 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Inventory of common encryption algorithms used in 90% of Python crawlers
Inventory of common encryption algorithms used in 90% of Python crawlers
Inventory of common encryption algorithms used in 90% of Python crawlers
I believe that when you capture data, you will encounter many encrypted parameters, such as "token", "sign", etc. Today I will take you there Take an inventory of these mainstream encryption algorithms in the data capture process, what are their characteristics, what are the encryption methods, etc. Knowing these will be a lot of help for us to reversely crack these encrypted parameters!
1. Basic common sense
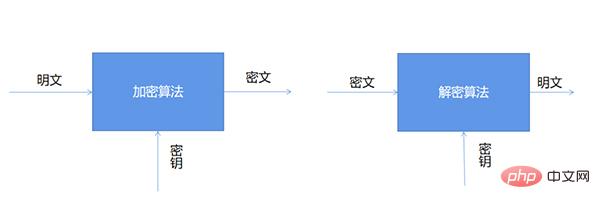
The first thing we need to understand is, what are encryption and decryption? As the name suggests
- Encryption: The process of converting plaintext data into ciphertext
- Decryption: The reverse process of encryption, that is, the process of recovering the original plaintext from ciphertext .
The operations of encryption and decryption algorithms are usually performed under the control of a set of keys, which are respectively the encryption key (Encryption Key) and the decryption key (Decryption Key), as shown below Shown:
The encryption algorithm is divided into symmetric encryption, asymmetric encryption and hash algorithm, among which
- Symmetric encryption: That is, the same key is used for encryption and decryption, such as RC4, AES, DES and other encryption algorithms
- Asymmetric encryption: that is, different keys are used for encryption and decryption, such as RSA encryption algorithm, etc.
- Hash algorithm: also known as hash function. Produces a fixed output for input messages of different lengths, and the output value is the hash value
2. Base64 pseudo-encryption
Base64 is not strictly an encryption algorithm. It is just an encoding method. It uses 64 characters, namely A-Z, a-z, 0-9, , /. These 64 characters are used to encode data. It can be used to transmit longer identifiers in the HTTP environment. information. Base64 encoding is unreadable and needs to be decoded before it can be read. We use Python to perform Base64 encoding on any URL. The code is as follows:
import base64
# 想将字符串转编码成base64,要先将字符串转换成二进制数据
url = "www.baidu.com"
bytes_url = url.encode("utf-8")
str_url = base64.b64encode(bytes_url)# 被编码的参数必须是二进制数据
print(str_url)Output:
b'd3d3LmJhaWR1LmNvbQ=='
Then similarly, we can also decode it, the code is as follows:
url = "d3d3LmJhaWR1LmNvbQ=="
str_url = base64.b64decode(url).decode("utf-8")
print(str_url)Output:
www.baidu.com
3. MD5 encryption
MD5 is a widely used linear hash algorithm, and the encryption result is a fixed-length (32-bit Or 16-bit) data, consisting of letters and numbers, with uniform uppercase and lowercase letters. The data generated by the final encryption is irreversible, which means that it cannot be easily restored to the original string through the encrypted data, unless through brute force cracking.
Let’s implement MD5 encryption in Python:
import hashlib
str = 'this is a md5 demo.'
hl = hashlib.md5()
hl.update(str.encode(encoding='utf-8'))
print('MD5加密前为 :' + str)
print('MD5加密后为 :' + hl.hexdigest())Output:
MD5加密前为 :this is a md5 demo. MD5加密后为 :b2caf2a298a9254b38a2e33b75cfbe75
As mentioned above, MD5 encryption can be cracked through brute force Reduce its security, so in the actual operation process, we will add salt value (Salt) or double MD5 encryption to increase its reliability. The code is as follows:
# post传入的参数
params = "123456"
# 加密后需拼接的盐值(Salt)
salt = "asdfkjalksdncxvm"
def md5_encrypt():
m = md5()
m.update(params.encode('utf8'))
sign1 = m.hexdigest()
return sign1
def md5_encrypt_with_salt():
m = md5()
m.update((md5_encrypt() + salt).encode('utf8'))
sign2 = m.hexdigest()
return sign24. AES/DES symmetric encryption
First of all, let’s talk about DES encryption. The full name is Data Encryption Standard, which is a data encryption standard. It is a common type of symmetric encryption, that is, the key used in the encryption and decryption processes is the same. Therefore, if you want to crack it, you can still crack it through brute force enumeration as long as the computing power is strong enough.
