 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Let's talk about Python private properties and private methods
Let's talk about Python private properties and private methods
Let's talk about Python private properties and private methods

1. Scenario definition
Private attributes
means that in the object-oriented development process of Python, some attributes of the object are only available in the object are used internally, but do not want these properties to be accessed externally.
That is: private attributes are attributes that the object is not willing to make public.
Private methods
means that in the object-oriented development process of Python, some methods or functions of the object only want to be used inside the object, but do not want to be accessed externally. these methods or functions.
That is: a private method is a method or function that the object does not want to make public.
2. Syntax definition
The syntax for defining private properties and private methods in Python is as follows:
class Staff:
def __init__(self, s_name, s_salary):
self.s_name = s_name
self.__salary = s_salary
def __secret(self):
print("%s 的工资是 %d" % (self.s_name, self.__salary))
(1). __salary is defined starting with two underscores Private property.
(2). __secret(self) is a private method defined starting with two underscores.
3. Call analysis
(1). In the object initialization method of __init__, the __salary attribute defined starting with two underscores is a private attribute.
Now call the __salary attribute outside the object to see if the private attribute can be accessed normally.
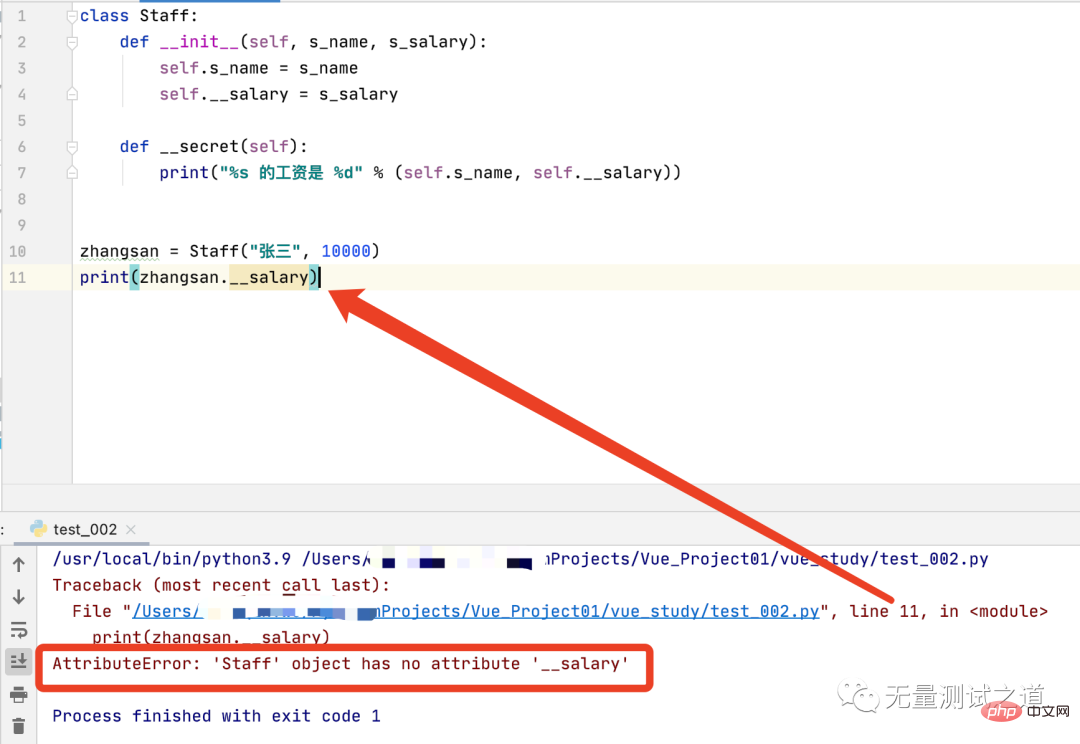
As can be seen from the running results in the above figure, line 11, that is, when accessing the private attribute __salary of the object outside the object, an AttributeError error is prompted, and the Staff object zhangsan has no attributes. __salary.
