 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 GPT-3 and Stable Diffusion work together to help the model understand Party A's needs for image retouching.
GPT-3 and Stable Diffusion work together to help the model understand Party A's needs for image retouching.
GPT-3 and Stable Diffusion work together to help the model understand Party A's needs for image retouching.
After the popularity of the diffusion model, many people have focused on how to use more effective prompts to generate the images they want. In the continuous attempts of some AI painting models, people have even summarized the keyword experience for making AI draw pictures well:

That is to say , if you master the correct AI skills, the effect of improving the quality of drawing will be very obvious (see: "How to draw "Alpaca Playing Basketball"? Someone spent 13 US dollars to force DALL· E 2 Show your true skills》).
In addition, some researchers are working in another direction: how to change a painting to what we want with just a few words.
Some time ago, we reported on a study from Google Research and other institutions . Just say what you want an image to look like and it will basically do what you want, generating photorealistic images of, for example, a puppy sitting down:

The input description given to the model here is "a dog that sits down", but according to people's daily communication habits, the most natural description should be "let this dog sit down". Some researchers believe that this is a problem that should be optimized, and the model should be more in line with human language habits.
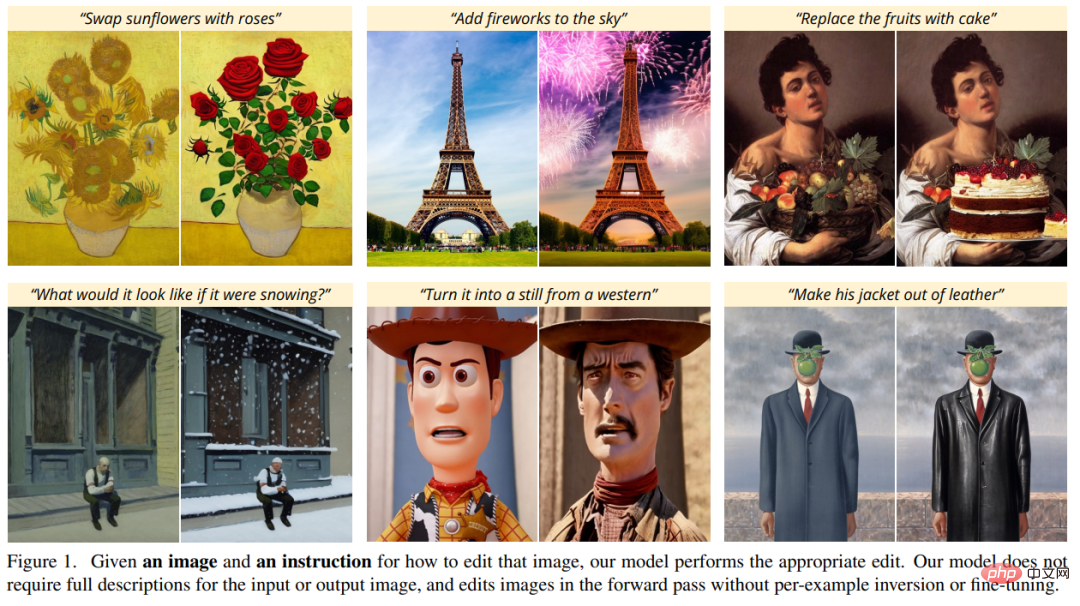
Recently, a research team from UC Berkeley proposed a new method for editing images based on human instructions: InstructPix2Pix: Given an input image and a text description that tells the model what to do, the model Ability to follow description instructions to edit images.

##Paper address: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2211.09800.pdf
For example, to change the sunflowers in the painting to roses, you only need to say directly to the model "Change the sunflowers to roses":
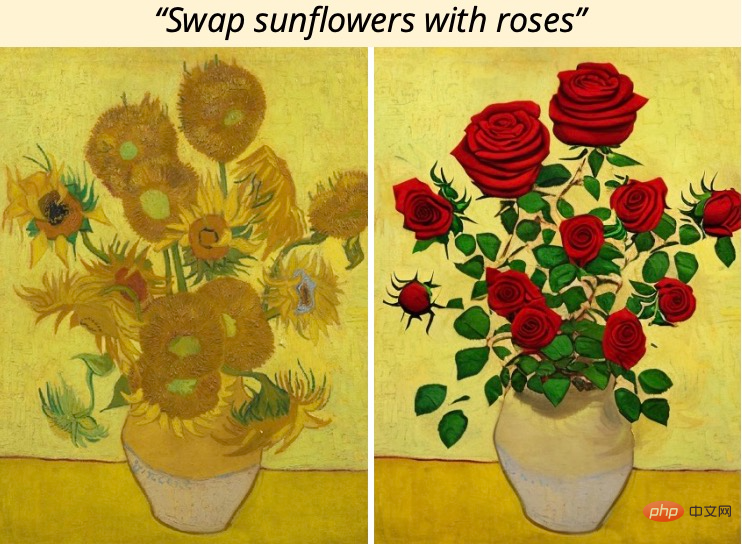

