 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Let's talk about what are the most commonly used statements and functions in Python?
Let's talk about what are the most commonly used statements and functions in Python?
Let's talk about what are the most commonly used statements and functions in Python?
1. Built-in functions
Built-in functions are the function methods that come with Python, you can use them as you like, such as zip, filter, isinstance, etc.

The following is a list of built-in functions given by Python official documents, which is quite complete

The following are common built-in functions:
1. enumerate(iterable,start=0)
enumerate() is a built-in function of python, which means enumeration and enumeration.
For an iterable/traversable object (such as a list, string), enumerate forms an index sequence, which can be used to obtain the index and value at the same time.
The usage of enumerate in python is mostly used to get the count in the for loop.
seasons = ['Spring', 'Summer', 'Fall', 'Winter'] list(enumerate(seasons)) [(0, 'Spring'), (1, 'Summer'), (2, 'Fall'), (3, 'Winter')] list(enumerate(seasons, start=1)) [(1, 'Spring'), (2, 'Summer'), (3, 'Fall'), (4, 'Winter')]
2. zip(*iterables,strict=False)
zip() function is used to take an iterable object as a parameter and pack the corresponding elements in the object into tuples. , and then returns a list of these tuples.
If the number of elements in each iterator is inconsistent, the length of the returned list is the same as the shortest object. Using the * operator, the tuple can be decompressed into a list.
zip(iterable1,iterable2, ...).
>>> for item in zip([1, 2, 3], ['sugar', 'spice', 'everything nice']): ... print(item) ... (1, 'sugar') (2, 'spice') (3, 'everything nice')
3. filter(function,iterable)
Filter filters a sequence, returns an iterator object, and removes sequences that do not meet the conditions.
filter(function,data).
function serves as a conditional selection function.
For example, define a function to check whether the input number is an even number. It will return True if the number is even, otherwise it will return False.
def is_even(x): if x % 2 == 0: return True else: return False
Then use filter to filter a list:
l1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] fl = filter(is_even, l1) list(fl)
4. isinstance(object,classinfo)
isinstance is used to determine whether a variable or object is It is not a function of a certain type.
If the parameter object is an instance of classinfo, or object is an instance of a subclass of the classinfo class, return True. If object is not an object of the given type, the return result is always False.
>>>a = 2 >>> isinstance (a,int) True >>> isinstance (a,str) False >>> isinstance (a,(str,int,list))# 是元组中的一个返回 True True
5. eval(expression[,globals[,locals]])
eval is used to evaluate the string str as a valid expression and return the calculation result.
Expression parses the parameter expression and evaluates it as a Python expression (technically a list of conditions), using the globals and locals dictionaries as global and local namespaces.
>>>x = 7
>>> eval( '3 * x' )
21
>>> eval('pow(2,2)')
4
>>> eval('2 + 2')
4
>>> n=81
>>> eval("n + 4")
85
Commonly used sentence patterns
In the daily coding process, there are actually many commonly used sentence patterns, which appear very frequently and are also common writing methods.
1. format string formatting
format treats the string as a template and formats it through the passed parameters. It is very practical and powerful.
# 格式化字符串
print('{} {}'.format('hello','world'))
# 浮点数
float1 = 563.78453
print("{:5.2f}".format(float1))
2. Connect strings
Use to connect two strings.
string1 = "Linux" string2 = "Hint" joined_string = string1 + string2 print(joined_string)
3. if...else conditional statement
Python conditional statement is a code block that is executed based on the execution result (True or False) of one or more statements.
The if...else statement is used to execute situations that require judgment.
# Assign a numeric value
number = 70
# Check the is more than 70 or not
if (number >= 70):
print("You have passed")
else:
print("You have not passed")
4. for...in, while loop statements
The loop statement is to traverse a sequence and perform a certain operation in a loop. The loop statements in Python include for and while.
for loop:
# Initialize the list
weekdays = ["Sunday", "Monday", "Tuesday","Wednesday", "Thursday","Friday", "Saturday"]
print("Seven Weekdays are:n")
# Iterate the list using for loop
for day in range(len(weekdays)):
print(weekdays[day])
while loop:
# Initialize counter
counter = 1
# Iterate the loop 5 times
while counter < 6:
# Print the counter value
print ("The current counter value: %d" % counter)
# Increment the counter
counter = counter + 1
5. Import function to import other scripts
Sometimes you need to use a script in another python file , this is actually very simple, just like using the import keyword to import any module.
vacations.py:
# Initialize values vacation1 = "Summer Vacation" vacation2 = "Winter Vacation"
For example, reference the code in vacations.py above in the script below.