In order to prove that the Staff class object does have the instance attribute __salary, it is just because the private attributes cannot be accessed outside the object.
I modified self.__salary to: self.salary, the __secret(self) method references the self.__salary attribute, and made corresponding modifications. See the running results as shown in the figure below.
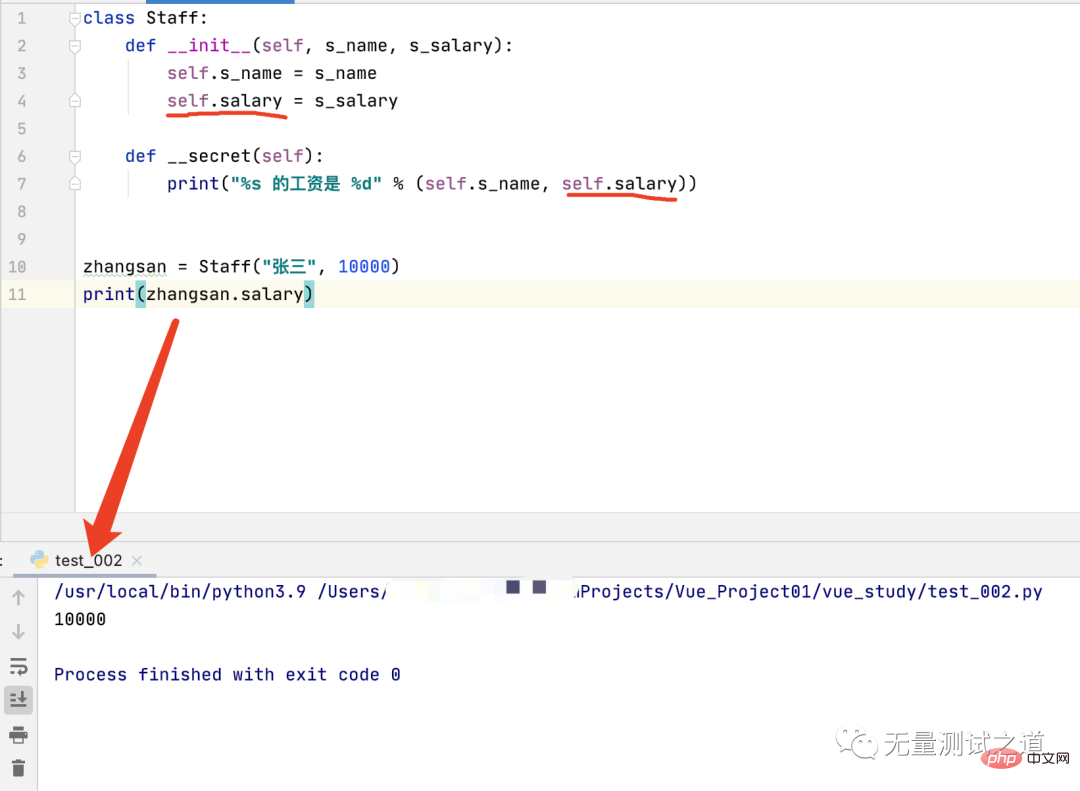
It can be seen from the running results that the external call of this non-private attribute is normal and no AttributeError error is prompted.
(2). In the __secret(self) instance method, the __secret(self) method defined starting with two underscores is a private method.
Same as the above test process, first call the private method __secret(self) outside the object to see if the private method can be called normally.
