Why AI design must prioritize data privacy
- Artificial intelligence is integral to the development of health care, technology and other fields, but there are concerns about how data privacy will be regulated.
- Data privacy is critical to gaining public trust in technological advancement.
Data privacy is often associated with artificial intelligence (AI) models based on consumer data. Users are understandably wary of automated technologies that capture and use their data, which may include sensitive information. Because AI
models rely on data quality to deliver significant results, their continued existence depends on privacy protection being an integral part of their design.
Good privacy and data management practices are more than just a way to allay customer fears and concerns. They have a lot to do with a company's core organizational values, business processes, and security management. Privacy issues have been widely researched and publicized, and privacy perception survey data show that privacy protection is an important issue for consumers.
It’s critical to address these issues in context, and for companies using consumer-facing AI, there are several methods and techniques that can help address the privacy concerns commonly associated with AI.
Some products and services require data, but they don’t need to invade anyone’s privacy
Businesses using artificial intelligence are already facing public doubts about privacy. According to a 2020 survey by the European Consumer Organization, 45-60% of Europeans agree that AI will lead to more misuse of personal data.
There are many popular online services and products that rely on large data sets to learn and improve their AI
algorithms. Some of the data in these datasets may be considered private to even the least privacy-conscious user. Streams of data from the web, social media pages, mobile phones and other devices increase the amount of information businesses use to train machine learning systems. Privacy protection is becoming a public policy issue around the world due to the overuse and mismanagement of personal data by some businesses.
Most of the sensitive data we collect is used to improve AI-enabled processes. Much of the data analyzed is also driven by machine learning adoption, as complex algorithms are required to make decisions in real time based on these data sets. Search algorithms, voice assistants, and recommendation engines are just a few of the solutions that leverage
AI based on large datasets of real-world user data.
Massive databases may contain a wide range of data, and one of the most pressing issues is that this data may be personally identifiable and sensitive. In fact, teaching an algorithm to make decisions does not rely on knowing who the data relates to. Companies behind such products should therefore focus on privatizing their datasets with few ways to identify users in the source data, and developing measures to remove edge cases from their algorithms to avoid reverse engineering and identification.
The relationship between data privacy and artificial intelligence is very delicate. While some algorithms may inevitably require private data, there are ways to use it in a more secure and non-intrusive way. The following methods are just some of the ways companies working with private data can become part of the solution.
AI Design with Privacy in Mind
We have discussed the problem of reverse engineering, in which bad actors discover vulnerabilities in an AI
model and extract from the model’s output Identify potentially critical information. Reverse engineering is why changing and improving databases and learning data in the face of this challenge is critical for AI use.
For example, combining conflicting data sets in a machine learning process (adversarial learning) is a good option for distinguishing flaws and biases in the output of an AI
algorithm. There are also options for using synthetic datasets that do not use actual personal data, but there are still questions about their effectiveness.
Healthcare is a pioneer in artificial intelligence and data privacy governance, especially when dealing with sensitive private data. It also does a lot of work on consent, whether for medical procedures or the processing of their data - the stakes are high and it's enforced by law.
For the overall design of AI products and algorithms, decoupling data from users through anonymization and aggregation is key for any enterprise that uses user data to train its AI models.
There are many considerations that can enhance privacy protection for AI companies:
- Put privacy at the core: Put privacy protection on developers’ radar and find ways to effectively strengthen security.
- Anonymize and aggregate data sets, removing all personal identifiers and unique data points.
- Strictly control who in the company has access to specific data sets and continually audit how this data is accessed, as this has been the reason behind some data breaches in the past.
- More data is not always the best solution. Test your algorithm with minimal data to understand the minimum amount of data you need to collect and process to make your use case feasible.
- A simplified method must be provided to eliminate personal data upon user request. Companies that only pseudo-anonymize user data should continually retrain their models using the latest data.
- Leverage powerful de-identification strategies, such as aggregated and synthetic datasets with fully anonymized, irreversible identifiers for algorithm training, auditing, quality assurance, and more.
- Protect user autonomy and privacy by rethinking how critical information is obtained and used from third parties - scrutinize data sources and only use those that collect data with the user’s explicit and informed consent .
