 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Complete code demonstration of document parsing using Python and OCR (code attached)
Complete code demonstration of document parsing using Python and OCR (code attached)
Complete code demonstration of document parsing using Python and OCR (code attached)

Document parsing involves examining the data in the document and extracting useful information. It can reduce a lot of manual work through automation. A popular parsing strategy is to convert documents into images and use computer vision for recognition. While Document Image Analysis refers to the technology of obtaining information from the pixel data of an image of a document, in some cases there is no clear answer to what the expected results should be (text, images, charts, numbers, Tables, formulas...).

OCR (Optical Character Recognition) is the process of detecting and extracting text in images through computer vision. It was invented during World War I, when Israeli scientist Emanuel Goldberg created a machine that could read characters and convert them into telegraph codes. By now the field has reached a very sophisticated level, mixing image processing, text localization, character segmentation and character recognition. Basically an object detection technique for text.
In this article I will show how to use OCR for document parsing. I'll show some useful Python code that can be easily used in other similar situations (just copy, paste, run) and provide a full source code download.
Here we will take the financial statements in PDF format of a listed company as an example (link below).
https://s2.q4cdn.com/470004039/files/doc_financials/2021/q4/_10-K-2021-(As-Filed).pdf

Detect and extract text, graphics, and tables from this PDF
Environment settings
The annoying part of document parsing is , there are so many tools for different types of data (text, graphics, tables) but none of them work perfectly. Here are some of the most popular methods and packages:
- Process documents as text: use PyPDF2 to extract text, Camelot or TabulaPy to extract tables, and PyMuPDF to extract graphics.
- Convert documents to images (OCR): use pdf2image for conversion, PyTesseract and many other libraries to extract data, or just use LayoutParser.
Maybe you will ask: "Why not process the PDF file directly, but convert the pages into images?" You can do this. The main disadvantage of this strategy is the encoding issue: documents can be in multiple encodings (i.e. UTF-8, ASCII, Unicode), so conversion to text may result in data loss. So in order to avoid this problem, I will use OCR and convert the page to an image with pdf2image. Note that the PDF rendering library Poppler is required.
# with pip pip install python-poppler # with conda conda install -c conda-forge poppler
You can read the file easily:
# READ AS IMAGE
import pdf2imagedoc = pdf2image.convert_from_path("doc_apple.pdf")
len(doc) #<-- check num pages
doc[0] #<-- visualize a pageIt is exactly the same as our screenshot. If you want to save the page image locally, you can use the following code:
# Save imgs import osfolder = "doc" if folder not in os.listdir(): os.makedirs(folder)p = 1 for page in doc: image_name = "page_"+str(p)+".jpg" page.save(os.path.join(folder, image_name), "JPEG") p = p+1
Finally, we need to set up the CV engine we will use. LayoutParser appears to be the first general-purpose package for OCR based on deep learning. It uses two well-known models to complete the task:
Detection: Facebook's most advanced object detection library (the second version Detectron2 will be used here).
pip install layoutparser torchvision && pip install "git+https://github.com/facebookresearch/detectron2.git@v0.5#egg=detectron2"
Tesseract: The most famous OCR system was created by HP in 1985 and is currently developed by Google.
pip install "layoutparser[ocr]"
Now you are ready to start the OCR program for information detection and extraction.
import layoutparser as lp import cv2 import numpy as np import io import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Detection
(Target) Detection is the process of finding pieces of information in an image and then surrounding them with a rectangular border. For document parsing, the information is titles, text, graphics, tables...