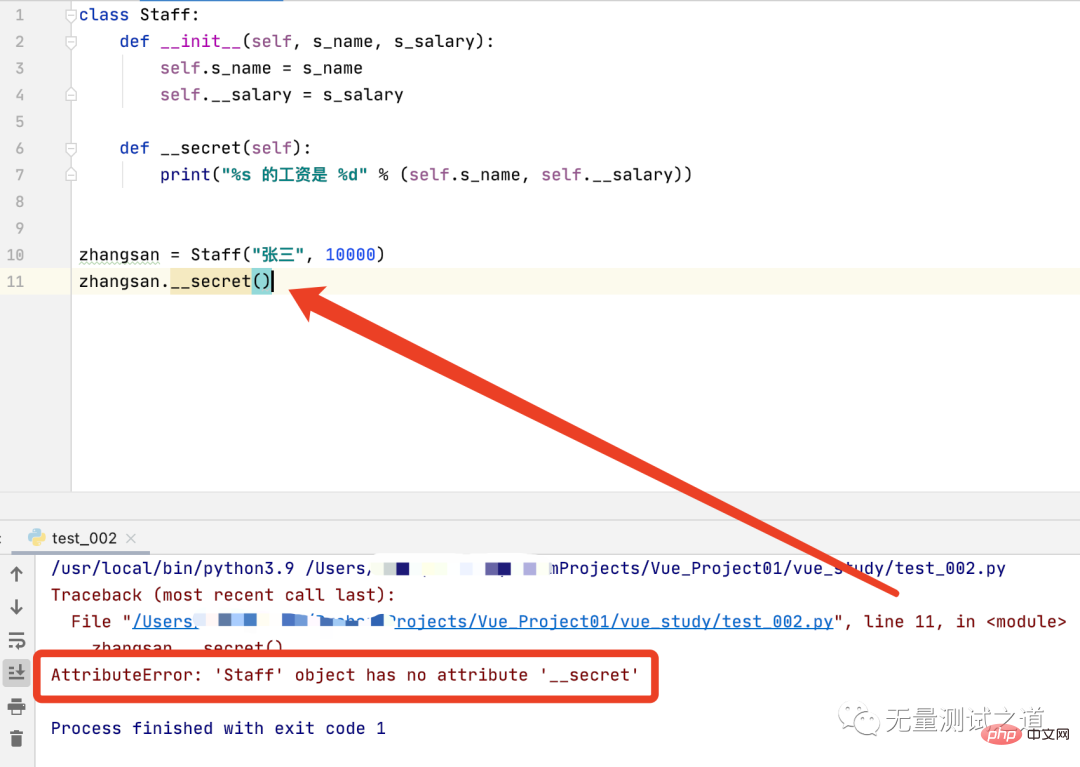
As can be seen from the running results in the above figure, line 11, that is, when accessing the private method __secret(self) of the object outside the object, an AttributeError error is prompted, the Staff object zhangsan does not have a __secret method.
To prove that the Staff class object has the instance method __secret(self), just because the private method cannot be accessed outside the object.
I modified the __secret(self) method to: secret(self), and other codes remain unchanged. See the running results as shown in the figure below.
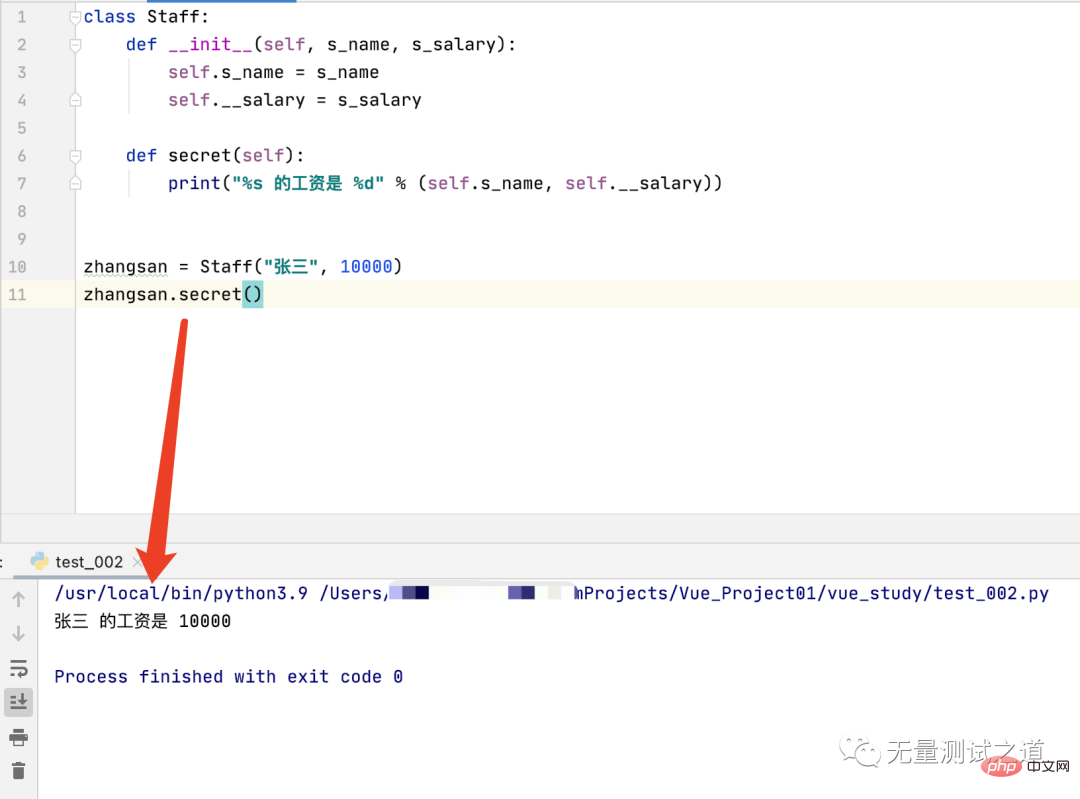
