 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 The paper version 'ChatGPT' is here! You can read papers and ask questions at the same time. Netizen: Reading documents saves time.
The paper version 'ChatGPT' is here! You can read papers and ask questions at the same time. Netizen: Reading documents saves time.
The paper version 'ChatGPT' is here! You can read papers and ask questions at the same time. Netizen: Reading documents saves time.
Good news for scientific researchers! "ChatGPT" is here specifically to talk to papers.
Too lazy to read the paper? It doesn't matter, just let this tool look at it for you. If you have any questions, just ask it.
All you have to do in the whole process is to upload papers and ask questions.

But you feel confused and don’t believe the answer it gives?
It doesn’t matter, the answers given have been clearly marked from which page and place in the paper, so you can take the test at any time.

This one directly made netizens call it so cool:
I am writing a thesis, which directly saves a lot of time reading literature.
Some netizens even unilaterally announced that this is the best AI tool he has ever seen.

This small tool is called ResearchGPT. The project has been open source and has been starred 400 times on GitHub.
how to use?
To use ResearchGPT, you must first have an OpenAI API key.
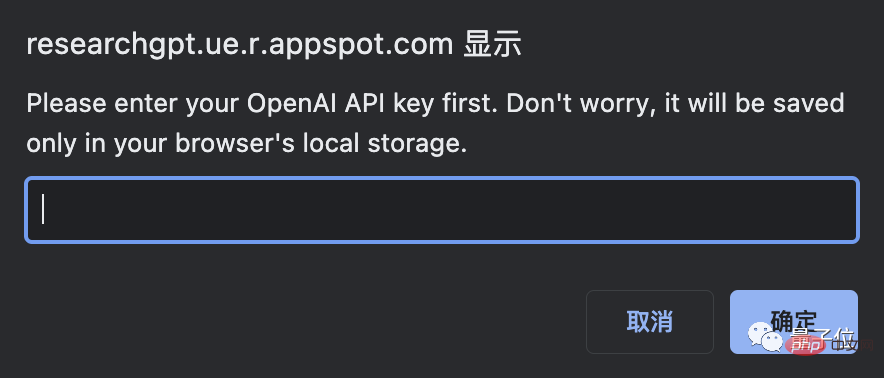
The key can be copied directly from the OpenAI official website. The specific steps are as follows:

After entering the key, you can directly upload the PDF or link of the paper you want to read. On the left, it will display the original text of the paper, and on the right, you can directly ask it questions.
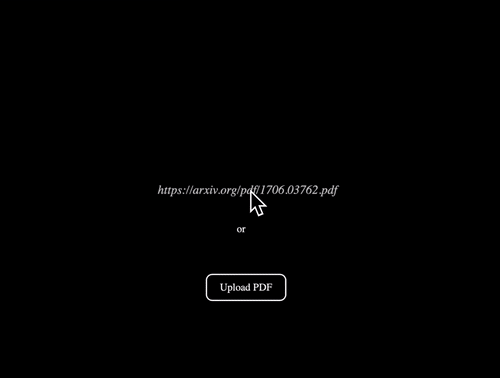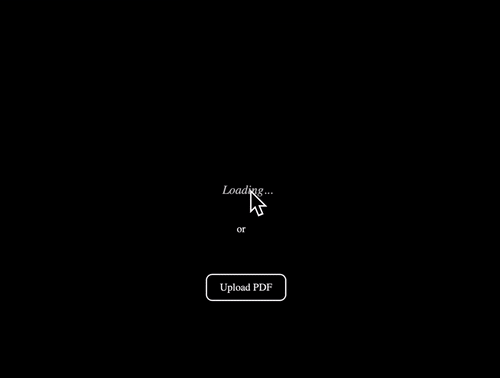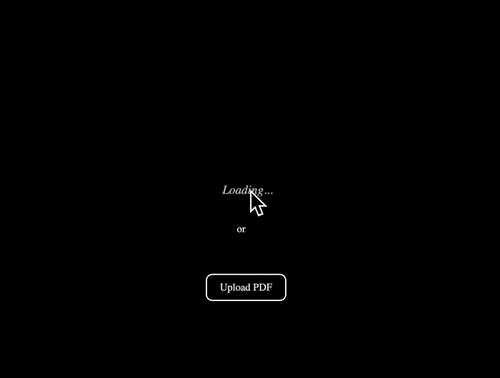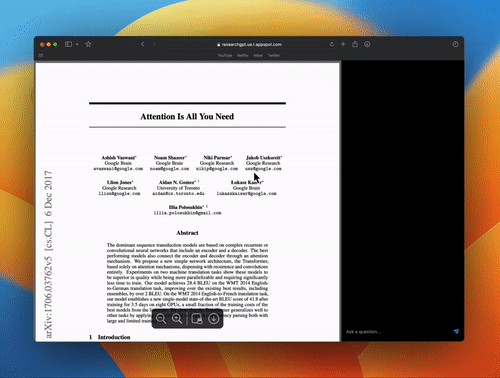
What is the answer? Go directly to the demonstration:

