 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 CMU publishes new dexterous robot algorithm that accurately learns how to operate everyday furniture
CMU publishes new dexterous robot algorithm that accurately learns how to operate everyday furniture
CMU publishes new dexterous robot algorithm that accurately learns how to operate everyday furniture
Most of the furniture that people come into contact with in daily life are "articulated objects", such as drawers with pull-out rails, doors with vertical rotation axes, doors with horizontal rotation Shaft oven, because the main parts of these objects are connected by various joints.
Due to the existence of these joints, the various parts of the parts of the connected object are kinematically constrained by the joints, so these parts have only one degree of freedom (1 DoF). These items are everywhere in our lives, especially in our daily homes. They are an important part of our daily lives. We as humans see that no matter what kind of furniture we have, we can quickly figure out how to manipulate and control it. It's as if we know how every joint of these objects moves.
So can robots predict how furniture will move like humans? This kind of predictive ability is hard to come by, and if robots could learn this ability, it would be a huge boost for home robots.
Recently, two students in the R-PAD laboratory of Professor David Held of the CMU School of Robotics, Ben Eisner and Harry Zhang, have made breakthroughs in manipulating complex joint objects and launched a 3D-based FlowBot 3D for Neural Networks, an algorithm that effectively expresses and predicts the motion trajectories of parts of articulated objects, such as everyday furniture. The algorithm contains two parts.
The first part is the perception part, which uses a 3D deep neural network to predict the three-dimensional instantaneous motion trajectory from the point cloud data of the manipulated furniture object ( 3D Articulated Flow).
The second part of the algorithm is the policy part, which uses the predicted 3D Articulated Flow to select the robot's next action. Both are fully learned in the simulator and can be implemented directly in the real world without retraining or tuning. With the help of the FlowBot 3D algorithm, the robot can manipulate articulated objects such as everyday furniture at will, just like humans.


