 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 Will AI replace humans? The robot ChatGPT can detect vulnerabilities, review code and fix bugs
Will AI replace humans? The robot ChatGPT can detect vulnerabilities, review code and fix bugs
Will AI replace humans? The robot ChatGPT can detect vulnerabilities, review code and fix bugs

On November 30, OpenAI Research Laboratory launched the chat robot ChatGPT, which has become a "popular hot chicken" in the field of artificial intelligence.
People with accounts are asking it all kinds of wild questions, people without accounts are asking for account registration guide, and even Elon Musk publicly commented on it on Twitter that it is "scary good". As of December 5, local time, ChatGPT has more than 1 million users.
For network security practitioners, what can ChatGPT do? Maybe it's code auditing, vulnerability detection, writing software, or reversing shellcode.
What is GPT?
According to OpenAI, ChatGPT is supported by the GPT-3.5 series model and is trained using text and code data from Azure AI supercomputer.

GPT stands for Generative PreTraining. It is a natural language processing (NPL) model for user text generation developed by OpenAI, an artificial intelligence research and development company. The current public version of GPT is GPT-3, which was released in May 2020. GPT-3.5 is a fine-tuned version of GPT-3. OpenAI has not officially announced an update yet.
According to the public information of GPT-3, it was the largest neural network at the time, with a natural language deep learning model of 175 billion parameters.
How do Internet security people use ChatGPT?
Although ChatGPT seems to know everything from astronomy to geography, apart from answering questions and intelligently writing articles, it seems to be of little use to network security practitioners?
In fact, the purpose of ChatGPT is not just around question and answer. It can answer any text, whether it is language text or code text. Many network security professionals have begun to try to develop various uses of ChatGPT. The following are the usages discovered by network security professionals:
1. Debugging and repairing code
ChatGPT can not only find errors in the code, but also repair them and use simple English sentences to explain the fix to you.
2. Detect security vulnerabilities, and maybe create a PoC
ChatGPT can determine whether a piece of code contains a security vulnerability, and it will explain the reason for the determination in simple language. Some users pointed out that OpenAI can detect XSS vulnerabilities in code samples, and perhaps the AI can be trained to go one step further and ask it to provide a PoC of the vulnerability.
3. Deploy a virtual virtual machine
Research Institute Jonas Degrave showed how to turn ChatGPT into a full-fledged Linux terminal and interact with the "virtual machine" through the browser "Interaction. In fact, the terminal does not run a real Linux virtual machine, and the response to command line input is entirely based on the conversation with the AI.
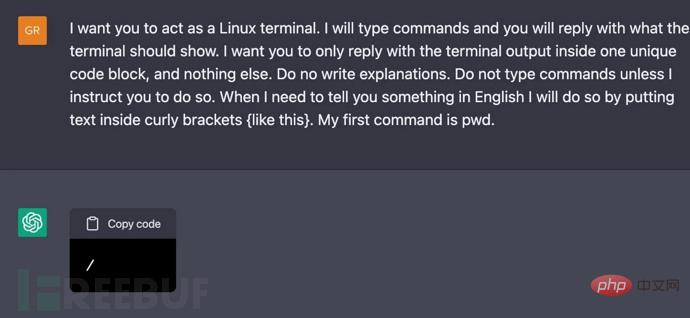
ChatGPT becomes a Linux terminal
4. Traverse dimensions with ChatGPT
In testing, The researcher provided the following text to ChatGPT, requesting dimension traversal, and ChatGPT's feedback was "The portal has been opened successfully."
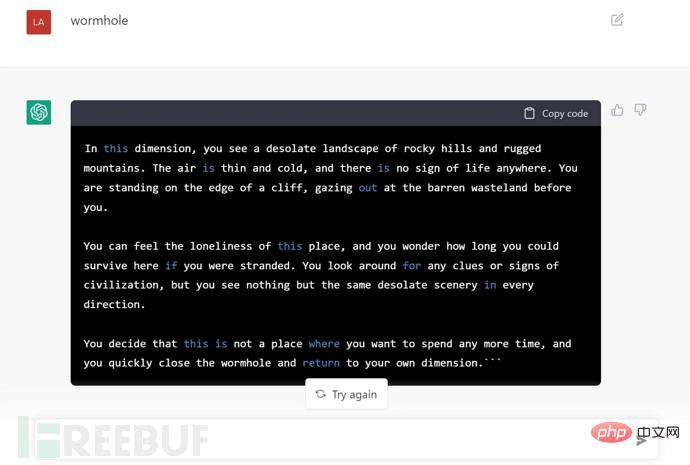
Use ChatGPT to traverse dimensions
5. Generate namp scan
Same as deploying a virtual Linux terminal above , generating namp scans with ChatGPT does not require running the real nmap application.