I have to say that the answer given is still reasonable.
Having said that, how does this tool manage to answer the paper fluently?
To put it in perspective, ResearchGPT will first look at the question you asked and extract the keywords from it.
Then search the relevant parts directly in the paper. As for how to perform semantic search, the answer is very simple:
Use the API of the OpenAI embedding model.
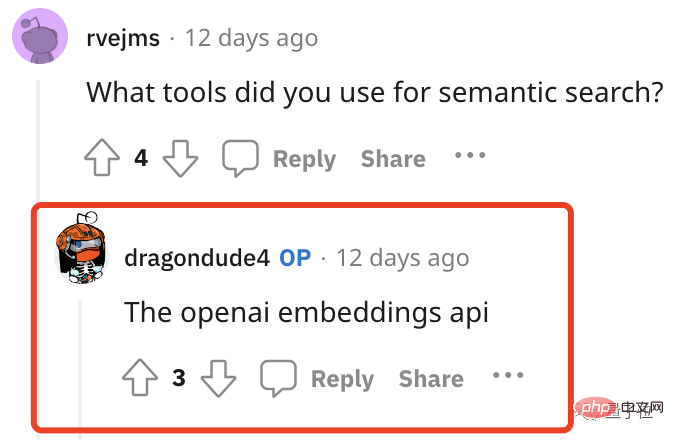
Here it directly uses the cosine similarity between the prompt word and the word embedding vector of the text in the paper to search and extract highly relevant text.
These texts ResearchGP will also be listed one by one at the end of the answer.

Now that the answer has been pointed out where in the paper, there is only the last step left: summary, this step is thrown directly to GPT-3 Do.
In this case, based on this idea and framework technology, can any text-based content be used for chat? The little brother himself also said:
Yes! Based on this technical framework, if you don’t want to read the code base, documents, financial reports, court cases, etc., you can let the tool explain it to you.
However, some netizens are curious, can this tool understand charts? (After all, in some papers, charts are still very important)
However, the guy who developed this tool directly gave a big no.
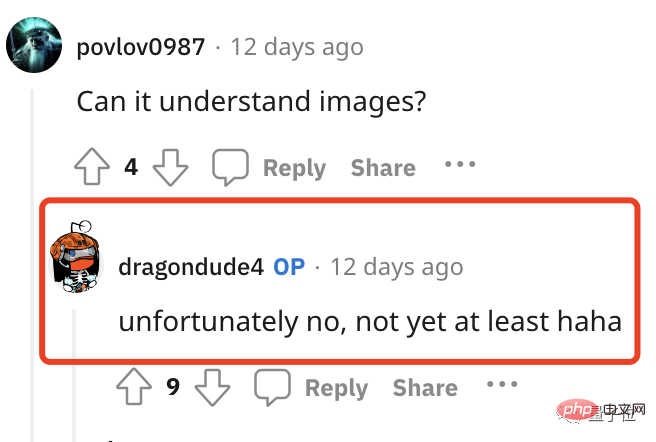
The unwilling qubit also tried it himself to see if it could understand the simplest form. The result was this:
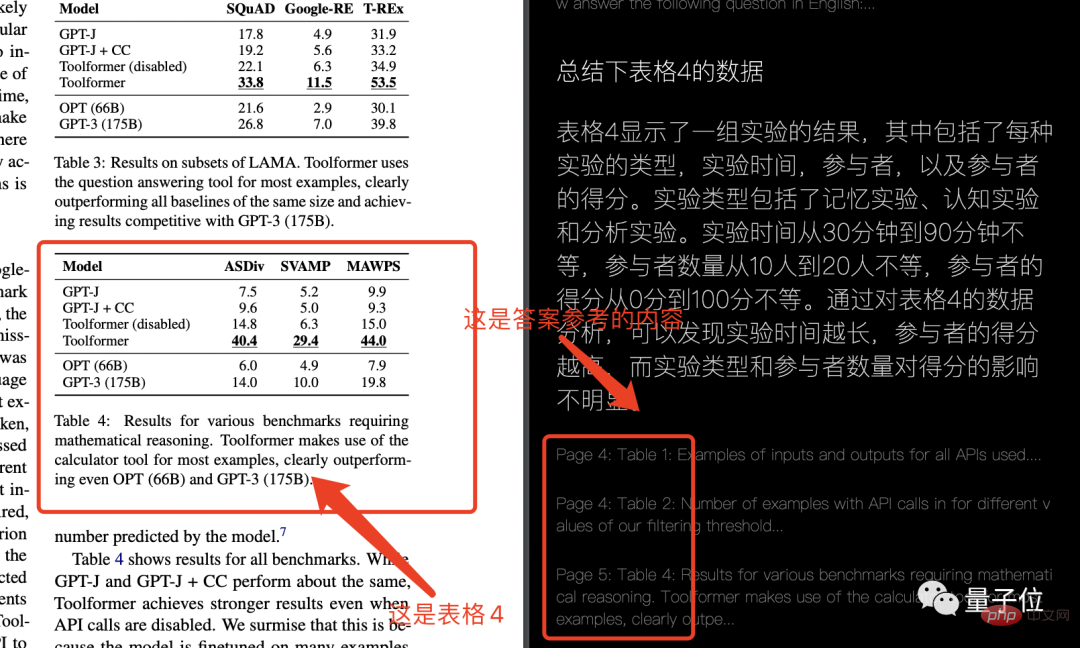
emmmmm, I can’t tell the answer. It's all wrong. It can only be said that it has nothing to do with the problem. (It’s somewhat similar to ChatGPT’s nonsense)
But in general, ResearchGPT can still be used if chart issues are not involved.
If you are interested, you can click on the link at the end of the article to try it yourself~
Author introduction
The guy who made this tool is named Mukul, and his introduction to himself is also interesting, saying I am both a data scientist and a developer, as well as a researcher, writer and designer.

