Performance management in the digital age: reality and future
Digital Intelligence Performance Management Reform
Digital Intelligence Goal Setting
Performance plan connects the company's prosperity strategy and operations. As the first link of performance management, it is the key to successful performance management. key factors for implementation. The large amount of data collected by organizations through digital intelligence technology can be used to set employees' goals. Digital intelligence goal setting includes two aspects: algorithmic task allocation and performance goal setting.
Algorithmic task allocation mainly exists in the gig economy and platform work. For example, in the context of the work of couriers, takeaway riders, and online ride-hailing drivers, algorithms link workers’ real-time geographical location information with task-related information (such as new orders, priority changes, deadlines), and the system intelligently dispatches orders. and provide optimal routes while providing accurate expected delivery times at the customer interface. A 15-day field experiment in an Alibaba warehouse that studied the algorithmic task allocation process showed that in labor-intensive environments, workers perceived the algorithmic task allocation process to be fairer than humans, further increasing their productivity. Nearly 20%.
Digital intelligence technology can also automatically set performance goals based on past performance, business needs, traffic conditions, weather and other data, such as Amazon's package volume goals for grassroots warehouse workers and cargo delivery goals for transportation drivers. For the relatively complex tasks of different positions within the organization, goal setting can also be carried out through modeling based on a certain scale of data. For example, the business calculation of the sales department, the goal setting of the securities company, the quality, time and cost setting of the production department, the stability goal planning of the supply chain, etc.
Although the algorithm can improve efficiency and accuracy, it also has many problems. Algorithmic task allocation is highly dependent on market demand and employee capabilities, and employees have little freedom to accept or reject algorithmically assigned tasks, so it will have a negative impact on employee autonomy. Often algorithms also continually raise task standards, leading to job insecurity and increased workload. In a knowledge-driven work environment, algorithmic goal setting will affect employee autonomy and limit employee creativity. Most algorithms blindly pursue "efficiency" and put employees under the pressure of the "system" for a long time. For example, in order to prevent missing tasks of real-time algorithm updates, platform workers can only stay online around the clock. The uncertainty of algorithm task allocation causes them to sometimes rush to work and sometimes be idle, exacerbating their work burnout.
digital intelligence monitoring, feedback and guidance
digital intelligence monitoring
Recently, a well-known company’s layoffs scandal included an “employee monitoring system” that can monitor employee turnover tendencies and slack. "Behavior Monitoring" system brought into public view. It is understood that the system can detect the number of times employees visit job search websites, the number of chat keywords, the number of search keywords, and the number of resume submissions, etc., so as to discover employees with potential resignation risks in advance and analyze the list and risk level of employees at risk of resignation for the organization. , and provide the basis for determining the risk of resignation. In addition, the system can also analyze employee slack. Employees' chat records on the company's intranet, online time spent on the Internet, and characteristics of accessed applications will all be monitored by this system, and the employee's work status will be determined through predefined rules. At the same time, by collecting irrelevant applications that affect work efficiency and time periods where slack is concentrated, the system can also automatically analyze the factors that cause employees to be passive and slack in work, and provide a ranking of departments and employees with the most serious slack.
Not only information is monitored, but also traffic. At the end of last year, a "Notice on Penalties for Violating Employee Code of Conduct" issued internally by Gome Group sparked heated discussions on the Internet. The report stated that some employees occupied the company's public network resources in the work area to engage in matters unrelated to work, and listed traffic data usage details. What websites employees visited during work and how long they viewed videos were all unable to escape the "eyes" of the digital intelligence system. ". A 2018 Gartner survey of 239 large enterprises showed that half of the companies were using non-traditional surveillance technologies to monitor employees - including tracking employees' activities around the office and their biometric data. This number was only 10% in 2015. 30%.