Let's look at a complex page that contains a few things:
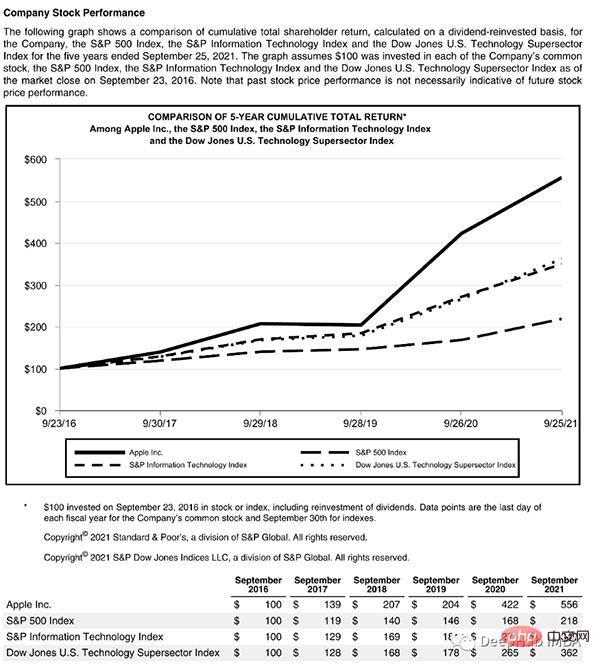
This page starts with a title, has a text block, then a figure and a table, so we need a trained model to recognize these objects. Luckily Detectron is able to do this, we just need to select a model from here and specify its path in code.
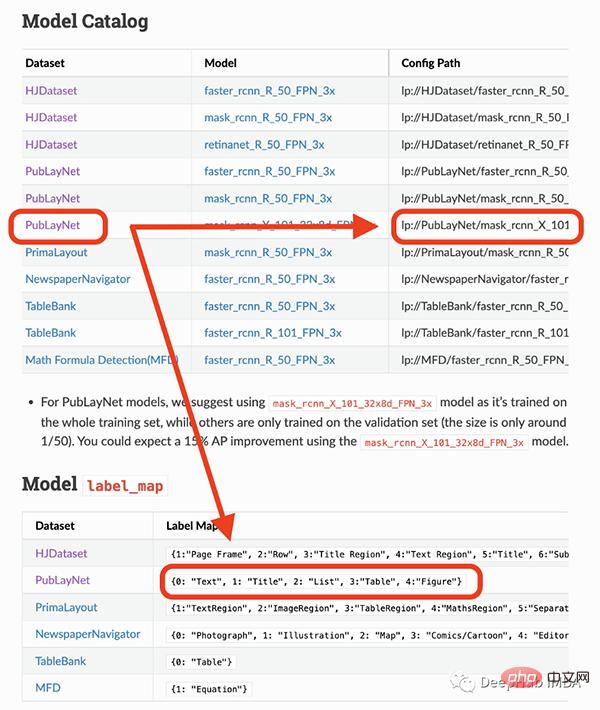
#The model I am going to use can only detect 4 objects (text, title, list, table, graph). Therefore, if you need to identify other things (like equations), you have to use other models.
## load pre-trained model
model = lp.Detectron2LayoutModel(
"lp://PubLayNet/mask_rcnn_X_101_32x8d_FPN_3x/config",
extra_config=["MODEL.ROI_HEADS.SCORE_THRESH_TEST", 0.8],
label_map={0:"Text", 1:"Title", 2:"List", 3:"Table", 4:"Figure"})
## turn img into array
i = 21
img = np.asarray(doc[i])
## predict
detected = model.detect(img)
## plot
lp.draw_box(img, detected, box_width=5, box_alpha=0.2,
show_element_type=True)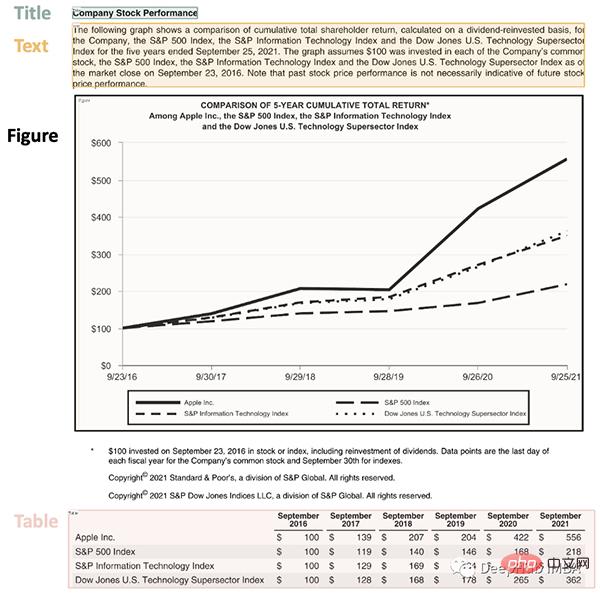
结果包含每个检测到的布局的细节,例如边界框的坐标。根据页面上显示的顺序对输出进行排序是很有用的:
## sort
new_detected = detected.sort(key=lambda x: x.coordinates[1])
## assign ids
detected = lp.Layout([block.set(id=idx) for idx,block in
enumerate(new_detected)])## check
for block in detected:
print("---", str(block.id)+":", block.type, "---")
print(block, end='nn')
完成OCR的下一步是正确提取检测到内容中的有用信息。
提取
我们已经对图像完成了分割,然后就需要使用另外一个模型处理分段的图像,并将提取的输出保存到字典中。
由于有不同类型的输出(文本,标题,图形,表格),所以这里准备了一个函数用来显示结果。
'''
{'0-Title': '...',
'1-Text': '...',
'2-Figure': array([[ [0,0,0], ...]]),
'3-Table': pd.DataFrame,
}
'''
def parse_doc(dic):
for k,v in dic.items():
if "Title" in k:
print('x1b[1;31m'+ v +'x1b[0m')
elif "Figure" in k:
plt.figure(figsize=(10,5))
plt.imshow(v)
plt.show()
else:
print(v)
print(" ")首先看看文字:
# load model
model = lp.TesseractAgent(languages='eng')
dic_predicted = {}
for block in [block for block in detected if block.type in ["Title","Text"]]:
## segmentation
segmented = block.pad(left=15, right=15, top=5,
bottom=5).crop_image(img)
## extraction
extracted = model.detect(segmented)
## save
dic_predicted[str(block.id)+"-"+block.type] =
extracted.replace('n',' ').strip()
# check
parse_doc(dic_predicted)
再看看图形报表
for block in [block for block in detected if block.type == "Figure"]: ## segmentation segmented = block.pad(left=15, right=15, top=5, bottom=5).crop_image(img) ## save dic_predicted[str(block.id)+"-"+block.type] = segmented # check parse_doc(dic_predicted)
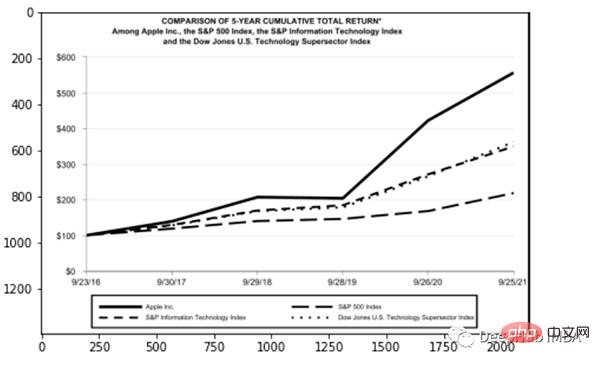
上面两个看着很不错,那是因为这两种类型相对简单,但是表格就要复杂得多。尤其是我们上看看到的的这个,因为它的行和列都是进行了合并后产生的。
