 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 We have compiled 12 essential Python functions. It is recommended to collect them.
We have compiled 12 essential Python functions. It is recommended to collect them.
We have compiled 12 essential Python functions. It is recommended to collect them.

Preface
Novices tend to get stuck when writing code, especially when they are exposed to a lot of functions and other knowledge. They often read the requirements after reading them. Later, I don’t know what method I should use to implement it. You may have the logic to implement it, but you have forgotten which function to use. This is actually because you have insufficient knowledge reserves. You can’t remember which function does what, and you are naturally confused. water.
In the past few days, I have specially compiled some commonly used functions in Python, from the most basic input and output functions to 12 sections such as regular expressions. There are a total of more than 100 commonly used functions, which is convenient for friends to quickly To memorize it, go through it quickly every day, and deepen it when you use it. Slowly you will get rid of the situation of being stuck in writing code.
Although when we learn programming by ourselves, we emphasize more on understanding and actually typing code, there are some things you must keep in mind, otherwise it will be difficult for you to write code. Of course, veterans have already memorized them. If novices want to develop quickly and easily, it is a good way to memorize frequently used functions.
1. Basic function
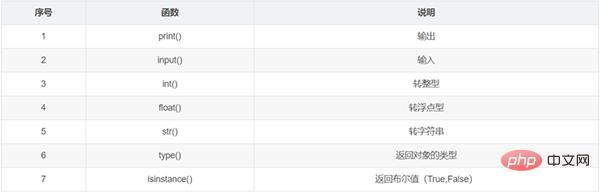
#Case: Convert floating point value to string and output the converted data type
f = 30.5 ff = str(f) print(type(ff)) #输出结果为 class 'str'
2. Process control

#Case: Judge the score based on the score entered by the user. When it is less than 50 points, it will prompt "Your score is less than 50 points", when the score is 5059, it prompts "your score is around 60 points", 60 points or more is considered a pass, 8090 points is excellent, and more than 90 points is excellent.
s = int(input("请输入分数:"))
if 80 >= s >= 60:
print("及格")
elif 80 < s <= 90:
print("优秀")
elif 90 < s <= 100:
print("非常优秀")
else:
print("不及格")
if s > 50:
print("你的分数在60分左右")
else:
print("你的分数低于50分")3. List

#Case: Determine whether the number 6 is in the list [1,2,2,3,6,4,5 ,6,8,9,78,564,456] and output its subscript.
l = [1,2,2,3,6,4,5,6,8,9,78,564,456] n = l.index(6, 0, 9) print(n) #输出结果为4
4. Tuple

Case: Modify tuple
#取元组下标在1~4之间的3个数,转换成列表 t = (1,2,3,4,5) print(t[1:4]) l = list(t) print(l) #在列表下标为2的位置插入1个6 l[2]=6 print(l) #讲修改后的列表转换成元组并输出 t=tuple(l) print(t)
#运行结果为: (2, 3, 4) [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] [1, 2, 6, 4, 5] (1, 2, 6, 4, 5)
5. Character String
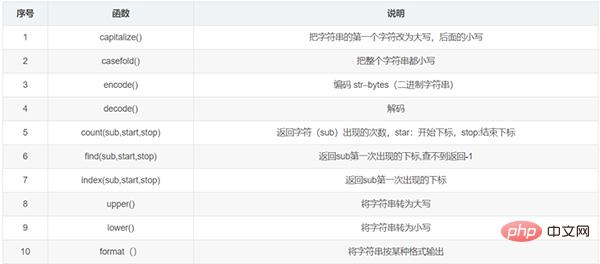
Case: Use format() in three ways to output a string
Method 1: Use numbers to account Digit (subscript):
"{0} 嘿嘿".format("Python")
a=100
s = "{0}{1}{2} 嘿嘿"
s2 = s.format(a,"JAVA","C++")
print(s2)
#运行结果为:100JAVAC++ 嘿嘿Method 2: Use {} placeholder:
a=100
s = "{}{}{} 嘿嘿"
s2 = s.format(a,"JAVA","C++","C# ")
print(s2)
#运行结果为:100JAVAC++ 嘿嘿Method 3: Use letter placeholder:
s = "{a}{b}{c} 嘿嘿"
s2 = s.format(b="JAVA",a="C++",c="C# ")
print(s2)
#运行结果为:C++JAVAC#嘿嘿6. Dictionary
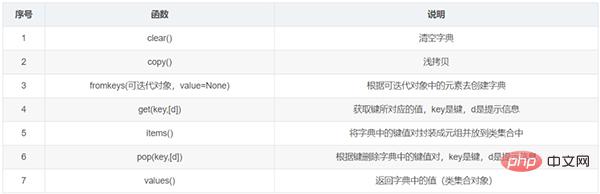
Case: Find data in dictionary:
d = {"name": "小黑"}
print(d.get("name2", "没有查到"))
print(d.get("name"))
#运行结果为:
没有查到
小黑7. Function
Function this The highlight of the block is more custom functions. There are not many commonly used built-in functions. The main ones are the following:
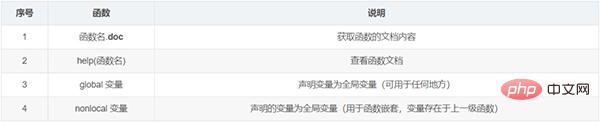
Case: In Define a local variable in the function, and the variable can still be called when exiting the function
def fun1(): global b b=100 print(b) fun1() print(b)
#运行结果为: 100 100
8. Processes and threads
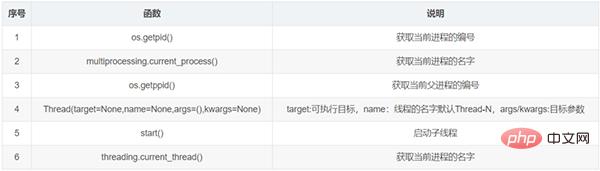
Case:Inherit Thread class implementation:
#多线程的创建
class MyThread(threading.Thread):
def __init__(self,name):
super().__init__()
self.name = name
def run(self):
#线程要做的事情
for i in range(5):
print(self.name)
time.sleep(0.2)
#实例化子线程
t1 = MyThread("凉凉")
t2 = MyThread("最亲的人")
t1.start()
t2.start()9. Modules and packages
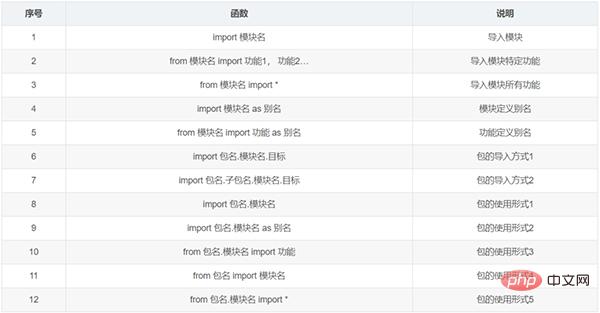
Case: How to use packages 4 :
from my_package1 import my_module3 print(my_module3.a) my_module3.fun4()
10. File operation
(1) Conventional file operation
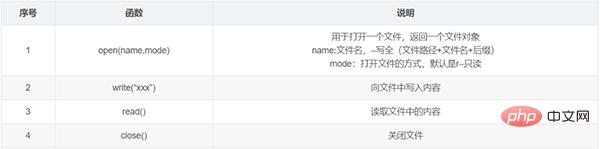