A key advantage of digital intelligence monitoring is that it can not only collect and record a large amount of information and indicators through multiple media, such as Internet usage, social media activities, activity trajectories, emotions and stress, work input, but also These heterogeneous data on employee behavior, actions and performance can be automatically and quickly analyzed and processed. The real-time analysis function of the digital intelligent performance management system can enhance the timeliness of organizational performance management information and avoid problems caused by lag, thereby helping to achieve continuous improvement of department and organizational performance. Existing research shows that digital intelligence monitoring will bring positive results to organizations and employees, such as providing organizations with more comprehensive information for effective management, providing employees with real-time feedback to enable them to adjust their behaviors in a timely manner, and reducing behaviors unrelated to performance. However, digital surveillance can also make employees feel that their privacy has been violated, create a sense of unfairness, reduce their job satisfaction, organizational commitment, and creativity, and even increase counterproductive performance, that is, "you have policies, I have countermeasures"—— This is exactly the opposite of what digital intelligence monitoring is trying to achieve.
Digital Feedback and Guidance
In the process of performance execution, the digital performance management system enters the process performance and result performance of employees into the big data platform in real time, and provides real-time performance feedback to employees , and can provide necessary guidance to employees with poor performance after analysis. Psychological research shows that feedback and guidance are one of the important conditions for improving performance. Traditional performance feedback and guidance are often completed by managers interviewing employees or providing written reports, but the introduction of digital intelligence technology has triggered the birth of new performance feedback and guidance methods.
In nearly 10% of Fortune 500 companies, transparent performance data has replaced traditional performance feedback. Bernstein and Li (2017)'s research on performance transparency found that transparent performance data that is more detailed, more real-time, and shared with a wider range of employees (i.e., performance transparency) can better improve employees' overall performance and motivate employees than traditional performance feedback. The unproductive behavior of employees is transformed into productive behavior. The immediacy and transparency of digital feedback allow employees to understand their own work performance at any time, while also sharing the performance data of other employees to promote self-regulation and thereby improve performance. At the same time, performance transparency can replace part of the manager's work and stimulate the role of informal social comparison; the results also confirm that employees who receive less support from their supervisors and have lower social comparison tendencies benefit more from performance transparency.
However, the application of digital intelligence technology in performance feedback has also triggered a lot of controversy. The feedback information provided by digital intelligence technology is more effective, but people's negative perception of machines will greatly weaken its effect. Specifically, on the one hand, digital intelligence feedback has a positive "deployment effect". Its powerful data analysis capabilities can enhance the accuracy, consistency and relevance of feedback, improve the quality of feedback, and promote the improvement of employee productivity, thus Improve organizational performance. The results showed that without knowing the source of the feedback, employees who received feedback generated by an AI system performed 12.9% better than employees who received feedback provided by human managers. On the other hand, once the application of digital intelligence technology in the feedback is disclosed to employees, the "disclosure effect" caused by negative perceptions and distrust of the new technology will damage employee productivity, and the business value brought by digital intelligence technology will be lost. Greatly weakened. The results of the study showed that the job performance of employees who were told to receive AI feedback was 5.4% lower than the job performance of employees who were told to receive feedback from human managers, and new employees were more likely to be negatively affected.
In addition to performance feedback, digital intelligence technology is increasingly used in performance guidance. AI coaches are different from humans who experience physical fatigue and mood swings. It handles training tasks in a more consistent, predictable and accurate manner across repeated trainings, while it can scale quickly to train thousands of employees simultaneously at minimal cost. Zoom uses AI coach Chorus to provide training for its sales team to improve the success rate of transactions.
One concern about digital intelligence guidance is that the information it provides is too standardized and comprehensive, making it appear redundant and wordy to employees with excellent performance, while it is difficult for new employees to fully absorb and learn. At the same time, the lack of "soft power" of interpersonal skills may lead to employees' resentment towards AI coaches and hinder employees' smooth learning and performance improvement. Luo et al. (2021) studied the training provided by AI coaches to sales staff and found that the guidance effect of AI coaches relative to human coaches showed an inverted U-shaped distribution among different sales staff. In other words, the sales performance of middle-ranking employees improved the most, but the performance of employees at the top and bottom received only limited increases. That’s because sales at the bottom of the rankings suffer the most from information overload, while sales at the top are the most averse to AI. Another important finding of the study is that the AI coach-human coach combination has the best effect, which is better than using only AI coaches or human coaches. Because this combination can not only utilize the "hard power" of AI coaches, but also combine the "soft power" of human coaches.