To obtain training data, this study combines two large pre-trained models - a language model (GPT-3) and a text-to-image generation model (Stable Diffusion) - to generate a large pairwise training data set of image editing examples. . The researchers trained a new model, InstructPix2Pix, on this large dataset and generalized to real images and user-written instructions at inference time.
InstructPix2Pix is a conditional diffusion model that generates an edited image given an input image and a text instruction to edit the image. The model performs image editing directly in the forward pass and does not require any additional example images, full descriptions of input/output images, or fine-tuning of each example, so the model can quickly edit images in just a few seconds. .
Although InstructPix2Pix is trained entirely on synthetic examples (i.e., text descriptions generated by GPT-3 and images generated by Stable Diffusion), the model achieves the accuracy of training on arbitrary real images and Zero-shot generalization to human-written text. The mockup supports intuitive image editing, including replacing objects, changing image styles, and more.
Method Overview
The researchers treated instruction-based image editing as a supervised learning problem: First, they generated a paired training dataset containing text editing instructions and images before and after editing ( Figure 2a-c), and then trained an image editing diffusion model on this generated dataset (Figure 2d). Although trained using generated images and editing instructions, the model is still able to edit real images using arbitrary instructions written by humans. Figure 2 below is an overview of the method.

Generate a multi-modal training data set
In the data In the set generation stage, the researchers combined the capabilities of a large language model (GPT-3) and a text-to-image model (Stable Diffusion) to generate a multi-modal training data set containing text editing instructions and corresponding images before and after editing. This process consists of the following steps:
- Fine-tune GPT-3 to generate a collection of text edits: Given a prompt describing an image, generate a text describing the changes to be made command and a prompt describing the changed image (Figure 2a);
- Use the text-to-image model to convert two text prompts (i.e. before editing and after editing) into a corresponding pair image (Fig. 2b).
InstructPix2Pix
The researchers used the generated training data to train a conditional diffusion model. Based on the Stable Diffusion model, images can be edited based on written instructions.
Diffusion models learn to generate data samples through a series of denoising autoencoders that estimate the fraction of the data distribution (pointing in the direction of high-density data). Latent diffusion is improved by operating in the latent space of a pretrained variational autoencoder with encoder and decoder ## Efficiency and quality of diffusion models.
For an image x, the diffusion process adds noise to the encoded latent , which produces a noisy latent z_t, where the noise The level increases with time step t∈T. We learn a network that predicts the noise added to a noisy latent z_t given an image conditioning C_I and a text instruction conditioning C_T. The researchers minimized the following latent diffusion goal:
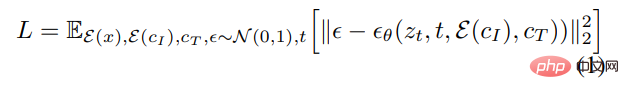
Previous studies (Wang et al.) have shown that for image translation (image translation ) task, especially when pairwise training data is limited, fine-tuning a large image diffusion model is better than training it from scratch. Therefore, in new research, the authors use pre-trained Stable Diffusion checkpoint to initialize the weights of the model, taking advantage of its powerful text-to-image generation capabilities.
To support image conditioning, the researchers added additional input channels to the first convolutional layer, connecting z_t and 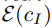 . All available weights of the diffusion model are initialized from the pretrained checkpoint, while weights operating on newly added input channels are initialized to zero. The author here reuses the same text conditioning mechanism originally used for caption without taking the text editing instruction c_T as input.
. All available weights of the diffusion model are initialized from the pretrained checkpoint, while weights operating on newly added input channels are initialized to zero. The author here reuses the same text conditioning mechanism originally used for caption without taking the text editing instruction c_T as input.
In the following figures, the authors show the image editing results of their new model. These results are for a different set of real photos and artwork. The new model successfully performs many challenging edits, including replacing objects, changing seasons and weather, replacing backgrounds, modifying material properties, converting art media, and more.
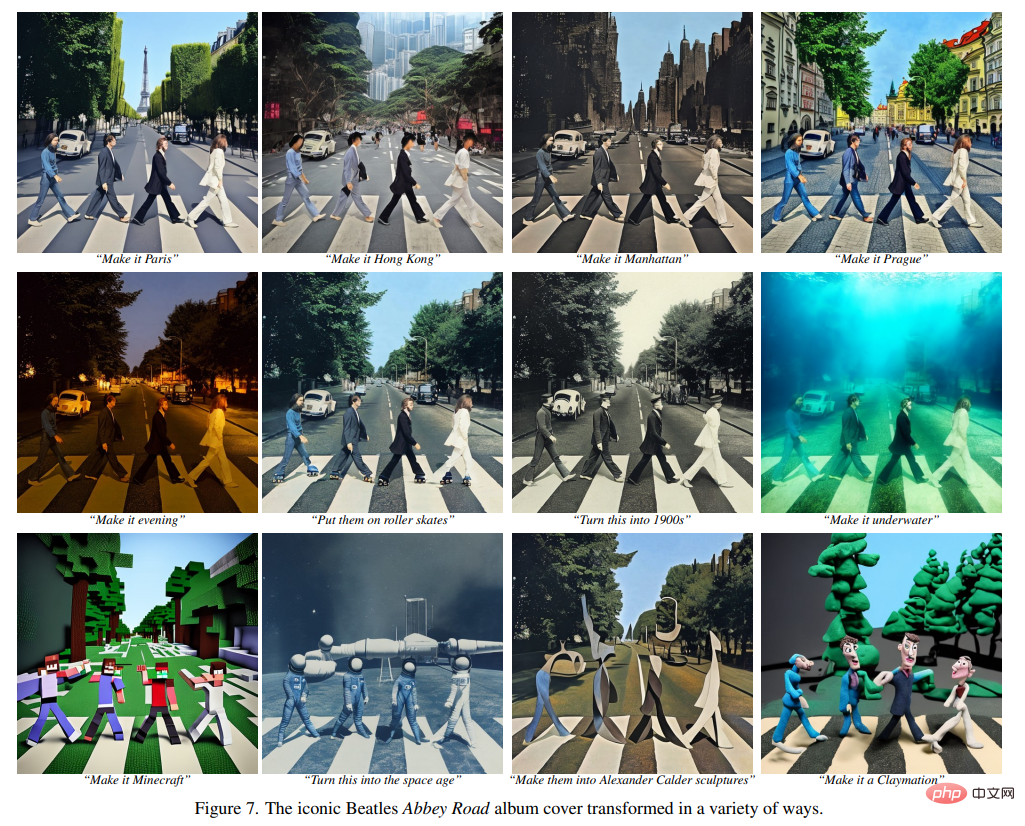