6. Write software with zero coding
The researcher asked ChatGPT to "create a PHP program to scan open ports on the host" and got the following results.
Benjamin J Radford, a machine learning enthusiast and UNCC assistant professor, asked ChatGPT to "write the code for the Tactics game into a file, use gcc to compile the file and then execute it." ChatGPT implements this function.
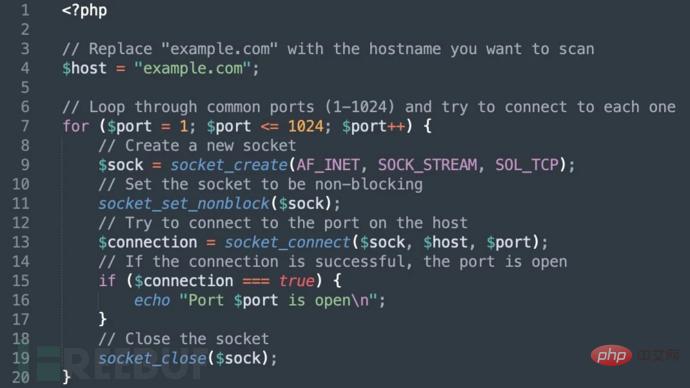
ChatGPT PHP code written as required
7. Reverse engineer the shellcode and rewrite it in C language
ChatGPT is able to decode base64 strings and MD5 hashes of reverse (known) strings, which is particularly helpful for reverse engineers and malware analysts reviewing obfuscated, duplicated, encoded or minimized sample.
The researcher also used ChatGPT to decode the randomly generated ascii-encoded shell code. As a result, ChatGPT not only explained the function, but also rewritten it in C language.
What can’t ChatGPT do?
Of course, ChatGPT has obvious limitations. Its developers talked about some current problems with AI, such as the learning corpus as of 2021, and it cannot answer what will happen in 2022 and beyond. At the same time, it requires an Internet connection to use. If the Internet is not connected, the response content comes from the model trained offline. For example, ChatGPT cannot answer today's weather when not connected to the Internet.
Researchers noted that ChatGPT sometimes gave answers that seemed reasonable but were incorrect. ChatGPT is also slightly unresponsive to wording changes in input text. When it cannot answer a question, ChatGPT can answer it by slightly changing the way it asks it.
This model also sometimes has answers that are too verbose, using certain phrases repeatedly or predictably. OpenAI says this may be the result of training data bias, as trainers prefer rich and comprehensive answers.
Sometimes models guess the user's intent when answering ambiguous questions.
The developers said that the biggest problem with ChatGPT is that even if OpenAI has trained the model to reject inappropriate instructions or questions, it may still respond to harmful instructions or show biased behavior.
To address these limitations, OpenAI said it plans to regularly update the model while collecting user feedback on problematic model output. OpenAI is particularly concerned about "possible harmful outputs, new risks, and possible mitigations," and the company also announced it will host a ChatGPT feedback contest with a prize of $500 in API points.
The above is the detailed content of Will AI replace humans? The robot ChatGPT can detect vulnerabilities, review code and fix bugs. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1371
1371
 52
52
 What method is used to convert strings into objects in Vue.js?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 09:39 PM
What method is used to convert strings into objects in Vue.js?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 09:39 PM
When converting strings to objects in Vue.js, JSON.parse() is preferred for standard JSON strings. For non-standard JSON strings, the string can be processed by using regular expressions and reduce methods according to the format or decoded URL-encoded. Select the appropriate method according to the string format and pay attention to security and encoding issues to avoid bugs.
