 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 Why should data in machine learning be represented by vectors/matrices?
Why should data in machine learning be represented by vectors/matrices?
Why should data in machine learning be represented by vectors/matrices?
In data science and machine learning, we often represent data as vectors and matrices. In mathematics and physics, a vector is a quantity that defines magnitude and direction (for example, a distance vector). However, usually the data we deal with do not necessarily follow the definition of vectors, but we still use vectors to represent data. For example, we can represent data on demographic information (e.g., race, age, gender, etc.) as a vector, but this has no purely geometric interpretation of magnitude or direction.
Similarly, in mathematics, a matrix is used to represent a linear mapping, which is defined as a mapping between two vector spaces that retain vector addition and scalar multiplication. However, the context of how matrices are used in data science/machine learning is different from this mathematical definition.
Given this difference, why are vectors and matrices so widely used when representing data? In this article, we will explore several reasons that explain this phenomenon.
Computational Efficiency
When processing data, we usually want to input them into a machine learning model. This process involves a lot of calculations, usually requiring addition and multiplication of many numbers. For example, when building a movie recommendation system, you might collect data on how long users watched each movie in your library. You can then recommend movies that have a higher average viewing time. This average is calculated by summing the time spent watching a movie by all users divided by the number of movies. Executing this process can be slow, especially as the number of users and movies grows (like Youku, which has more than 267 million users and nearly 20,000 movies).
However, computer scientists have developed very efficient linear algebra algorithms that add and multiply vectors and matrices much faster than traditional element-based addition/multiplication. For Python, the NumPy library for scientific computing and linear algebra provides greater speed and efficiency. Revisiting our recommender system problem again, we can associate each user with a viewing time vector of dimension n, where n is the number of movies. Our data will then be a matrix set of these vectors, with n rows and m columns, where n is the number of movies and m is the number of users. To find movies to recommend, we can average along the rows, find the average time all users watched each movie, and then sort by the movies with the highest average viewing time. Implementing this problem with vectors and matrices results in faster calculations due to highly optimized algorithms.
To demonstrate, here is a Python script that compares the time required to calculate row averages using regular Python and the NumPy library (optimized for matrices and vectors). To evaluate computational efficiency, we will measure the time it takes for the program to run on a dataset of 500 movies and 200 users.
# <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">import</span> <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">necessary</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">libraries</span><br><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">import</span> <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">random</span><br><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">import</span> <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">numpy</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">as</span> <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">np</span><br><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">import</span> <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">time</span><br><br><br># <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">defining</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">the</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">dimensions</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">for</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">our</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">data</span><br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">n</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">500</span> # <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">number</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">of</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">movies</span><br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">m</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">200</span> # <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">number</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">of</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">users</span><br><br><br># <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">generating</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">the</span> (<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">random</span>) <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">data</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">with</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">n</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">rows</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">and</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">m</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">columns</span><br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">data</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> []<br><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">for</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">_</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">in</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">range</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">n</span>):<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">data</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">append</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">random</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">choices</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">range</span>(<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">0</span>, <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">90</span>), <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">k</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">m</span>)) # <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">generate</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">random</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">watch</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">time</span><br><br><br># <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">normal</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">array</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">iterations</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">to</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">calculate</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">the</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">means</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">along</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">the</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">rows</span><br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">start_time</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">time</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">time</span>() <br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">averages</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> []<br><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">for</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">i</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">in</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">range</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">n</span>):<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">row_average</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">0</span><br><span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">for</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">j</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">in</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">range</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">m</span>):<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">row_average</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">+=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">data</span>[<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">i</span>][<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">j</span>] <br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">row_average</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">row_average</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">/</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">m</span><br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">averages</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">append</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">row_average</span>)<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">end_time</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">time</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">time</span>()<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">total_time</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">end_time</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">start_time</span> # <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">time</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">for</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">normal</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">array</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">implementation</span><br><br><br># <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">using</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">NumPy</span><br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">np_data</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">np</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">array</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">data</span>) # <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">convert</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">data</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">into</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">numpy</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">array</span><br><br><br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">np_start_time</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">time</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">time</span>()<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">np_average</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">np</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">mean</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">np_data</span>, <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">axis</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">1</span>) # <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">using</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">numpy</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">mean</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">function</span><br><span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">np_end_time</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">time</span>.<span style="color: rgb(0, 92, 197); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">time</span>()<br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">np_total_time</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">=</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">np_end_time</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">-</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">np_start_time</span> # <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">time</span> <span style="color: rgb(215, 58, 73); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">for</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">numpy</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">array</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">implementation</span><br><br><br><span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">print</span>(<span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">f</span><span style="color: rgb(102, 153, 0); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">"Regular Python: {total_time:4f}; NumPy: {np_total_time:4f}"</span>) # <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">print</span> <span style="color: rgb(89, 89, 89); margin: 0px; padding: 0px; background: none 0% 0% / auto repeat scroll padding-box border-box rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);">results</span>You can run the Python code ten times and average the results. Regular Python takes 9.088 milliseconds, while NumPy takes 0.427 milliseconds. The NumPy implementation is about 20 times faster than regular Python.