for block in [block for block in detected if block.type == "Table"]: ## segmentation segmented = block.pad(left=15, right=15, top=5, bottom=5).crop_image(img) ## extraction extracted = model.detect(segmented) ## save dic_predicted[str(block.id)+"-"+block.type] = pd.read_csv( io.StringIO(extracted) ) # check parse_doc(dic_predicted)

正如我们的预料提取的表格不是很好。好在Python有专门处理表格的包,我们可以直接处理而不将其转换为图像。这里使用TabulaPy 包:
import tabula
tables = tabula.read_pdf("doc_apple.pdf", pages=i+1)
tables[0]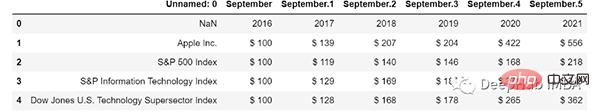
结果要好一些,但是名称仍然错了,但是效果要比直接OCR好的多。
总结
本文是一个简单教程,演示了如何使用OCR进行文档解析。使用Layoutpars软件包进行了整个检测和提取过程。并展示了如何处理PDF文档中的文本,数字和表格。
The above is the detailed content of Complete code demonstration of document parsing using Python and OCR (code attached). For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
Is the conversion speed fast when converting XML to PDF on mobile phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:09 PM
The speed of mobile XML to PDF depends on the following factors: the complexity of XML structure. Mobile hardware configuration conversion method (library, algorithm) code quality optimization methods (select efficient libraries, optimize algorithms, cache data, and utilize multi-threading). Overall, there is no absolute answer and it needs to be optimized according to the specific situation.
 How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to convert XML files to PDF on your phone?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
It is impossible to complete XML to PDF conversion directly on your phone with a single application. It is necessary to use cloud services, which can be achieved through two steps: 1. Convert XML to PDF in the cloud, 2. Access or download the converted PDF file on the mobile phone.
 What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
What is the function of C language sum?
Apr 03, 2025 pm 02:21 PM
There is no built-in sum function in C language, so it needs to be written by yourself. Sum can be achieved by traversing the array and accumulating elements: Loop version: Sum is calculated using for loop and array length. Pointer version: Use pointers to point to array elements, and efficient summing is achieved through self-increment pointers. Dynamically allocate array version: Dynamically allocate arrays and manage memory yourself, ensuring that allocated memory is freed to prevent memory leaks.
 Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
Is there any mobile app that can convert XML into PDF?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 08:54 PM
