What are the latest technology trends in biometrics?

Biometric technology is both a mature technology in the field of physical security and an innovation that is always at the forefront. Biometric technology has received a boost during COVID-19, with “contactless” becoming a buzzword particularly relevant to the biometric world. Higher security requirements, such as “two-factor authentication”, are also driving the demand for biometric products. So, what are the latest technology trends in biometrics?
While businesses are grappling with the complexities of new biometric laws, biometrics have become an important part of access control as standard proximity cards no longer Provides adequate protection for most businesses. Biometric technology that works hand-in-hand with card readers, in the form of fingerprints and facial recognition combined with Bluetooth and smartphones, is growing in popularity.
Additionally, the rise of edge computing for biometric access control solutions increases efficiencies across the enterprise to save time and costs. Therefore, the biggest challenge for enterprises is to manage and protect this large-scale aggregation of data points, avoiding piecemeal systems and moving to a complete surveillance system that integrates access control, video, audio and any other physical Security Measures.
Biometric technology has the potential to transform digital identity verification for a variety of applications, including securing access to sensitive areas, creating frictionless traveler journeys, automating border controls, ensuring online identity verification, authenticating payment transactions, and more.
Biometrics are increasingly used as an advanced and secure multi-factor authentication method because physical characteristics are harder to counterfeit than passwords, PINs or cards. Additionally, frictionless biometric technologies, such as facial recognition readers, can provide a safer and more hygienic way to implement multi-factor authentication.
Artificial intelligence and deep learning algorithms are used to enhance the performance of biometrics and authentication, including bias removal and liveness detection in facial recognition. These algorithms are rigorously designed, tested, and verified by recognized authorities such as NIST to ensure accuracy and efficiency in real-life situations.
We are seeing more and more facial recognition products that combine various elements, such as face with iris, card and PIN from Princeton Identity Enterprises; and the upcoming one with SABR card and PIN’s face.
These multi-factor readers greatly improve the identification capabilities of this biometric technology, improving performance and end-user perception of its flexibility and security.
Another exciting area of development is facial recognition in video analysis. This is increasingly happening in this space, and while there are data privacy requirements to be aware of, it opens up many possibilities for the future.
And there has been an increase in the use of multi-factor authentication, which may include biometrics such as fingerprint or facial recognition. However, biometrics can be simulated, so the effectiveness of the technology depends on the quality of the reader and the liveness detection implemented by the manufacturer.
In 2020, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) updated standard SP800-63B, which defines certification. Identity verification is the process of proving that a person is who they say they are.
Single-factor authentication like an access card does not completely prove who the person is because someone could have stolen the card. So, are fingerprint or facial recognition readers the ideal technology for any door?
In SP800-63B, NIST concluded that biometrics are not recommended as single-factor authentication for high-security authentication, Because the process of identifying a person from biometrics is statistical, it is possible for different people to match another person's biometrics.
However, the SP800-63B does show that biometrics are an excellent authenticator or second factor. Since the verification has already identified the person, the statistical match of the biometrics can be closer and there is less chance of false positives.
Summary
Biometric products and capabilities continue to evolve, even as they find new and expanded applications in the physical security market. The origins of biometrics date back to at least the 14th century, when China introduced fingerprint recognition to track merchants and their children. Although biometric technology is not new, it is a "new technology for good" that is constantly evolving to meet the needs of physical security and other applications.
The above is the detailed content of What are the latest technology trends in biometrics?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 I Tried Vibe Coding with Cursor AI and It's Amazing!
Mar 20, 2025 pm 03:34 PM
I Tried Vibe Coding with Cursor AI and It's Amazing!
Mar 20, 2025 pm 03:34 PM
Vibe coding is reshaping the world of software development by letting us create applications using natural language instead of endless lines of code. Inspired by visionaries like Andrej Karpathy, this innovative approach lets dev
 Top 5 GenAI Launches of February 2025: GPT-4.5, Grok-3 & More!
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:58 AM
Top 5 GenAI Launches of February 2025: GPT-4.5, Grok-3 & More!
Mar 22, 2025 am 10:58 AM
February 2025 has been yet another game-changing month for generative AI, bringing us some of the most anticipated model upgrades and groundbreaking new features. From xAI’s Grok 3 and Anthropic’s Claude 3.7 Sonnet, to OpenAI’s G
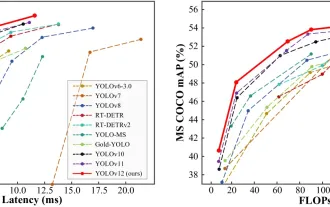 How to Use YOLO v12 for Object Detection?
Mar 22, 2025 am 11:07 AM
How to Use YOLO v12 for Object Detection?
Mar 22, 2025 am 11:07 AM
YOLO (You Only Look Once) has been a leading real-time object detection framework, with each iteration improving upon the previous versions. The latest version YOLO v12 introduces advancements that significantly enhance accuracy
 Best AI Art Generators (Free & Paid) for Creative Projects
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:10 PM
Best AI Art Generators (Free & Paid) for Creative Projects
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:10 PM
The article reviews top AI art generators, discussing their features, suitability for creative projects, and value. It highlights Midjourney as the best value for professionals and recommends DALL-E 2 for high-quality, customizable art.
 Is ChatGPT 4 O available?
Mar 28, 2025 pm 05:29 PM
Is ChatGPT 4 O available?
Mar 28, 2025 pm 05:29 PM
ChatGPT 4 is currently available and widely used, demonstrating significant improvements in understanding context and generating coherent responses compared to its predecessors like ChatGPT 3.5. Future developments may include more personalized interactions and real-time data processing capabilities, further enhancing its potential for various applications.
 Best AI Chatbots Compared (ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude & More)
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:09 PM
Best AI Chatbots Compared (ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude & More)
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:09 PM
The article compares top AI chatbots like ChatGPT, Gemini, and Claude, focusing on their unique features, customization options, and performance in natural language processing and reliability.
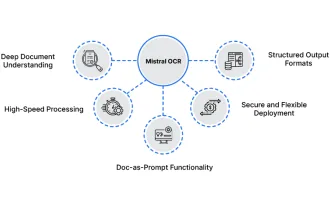 How to Use Mistral OCR for Your Next RAG Model
Mar 21, 2025 am 11:11 AM
How to Use Mistral OCR for Your Next RAG Model
Mar 21, 2025 am 11:11 AM
Mistral OCR: Revolutionizing Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Multimodal Document Understanding Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) systems have significantly advanced AI capabilities, enabling access to vast data stores for more informed respons
 Top AI Writing Assistants to Boost Your Content Creation
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:11 PM
Top AI Writing Assistants to Boost Your Content Creation
Apr 02, 2025 pm 06:11 PM
The article discusses top AI writing assistants like Grammarly, Jasper, Copy.ai, Writesonic, and Rytr, focusing on their unique features for content creation. It argues that Jasper excels in SEO optimization, while AI tools help maintain tone consist