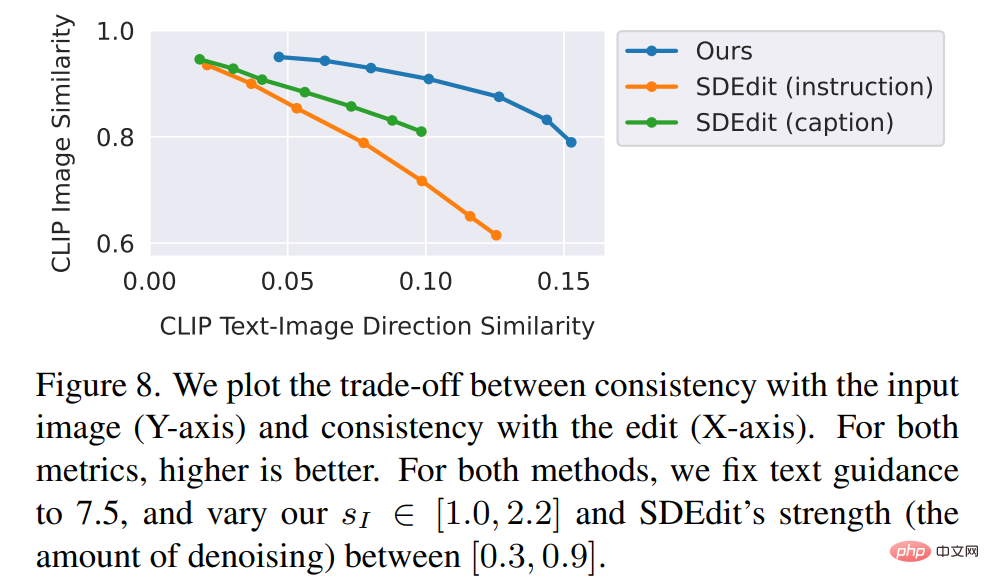
##The researchers compared the new method to recent Some technologies such as SDEdit, Text2Live, etc. are compared. The new model follows instructions for editing images, whereas other methods, including baseline methods, require descriptions of images or editing layers. Therefore, when comparing, the author provides "edited" text annotations for the latter instead of editing instructions. The authors also quantitatively compare the new method with SDEdit, using two metrics that measure image consistency and editing quality. Finally, the authors show how the size and quality of generated training data affects ablation results in model performance.

