information or Views most likely consumers. For example, Google has implemented its RankBrain algorithm in 2015 to improve its ability to identify authoritative results.
To distinguish computer-generated material from human-generated articles, AI-based technology can perform linguistic analysis of text content and find clues such as word patterns, syntactic structure and readability. These algorithms can analyze any text to find instances of hate speech by looking at word vectors, word positions and connotations.
New Applications and Projects
The source of fake news usually comes from an illegal source before the information spreads. Project Fandango looks for social media posts or internet sites with the same term or claim after using articles deemed false by human fact-checkers. This allows journalists and experts to track the source of disinformation and neutralize any dangers before they have a chance to get out of control.
Politifact, Snopes and FactCheck use human editors to conduct the primary investigation necessary to confirm the authenticity of a story or image. Once a fake is identified, the AI system searches the web for similar information that could spark social unrest. Additionally, the application can assign a reputation score to a website article if the material is determined to be authentic.
Some AI engines currently use the following measures in their evaluation scores:
• Sentiment analysis: Journalists’ attitudes toward news in general or specific topics they write about.
•Opinion analysis: personal feelings, opinions, beliefs, or evaluations of a journalist's work
•Revision analysis: the study of how a news story changes over time and how it manipulates the public opinions and emotions.
•Propaganda Analysis: Use Propaganda Analysis to detect up to 18 different persuasion strategies, which can help you uncover potential disinformation.
All four of these combined provide a complete picture of an article’s credibility, and the issues we face.
Challenges of Artificial Intelligence and How to Overcome Them
Language models like GPT-3 can already create articles, poetry, and prose based on a single line of prompts. Artificial intelligence has come close to perfecting the creation of materials that resemble humans. Artificial intelligence has made it so easy to manipulate all kinds of information that open-source programs like FaceSwap and DeepFaceLab could put new, inexperienced users at the center of potential social unrest.
These problems are made worse because these semantic analysis algorithms are unable to decipher the essence of hate speech images, which are not modified but instead circulated in harmful or inaccurate contexts.
Once fraudulent content is discovered, removing it is more challenging than it seems. Some organizations may be accused of censorship and trying to hide information that one organization or another considers to be untrue. Finding a balance between free speech rights and combating disinformation and fake news is difficult.
AI also generally lacks the ability to recognize humor and pranks. Therefore, if fake news or disinformation is used in a light-hearted or joking manner, it can be classified as malicious disinformation. But there’s no denying that AI can be a huge asset in the fight against fake news. In the battle against fake internet news, technology is crucial because it can handle the vast amounts of material.
Fake news is not a problem that can be solved by algorithms alone – we need to change our mindset in how we acquire knowledge. While crowdsourcing of collaborative knowledge among professional groups is critical for evaluating raw data, a community of knowledgeable users can also support ethical monitoring initiatives.
Active action without the participation of all parties may accelerate the loss of public confidence in institutions and media, which is a precursor to anarchy. Until humans can develop the ability to objectively analyze online content, AI-based technologies must become partners in the fight against misinformation on the Internet.
The above is the detailed content of How Artificial Intelligence Can Eliminate Fake News and Bias on the Internet. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Bytedance Cutting launches SVIP super membership: 499 yuan for continuous annual subscription, providing a variety of AI functions
Jun 28, 2024 am 03:51 AM
Bytedance Cutting launches SVIP super membership: 499 yuan for continuous annual subscription, providing a variety of AI functions
Jun 28, 2024 am 03:51 AM
This site reported on June 27 that Jianying is a video editing software developed by FaceMeng Technology, a subsidiary of ByteDance. It relies on the Douyin platform and basically produces short video content for users of the platform. It is compatible with iOS, Android, and Windows. , MacOS and other operating systems. Jianying officially announced the upgrade of its membership system and launched a new SVIP, which includes a variety of AI black technologies, such as intelligent translation, intelligent highlighting, intelligent packaging, digital human synthesis, etc. In terms of price, the monthly fee for clipping SVIP is 79 yuan, the annual fee is 599 yuan (note on this site: equivalent to 49.9 yuan per month), the continuous monthly subscription is 59 yuan per month, and the continuous annual subscription is 499 yuan per year (equivalent to 41.6 yuan per month) . In addition, the cut official also stated that in order to improve the user experience, those who have subscribed to the original VIP
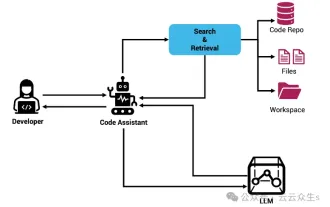 Context-augmented AI coding assistant using Rag and Sem-Rag
Jun 10, 2024 am 11:08 AM
Context-augmented AI coding assistant using Rag and Sem-Rag
Jun 10, 2024 am 11:08 AM
Improve developer productivity, efficiency, and accuracy by incorporating retrieval-enhanced generation and semantic memory into AI coding assistants. Translated from EnhancingAICodingAssistantswithContextUsingRAGandSEM-RAG, author JanakiramMSV. While basic AI programming assistants are naturally helpful, they often fail to provide the most relevant and correct code suggestions because they rely on a general understanding of the software language and the most common patterns of writing software. The code generated by these coding assistants is suitable for solving the problems they are responsible for solving, but often does not conform to the coding standards, conventions and styles of the individual teams. This often results in suggestions that need to be modified or refined in order for the code to be accepted into the application