Going a step further, below we plot the time it takes for the Python and NumPy implementations to calculate the average while varying the number of users from 1 to 1000 while keeping the number of movies at 500.
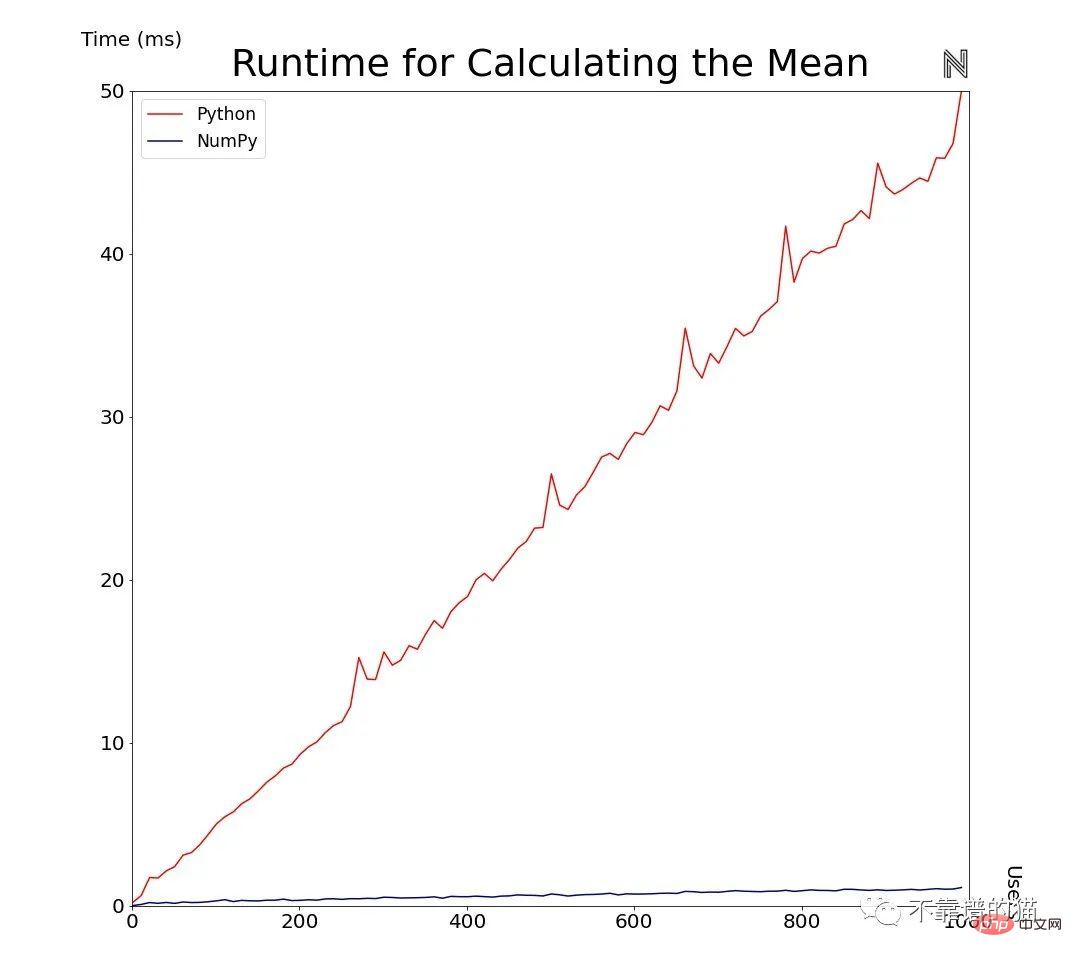
As the amount of data increases, the difference between regular Python and NumPy will become larger and larger. We can also visualize this by plotting the ratio between the two implementations.