digital intelligence evaluation
The important means of enterprise performance evaluation in the digital intelligence era is based on the massive multi-dimensional big data obtained by digital intelligence monitoring, and continuously analyzes the data through intelligent algorithms to make evaluations. The evaluation results combined with the actual situation are then fed back to the algorithm for iterative optimization to make it more accurate. Relatively simple ones, such as in the digital labor platform, ride-hailing platforms such as Didi Chuxing use mobile applications to analyze drivers’ order acceptance rate, order rejection rate, punctuality rate and other indicators and obtain passengers’ ratings of consumer experience to establish the driver’s reputation. points; food delivery platforms such as Meituan and Ele.me track the response speed, number of completed orders, total mileage, and delivery punctuality of delivery riders in real time, and evaluate them based on customer praise rates. More complexly, the performance evaluation of sales personnel as introduced above includes both objective evaluation of the number of results and intelligent evaluation of the sales behavior process.
But can this kind of assessment be objective and fair? It is true that machines will not engage in "favoritism" and digital intelligence evaluation can indeed avoid the subjectivity and "human feelings" of manual evaluation. However, the lack of emotion and insensitivity to external emergencies (such as traffic accidents, heavy rain, etc.) are easy to As a result, the evaluation is too rigid, making it not only unemotional but also devoid of “humanity”. As shown in the article "Talk Delivery Riders, Trapped in the System" that detonated the Internet, riders can never rely on their personal strength to fight against the algorithm. They can only comply with its rules by driving illegally, driving in the wrong direction, running red lights, etc.
Of course, digital intelligence assessments have a positive impact on organizational performance. Algorithms actually convey to employees the work standards and norms established and advocated by the organization. When this information is internalized and understood by employees and they form their own value judgments, most employees will follow the instructions of the algorithm to behave in line with the organization's expectations. For example, after online ride-hailing drivers learn that the algorithm implements a preferential dispatch policy based on their favorable ratings, they will proactively perform service actions to obtain favorable comments and improve their ratings. However, the opacity and unexplainability of algorithms can also confuse employees. At the same time, due to the lack of intuition and subjective judgment, digital intelligence assessment is often considered by employees to be a dehumanizing experience. How to reasonably use digital intelligence assessment to motivate employees and promote organizational performance improvement is an unavoidable proposition for managers.
Let us take a look at the practices of leading Internet companies. In order to reduce the impact of subjective judgment, Baidu uses algorithms to analyze internal communication frequency, communication period, size and frequency of emails, etc., and then automatically selects the appropriate employees to participate in specific employee performance evaluations through steps such as data modeling, machine learning, and analysis verification. , relevant candidates. ByteDance, which uses OKR management, uses 360-degree evaluation in the evaluation process. However, unlike traditional 360 evaluation, the digital intelligence evaluation system can score each person's evaluation style based on data, from 1.0 (strict) to 6.0 (loose). , this can prevent a certain person's evaluation style from overly affecting the evaluation results of the employee being evaluated. At the same time, the system also designed a performance calibration matrix to calibrate team performance through intelligent analysis to avoid deviations caused by managers' inexperience and assist in making more reasonable judgments. In fact, this is a classic manifestation of human-machine collaboration in performance management. The digital intelligence technology behind the system helps human managers align their standards and hold the "same ruler" through its powerful data analysis and processing capabilities, while human managers Use your own management experience and comprehensive judgment to give the most scientific assessment.
numerical intelligence rewards and punishments
numerical intelligence rewards and punishments are based on the results of digital intelligence assessments and reward and punish employees in an interactive and dynamic manner through algorithms. For high-performing employees, they will receive more opportunities, higher pay and promotions, while low-performing employees will have their salaries and bonuses deducted, and in serious cases, they will be fired directly. For many online gig labor platforms, such as Didi, Meituan, M-turk, etc., workers’ compensation is almost entirely determined by algorithms. IBM's number one artificial intelligence, Watson, analyzes and predicts future potential by accessing employees' historical performance, project information, etc., and determines whether employees can be promoted and whether their salaries should be increased. Google also uses algorithms in engineering promotion decisions to reduce human bias in the decision-making. Amazon's algorithm will track the work efficiency of each logistics and warehousing department employee and count each employee's "fishing" time. Once someone leaves the job for too long, the AI will automatically generate a dismissal order. Xsolla, a Russian game payment service company, fired 150 employees last year using AI algorithms, causing an uproar. More and more people are beginning to worry about digital intelligence rewards and punishments. As labor is controlled by algorithms, rewards and punishments that should have humanistic care have also become cold due to the addition of algorithms.