It can be seen from the running results that the external call of this non-private method is normal and no AttributeError error is prompted.
(3). As can be seen from the figure below, private methods and private properties can be called inside the object.
The work method in the figure calls the private method __secret(self), and the private method __secret(self) calls the private attribute __salary.
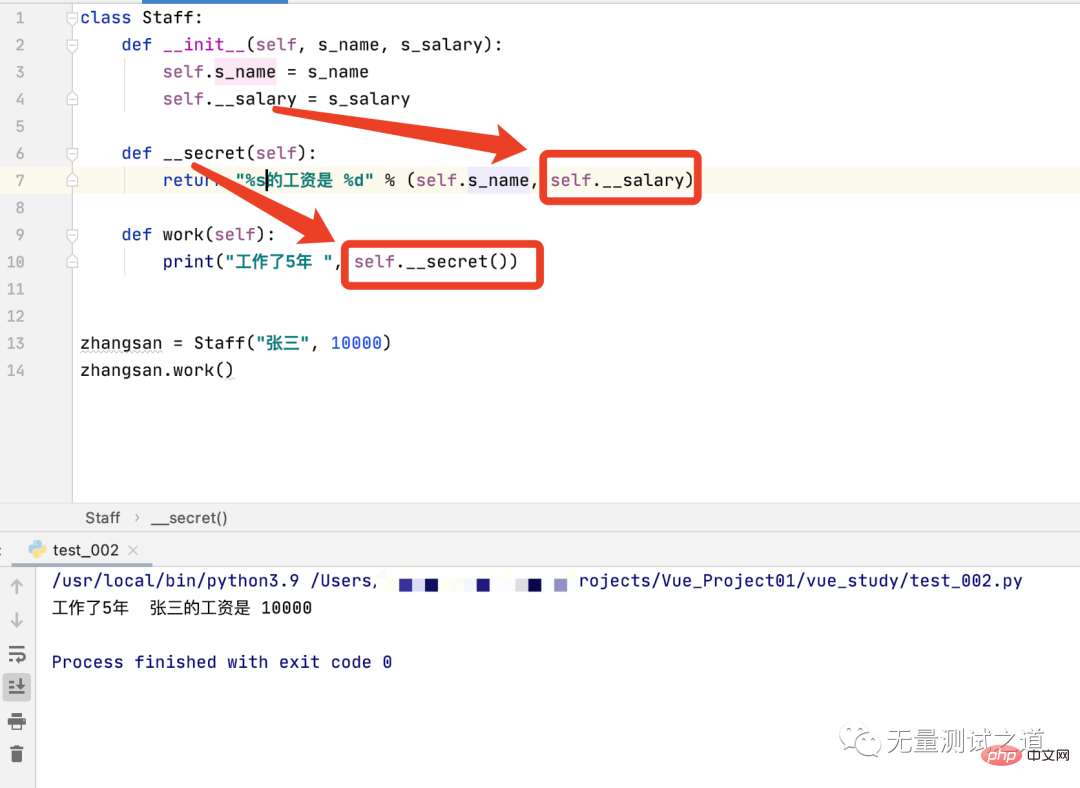
Use the Staff class object zhangsan outside the object to call the work method, which can indirectly access the private properties and private methods of the object.