The above is the detailed content of GPT-3 and Stable Diffusion work together to help the model understand Party A's needs for image retouching.. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 What are the types of return values of c language function? Summary of types of return values of c language function?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:18 PM
What are the types of return values of c language function? Summary of types of return values of c language function?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:18 PM
The return value types of C language function include int, float, double, char, void and pointer types. int is used to return integers, float and double are used to return floats, and char returns characters. void means that the function does not return any value. The pointer type returns the memory address, be careful to avoid memory leakage.结构体或联合体可返回多个相关数据。
 What are the pointer parameters in the parentheses of the C language function?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
What are the pointer parameters in the parentheses of the C language function?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
The pointer parameters of C language function directly operate the memory area passed by the caller, including pointers to integers, strings, or structures. When using pointer parameters, you need to be careful to modify the memory pointed to by the pointer to avoid errors or memory problems. For double pointers to strings, modifying the pointer itself will lead to pointing to new strings, and memory management needs to be paid attention to. When handling pointer parameters to structures or arrays, you need to carefully check the pointer type and boundaries to avoid out-of-bounds access.
 How to use C language function pointer to find the maximum value of a one-dimensional array
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:45 PM
How to use C language function pointer to find the maximum value of a one-dimensional array
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:45 PM
Flexible application of function pointers: use comparison functions to find the maximum value of an array. First, define the comparison function type CompareFunc, and then write the comparison function compareMax(a, b). The findMax function accepts array, array size, and comparison function parameters, and uses the comparison function to loop to compare array elements to find the maximum value. This method has strong code reusability, reflects the idea of higher-order programming, and is conducive to solving more complex problems.
 How to output a countdown in C language
Apr 04, 2025 am 08:54 AM
How to output a countdown in C language
Apr 04, 2025 am 08:54 AM
How to output a countdown in C? Answer: Use loop statements. Steps: 1. Define the variable n and store the countdown number to output; 2. Use the while loop to continuously print n until n is less than 1; 3. In the loop body, print out the value of n; 4. At the end of the loop, subtract n by 1 to output the next smaller reciprocal.
 How to define the call declaration format of c language function
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:03 AM
How to define the call declaration format of c language function
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:03 AM
C language functions include definitions, calls and declarations. Function definition specifies function name, parameters and return type, function body implements functions; function calls execute functions and provide parameters; function declarations inform the compiler of function type. Value pass is used for parameter pass, pay attention to the return type, maintain a consistent code style, and handle errors in functions. Mastering this knowledge can help write elegant, robust C code.
 CS-Week 3
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:06 AM
CS-Week 3
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:06 AM
Algorithms are the set of instructions to solve problems, and their execution speed and memory usage vary. In programming, many algorithms are based on data search and sorting. This article will introduce several data retrieval and sorting algorithms. Linear search assumes that there is an array [20,500,10,5,100,1,50] and needs to find the number 50. The linear search algorithm checks each element in the array one by one until the target value is found or the complete array is traversed. The algorithm flowchart is as follows: The pseudo-code for linear search is as follows: Check each element: If the target value is found: Return true Return false C language implementation: #include#includeintmain(void){i
 What are the rules for function definition and call in C language?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
What are the rules for function definition and call in C language?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
A C language function consists of a parameter list, function body, return value type and function name. When a function is called, the parameters are copied to the function through the value transfer mechanism, and will not affect external variables. Pointer passes directly to the memory address, modifying the pointer will affect external variables. Function prototype declaration is used to inform the compiler of function signatures to avoid compilation errors. Stack space is used to store function local variables and parameters. Too much recursion or too much space can cause stack overflow.
 Integers in C: a little history
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:09 AM
Integers in C: a little history
Apr 04, 2025 am 06:09 AM
Integers are the most basic data type in programming and can be regarded as the cornerstone of programming. The job of a programmer is to give these numbers meanings. No matter how complex the software is, it ultimately comes down to integer operations, because the processor only understands integers. To represent negative numbers, we introduced two's complement; to represent decimal numbers, we created scientific notation, so there are floating-point numbers. But in the final analysis, everything is still inseparable from 0 and 1. A brief history of integers In C, int is almost the default type. Although the compiler may issue a warning, in many cases you can still write code like this: main(void){return0;} From a technical point of view, this is equivalent to the following code: intmain(void){return0;}