# Import another python script
import vacations as v
# Initialize the month list
months = ["January", "February", "March", "April", "May", "June",
"July", "August", "September", "October", "November", "December"]
# Initial flag variable to print summer vacation one time
flag = 0
# Iterate the list using for loop
for month in months:
if month == "June" or month == "July":
if flag == 0:
print("Now",v.vacation1)
flag = 1
elif month == "December":
print("Now",v.vacation2)
else:
print("The current month is",month)
6. List comprehension
Python list comprehension is a method to quickly and concisely create data types from one or more iterators. It combines loops and conditional judgments, thus Avoid code with lengthy syntax and improve code running efficiency. Being able to use derivation proficiently can also indirectly indicate that you have surpassed the level of Python beginners.
# Create a list of characters using list comprehension
char_list = [ char for char in "linuxhint" ]
print(char_list)
# Define a tuple of websites
websites = ("google.com","yahoo.com", "ask.com", "bing.com")
# Create a list from tuple using list comprehension
site_list = [ site for site in websites ]
print(site_list)
7. Reading and writing files
One of the most commonly used scenarios for interactive Python with calculations is to read the CSV file in the D drive, then rewrite the data and save it. This requires Python to perform operations of reading and writing files, which is also a core skill that beginners need to master.
#Assign the filename
filename = "languages.txt"
# Open file for writing
fileHandler = open(filename, "w")
# Add some text
fileHandler.write("Bashn")
fileHandler.write("Pythonn")
fileHandler.write("PHPn")
# Close the file
fileHandler.close()
# Open file for reading
fileHandler = open(filename, "r")
# Read a file line by line
for line in fileHandler:
print(line)
# Close the file
fileHandler.close()
8. Slicing and indexing
Sequences in the form of lists, strings, tuples, etc. all have the need for slicing and indexing, because we need to intercept data from them, so this is also very core. skills.
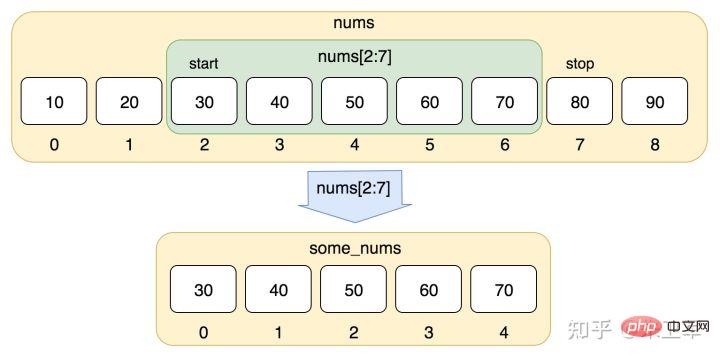
var1 = 'Hello World!'
var2 = "zhihu"
print ("var1[0]: ", var1[0])
print ("var2[1:5]: ", var2[1:5])
9、使用函数和类
函数和类是一种封装好的代码块,可以让代码更加简洁、实用、高效、强壮,是python的核心语法之一。
定义和调用函数。
# Define addition function
def addition(number1, number2):
result = number1 + number2
print("Addition result:",result)
# Define area function with return statement
def area(radius):
result = 3.14 * radius * radius
return result
# Call addition function
addition(400, 300)
# Call area function
print("Area of the circle is",area(4))
定义和实例化类。
# Define the class
class Employee:
name = "Mostak Mahmud"
# Define the method
def details(self):
print("Post: Marketing Officer")
print("Department: Sales")
print("Salary: $1000")
# Create the employee object
emp = Employee()
# Print the class variable
print("Name:",emp.name)
# Call the class method
emp.details()
10、错误异常处理
编程过程中难免会遇到错误和异常,所以我们要及时处理它,避免对后续代码造成影响。
所有的标准异常都使用类来实现,都是基类Exception的成员,都从基类Exception继承,而且都在exceptions模块中定义。
Python自动将所有异常名称放在内建命名空间中,所以程序不必导入exceptions模块即可使用异常。一旦引发而且没有捕捉SystemExit异常,程序执行就会终止。
异常的处理过程、如何引发或抛出异常及如何构建自己的异常类都是需要深入理解的。
# Try block
try:
# Take a number
number = int(input("Enter a number: "))
if number % 2 == 0:
print("Number is even")
else:
print("Number is odd")
# Exception block
except (ValueError):
# Print error message
print("Enter a numeric value")
小结
当然Python还有很多有用的函数和方法,需要大家自己去总结,这里抛砖引玉,希望能帮助到需要的小伙伴。
The above is the detailed content of Let's talk about what are the most commonly used statements and functions in Python?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to use Debian Apache logs to improve website performance
Apr 12, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use Debian Apache logs to improve website performance
Apr 12, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
This article will explain how to improve website performance by analyzing Apache logs under the Debian system. 1. Log Analysis Basics Apache log records the detailed information of all HTTP requests, including IP address, timestamp, request URL, HTTP method and response code. In Debian systems, these logs are usually located in the /var/log/apache2/access.log and /var/log/apache2/error.log directories. Understanding the log structure is the first step in effective analysis. 2. Log analysis tool You can use a variety of tools to analyze Apache logs: Command line tools: grep, awk, sed and other command line tools.