From the console output, it can be seen that the work method can normally access the private properties and private methods defined inside the object.
4. Python pseudo-private properties and private methods
In Python, there is no real sense of privateness, because Python internally makes some special names when naming properties and methods. Processing makes the corresponding properties and methods inaccessible to the outside world.
Taking private attributes and private methods as an example, Python’s internal processing method is:
(1). Attribute: __salary, the processed attribute name is: _Staff__salary(_class name__ Attribute name)
(2). Method: __secret, the processed method name is: _Staff__secret(_class name__method name)
I know Python internally for private attributes and private Method processing, now use this processed naming method to access private properties and private methods outside the object to see if the access is normal.
class Staff:
def __init__(self, s_name, s_salary):
self.s_name = s_name
self.__salary = s_salary
def __secret(self):
return "%s的工资是 %d" % (self.s_name, self.__salary)
zhangsan = Staff("张三", 10000)
print(zhangsan._Staff__salary)
print(zhangsan._Staff__secret())
The running results are shown in the figure below
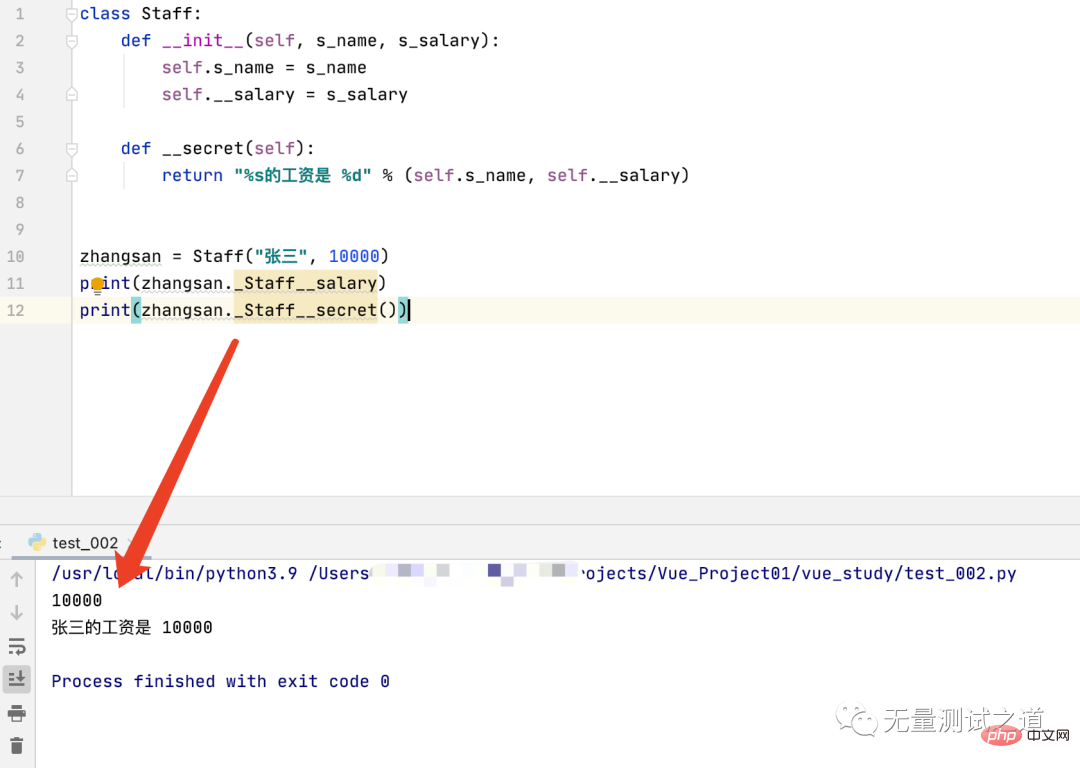
The console did not throw any exceptions, and the previous AttributeError error message disappeared.
