 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 IBM develops cloud-native AI supercomputer Vela to flexibly deploy and train tens of billions of parameter models
IBM develops cloud-native AI supercomputer Vela to flexibly deploy and train tens of billions of parameter models
IBM develops cloud-native AI supercomputer Vela to flexibly deploy and train tens of billions of parameter models
ChatGPT is popular on the Internet, and the AI model training behind it has also attracted widespread attention. IBM Research recently announced that the cloud-native supercomputer Vela it developed can be quickly deployed and used to train basic AI models. Since May 2022, dozens of the company’s researchers have been using this supercomputer to train AI models with tens of billions of parameters.
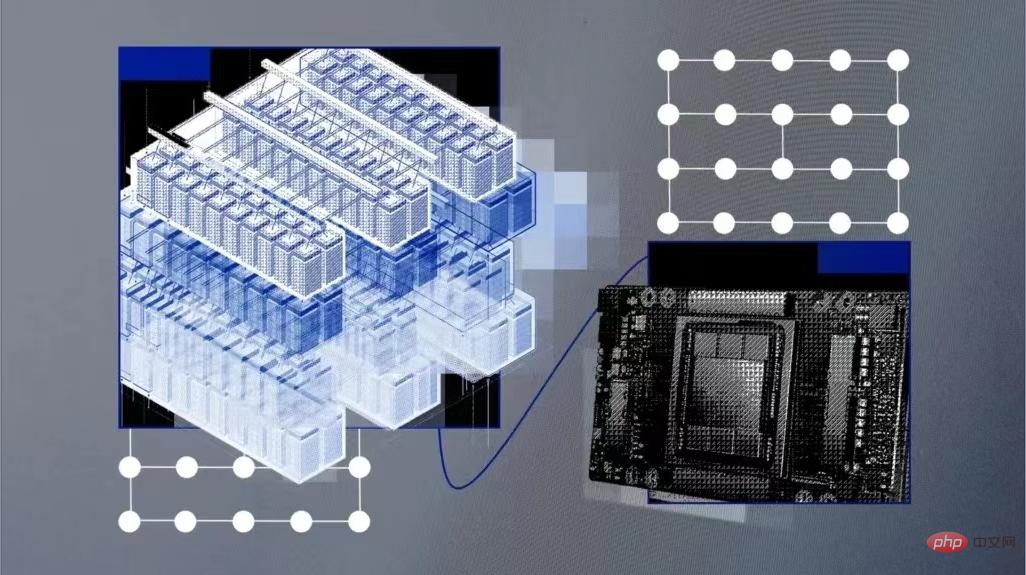
Basic models are AI models trained on large amounts of unlabeled data, and their versatility means they can be used for a range of different tasks with just fine-tuning. Their scale is enormous and requires massive and costly computing power. Therefore, as experts say, computing power will become the biggest bottleneck in developing the next generation of large-scale basic models, and training them requires a lot of computing power and time.
Training a model that can run tens of billions or hundreds of billions of parameters requires the use of high-performance computing hardware, including networks, parallel file systems, and bare metal nodes. This hardware is difficult to deploy and expensive to run. Microsoft built an AI supercomputer for OpenAI in May 2020 and hosted it in the Azure cloud platform. But IBM says they are hardware-driven, which increases cost and limits flexibility.
Cloud AI Supercomputer
So IBM created a system called Vela that is “specifically focused on large-scale AI.”
Vela can be deployed to any of IBM's cloud data centers as needed, and it is itself a "virtual cloud". While this approach reduces computing power compared to building physics-based supercomputers, it creates a more flexible solution. Cloud computing solutions provide engineers with resources through API interfaces, easier access to the broad IBM cloud ecosystem for deeper integration, and the ability to scale performance as needed.
IBM engineers explained that Vela is able to access data sets on IBM Cloud Object Storage instead of building a custom storage backend. Previously this infrastructure had to be built separately into supercomputers.
The key component of any AI supercomputer is a large number of GPUs and the nodes connecting them. Vela actually configures each node as a virtual machine (rather than bare metal). This is the most common method and is widely considered to be the most ideal method for AI training.
How is Vela built?
One of the disadvantages of cloud virtual computers is that performance cannot be guaranteed. To address performance degradation and deliver bare-metal performance inside virtual machines, IBM engineers found a way to unlock full node performance (including GPU, CPU, network and storage) and reduce load losses to less than 5%.
This involves configuring a bare metal host for virtualization, supporting virtual machine scaling, large page and single root IO virtualization, and realistic representation of all devices and connections within the virtual machine; also includes network cards and CPUs and GPUs matches, and how they bridge each other. After completing this work, they found that the performance of the virtual machine nodes was "close to bare metal."
In addition, they are also committed to designing AI nodes with large GPU memory and large amounts of local storage for caching AI training data, models and finished products. In tests using PyTorch, they found that by optimizing workload communication patterns, they were also able to bridge the bottleneck of relatively slow Ethernet networks compared to faster networks like Infiniband used in supercomputing.
In terms of configuration, each Vela uses eight 80GB A100 GPUs, two second-generation Intel Xeon scalable processors, 1.5TB of memory and four 3.2TB NVMe hard drives, and can be used at any scale Deploy to any IBM cloud data center around the world.