 Python: Games, GUIs, and More
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Games, GUIs, and More
Apr 13, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in gaming and GUI development. 1) Game development uses Pygame, providing drawing, audio and other functions, which are suitable for creating 2D games. 2) GUI development can choose Tkinter or PyQt. Tkinter is simple and easy to use, PyQt has rich functions and is suitable for professional development.
 PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python: Comparing Two Popular Programming Languages
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:13 AM
PHP and Python each have their own advantages, and choose according to project requirements. 1.PHP is suitable for web development, especially for rapid development and maintenance of websites. 2. Python is suitable for data science, machine learning and artificial intelligence, with concise syntax and suitable for beginners.
 The role of Debian Sniffer in DDoS attack detection
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:42 PM
The role of Debian Sniffer in DDoS attack detection
Apr 12, 2025 pm 10:42 PM
This article discusses the DDoS attack detection method. Although no direct application case of "DebianSniffer" was found, the following methods can be used for DDoS attack detection: Effective DDoS attack detection technology: Detection based on traffic analysis: identifying DDoS attacks by monitoring abnormal patterns of network traffic, such as sudden traffic growth, surge in connections on specific ports, etc. This can be achieved using a variety of tools, including but not limited to professional network monitoring systems and custom scripts. For example, Python scripts combined with pyshark and colorama libraries can monitor network traffic in real time and issue alerts. Detection based on statistical analysis: By analyzing statistical characteristics of network traffic, such as data
 Nginx SSL Certificate Update Debian Tutorial
Apr 13, 2025 am 07:21 AM
Nginx SSL Certificate Update Debian Tutorial
Apr 13, 2025 am 07:21 AM
This article will guide you on how to update your NginxSSL certificate on your Debian system. Step 1: Install Certbot First, make sure your system has certbot and python3-certbot-nginx packages installed. If not installed, please execute the following command: sudoapt-getupdatesudoapt-getinstallcertbotpython3-certbot-nginx Step 2: Obtain and configure the certificate Use the certbot command to obtain the Let'sEncrypt certificate and configure Nginx: sudocertbot--nginx Follow the prompts to select
 How debian readdir integrates with other tools
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
How debian readdir integrates with other tools
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
The readdir function in the Debian system is a system call used to read directory contents and is often used in C programming. This article will explain how to integrate readdir with other tools to enhance its functionality. Method 1: Combining C language program and pipeline First, write a C program to call the readdir function and output the result: #include#include#include#includeintmain(intargc,char*argv[]){DIR*dir;structdirent*entry;if(argc!=2){
 Python and Time: Making the Most of Your Study Time
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
Python and Time: Making the Most of Your Study Time
Apr 14, 2025 am 12:02 AM
To maximize the efficiency of learning Python in a limited time, you can use Python's datetime, time, and schedule modules. 1. The datetime module is used to record and plan learning time. 2. The time module helps to set study and rest time. 3. The schedule module automatically arranges weekly learning tasks.
 How to configure HTTPS server in Debian OpenSSL
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:03 AM
How to configure HTTPS server in Debian OpenSSL
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:03 AM
Configuring an HTTPS server on a Debian system involves several steps, including installing the necessary software, generating an SSL certificate, and configuring a web server (such as Apache or Nginx) to use an SSL certificate. Here is a basic guide, assuming you are using an ApacheWeb server. 1. Install the necessary software First, make sure your system is up to date and install Apache and OpenSSL: sudoaptupdatesudoaptupgradesudoaptinsta