The full name of AES is Advanced Encryption Standard. It is a replacement for the DES algorithm and one of the most popular symmetric encryption algorithms today. To understand the AES algorithm, you must first understand three basic concepts: key, padding and mode.
Key
We have talked about the key a lot before. You can think of it as a key, which can be used to lock or unlock. . AES supports three key lengths: 128 bits, 192 bits, and 256 bits.
填充
而至于填充这一概念,AES的分组加密的特性我们需要了解,具体如下图所示:
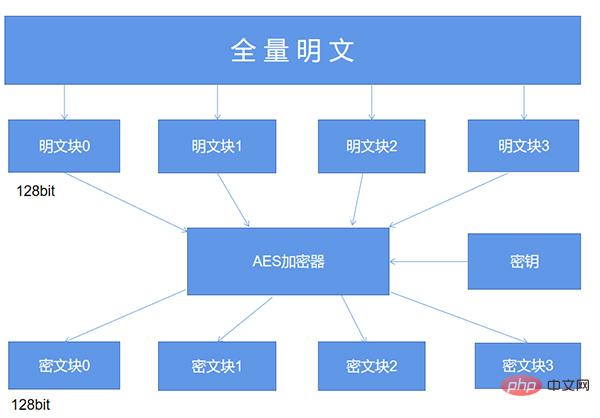
简单来说,AES算法在对明文加密的时候,并不是把整个明文一股脑儿地加密成一整段密文,而是把明文拆分成一个个独立的明文块,每一个明文块的长度为128比特。
这些明文块经过AES加密器的复杂处理之后,生成一个个独立的密文块,将这些密文块拼接到一起就是最终的AES加密的结果了。
那么这里就有一个问题了,要是有一段明文的长度是196比特,如果按照每128比特一个明文块来拆分的话,第二个明文块只有64比特了,不足128比特该怎么办呢?这个时候就轮到填充来发挥作用了,默认的填充方式是PKCS5Padding以及ISO10126Padding。
不过在AES加密的时候使用了某一种填充方式,解密的时候也必须采用同样的填充方式。
模式
AES的工作模式,体现在了把明文块加密成密文块的处理过程中,主要有五种不同的工作模式,分别是CBC、ECB、CTR、CFB以及OFB模式,同样地,如果在AES加密过程当中使用了某一种工作模式,解密的时候也必须采用同样地工作模式。最后我们用Python来实现一下AES加密。
import base64
from Crypto.Cipher import AES
def AES_encrypt(text, key):
pad = 16 - len(text) % 16
text = text + pad * chr(pad)
text = text.encode("utf-8")
encryptor = AES.new(key.encode('utf-8'), AES.MODE_ECB)
encrypt_text = encryptor.encrypt(text)
encrypt_text = base64.b64encode(encrypt_text)
return encrypt_text.decode('utf-8')或者大家也可以看一下网上其他的AES加密算法的实现过程,基本上也都是大同小异的,由于篇幅有限,今天暂时就先介绍到这里,后面要是大家感兴趣的话,会去分享一下其他加密算法的实现原理与特征。
The above is the detailed content of Inventory of common encryption algorithms used in 90% of Python crawlers. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP and Python: A Deep Dive into Their History
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:25 AM
PHP originated in 1994 and was developed by RasmusLerdorf. It was originally used to track website visitors and gradually evolved into a server-side scripting language and was widely used in web development. Python was developed by Guidovan Rossum in the late 1980s and was first released in 1991. It emphasizes code readability and simplicity, and is suitable for scientific computing, data analysis and other fields.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.
 How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
In VS Code, you can run the program in the terminal through the following steps: Prepare the code and open the integrated terminal to ensure that the code directory is consistent with the terminal working directory. Select the run command according to the programming language (such as Python's python your_file_name.py) to check whether it runs successfully and resolve errors. Use the debugger to improve debugging efficiency.
 Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VS Code extensions pose malicious risks, such as hiding malicious code, exploiting vulnerabilities, and masturbating as legitimate extensions. Methods to identify malicious extensions include: checking publishers, reading comments, checking code, and installing with caution. Security measures also include: security awareness, good habits, regular updates and antivirus software.