##This paper is currently the world’s top robotics conference Robotics Science and Systems (RSS) 2022 best paper candidates (top 3%), and will be exhibited in New York, USA in July, competing with 7 other outstanding articles for the honor of the best paper.
- Paper address: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2205.04382.pdf
- Project homepage: https:// sites.google.com/view/articulated-flowbot-3d
FlowBot 3D relies solely on the simulator and performs supervised learning on simulated data to learn articulated objects such as everyday furniture Instantaneous motion trajectory of the part (3D Articulated Flow). 3D Articulated Flow is a visual point cloud trajectory representation method that can greatly simplify the complexity of the robot's next strategy and improve generalization and efficiency. The robot can complete the task of manipulating joint objects by simply following this instantaneous trajectory and re-predicting this trajectory in a closed loop.
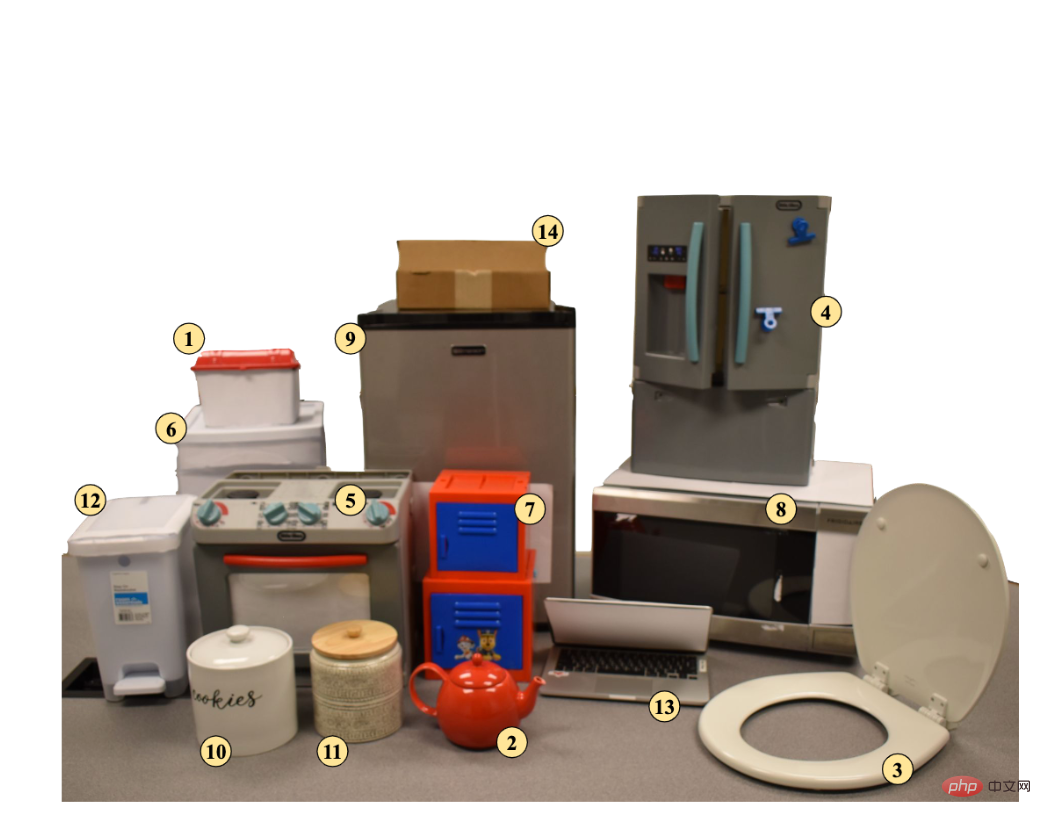
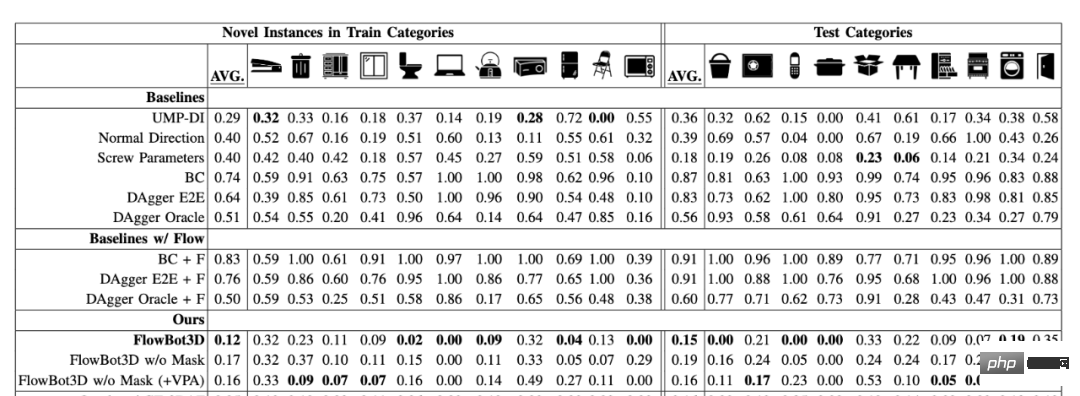
Previously, the conventional method in academia for manipulating joint objects such as furniture was to calculate the movement direction of the part through the geometric characteristics of the manipulated object (such as the position and direction of the connected parts). , or by imitating expert strategies (usually from humans) to learn the operation of specific objects to complete complex actions of joint object manipulation. These traditional methods in academia do not have good generalization, and the efficiency of utilizing data is low. Training requires the collection of a large amount of human demonstration data. Unlike these, FlowBot 3D is the first purely simulator-based learning that does not require humans to provide any demonstration data, and the algorithm allows the robot to calculate the optimal object manipulation path by learning the instantaneous motion trajectory of each part, so the The algorithm has great generalizability. It is this feature that allows FlowBot 3D to generalize to objects invisible during simulator training, successfully manipulating real, everyday furniture items directly in the real world.
The following animations demonstrate the manipulation process of FlowBot 3D. On the left is the manipulated video, and on the right is the predicted instantaneous motion trajectory of the point cloud 3D Articulated Flow. The FlowBot 3D algorithm first enables the robot to identify which part on an object can be manipulated and then predict the direction of movement of that part.