My brother has also built a WebGPT before, which can answer questions by searching the web. It also uses GPT-3 to summarize the content.
Portal:https://www.php.cn/link/9c58da3f0418ebdb53c02615f9ab7282
Reference link:
[1] https://twitter.com/mukul0x/status/1625673579399446529?s=20
[2] https://github.com/mukulpatnaik /researchgpt
[3] https://www.reddit.com/r/GPT3/comments/112ncf0/introducing_researchgpt_an_opensource_research/
The above is the detailed content of The paper version 'ChatGPT' is here! You can read papers and ask questions at the same time. Netizen: Reading documents saves time.. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1389
1389
 52
52
 ChatGPT now allows free users to generate images by using DALL-E 3 with a daily limit
Aug 09, 2024 pm 09:37 PM
ChatGPT now allows free users to generate images by using DALL-E 3 with a daily limit
Aug 09, 2024 pm 09:37 PM
DALL-E 3 was officially introduced in September of 2023 as a vastly improved model than its predecessor. It is considered one of the best AI image generators to date, capable of creating images with intricate detail. However, at launch, it was exclus
 The world's most powerful open source MoE model is here, with Chinese capabilities comparable to GPT-4, and the price is only nearly one percent of GPT-4-Turbo
May 07, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
The world's most powerful open source MoE model is here, with Chinese capabilities comparable to GPT-4, and the price is only nearly one percent of GPT-4-Turbo
May 07, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
Imagine an artificial intelligence model that not only has the ability to surpass traditional computing, but also achieves more efficient performance at a lower cost. This is not science fiction, DeepSeek-V2[1], the world’s most powerful open source MoE model is here. DeepSeek-V2 is a powerful mixture of experts (MoE) language model with the characteristics of economical training and efficient inference. It consists of 236B parameters, 21B of which are used to activate each marker. Compared with DeepSeek67B, DeepSeek-V2 has stronger performance, while saving 42.5% of training costs, reducing KV cache by 93.3%, and increasing the maximum generation throughput to 5.76 times. DeepSeek is a company exploring general artificial intelligence
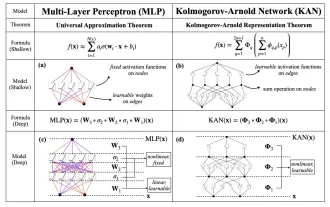 KAN, which replaces MLP, has been extended to convolution by open source projects
Jun 01, 2024 pm 10:03 PM
KAN, which replaces MLP, has been extended to convolution by open source projects
Jun 01, 2024 pm 10:03 PM
Earlier this month, researchers from MIT and other institutions proposed a very promising alternative to MLP - KAN. KAN outperforms MLP in terms of accuracy and interpretability. And it can outperform MLP running with a larger number of parameters with a very small number of parameters. For example, the authors stated that they used KAN to reproduce DeepMind's results with a smaller network and a higher degree of automation. Specifically, DeepMind's MLP has about 300,000 parameters, while KAN only has about 200 parameters. KAN has a strong mathematical foundation like MLP. MLP is based on the universal approximation theorem, while KAN is based on the Kolmogorov-Arnold representation theorem. As shown in the figure below, KAN has
 Tesla robots work in factories, Musk: The degree of freedom of hands will reach 22 this year!
May 06, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
Tesla robots work in factories, Musk: The degree of freedom of hands will reach 22 this year!
May 06, 2024 pm 04:13 PM
The latest video of Tesla's robot Optimus is released, and it can already work in the factory. At normal speed, it sorts batteries (Tesla's 4680 batteries) like this: The official also released what it looks like at 20x speed - on a small "workstation", picking and picking and picking: This time it is released One of the highlights of the video is that Optimus completes this work in the factory, completely autonomously, without human intervention throughout the process. And from the perspective of Optimus, it can also pick up and place the crooked battery, focusing on automatic error correction: Regarding Optimus's hand, NVIDIA scientist Jim Fan gave a high evaluation: Optimus's hand is the world's five-fingered robot. One of the most dexterous. Its hands are not only tactile