Reconstructing an efficient and flexible performance management system in the future
Anthropologist and data sociologist Nick Silver proposed the concept of "algorithmic culture". In his view, algorithms are not only formed by rational procedures, but also composed of human collective practices such as institutions, social ethics, and ordinary cultural life. The development and application of digital intelligence technology has brought conceptual and technical changes to performance management, but it has also brought some negative impacts while empowering organizational management and employee work, improving management efficiency and service quality.
How to build performance management that is both efficient and humane in the future? It is advisable to adopt the idea of "human-machine collaboration", that is, neither sticking to the traditional "man-governed" nor falling into complete dependence on algorithms. Through the complementary advantages of humans and machines, a new model of efficient and flexible performance management can be built.
The pros and cons of digital intelligence technology
Although digital intelligence technology has the advantages of speed, efficiency, objectivity, and quantification, it eliminates more interpersonal relationships and empathy in performance management , this data-led approach turns work into a dehumanizing form. Existing research shows that most people believe that using algorithms and machines to manage humans is a dehumanizing behavior. For example, algorithm technology fails to take into account changing scene factors, which increases the probability that the algorithm will misjudge employee performance.
The Advantages and Disadvantages of Humans
Humans’ unique emotions, intuition, creativity, imagination, abstract thinking, etc. make them indispensable in issues such as value judgment, emotional representation, unconventionality, and creativity. These characteristics of human beings can help solve the problems caused by digital intelligence performance management, constantly correct and improve the algorithm, and inject humanity into the algorithm.
Specifically, humans tend to maintain relative advantages in situations that require holistic, macroscopic and far-sighted thinking, and have imagination and creativity that machines do not have. Therefore, digital intelligence technology can be better optimized decision results. Humans’ unique experiences and emotions help them coordinate the interests of all parties in intricate dynamics and eliminate possible conflicts. Using human wisdom to improve artificial intelligence can not only solve the problems caused by digital intelligence technology and realize the organic unity of digital intelligence technology and human wisdom, but also help prevent digital intelligence technology from breaking away from human control. Of course, it is undeniable that in terms of decision-making speed, accuracy, cost, etc., humans are still no match for digital intelligence technology in solving objective and structured problems.
The collaborative symbiosis of digital intelligence technology and humans
Machines and humans have complementary advantages and problem-solving abilities. The effectiveness of digital intelligence technology in improving management efficiency is significant, but efficiency is only one dimension of measuring management. What deserves more attention is the management effect, that is, the degree of fit between organizational goals and social vision, emphasizing corporate social responsibility and mission, and involving management ethics issues. With the continuous development of digital intelligence technology, although a large number of standardized jobs will be replaced by machines, jobs and skills that are rich in emotional experience, creative and valuable, and more "warm" still require humans. Specifically, the rational thinking of machines puts more emphasis on "truth", while human thinking puts more emphasis on the harmony and unity of "truth, goodness and beauty", and focuses more on value connotation and ethics and moral considerations.
As a non-human existence, technology itself is equivalent to humans and can form a coalition of actors together with humans. The automation and intelligence features embodied by digital intelligence technology may induce technology developers and users to blindly pursue improving efficiency and reducing costs, ignoring the autonomy of human behavior. But we believe that no matter how complex an intelligent system is, humans should always actively participate in its decision-making loop. Over time, the interaction between humans and machines can make both parties smarter. This is the guarantee for the integration of digital intelligence technology into human society and the establishment of a responsible human-machine collaborative working system.