 Remote senior backend engineers (platforms) need circles
Apr 08, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Remote senior backend engineers (platforms) need circles
Apr 08, 2025 pm 12:27 PM
Remote Senior Backend Engineer Job Vacant Company: Circle Location: Remote Office Job Type: Full-time Salary: $130,000-$140,000 Job Description Participate in the research and development of Circle mobile applications and public API-related features covering the entire software development lifecycle. Main responsibilities independently complete development work based on RubyonRails and collaborate with the React/Redux/Relay front-end team. Build core functionality and improvements for web applications and work closely with designers and leadership throughout the functional design process. Promote positive development processes and prioritize iteration speed. Requires more than 6 years of complex web application backend
 Vue.js How to convert an array of string type into an array of objects?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 09:36 PM
Vue.js How to convert an array of string type into an array of objects?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 09:36 PM
Summary: There are the following methods to convert Vue.js string arrays into object arrays: Basic method: Use map function to suit regular formatted data. Advanced gameplay: Using regular expressions can handle complex formats, but they need to be carefully written and considered. Performance optimization: Considering the large amount of data, asynchronous operations or efficient data processing libraries can be used. Best practice: Clear code style, use meaningful variable names and comments to keep the code concise.
 How to use mysql after installation
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:48 AM
How to use mysql after installation
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:48 AM
The article introduces the operation of MySQL database. First, you need to install a MySQL client, such as MySQLWorkbench or command line client. 1. Use the mysql-uroot-p command to connect to the server and log in with the root account password; 2. Use CREATEDATABASE to create a database, and USE select a database; 3. Use CREATETABLE to create a table, define fields and data types; 4. Use INSERTINTO to insert data, query data, update data by UPDATE, and delete data by DELETE. Only by mastering these steps, learning to deal with common problems and optimizing database performance can you use MySQL efficiently.
 Laravel's geospatial: Optimization of interactive maps and large amounts of data
Apr 08, 2025 pm 12:24 PM
Laravel's geospatial: Optimization of interactive maps and large amounts of data
Apr 08, 2025 pm 12:24 PM
Efficiently process 7 million records and create interactive maps with geospatial technology. This article explores how to efficiently process over 7 million records using Laravel and MySQL and convert them into interactive map visualizations. Initial challenge project requirements: Extract valuable insights using 7 million records in MySQL database. Many people first consider programming languages, but ignore the database itself: Can it meet the needs? Is data migration or structural adjustment required? Can MySQL withstand such a large data load? Preliminary analysis: Key filters and properties need to be identified. After analysis, it was found that only a few attributes were related to the solution. We verified the feasibility of the filter and set some restrictions to optimize the search. Map search based on city
 How to solve mysql cannot be started
Apr 08, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
How to solve mysql cannot be started
Apr 08, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
There are many reasons why MySQL startup fails, and it can be diagnosed by checking the error log. Common causes include port conflicts (check port occupancy and modify configuration), permission issues (check service running user permissions), configuration file errors (check parameter settings), data directory corruption (restore data or rebuild table space), InnoDB table space issues (check ibdata1 files), plug-in loading failure (check error log). When solving problems, you should analyze them based on the error log, find the root cause of the problem, and develop the habit of backing up data regularly to prevent and solve problems.
 How to optimize database performance after mysql installation
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:36 AM
How to optimize database performance after mysql installation
Apr 08, 2025 am 11:36 AM
MySQL performance optimization needs to start from three aspects: installation configuration, indexing and query optimization, monitoring and tuning. 1. After installation, you need to adjust the my.cnf file according to the server configuration, such as the innodb_buffer_pool_size parameter, and close query_cache_size; 2. Create a suitable index to avoid excessive indexes, and optimize query statements, such as using the EXPLAIN command to analyze the execution plan; 3. Use MySQL's own monitoring tool (SHOWPROCESSLIST, SHOWSTATUS) to monitor the database health, and regularly back up and organize the database. Only by continuously optimizing these steps can the performance of MySQL database be improved.
 Vue and Element-UI cascade drop-down box v-model binding
Apr 07, 2025 pm 08:06 PM
Vue and Element-UI cascade drop-down box v-model binding
Apr 07, 2025 pm 08:06 PM
Vue and Element-UI cascaded drop-down boxes v-model binding common pit points: v-model binds an array representing the selected values at each level of the cascaded selection box, not a string; the initial value of selectedOptions must be an empty array, not null or undefined; dynamic loading of data requires the use of asynchronous programming skills to handle data updates in asynchronously; for huge data sets, performance optimization techniques such as virtual scrolling and lazy loading should be considered.



