
Linux single-user mode is a mode with superuser privileges when working on a Linux system. This mode can usually be entered by giving 1 or S parameter in the startup menu. This mode can only be entered through the boot menu when facing the host entity, thus ensuring that the super privilege is granted to the super user who has access to the host. This operation is usually used to maintain hard disk partitions or change the superuser password and other maintenance that need to be performed before the disk is mounted.

The operating environment of this tutorial: linux5.18.14 system, Dell G3 computer.
0: Shutdown
1: Single user mode
2: Multi-user mode without network support
3: Multi-user mode with network support
4: Reserved, not used
5: Multi-user mode with network support and X-Window support
6 : Reboot the system, that is, restart
Single user mode (English: Single user mode) is a kind of super user when working on a Linux system. Permission mode. This mode can usually be entered by giving 1 or S parameter in the startup menu. This mode can only be entered through the boot menu when facing the host entity, thus ensuring that the super privilege is granted to the super user who has access to the host. This operation is usually used to maintain hard disk partitions or change the superuser password and other maintenance that need to be performed before the disk is mounted.
1. Single-user method
Since there are many ways to boot a Linux system, including common floppy disk boot, LILO boot, and GRUB boot, I have discussed several ways. Explain separately:
1.1 Floppy disk boot
When "BOOT:" appears after the floppy disk starts, you can set the startup parameters. Type "Linux single" here. "After that, you can start the system in single-user mode.
1.2 LILO mode
When starting in LILO mode, after the LILO prompt appears, you should quickly enter kernel/boot/vmlinuz-2.4.7-10 single roo= /dev/hda3, here I use REDHAT7.2, the kernel is 2.4.7-10, the general file name is vmlinuz when using it, you can copy this kernel file or establish a connection when the system is normal. single means single use. root=/dev/hda3 is the location of the root of the Linux system. My computer is equipped with 98, if it only has Linux. It may be /dev/hda1. On the second hard disk, it is /dev/hdb1. Here is how Linux identifies partitions.
1.3GRUB method
This method is more complicated to boot. When entering the GRUB startup screen, press "C" to enter the GRUB command line. When you have a password, press "P "After that enter the password and then proceed to the GRUB command line.
Enter the following command on the command line to enable single user. I still use REDHAT7.2 as an example to illustrate kernel /boot/vmlinuz-2.4.7-10 single root=/dev/hda3initrd/boot/initrd -2.4.7-10.img boot (hd0,2) The first and second sentences indicate the kernel file. The keyword for single user is still single. Depending on the system, the file name may be different. The meaning of boot (hd0,2) is to boot from the third partition of the
first hard disk.
Since a single user has complete control over the system, if the operation is improper or is entered by others, the consequences will be disastrous. How to prevent single-user entry? , there are the following aspects to pay attention to.
2.1 Protect the /etc/inittab file. If you change 3 in id:3:initdefault to 1, you can directly enter single-user mode every time you start. For the /etc/inittab file, just enter chown700 /etc/inittab as root and set the properties so that other users cannot modify it.
2.2 If you are using lilo to boot, you may set the waiting input time during boot to 0 or the shortest time through Linuxconf or directly modify lilo.conf. In this case, if you enter single-user mode, you can use a floppy disk to boot.
2.3 If you use GRUB to boot, the simplest method is to use the GRUB password to protect the startup options.
2.4 In order to prevent others from remotely damaging and restarting the system, in addition to effectively managing the ROOT password and files in the /etc directory, the CMOS password should also be set, so that even if the system is changed to Even in single-user mode, you cannot directly start the computer to operate.
To enter single-user mode in ubuntu, you can use the command sudo init 1
Because there is a problem with the sudoer configuration file of the virtual machine, there is no way Using the sudo command, I couldn't remember the root password, so I studied how to enter single-user mode through recovery mode. Not much to say, the picture above: long press the shift key when starting the system to enter the grub menu:
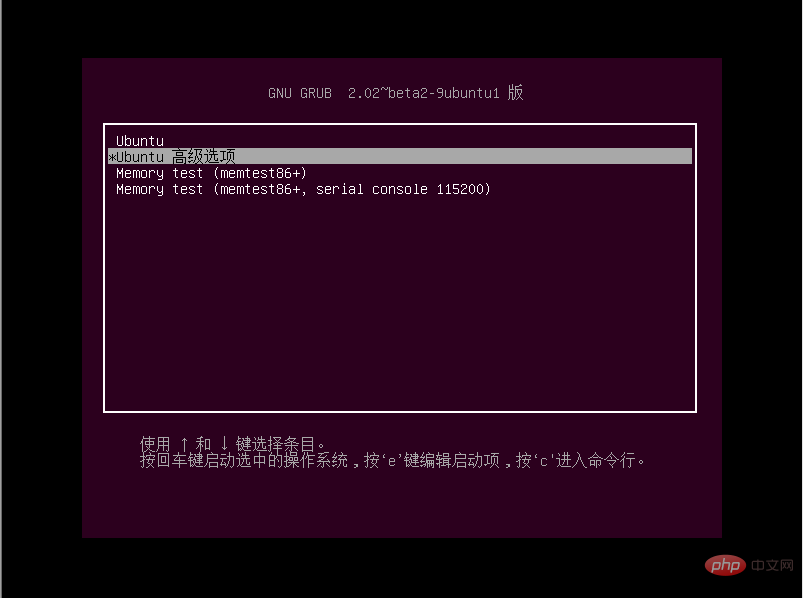
Select ubuntu advanced options, press the e key

Select recovery mode, press e to enter the

modification The linux line
before modification:

after modification:

ctrl x Exit and enter single-user mode
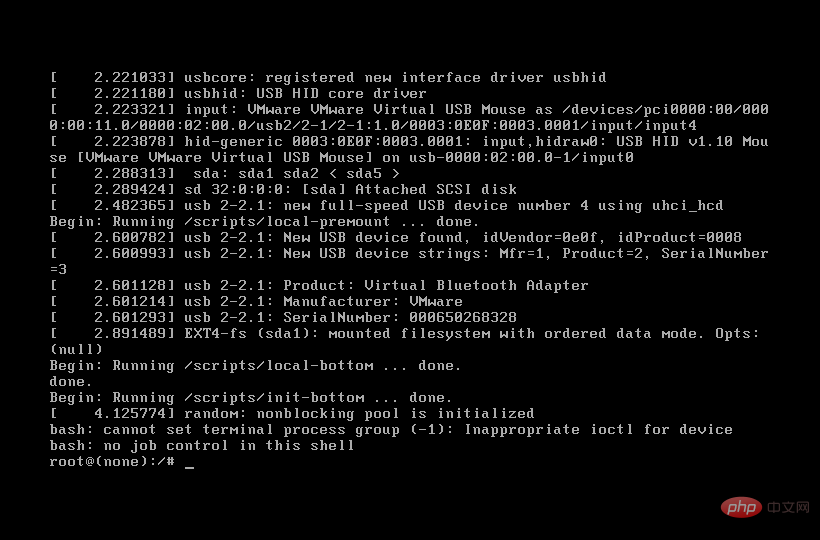
Success
Note:
a. After modifying the grub configuration, the next time you enter recovery mode, the The content remains unmodified. If you want to enter single-user mode again, you need to modify it again.
b. If you want to restart after modification, reboot, shutdown -r, etc. are not feasible. You need to use ctrl alt delete through vmware.
The above is the detailed content of what is linux single user mode. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!