In the future, we should adopt the idea of "human-machine collaboration" to build efficient and flexible performance management, give full play to the technical advantages of machines to "empower people", and combine human experience and sensibility to promote harmonious human-machine collaboration. Help employees gain a sense of meaning and happiness at work. Under the collaborative working model of human-machine symbiosis, humans can help optimize machine algorithms, and machine practice will in turn assist human activities. This is a win-win situation.
Future digital and intelligent performance management should have the following characteristics: First, it should be intelligent and efficient. Organizations should give full play to their technological advantages and use large amounts of data collected through the performance monitoring process and artificial intelligence analysis to set goals and Evaluation, assessment, rewards and punishments provide fast and objective decision-making assistance; secondly, agile and transparent, digital intelligence technology gives performance feedback unprecedented frequency and transparency. Annual feedback and quarterly feedback have become a thing of the past, and real-time and transparent performance feedback It will provide information to the organization and employees at any time and enhance the collaboration of the entire organization; thirdly, it is comprehensive and multi-dimensional. Big data’s powerful acquisition of internal and external information makes performance management more comprehensive and without dead ends. The inclusion of audio, video, and behavioral monitoring allows leaders, Through the comprehensive evaluation of subordinates, external customers, and internal colleagues, "people" are portrayed in a more three-dimensional manner; fourth, humanistic flexibility, the "soft" skills of human managers are essential in this system, and managers are aware of the subtleties of interpersonal relationships. The grasp of communication that is difficult to automate, the consideration of special situations, ethics and morality, the macro level and the overall situation can reduce employees' resistance to algorithms, enhance the height of management thinking, and more effectively apply digital intelligence technology. Advantages and improve employee and organizational performance.
Conclusion
With the development and improvement of digital intelligence technology, managers and employees must re-adapt to the performance management of the new era. Mature managers should not be trapped by digital intelligence technology and regard the suggestions of algorithms as edicts. Instead, they should use their unique experience and emotions to make judgments and make good use of the power of intelligent machines. Employees in the new era should also give full play to their personal initiative, actively participate in interactions with digital technologies, release their personalities and potential, and create a positive and enjoyable work experience.
The food delivery riders "stuck in the algorithm" can coexist harmoniously with the algorithm through the reshaping of work. The managers behind the algorithm also need to write human nature and values into the algorithm, fulfill corporate responsibilities, and set reasonable digital intelligence goals. . There is no right or wrong in digital intelligence monitoring. Managers should obtain data through reasonable channels, then balance efficiency and ethics to draw conclusions, and then empower employees. Efficient and accurate digital intelligence feedback is a little less impersonal. In order to alleviate the "disclosure effect", managers should proactively intervene and inform employees of the goals and benefits of digital intelligence technology applications to alleviate their concerns. At the same time, different approaches should be adopted according to the situation, and "one size fits all" cannot be adopted. For example, AI can be used to provide performance feedback to older employees, but managers can still provide performance feedback to new employees. In digital intelligence coaching, it is recommended that organizations use a combination of AI coaches and human managers. In this combination, AI provides powerful data-crunching skills and personalized feedback, while human coaches focus on nuanced interpersonal communication that is difficult to automate. Finally, in the key link of application of performance results, it is recommended that managers’ intervention can effectively reduce employees’ negative emotions such as unfairness and better demonstrate corporate culture and values.
After all, no matter how much data or how powerful the algorithm is, it cannot penetrate the "01 logic" behind it and reach people's hearts directly.
The above is the detailed content of Performance management in the digital age: reality and future. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1385
1385
 52
52
 The Stable Diffusion 3 paper is finally released, and the architectural details are revealed. Will it help to reproduce Sora?
Mar 06, 2024 pm 05:34 PM
The Stable Diffusion 3 paper is finally released, and the architectural details are revealed. Will it help to reproduce Sora?