Open the refrigerator door:


Open the toilet seat:

##Open the drawer:

When humans see a new furniture item, such as a door, we know that the door rotates through a door axis, and we know the constraints of the door axis. This door can only rotate in one direction, so we can follow the direction imagined in our minds to open the door. Therefore, if you want a robot to be truly dexterous and effective in predicting the manipulation methods and motion trajectories of joint objects such as furniture, an effective way is to let the robot understand the kinematic constraints of these parts, so that it can predict the movement of these objects. trajectory.
The specific method of FlowBot 3D is not complicated and relies only on the simulator without the need for complicated real human data. In addition, another benefit of the simulator is that in the simulator, the 3D data files (URDF) of these household objects contain the kinematic constraints of each part and the specific parameters of the constraints, so the motion trajectory of each part is in the simulator. can be calculated accurately.
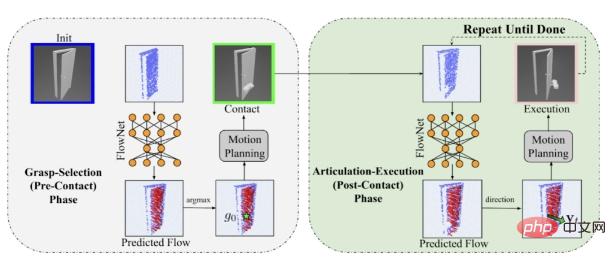

Two modules for FlowBot 3D.
During simulator training, the robot observes the three-dimensional point cloud data of the manipulated object as input data to the robot vision module. The vision module (perception module) uses PointNet to predict the 3D articulated flow of the instantaneous motion trajectory of each point in the input point cloud under the action of external force (for example, after the drawer is opened 1cm, the door opens outward 5 degrees), using the three-dimensional coordinate vector expressed in poor form. The actual data of this motion trajectory can be accurately calculated through forward kinematics. By subtracting the current three-dimensional vector coordinate from the next three-dimensional vector coordinate, the motion trajectory of the manipulated object part can be obtained. Therefore, during training, only the L2 loss of the predicted 3D Articulated flow needs to be minimized for supervised learning.
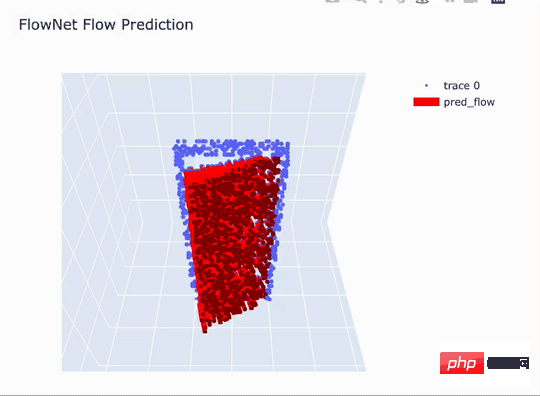
In this picture, the blue points are the observed point cloud data, and the red arrows represent the predicted facade. Motion trajectory 3D Articulated Flow.