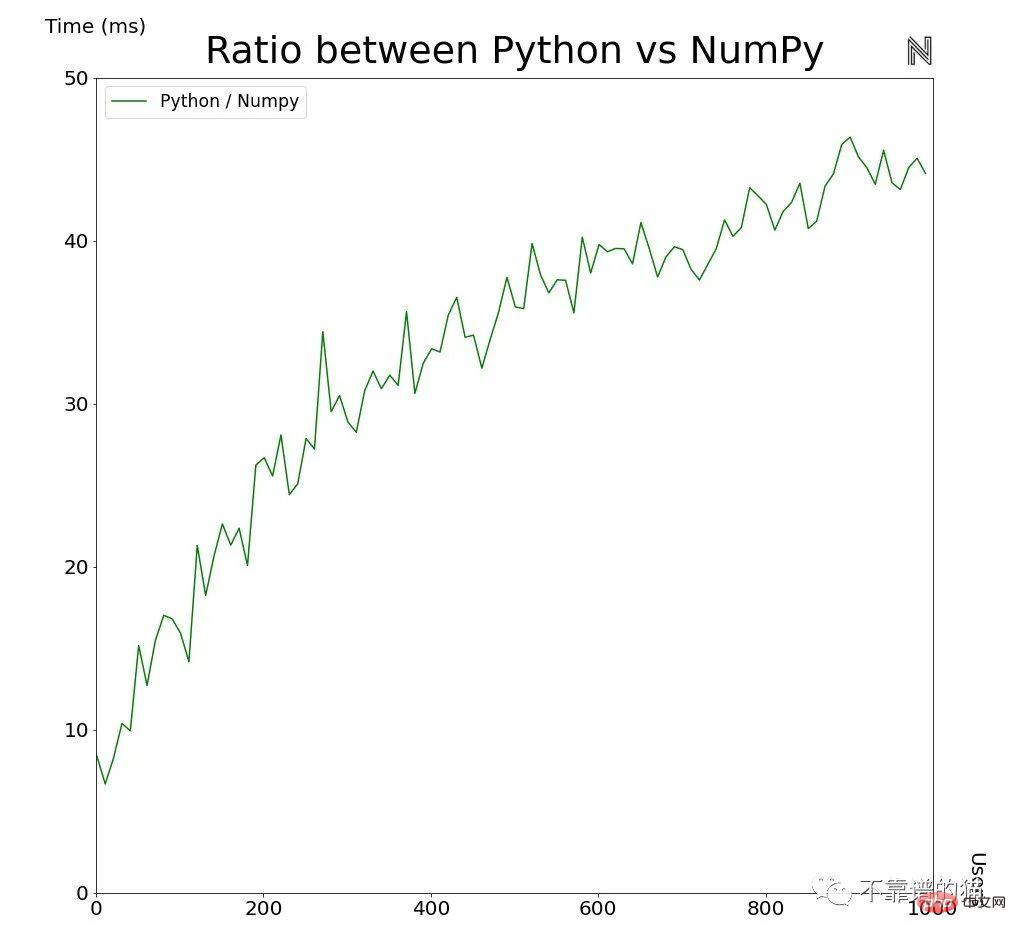
As the amount of data increases, this ratio is also increasing, which also proves that using NumPy can improve efficiency. For very large data sources or complex models, this efficiency is even more valuable. Consider the increasingly common field of big data, which often has billions to trillions of data points. For a deep neural network model, it may be composed of millions of nodes/parameters, and the weights and biases of each node/parameter are multiplied or added (for example, the GPT-3 language model has more than 175 billion parameters ).
Linear Algebra Tools
Another advantage of using vectors/matrices to represent data is that we can take advantage of linear algebra and mathematical tools. A good example is in computer vision, where matrices are used to describe image transformations (e.g., translation, rotation, reflection, affine, projection, etc.).
For image rotation, the goal is to determine a function that rotates a certain angle from each pixel of the image. In linear algebra, a rotation matrix is used to rotate a vector/matrix. By representing the image as a matrix, we can take advantage of the rotation matrix. Similarly, there are matrices for translation, reflection, and affine transformations.
Additionally, representing an image as a matrix also facilitates projective transformations, i.e. the mapping of lines from one plane to another. This is useful for image stitching and making panoramic photos. In addition, there are further applications when processing 3D graphics images.
More concise
When dealing with complex data situations, using vectors and matrices to represent concepts can be more convenient, clear and concise. Instead of giving each data point a name, we can group the data into a specified vector or matrix. Additionally, we can use vector/matrix conventions to represent operations on data.