Mar 06, 2024 pm 05:34 PM
StableDiffusion3’s paper is finally here! This model was released two weeks ago and uses the same DiT (DiffusionTransformer) architecture as Sora. It caused quite a stir once it was released. Compared with the previous version, the quality of the images generated by StableDiffusion3 has been significantly improved. It now supports multi-theme prompts, and the text writing effect has also been improved, and garbled characters no longer appear. StabilityAI pointed out that StableDiffusion3 is a series of models with parameter sizes ranging from 800M to 8B. This parameter range means that the model can be run directly on many portable devices, significantly reducing the use of AI
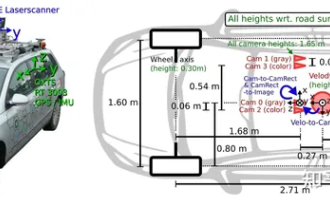 Have you really mastered coordinate system conversion? Multi-sensor issues that are inseparable from autonomous driving
Oct 12, 2023 am 11:21 AM
Have you really mastered coordinate system conversion? Multi-sensor issues that are inseparable from autonomous driving
Oct 12, 2023 am 11:21 AM
The first pilot and key article mainly introduces several commonly used coordinate systems in autonomous driving technology, and how to complete the correlation and conversion between them, and finally build a unified environment model. The focus here is to understand the conversion from vehicle to camera rigid body (external parameters), camera to image conversion (internal parameters), and image to pixel unit conversion. The conversion from 3D to 2D will have corresponding distortion, translation, etc. Key points: The vehicle coordinate system and the camera body coordinate system need to be rewritten: the plane coordinate system and the pixel coordinate system. Difficulty: image distortion must be considered. Both de-distortion and distortion addition are compensated on the image plane. 2. Introduction There are four vision systems in total. Coordinate system: pixel plane coordinate system (u, v), image coordinate system (x, y), camera coordinate system () and world coordinate system (). There is a relationship between each coordinate system,
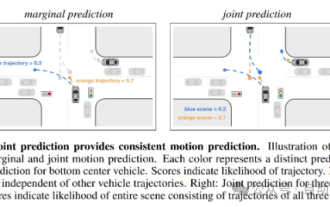 This article is enough for you to read about autonomous driving and trajectory prediction!
Feb 28, 2024 pm 07:20 PM
This article is enough for you to read about autonomous driving and trajectory prediction!
Feb 28, 2024 pm 07:20 PM
Trajectory prediction plays an important role in autonomous driving. Autonomous driving trajectory prediction refers to predicting the future driving trajectory of the vehicle by analyzing various data during the vehicle's driving process. As the core module of autonomous driving, the quality of trajectory prediction is crucial to downstream planning control. The trajectory prediction task has a rich technology stack and requires familiarity with autonomous driving dynamic/static perception, high-precision maps, lane lines, neural network architecture (CNN&GNN&Transformer) skills, etc. It is very difficult to get started! Many fans hope to get started with trajectory prediction as soon as possible and avoid pitfalls. Today I will take stock of some common problems and introductory learning methods for trajectory prediction! Introductory related knowledge 1. Are the preview papers in order? A: Look at the survey first, p
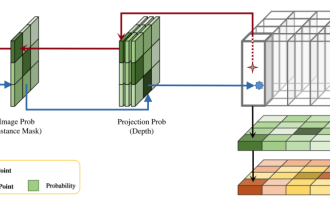 DualBEV: significantly surpassing BEVFormer and BEVDet4D, open the book!
Mar 21, 2024 pm 05:21 PM
DualBEV: significantly surpassing BEVFormer and BEVDet4D, open the book!
Mar 21, 2024 pm 05:21 PM
This paper explores the problem of accurately detecting objects from different viewing angles (such as perspective and bird's-eye view) in autonomous driving, especially how to effectively transform features from perspective (PV) to bird's-eye view (BEV) space. Transformation is implemented via the Visual Transformation (VT) module. Existing methods are broadly divided into two strategies: 2D to 3D and 3D to 2D conversion. 2D-to-3D methods improve dense 2D features by predicting depth probabilities, but the inherent uncertainty of depth predictions, especially in distant regions, may introduce inaccuracies. While 3D to 2D methods usually use 3D queries to sample 2D features and learn the attention weights of the correspondence between 3D and 2D features through a Transformer, which increases the computational and deployment time.