By learning in this way, FlowBot 3D can learn the movement direction of each part under kinematic constraints and the situation where each point on the part is subject to the same force. The relative speed and relative direction of motion (velocity). Common household joint items are prismatic and revolute. For twitch parts, such as drawers, the movement direction and speed of each point on the drawer surface are the same when receiving the same external force. For rotating parts, such as doors, the direction of movement of each point on the door surface is the same when receiving the same external force, but the speed increases the further away from the rotation axis. The researchers used the physical laws in robotics (screw theory) to prove that the longest 3D Articulated Flow can maximize the acceleration of the object. According to Newton's second law, this strategy is the optimal solution.#Based on theoretical basis, in actual operation , what the robot needs to do is to predict the movement trajectory of each point through the vision module of FlowBot 3D. In each point trajectory, find the point corresponding to the longest 3D articulated flow direction as the manipulation point, and predict this manipulation in a closed loop The movement trajectory of the point. If the selected manipulation point cannot be successfully grasped (for example, the surface does not meet the grasping conditions of the robot hand), then FlowBot 3D will select the point with the second longest length that meets the grasping conditions. In addition, due to the characteristics of PointNet, FlowBot 3D predicts the motion trajectory of each point and does not rely on the geometric characteristics of the object itself. It has a strong influence on the possible occlusion of the object by the robot. robustness. In addition, because this algorithm is closed-loop, the robot can correct its possible errors in the next step of prediction. FlowBot 3D’s performance in the real worldFlowBot 3D has the ability to overcome generalization challenges in the real world. The design concept of FlowBot 3D is that as long as it can accurately predict the movement trajectory of the manipulated object 3D articulated flow, then the next step is to follow this trajectory to complete the task. Another important point is that FlowBot 3D uses a single training model to manipulate multiple categories of items, including categories that have not been seen in training. And in the real world, the robot only needs to use the model obtained through this pure simulator training to manipulate a variety of real objects. Therefore, in the real world, since the kinematic constraints of household objects are overwhelmingly the same as in the simulator, FlowBot 3D can be directly generalized to the real world. Household items used by FlowBot3D in real-world experiments (including trash cans, refrigerators, toilet seats, boxes, safes, etc. In the simulator, the robot is trained using some categories of household items, including staplers, bins, drawers, windows, refrigerators, etc. In the simulator and real-world tests, test data New objects from training categories and categories not seen during training. In comparison, imitation-based simulations commonly seen in academia The learning method requires manual guidance to learn how to manipulate new objects, making it unrealistic for these robots to be implemented in the real world, especially in home robot scenarios. In addition, 3D point cloud data is stronger than the 2D RGB data used by other methods. Because point cloud allows the robot to understand each joint and the relationship between joints, it can understand and predict the movement trajectory of parts at a higher level, greatly enhancing generalization. Experimental results show that FlowBot 3D can achieve a distance of less than 10% to "full open" when operating most objects (whether they are categories seen or not seen during training), and Success Ridge can reach More than 90. In comparison, other methods based on imitation learning (DAgger) or reinforcement learning (SAC) are far behind and lack generalization. In short, FlowBot 3D is a job with great potential. It can be deployed efficiently in the real world without the need for fine-tuning. This work also shows that advances in computer