About the conventional mode of file operation:
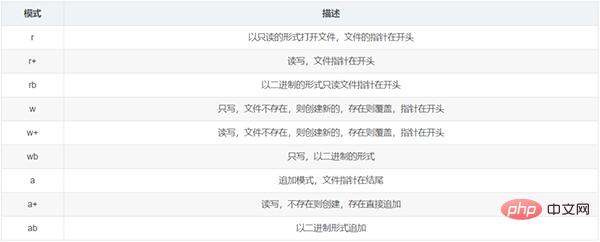
Object properties of file
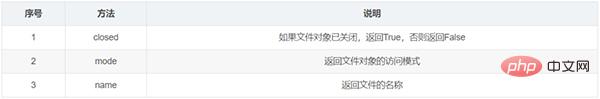
file对象的方法
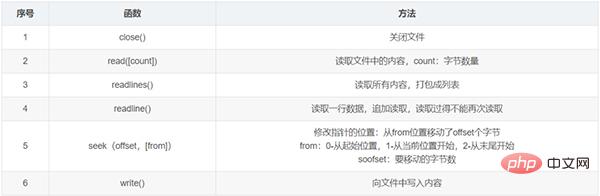
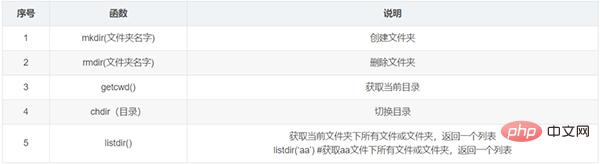
(2)OS模块
- 关于文件的功能

- 关于文件夹的功能
11. 修饰器/装饰器
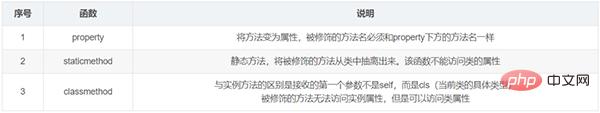
案例:classmethod的用法举例:
class B:
age = 10
def __init__(self,name):
self.name = name
@classmethod
def eat(cls): #普通函数
print(cls.age)
def sleep(self):
print(self)
b = B("小贱人")
b.eat()
#运行结果为:1012. 正则
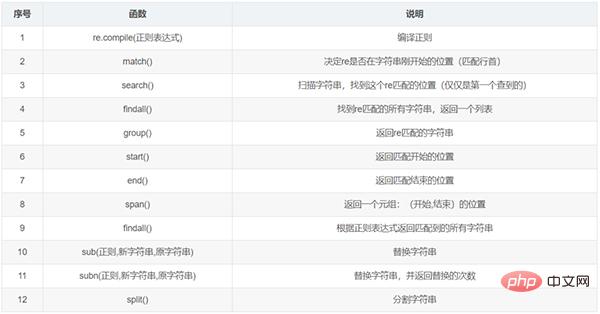
案例:用split()函数分割一个字符串并转换成列表:
import re
s = "abcabcacc"
l = re.split("b",s)
print(l)
#运行结果为:['a', 'ca', 'cacc']结语
这篇文章的目的,不是为了教大家怎么使用函数,而是为了快速、便捷地记住常用的函数名,所以没有把每个函数的用法都给大家举例,你只有记住了函数名字和它的作用之后,你才会有头绪,至于函数的用法,百度一下就出来,用了几次你就会了。
如果连函数名和它的用途都不知道,你要花的时间和精力就更多了,必然不如我们带着目的性地去查资料会更快些。
The above is the detailed content of We have compiled 12 essential Python functions. It is recommended to collect them.. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1384
1384
 52
52
 PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python: Code Examples and Comparison
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:07 AM
PHP and Python have their own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on project needs and personal preferences. 1.PHP is suitable for rapid development and maintenance of large-scale web applications. 2. Python dominates the field of data science and machine learning.
 Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and Resources
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: Community, Libraries, and Resources
Apr 15, 2025 am 12:16 AM
Python and JavaScript have their own advantages and disadvantages in terms of community, libraries and resources. 1) The Python community is friendly and suitable for beginners, but the front-end development resources are not as rich as JavaScript. 2) Python is powerful in data science and machine learning libraries, while JavaScript is better in front-end development libraries and frameworks. 3) Both have rich learning resources, but Python is suitable for starting with official documents, while JavaScript is better with MDNWebDocs. The choice should be based on project needs and personal interests.