For example, consider the example of multiple linear regression with 5 feature variables. This can be represented as:
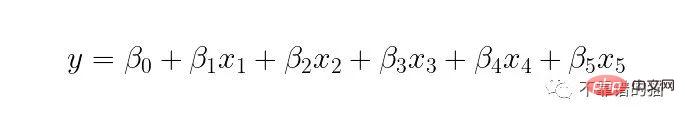 Using vectors/matrices we can convey the same idea (features and coefficients on features are now vectors):
Using vectors/matrices we can convey the same idea (features and coefficients on features are now vectors):
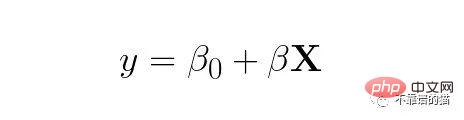 Note that this representation is much shorter and still captures our linear regression model. This representation still works if we have more variables (it's the same expression for 10 or 1000 feature variables). In addition, vectors and matrices can be used to represent many data operations and models (such as logistic regression, random forests, neural networks, etc.).
Note that this representation is much shorter and still captures our linear regression model. This representation still works if we have more variables (it's the same expression for 10 or 1000 feature variables). In addition, vectors and matrices can be used to represent many data operations and models (such as logistic regression, random forests, neural networks, etc.).
In addition, the vector/matrix convention is very common in many fields (such as physics, engineering, computing, etc.). This means that practitioners are generally familiar with it, which reduces cognitive load (as they don't need to learn new data/model conventions).
Conclusion
The reason why many data and model operations are represented by vectors/matrices is that data represented by vectors and matrices can achieve efficient and faster calculations, and can also use linear algebra techniques .
The above is the detailed content of Why should data in machine learning be represented by vectors/matrices?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
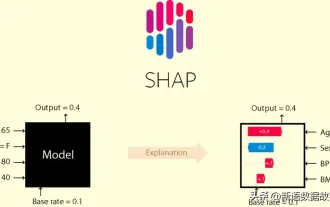 This article will take you to understand SHAP: model explanation for machine learning
Jun 01, 2024 am 10:58 AM
This article will take you to understand SHAP: model explanation for machine learning
Jun 01, 2024 am 10:58 AM
In the fields of machine learning and data science, model interpretability has always been a focus of researchers and practitioners. With the widespread application of complex models such as deep learning and ensemble methods, understanding the model's decision-making process has become particularly important. Explainable AI|XAI helps build trust and confidence in machine learning models by increasing the transparency of the model. Improving model transparency can be achieved through methods such as the widespread use of multiple complex models, as well as the decision-making processes used to explain the models. These methods include feature importance analysis, model prediction interval estimation, local interpretability algorithms, etc. Feature importance analysis can explain the decision-making process of a model by evaluating the degree of influence of the model on the input features. Model prediction interval estimate
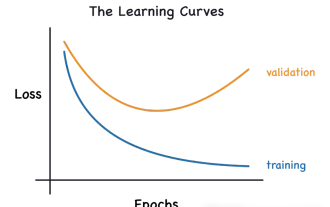 Identify overfitting and underfitting through learning curves
Apr 29, 2024 pm 06:50 PM
Identify overfitting and underfitting through learning curves
Apr 29, 2024 pm 06:50 PM
This article will introduce how to effectively identify overfitting and underfitting in machine learning models through learning curves. Underfitting and overfitting 1. Overfitting If a model is overtrained on the data so that it learns noise from it, then the model is said to be overfitting. An overfitted model learns every example so perfectly that it will misclassify an unseen/new example. For an overfitted model, we will get a perfect/near-perfect training set score and a terrible validation set/test score. Slightly modified: "Cause of overfitting: Use a complex model to solve a simple problem and extract noise from the data. Because a small data set as a training set may not represent the correct representation of all data." 2. Underfitting Heru
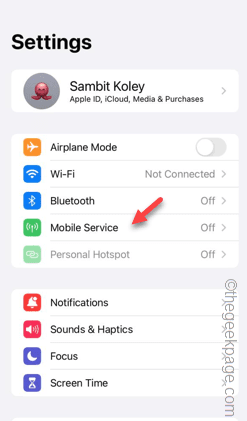 Slow Cellular Data Internet Speeds on iPhone: Fixes
May 03, 2024 pm 09:01 PM
Slow Cellular Data Internet Speeds on iPhone: Fixes
May 03, 2024 pm 09:01 PM
Facing lag, slow mobile data connection on iPhone? Typically, the strength of cellular internet on your phone depends on several factors such as region, cellular network type, roaming type, etc. There are some things you can do to get a faster, more reliable cellular Internet connection. Fix 1 – Force Restart iPhone Sometimes, force restarting your device just resets a lot of things, including the cellular connection. Step 1 – Just press the volume up key once and release. Next, press the Volume Down key and release it again. Step 2 – The next part of the process is to hold the button on the right side. Let the iPhone finish restarting. Enable cellular data and check network speed. Check again Fix 2 – Change data mode While 5G offers better network speeds, it works better when the signal is weaker
 Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Implementing Machine Learning Algorithms in C++: Common Challenges and Solutions
Jun 03, 2024 pm 01:25 PM
Common challenges faced by machine learning algorithms in C++ include memory management, multi-threading, performance optimization, and maintainability. Solutions include using smart pointers, modern threading libraries, SIMD instructions and third-party libraries, as well as following coding style guidelines and using automation tools. Practical cases show how to use the Eigen library to implement linear regression algorithms, effectively manage memory and use high-performance matrix operations.