- Consider the risks: Could an attack compromise user privacy from your AI system output?
What is the future of data privacy and artificial intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence Systems require massive amounts of data, and some of the top online services and products cannot function without the personal data used to train AI algorithms. However, there are many ways to improve the acquisition, management and use of data, including the algorithms themselves and overall data management. Privacy-respecting AI requires privacy-respecting companies.
The author of this article: Einaras von Gravrock, CEO and founder of CUJO AI
The above is the detailed content of Why AI design must prioritize data privacy. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1382
1382
 52
52
 Bytedance Cutting launches SVIP super membership: 499 yuan for continuous annual subscription, providing a variety of AI functions
Jun 28, 2024 am 03:51 AM
Bytedance Cutting launches SVIP super membership: 499 yuan for continuous annual subscription, providing a variety of AI functions
Jun 28, 2024 am 03:51 AM
This site reported on June 27 that Jianying is a video editing software developed by FaceMeng Technology, a subsidiary of ByteDance. It relies on the Douyin platform and basically produces short video content for users of the platform. It is compatible with iOS, Android, and Windows. , MacOS and other operating systems. Jianying officially announced the upgrade of its membership system and launched a new SVIP, which includes a variety of AI black technologies, such as intelligent translation, intelligent highlighting, intelligent packaging, digital human synthesis, etc. In terms of price, the monthly fee for clipping SVIP is 79 yuan, the annual fee is 599 yuan (note on this site: equivalent to 49.9 yuan per month), the continuous monthly subscription is 59 yuan per month, and the continuous annual subscription is 499 yuan per year (equivalent to 41.6 yuan per month) . In addition, the cut official also stated that in order to improve the user experience, those who have subscribed to the original VIP
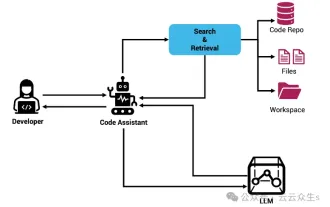 Context-augmented AI coding assistant using Rag and Sem-Rag
Jun 10, 2024 am 11:08 AM
Context-augmented AI coding assistant using Rag and Sem-Rag
Jun 10, 2024 am 11:08 AM
Improve developer productivity, efficiency, and accuracy by incorporating retrieval-enhanced generation and semantic memory into AI coding assistants. Translated from EnhancingAICodingAssistantswithContextUsingRAGandSEM-RAG, author JanakiramMSV. While basic AI programming assistants are naturally helpful, they often fail to provide the most relevant and correct code suggestions because they rely on a general understanding of the software language and the most common patterns of writing software. The code generated by these coding assistants is suitable for solving the problems they are responsible for solving, but often does not conform to the coding standards, conventions and styles of the individual teams. This often results in suggestions that need to be modified or refined in order for the code to be accepted into the application
 Can fine-tuning really allow LLM to learn new things: introducing new knowledge may make the model produce more hallucinations
Jun 11, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Can fine-tuning really allow LLM to learn new things: introducing new knowledge may make the model produce more hallucinations
Jun 11, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Large Language Models (LLMs) are trained on huge text databases, where they acquire large amounts of real-world knowledge. This knowledge is embedded into their parameters and can then be used when needed. The knowledge of these models is "reified" at the end of training. At the end of pre-training, the model actually stops learning. Align or fine-tune the model to learn how to leverage this knowledge and respond more naturally to user questions. But sometimes model knowledge is not enough, and although the model can access external content through RAG, it is considered beneficial to adapt the model to new domains through fine-tuning. This fine-tuning is performed using input from human annotators or other LLM creations, where the model encounters additional real-world knowledge and integrates it
 Seven Cool GenAI & LLM Technical Interview Questions
Jun 07, 2024 am 10:06 AM
Seven Cool GenAI & LLM Technical Interview Questions
Jun 07, 2024 am 10:06 AM