 How is the GPU support for PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:48 PM
How is the GPU support for PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:48 PM
Enable PyTorch GPU acceleration on CentOS system requires the installation of CUDA, cuDNN and GPU versions of PyTorch. The following steps will guide you through the process: CUDA and cuDNN installation determine CUDA version compatibility: Use the nvidia-smi command to view the CUDA version supported by your NVIDIA graphics card. For example, your MX450 graphics card may support CUDA11.1 or higher. Download and install CUDAToolkit: Visit the official website of NVIDIACUDAToolkit and download and install the corresponding version according to the highest CUDA version supported by your graphics card. Install cuDNN library:
 Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Detailed explanation of docker principle
Apr 14, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Docker uses Linux kernel features to provide an efficient and isolated application running environment. Its working principle is as follows: 1. The mirror is used as a read-only template, which contains everything you need to run the application; 2. The Union File System (UnionFS) stacks multiple file systems, only storing the differences, saving space and speeding up; 3. The daemon manages the mirrors and containers, and the client uses them for interaction; 4. Namespaces and cgroups implement container isolation and resource limitations; 5. Multiple network modes support container interconnection. Only by understanding these core concepts can you better utilize Docker.
 MiniOpen Centos compatibility
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:45 PM
MiniOpen Centos compatibility
Apr 14, 2025 pm 05:45 PM
MinIO Object Storage: High-performance deployment under CentOS system MinIO is a high-performance, distributed object storage system developed based on the Go language, compatible with AmazonS3. It supports a variety of client languages, including Java, Python, JavaScript, and Go. This article will briefly introduce the installation and compatibility of MinIO on CentOS systems. CentOS version compatibility MinIO has been verified on multiple CentOS versions, including but not limited to: CentOS7.9: Provides a complete installation guide covering cluster configuration, environment preparation, configuration file settings, disk partitioning, and MinI
 How to operate distributed training of PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:36 PM
How to operate distributed training of PyTorch on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:36 PM
PyTorch distributed training on CentOS system requires the following steps: PyTorch installation: The premise is that Python and pip are installed in CentOS system. Depending on your CUDA version, get the appropriate installation command from the PyTorch official website. For CPU-only training, you can use the following command: pipinstalltorchtorchvisiontorchaudio If you need GPU support, make sure that the corresponding version of CUDA and cuDNN are installed and use the corresponding PyTorch version for installation. Distributed environment configuration: Distributed training usually requires multiple machines or single-machine multiple GPUs. Place
 How to choose the PyTorch version on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:51 PM
How to choose the PyTorch version on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:51 PM
When installing PyTorch on CentOS system, you need to carefully select the appropriate version and consider the following key factors: 1. System environment compatibility: Operating system: It is recommended to use CentOS7 or higher. CUDA and cuDNN:PyTorch version and CUDA version are closely related. For example, PyTorch1.9.0 requires CUDA11.1, while PyTorch2.0.1 requires CUDA11.3. The cuDNN version must also match the CUDA version. Before selecting the PyTorch version, be sure to confirm that compatible CUDA and cuDNN versions have been installed. Python version: PyTorch official branch
 How to update PyTorch to the latest version on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:15 PM
How to update PyTorch to the latest version on CentOS
Apr 14, 2025 pm 06:15 PM
Updating PyTorch to the latest version on CentOS can follow the following steps: Method 1: Updating pip with pip: First make sure your pip is the latest version, because older versions of pip may not be able to properly install the latest version of PyTorch. pipinstall--upgradepip uninstalls old version of PyTorch (if installed): pipuninstalltorchtorchvisiontorchaudio installation latest