 Can fine-tuning really allow LLM to learn new things: introducing new knowledge may make the model produce more hallucinations
Jun 11, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Can fine-tuning really allow LLM to learn new things: introducing new knowledge may make the model produce more hallucinations
Jun 11, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Large Language Models (LLMs) are trained on huge text databases, where they acquire large amounts of real-world knowledge. This knowledge is embedded into their parameters and can then be used when needed. The knowledge of these models is "reified" at the end of training. At the end of pre-training, the model actually stops learning. Align or fine-tune the model to learn how to leverage this knowledge and respond more naturally to user questions. But sometimes model knowledge is not enough, and although the model can access external content through RAG, it is considered beneficial to adapt the model to new domains through fine-tuning. This fine-tuning is performed using input from human annotators or other LLM creations, where the model encounters additional real-world knowledge and integrates it
 Seven Cool GenAI & LLM Technical Interview Questions
Jun 07, 2024 am 10:06 AM
Seven Cool GenAI & LLM Technical Interview Questions
Jun 07, 2024 am 10:06 AM
To learn more about AIGC, please visit: 51CTOAI.x Community https://www.51cto.com/aigc/Translator|Jingyan Reviewer|Chonglou is different from the traditional question bank that can be seen everywhere on the Internet. These questions It requires thinking outside the box. Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly important in the fields of data science, generative artificial intelligence (GenAI), and artificial intelligence. These complex algorithms enhance human skills and drive efficiency and innovation in many industries, becoming the key for companies to remain competitive. LLM has a wide range of applications. It can be used in fields such as natural language processing, text generation, speech recognition and recommendation systems. By learning from large amounts of data, LLM is able to generate text
 Five schools of machine learning you don't know about
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Five schools of machine learning you don't know about
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Machine learning is an important branch of artificial intelligence that gives computers the ability to learn from data and improve their capabilities without being explicitly programmed. Machine learning has a wide range of applications in various fields, from image recognition and natural language processing to recommendation systems and fraud detection, and it is changing the way we live. There are many different methods and theories in the field of machine learning, among which the five most influential methods are called the "Five Schools of Machine Learning". The five major schools are the symbolic school, the connectionist school, the evolutionary school, the Bayesian school and the analogy school. 1. Symbolism, also known as symbolism, emphasizes the use of symbols for logical reasoning and expression of knowledge. This school of thought believes that learning is a process of reverse deduction, through existing
 To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
Editor |ScienceAI Question Answering (QA) data set plays a vital role in promoting natural language processing (NLP) research. High-quality QA data sets can not only be used to fine-tune models, but also effectively evaluate the capabilities of large language models (LLM), especially the ability to understand and reason about scientific knowledge. Although there are currently many scientific QA data sets covering medicine, chemistry, biology and other fields, these data sets still have some shortcomings. First, the data form is relatively simple, most of which are multiple-choice questions. They are easy to evaluate, but limit the model's answer selection range and cannot fully test the model's ability to answer scientific questions. In contrast, open-ended Q&A
 SOTA performance, Xiamen multi-modal protein-ligand affinity prediction AI method, combines molecular surface information for the first time
Jul 17, 2024 pm 06:37 PM
SOTA performance, Xiamen multi-modal protein-ligand affinity prediction AI method, combines molecular surface information for the first time
Jul 17, 2024 pm 06:37 PM
Editor | KX In the field of drug research and development, accurately and effectively predicting the binding affinity of proteins and ligands is crucial for drug screening and optimization. However, current studies do not take into account the important role of molecular surface information in protein-ligand interactions. Based on this, researchers from Xiamen University proposed a novel multi-modal feature extraction (MFE) framework, which for the first time combines information on protein surface, 3D structure and sequence, and uses a cross-attention mechanism to compare different modalities. feature alignment. Experimental results demonstrate that this method achieves state-of-the-art performance in predicting protein-ligand binding affinities. Furthermore, ablation studies demonstrate the effectiveness and necessity of protein surface information and multimodal feature alignment within this framework. Related research begins with "S
 SK Hynix will display new AI-related products on August 6: 12-layer HBM3E, 321-high NAND, etc.
Aug 01, 2024 pm 09:40 PM
SK Hynix will display new AI-related products on August 6: 12-layer HBM3E, 321-high NAND, etc.
Aug 01, 2024 pm 09:40 PM
According to news from this site on August 1, SK Hynix released a blog post today (August 1), announcing that it will attend the Global Semiconductor Memory Summit FMS2024 to be held in Santa Clara, California, USA from August 6 to 8, showcasing many new technologies. generation product. Introduction to the Future Memory and Storage Summit (FutureMemoryandStorage), formerly the Flash Memory Summit (FlashMemorySummit) mainly for NAND suppliers, in the context of increasing attention to artificial intelligence technology, this year was renamed the Future Memory and Storage Summit (FutureMemoryandStorage) to invite DRAM and storage vendors and many more players. New product SK hynix launched last year