vision can change the field of robotics, especially the visual expression of motion trajectories called 3D articulated flow, which can be applied to multiple tasks to simplify the robot strategy selection and decision-making process. With this generalizable expression, simulator learning methods will have the potential to be directly deployed in the real world, which will greatly reduce the cost of future home robot training and learning. FlowBot 3D’s next planCurrently, the research team is trying to apply the flow understanding and prediction method to objects other than joint objects, such as how to use flow Predict object trajectories with 6 degrees of freedom. At the same time, the author is trying to use flow as a general visual expression to apply it to other robot learning tasks, such as reinforcement learning, thereby increasing learning efficiency, robustness, and generalizability. Associate Professor David Held’s homepage: https://davheld.github.io/Ben Eisner’s homepage: https://beisner.me/Harry Zhang’s homepage: https:// harryzhangog.github.io/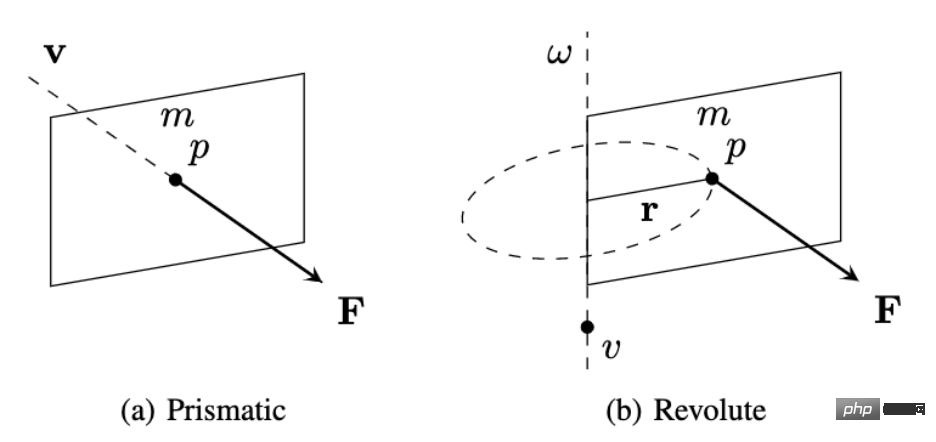
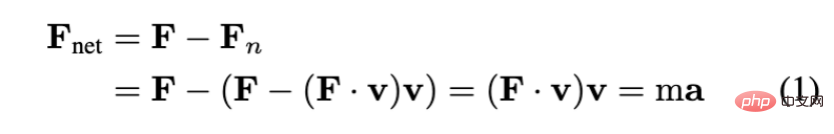
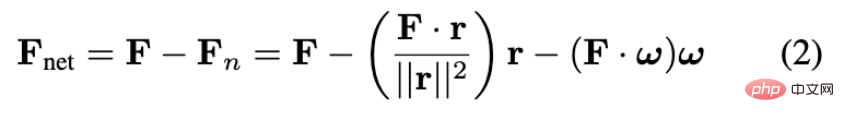






The above is the detailed content of CMU publishes new dexterous robot algorithm that accurately learns how to operate everyday furniture. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 The world's most powerful open source MoE model is here, with Chinese capabilities comparable to GPT-4, and the price is only nearly one percent of GPT-4-Turbo
May 07, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
The world's most powerful open source MoE model is here, with Chinese capabilities comparable to GPT-4, and the price is only nearly one percent of GPT-4-Turbo
May 07, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
Imagine an artificial intelligence model that not only has the ability to surpass traditional computing, but also achieves more efficient performance at a lower cost. This is not science fiction, DeepSeek-V2[1], the world’s most powerful open source MoE model is here. DeepSeek-V2 is a powerful mixture of experts (MoE) language model with the characteristics of economical training and efficient inference. It consists of 236B parameters, 21B of which are used to activate each marker. Compared with DeepSeek67B, DeepSeek-V2 has stronger performance, while saving 42.5% of training costs, reducing KV cache by 93.3%, and increasing the maximum generation throughput to 5.76 times. DeepSeek is a company exploring general artificial intelligence
 KAN, which replaces MLP, has been extended to convolution by open source projects
Jun 01, 2024 pm 10:03 PM
KAN, which replaces MLP, has been extended to convolution by open source projects
Jun 01, 2024 pm 10:03 PM
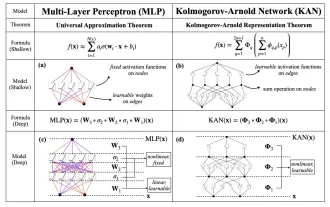
Earlier this month, researchers from MIT and other institutions proposed a very promising alternative to MLP - KAN. KAN outperforms MLP in terms of accuracy and interpretability. And it can outperform MLP running with a larger number of parameters with a very small number of parameters. For example, the authors stated that they used KAN to reproduce DeepMind's results with a smaller network and a higher degree of automation. Specifically, DeepMind's MLP has about 300,000 parameters, while KAN only has about 200 parameters. KAN has a strong mathematical foundation like MLP. MLP is based on the universal approximation theorem, while KAN is based on the Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theorem. As shown in the figure below, KAN has
 Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Common challenges faced by machine learning algorithms in C++ include memory management, multi-threading, performance optimization, and maintainability. Solutions include using smart pointers, modern threading libraries, SIMD instructions and third-party libraries, as well as following coding style guidelines and using automation tools. Practical cases show how to use the Eigen library to implement linear regression algorithms, effectively manage memory and use high-performance matrix operations.
 How can AI make robots more autonomous and adaptable?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 07:18 PM
How can AI make robots more autonomous and adaptable?