An application that converts XML directly to PDF cannot be found because they are two fundamentally different formats. XML is used to store data, while PDF is used to display documents. To complete the transformation, you can use programming languages and libraries such as Python and ReportLab to parse XML data and generate PDF documents.
 How to convert xml into pictures
Apr 03, 2025 am 07:39 AM
How to convert xml into pictures
Apr 03, 2025 am 07:39 AM
XML can be converted to images by using an XSLT converter or image library. XSLT Converter: Use an XSLT processor and stylesheet to convert XML to images. Image Library: Use libraries such as PIL or ImageMagick to create images from XML data, such as drawing shapes and text.
 How to control the size of XML converted to images?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
How to control the size of XML converted to images?
Apr 02, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
To generate images through XML, you need to use graph libraries (such as Pillow and JFreeChart) as bridges to generate images based on metadata (size, color) in XML. The key to controlling the size of the image is to adjust the values of the <width> and <height> tags in XML. However, in practical applications, the complexity of XML structure, the fineness of graph drawing, the speed of image generation and memory consumption, and the selection of image formats all have an impact on the generated image size. Therefore, it is necessary to have a deep understanding of XML structure, proficient in the graphics library, and consider factors such as optimization algorithms and image format selection.
 How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
How to open xml format
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:00 PM
Use most text editors to open XML files; if you need a more intuitive tree display, you can use an XML editor, such as Oxygen XML Editor or XMLSpy; if you process XML data in a program, you need to use a programming language (such as Python) and XML libraries (such as xml.etree.ElementTree) to parse.
 Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
Recommended XML formatting tool
Apr 02, 2025 pm 09:03 PM
XML formatting tools can type code according to rules to improve readability and understanding. When selecting a tool, pay attention to customization capabilities, handling of special circumstances, performance and ease of use. Commonly used tool types include online tools, IDE plug-ins, and command-line tools.