 The vitality of super intelligence awakens! But with the arrival of self-updating AI, mothers no longer have to worry about data bottlenecks
Apr 29, 2024 pm 06:55 PM
The vitality of super intelligence awakens! But with the arrival of self-updating AI, mothers no longer have to worry about data bottlenecks
Apr 29, 2024 pm 06:55 PM
I cry to death. The world is madly building big models. The data on the Internet is not enough. It is not enough at all. The training model looks like "The Hunger Games", and AI researchers around the world are worrying about how to feed these data voracious eaters. This problem is particularly prominent in multi-modal tasks. At a time when nothing could be done, a start-up team from the Department of Renmin University of China used its own new model to become the first in China to make "model-generated data feed itself" a reality. Moreover, it is a two-pronged approach on the understanding side and the generation side. Both sides can generate high-quality, multi-modal new data and provide data feedback to the model itself. What is a model? Awaker 1.0, a large multi-modal model that just appeared on the Zhongguancun Forum. Who is the team? Sophon engine. Founded by Gao Yizhao, a doctoral student at Renmin University’s Hillhouse School of Artificial Intelligence.
 Tesla robots work in factories, Musk: The degree of freedom of hands will reach 22 this year!
May 06, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
Tesla robots work in factories, Musk: The degree of freedom of hands will reach 22 this year!
May 06, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
The latest video of Tesla's robot Optimus is released, and it can already work in the factory. At normal speed, it sorts batteries (Tesla's 4680 batteries) like this: The official also released what it looks like at 20x speed - on a small "workstation", picking and picking and picking: This time it is released One of the highlights of the video is that Optimus completes this work in the factory, completely autonomously, without human intervention throughout the process. And from the perspective of Optimus, it can also pick up and place the crooked battery, focusing on automatic error correction: Regarding Optimus's hand, NVIDIA scientist Jim Fan gave a high evaluation: Optimus's hand is the world's five-fingered robot. One of the most dexterous. Its hands are not only tactile
 The U.S. Air Force showcases its first AI fighter jet with high profile! The minister personally conducted the test drive without interfering during the whole process, and 100,000 lines of code were tested for 21 times.
May 07, 2024 pm 05:00 PM
The U.S. Air Force showcases its first AI fighter jet with high profile! The minister personally conducted the test drive without interfering during the whole process, and 100,000 lines of code were tested for 21 times.
May 07, 2024 pm 05:00 PM
Recently, the military circle has been overwhelmed by the news: US military fighter jets can now complete fully automatic air combat using AI. Yes, just recently, the US military’s AI fighter jet was made public for the first time and the mystery was unveiled. The full name of this fighter is the Variable Stability Simulator Test Aircraft (VISTA). It was personally flown by the Secretary of the US Air Force to simulate a one-on-one air battle. On May 2, U.S. Air Force Secretary Frank Kendall took off in an X-62AVISTA at Edwards Air Force Base. Note that during the one-hour flight, all flight actions were completed autonomously by AI! Kendall said - "For the past few decades, we have been thinking about the unlimited potential of autonomous air-to-air combat, but it has always seemed out of reach." However now,
 Five schools of machine learning you don't know about
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Five schools of machine learning you don't know about
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Machine learning is an important branch of artificial intelligence that gives computers the ability to learn from data and improve their capabilities without being explicitly programmed. Machine learning has a wide range of applications in various fields, from image recognition and natural language processing to recommendation systems and fraud detection, and it is changing the way we live. There are many different methods and theories in the field of machine learning, among which the five most influential methods are called the "Five Schools of Machine Learning". The five major schools are the symbolic school, the connectionist school, the evolutionary school, the Bayesian school and the analogy school. 1. Symbolism, also known as symbolism, emphasizes the use of symbols for logical reasoning and expression of knowledge. This school of thought believes that learning is a process of reverse deduction, through existing