This example proves that Python is not private in the true sense. After knowing its internal processing method, you can still use the _class name__ attribute name (method name) method to access outside the object. To the private properties and private methods defined inside the object.
But this method is not recommended in daily work. Since when properties and methods are defined inside the object, they are declared private, and the caller needs to abide by its rules.
I just want to use this small example to illustrate that Python does not have real privacy.
The above is the detailed content of Let's talk about Python private properties and private methods. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
Use most text editors to open XML files; if you need a more intuitive tree display, you can use an XML editor, such as Oxygen XML Editor or XMLSpy; if you process XML data in a program, you need to use a programming language (such as Python) and XML libraries (such as xml.etree.ElementTree) to parse.
 Is there a free XML to PDF tool for mobile phones?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
Is there a free XML to PDF tool for mobile phones?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:12 PM
There is no simple and direct free XML to PDF tool on mobile. The required data visualization process involves complex data understanding and rendering, and most of the so-called "free" tools on the market have poor experience. It is recommended to use computer-side tools or use cloud services, or develop apps yourself to obtain more reliable conversion effects.
 How to beautify the XML format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:57 PM
How to beautify the XML format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:57 PM
XML beautification is essentially improving its readability, including reasonable indentation, line breaks and tag organization. The principle is to traverse the XML tree, add indentation according to the level, and handle empty tags and tags containing text. Python's xml.etree.ElementTree library provides a convenient pretty_xml() function that can implement the above beautification process.
 Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
The speed of mobile XML to PDF depends on the following factors: the complexity of XML structure. Mobile hardware configuration conversion method (library, algorithm) code quality optimization methods (select efficient libraries, optimize algorithms, cache data, and utilize multi-threading). Overall, there is no absolute answer and it needs to be optimized according to the specific situation.
 How to convert XML to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
How to convert XML to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:18 PM
It is not easy to convert XML to PDF directly on your phone, but it can be achieved with the help of cloud services. It is recommended to use a lightweight mobile app to upload XML files and receive generated PDFs, and convert them with cloud APIs. Cloud APIs use serverless computing services, and choosing the right platform is crucial. Complexity, error handling, security, and optimization strategies need to be considered when handling XML parsing and PDF generation. The entire process requires the front-end app and the back-end API to work together, and it requires some understanding of a variety of technologies.
 Does XML modification require programming?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:51 PM
Does XML modification require programming?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:51 PM
Modifying XML content requires programming, because it requires accurate finding of the target nodes to add, delete, modify and check. The programming language has corresponding libraries to process XML and provides APIs to perform safe, efficient and controllable operations like operating databases.
 Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
An application that converts XML directly to PDF cannot be found because they are two fundamentally different formats. XML is used to store data, while PDF is used to display documents. To complete the transformation, you can use programming languages and libraries such as Python and ReportLab to parse XML data and generate PDF documents.
 How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
It is impossible to complete XML to PDF conversion directly on your phone with a single application. It is necessary to use cloud services, which can be achieved through two steps: 1. Convert XML to PDF in the cloud, 2. Access or download the converted PDF file on the mobile phone.