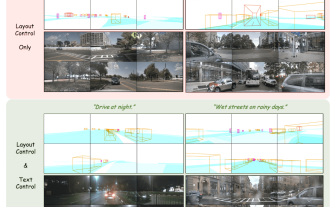 The first multi-view autonomous driving scene video generation world model | DrivingDiffusion: New ideas for BEV data and simulation
Oct 23, 2023 am 11:13 AM
The first multi-view autonomous driving scene video generation world model | DrivingDiffusion: New ideas for BEV data and simulation
Oct 23, 2023 am 11:13 AM
Some of the author’s personal thoughts In the field of autonomous driving, with the development of BEV-based sub-tasks/end-to-end solutions, high-quality multi-view training data and corresponding simulation scene construction have become increasingly important. In response to the pain points of current tasks, "high quality" can be decoupled into three aspects: long-tail scenarios in different dimensions: such as close-range vehicles in obstacle data and precise heading angles during car cutting, as well as lane line data. Scenes such as curves with different curvatures or ramps/mergings/mergings that are difficult to capture. These often rely on large amounts of data collection and complex data mining strategies, which are costly. 3D true value - highly consistent image: Current BEV data acquisition is often affected by errors in sensor installation/calibration, high-precision maps and the reconstruction algorithm itself. this led me to
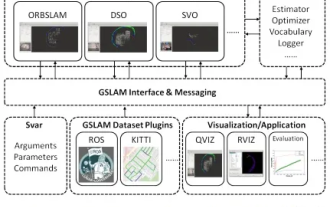 GSLAM | A general SLAM architecture and benchmark
Oct 20, 2023 am 11:37 AM
GSLAM | A general SLAM architecture and benchmark
Oct 20, 2023 am 11:37 AM
Suddenly discovered a 19-year-old paper GSLAM: A General SLAM Framework and Benchmark open source code: https://github.com/zdzhaoyong/GSLAM Go directly to the full text and feel the quality of this work ~ 1 Abstract SLAM technology has achieved many successes recently and attracted many attracted the attention of high-tech companies. However, how to effectively perform benchmarks on speed, robustness, and portability with interfaces to existing or emerging algorithms remains a problem. In this paper, a new SLAM platform called GSLAM is proposed, which not only provides evaluation capabilities but also provides researchers with a useful way to quickly develop their own SLAM systems.
 'Minecraft' turns into an AI town, and NPC residents role-play like real people
Jan 02, 2024 pm 06:25 PM
'Minecraft' turns into an AI town, and NPC residents role-play like real people
Jan 02, 2024 pm 06:25 PM
Please note that this square man is frowning, thinking about the identities of the "uninvited guests" in front of him. It turned out that she was in a dangerous situation, and once she realized this, she quickly began a mental search to find a strategy to solve the problem. Ultimately, she decided to flee the scene and then seek help as quickly as possible and take immediate action. At the same time, the person on the opposite side was thinking the same thing as her... There was such a scene in "Minecraft" where all the characters were controlled by artificial intelligence. Each of them has a unique identity setting. For example, the girl mentioned before is a 17-year-old but smart and brave courier. They have the ability to remember and think, and live like humans in this small town set in Minecraft. What drives them is a brand new,
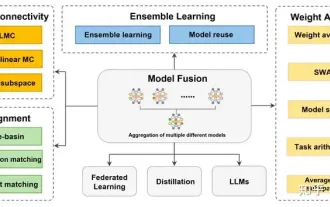 Review! Deep model fusion (LLM/basic model/federated learning/fine-tuning, etc.)
Apr 18, 2024 pm 09:43 PM
Review! Deep model fusion (LLM/basic model/federated learning/fine-tuning, etc.)
Apr 18, 2024 pm 09:43 PM
In September 23, the paper "DeepModelFusion:ASurvey" was published by the National University of Defense Technology, JD.com and Beijing Institute of Technology. Deep model fusion/merging is an emerging technology that combines the parameters or predictions of multiple deep learning models into a single model. It combines the capabilities of different models to compensate for the biases and errors of individual models for better performance. Deep model fusion on large-scale deep learning models (such as LLM and basic models) faces some challenges, including high computational cost, high-dimensional parameter space, interference between different heterogeneous models, etc. This article divides existing deep model fusion methods into four categories: (1) "Pattern connection", which connects solutions in the weight space through a loss-reducing path to obtain a better initial model fusion