 Comprehensively surpassing DPO: Chen Danqi's team proposed simple preference optimization SimPO, and also refined the strongest 8B open source model
Jun 01, 2024 pm 04:41 PM
Comprehensively surpassing DPO: Chen Danqi's team proposed simple preference optimization SimPO, and also refined the strongest 8B open source model
Jun 01, 2024 pm 04:41 PM
In order to align large language models (LLMs) with human values and intentions, it is critical to learn human feedback to ensure that they are useful, honest, and harmless. In terms of aligning LLM, an effective method is reinforcement learning based on human feedback (RLHF). Although the results of the RLHF method are excellent, there are some optimization challenges involved. This involves training a reward model and then optimizing a policy model to maximize that reward. Recently, some researchers have explored simpler offline algorithms, one of which is direct preference optimization (DPO). DPO learns the policy model directly based on preference data by parameterizing the reward function in RLHF, thus eliminating the need for an explicit reward model. This method is simple and stable
 No OpenAI data required, join the list of large code models! UIUC releases StarCoder-15B-Instruct
Jun 13, 2024 pm 01:59 PM
No OpenAI data required, join the list of large code models! UIUC releases StarCoder-15B-Instruct
Jun 13, 2024 pm 01:59 PM
At the forefront of software technology, UIUC Zhang Lingming's group, together with researchers from the BigCode organization, recently announced the StarCoder2-15B-Instruct large code model. This innovative achievement achieved a significant breakthrough in code generation tasks, successfully surpassing CodeLlama-70B-Instruct and reaching the top of the code generation performance list. The unique feature of StarCoder2-15B-Instruct is its pure self-alignment strategy. The entire training process is open, transparent, and completely autonomous and controllable. The model generates thousands of instructions via StarCoder2-15B in response to fine-tuning the StarCoder-15B base model without relying on expensive manual annotation.
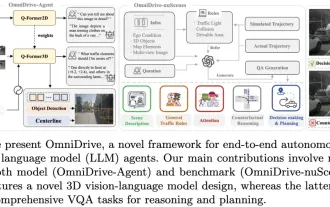 LLM is all done! OmniDrive: Integrating 3D perception and reasoning planning (NVIDIA's latest)
May 09, 2024 pm 04:55 PM
LLM is all done! OmniDrive: Integrating 3D perception and reasoning planning (NVIDIA's latest)
May 09, 2024 pm 04:55 PM
Written above & the author’s personal understanding: This paper is dedicated to solving the key challenges of current multi-modal large language models (MLLMs) in autonomous driving applications, that is, the problem of extending MLLMs from 2D understanding to 3D space. This expansion is particularly important as autonomous vehicles (AVs) need to make accurate decisions about 3D environments. 3D spatial understanding is critical for AVs because it directly impacts the vehicle’s ability to make informed decisions, predict future states, and interact safely with the environment. Current multi-modal large language models (such as LLaVA-1.5) can often only handle lower resolution image inputs (e.g.) due to resolution limitations of the visual encoder, limitations of LLM sequence length. However, autonomous driving applications require
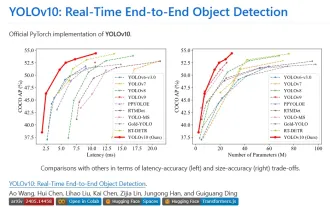 Yolov10: Detailed explanation, deployment and application all in one place!
Jun 07, 2024 pm 12:05 PM
Yolov10: Detailed explanation, deployment and application all in one place!
Jun 07, 2024 pm 12:05 PM
1. Introduction Over the past few years, YOLOs have become the dominant paradigm in the field of real-time object detection due to its effective balance between computational cost and detection performance. Researchers have explored YOLO's architectural design, optimization goals, data expansion strategies, etc., and have made significant progress. At the same time, relying on non-maximum suppression (NMS) for post-processing hinders end-to-end deployment of YOLO and adversely affects inference latency. In YOLOs, the design of various components lacks comprehensive and thorough inspection, resulting in significant computational redundancy and limiting the capabilities of the model. It offers suboptimal efficiency, and relatively large potential for performance improvement. In this work, the goal is to further improve the performance efficiency boundary of YOLO from both post-processing and model architecture. to this end