Jun 03, 2024 pm 07:18 PM
In the field of industrial automation technology, there are two recent hot spots that are difficult to ignore: artificial intelligence (AI) and Nvidia. Don’t change the meaning of the original content, fine-tune the content, rewrite the content, don’t continue: “Not only that, the two are closely related, because Nvidia is expanding beyond just its original graphics processing units (GPUs). The technology extends to the field of digital twins and is closely connected to emerging AI technologies. "Recently, NVIDIA has reached cooperation with many industrial companies, including leading industrial automation companies such as Aveva, Rockwell Automation, Siemens and Schneider Electric, as well as Teradyne Robotics and its MiR and Universal Robots companies. Recently,Nvidiahascoll
 Tesla robots work in factories, Musk: The degree of freedom of hands will reach 22 this year!
May 06, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
Tesla robots work in factories, Musk: The degree of freedom of hands will reach 22 this year!
May 06, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
The latest video of Tesla's robot Optimus is released, and it can already work in the factory. At normal speed, it sorts batteries (Tesla's 4680 batteries) like this: The official also released what it looks like at 20x speed - on a small "workstation", picking and picking and picking: This time it is released One of the highlights of the video is that Optimus completes this work in the factory, completely autonomously, without human intervention throughout the process. And from the perspective of Optimus, it can also pick up and place the crooked battery, focusing on automatic error correction: Regarding Optimus's hand, NVIDIA scientist Jim Fan gave a high evaluation: Optimus's hand is the world's five-fingered robot. One of the most dexterous. Its hands are not only tactile
 Comprehensively surpassing DPO: Chen Danqi's team proposed simple preference optimization SimPO, and also refined the strongest 8B open source model
Jun 01, 2024 pm 04:41 PM
Comprehensively surpassing DPO: Chen Danqi's team proposed simple preference optimization SimPO, and also refined the strongest 8B open source model
Jun 01, 2024 pm 04:41 PM
In order to align large language models (LLMs) with human values and intentions, it is critical to learn human feedback to ensure that they are useful, honest, and harmless. In terms of aligning LLM, an effective method is reinforcement learning based on human feedback (RLHF). Although the results of the RLHF method are excellent, there are some optimization challenges involved. This involves training a reward model and then optimizing a policy model to maximize that reward. Recently, some researchers have explored simpler offline algorithms, one of which is direct preference optimization (DPO). DPO learns the policy model directly based on preference data by parameterizing the reward function in RLHF, thus eliminating the need for an explicit reward model. This method is simple and stable
 No OpenAI data required, join the list of large code models! UIUC releases StarCoder-15B-Instruct
Jun 13, 2024 pm 01:59 PM
No OpenAI data required, join the list of large code models! UIUC releases StarCoder-15B-Instruct
Jun 13, 2024 pm 01:59 PM
At the forefront of software technology, UIUC Zhang Lingming's group, together with researchers from the BigCode organization, recently announced the StarCoder2-15B-Instruct large code model. This innovative achievement achieved a significant breakthrough in code generation tasks, successfully surpassing CodeLlama-70B-Instruct and reaching the top of the code generation performance list. The unique feature of StarCoder2-15B-Instruct is its pure self-alignment strategy. The entire training process is open, transparent, and completely autonomous and controllable. The model generates thousands of instructions via StarCoder2-15B in response to fine-tuning the StarCoder-15B base model without relying on expensive manual annotation.
 Improved detection algorithm: for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:33 PM
Improved detection algorithm: for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:33 PM
01 Outlook Summary Currently, it is difficult to achieve an appropriate balance between detection efficiency and detection results. We have developed an enhanced YOLOv5 algorithm for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images, using multi-layer feature pyramids, multi-detection head strategies and hybrid attention modules to improve the effect of the target detection network in optical remote sensing images. According to the SIMD data set, the mAP of the new algorithm is 2.2% better than YOLOv5 and 8.48% better than YOLOX, achieving a better balance between detection results and speed. 02 Background & Motivation With the rapid development of remote sensing technology, high-resolution optical remote sensing images have been used to describe many objects on the earth’s surface, including aircraft, cars, buildings, etc. Object detection in the interpretation of remote sensing images