To learn more about AIGC, please visit: 51CTOAI.x Community https://www.51cto.com/aigc/Translator|Jingyan Reviewer|Chonglou is different from the traditional question bank that can be seen everywhere on the Internet. These questions It requires thinking outside the box. Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly important in the fields of data science, generative artificial intelligence (GenAI), and artificial intelligence. These complex algorithms enhance human skills and drive efficiency and innovation in many industries, becoming the key for companies to remain competitive. LLM has a wide range of applications. It can be used in fields such as natural language processing, text generation, speech recognition and recommendation systems. By learning from large amounts of data, LLM is able to generate text
 To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
Editor |ScienceAI Question Answering (QA) data set plays a vital role in promoting natural language processing (NLP) research. High-quality QA data sets can not only be used to fine-tune models, but also effectively evaluate the capabilities of large language models (LLM), especially the ability to understand and reason about scientific knowledge. Although there are currently many scientific QA data sets covering medicine, chemistry, biology and other fields, these data sets still have some shortcomings. First, the data form is relatively simple, most of which are multiple-choice questions. They are easy to evaluate, but limit the model's answer selection range and cannot fully test the model's ability to answer scientific questions. In contrast, open-ended Q&A
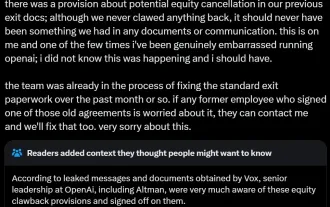 AI startups collectively switched jobs to OpenAI, and the security team regrouped after Ilya left!
Jun 08, 2024 pm 01:00 PM
AI startups collectively switched jobs to OpenAI, and the security team regrouped after Ilya left!
Jun 08, 2024 pm 01:00 PM
Last week, amid the internal wave of resignations and external criticism, OpenAI was plagued by internal and external troubles: - The infringement of the widow sister sparked global heated discussions - Employees signing "overlord clauses" were exposed one after another - Netizens listed Ultraman's "seven deadly sins" Rumors refuting: According to leaked information and documents obtained by Vox, OpenAI’s senior leadership, including Altman, was well aware of these equity recovery provisions and signed off on them. In addition, there is a serious and urgent issue facing OpenAI - AI safety. The recent departures of five security-related employees, including two of its most prominent employees, and the dissolution of the "Super Alignment" team have once again put OpenAI's security issues in the spotlight. Fortune magazine reported that OpenA
 Improved detection algorithm: for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:33 PM
Improved detection algorithm: for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:33 PM
01 Outlook Summary Currently, it is difficult to achieve an appropriate balance between detection efficiency and detection results. We have developed an enhanced YOLOv5 algorithm for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images, using multi-layer feature pyramids, multi-detection head strategies and hybrid attention modules to improve the effect of the target detection network in optical remote sensing images. According to the SIMD data set, the mAP of the new algorithm is 2.2% better than YOLOv5 and 8.48% better than YOLOX, achieving a better balance between detection results and speed. 02 Background & Motivation With the rapid development of remote sensing technology, high-resolution optical remote sensing images have been used to describe many objects on the earth’s surface, including aircraft, cars, buildings, etc. Object detection in the interpretation of remote sensing images
 SOTA performance, Xiamen multi-modal protein-ligand affinity prediction AI method, combines molecular surface information for the first time
Jul 17, 2024 pm 06:37 PM
SOTA performance, Xiamen multi-modal protein-ligand affinity prediction AI method, combines molecular surface information for the first time
Jul 17, 2024 pm 06:37 PM
Editor | KX In the field of drug research and development, accurately and effectively predicting the binding affinity of proteins and ligands is crucial for drug screening and optimization. However, current studies do not take into account the important role of molecular surface information in protein-ligand interactions. Based on this, researchers from Xiamen University proposed a novel multi-modal feature extraction (MFE) framework, which for the first time combines information on protein surface, 3D structure and sequence, and uses a cross-attention mechanism to compare different modalities. feature alignment. Experimental results demonstrate that this method achieves state-of-the-art performance in predicting protein-ligand binding affinities. Furthermore, ablation studies demonstrate the effectiveness and necessity of protein surface information and multimodal feature alignment within this framework. Related research begins with "S