IBM engineers said: "Having the right tools and infrastructure is a key factor in improving R&D efficiency. Many teams choose to follow the tried-and-true path of building traditional supercomputers for AI... We have been working on a better solutions to provide the dual benefits of high-performance computing and high-end user productivity.”
The above is the detailed content of IBM develops cloud-native AI supercomputer Vela to flexibly deploy and train tens of billions of parameter models. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 How to configure Debian Apache log format
Apr 12, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
How to configure Debian Apache log format
Apr 12, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
This article describes how to customize Apache's log format on Debian systems. The following steps will guide you through the configuration process: Step 1: Access the Apache configuration file The main Apache configuration file of the Debian system is usually located in /etc/apache2/apache2.conf or /etc/apache2/httpd.conf. Open the configuration file with root permissions using the following command: sudonano/etc/apache2/apache2.conf or sudonano/etc/apache2/httpd.conf Step 2: Define custom log formats to find or
 How Tomcat logs help troubleshoot memory leaks
Apr 12, 2025 pm 11:42 PM
How Tomcat logs help troubleshoot memory leaks
Apr 12, 2025 pm 11:42 PM
Tomcat logs are the key to diagnosing memory leak problems. By analyzing Tomcat logs, you can gain insight into memory usage and garbage collection (GC) behavior, effectively locate and resolve memory leaks. Here is how to troubleshoot memory leaks using Tomcat logs: 1. GC log analysis First, enable detailed GC logging. Add the following JVM options to the Tomcat startup parameters: -XX: PrintGCDetails-XX: PrintGCDateStamps-Xloggc:gc.log These parameters will generate a detailed GC log (gc.log), including information such as GC type, recycling object size and time. Analysis gc.log
 How to implement file sorting by debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:06 AM
How to implement file sorting by debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:06 AM
In Debian systems, the readdir function is used to read directory contents, but the order in which it returns is not predefined. To sort files in a directory, you need to read all files first, and then sort them using the qsort function. The following code demonstrates how to sort directory files using readdir and qsort in Debian system: #include#include#include#include#include//Custom comparison function, used for qsortintcompare(constvoid*a,constvoid*b){returnstrcmp(*(
 How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
How to optimize the performance of debian readdir
Apr 13, 2025 am 08:48 AM
In Debian systems, readdir system calls are used to read directory contents. If its performance is not good, try the following optimization strategy: Simplify the number of directory files: Split large directories into multiple small directories as much as possible, reducing the number of items processed per readdir call. Enable directory content caching: build a cache mechanism, update the cache regularly or when directory content changes, and reduce frequent calls to readdir. Memory caches (such as Memcached or Redis) or local caches (such as files or databases) can be considered. Adopt efficient data structure: If you implement directory traversal by yourself, select more efficient data structures (such as hash tables instead of linear search) to store and access directory information
 How to configure firewall rules for Debian syslog
Apr 13, 2025 am 06:51 AM
How to configure firewall rules for Debian syslog
Apr 13, 2025 am 06:51 AM
This article describes how to configure firewall rules using iptables or ufw in Debian systems and use Syslog to record firewall activities. Method 1: Use iptablesiptables is a powerful command line firewall tool in Debian system. View existing rules: Use the following command to view the current iptables rules: sudoiptables-L-n-v allows specific IP access: For example, allow IP address 192.168.1.100 to access port 80: sudoiptables-AINPUT-ptcp--dport80-s192.16
 How debian readdir integrates with other tools
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
How debian readdir integrates with other tools
Apr 13, 2025 am 09:42 AM
The readdir function in the Debian system is a system call used to read directory contents and is often used in C programming. This article will explain how to integrate readdir with other tools to enhance its functionality. Method 1: Combining C language program and pipeline First, write a C program to call the readdir function and output the result: #include#include#include#includeintmain(intargc,char*argv[]){DIR*dir;structdirent*entry;if(argc!=2){
 How to learn Debian syslog
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:51 AM
How to learn Debian syslog
Apr 13, 2025 am 11:51 AM
This guide will guide you to learn how to use Syslog in Debian systems. Syslog is a key service in Linux systems for logging system and application log messages. It helps administrators monitor and analyze system activity to quickly identify and resolve problems. 1. Basic knowledge of Syslog The core functions of Syslog include: centrally collecting and managing log messages; supporting multiple log output formats and target locations (such as files or networks); providing real-time log viewing and filtering functions. 2. Install and configure Syslog (using Rsyslog) The Debian system uses Rsyslog by default. You can install it with the following command: sudoaptupdatesud
 Where is the Debian Nginx log path
Apr 12, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Where is the Debian Nginx log path
Apr 12, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
In the Debian system, the default storage locations of Nginx's access log and error log are as follows: Access log (accesslog):/var/log/nginx/access.log Error log (errorlog):/var/log/nginx/error.log The above path is the default configuration of standard DebianNginx installation. If you have modified the log file storage location during the installation process, please check your Nginx configuration file (usually located in /etc/nginx/nginx.conf or /etc/nginx/sites-available/ directory). In the configuration file



