Let's talk about how to use watch and computed in vue3
This article will help you learn vue3 and talk in depth about the use of computed properties and listener watch. I hope it will be helpful to everyone!

1. watch
1. Detecting reactive internal data
<template>
<p>{{ obj.hobby.eat }}</p>
<button @click="obj.hobby.eat = '面条'">click</button>
</template>
<script>
import { watch, reactive } from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
setup() {
const obj = reactive({
name: 'ifer',
hobby: {
eat: '西瓜',
},
})
watch(obj, (newValue, oldValue) => {
// 注意1:监听对象的时候,新旧值是相等的
// 注意2:强制开启深度监听,配置无效
console.log('触发监听');
console.log(newValue === oldValue) // true
})
return { obj }
},
}
</script>Note: Modifications to reactive itself will not trigger monitoring. [Related recommendations: vuejs video tutorial, web front-end development]
<template>
<p>{{ obj.hobby.eat }}</p>
<button @click="obj.hobby = { eat: '面条' }">click</button>
</template>
<script>
import { watch, reactive } from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
setup() {
const obj = reactive({
name: 'ifer',
hobby: {
eat: '西瓜',
},
})
watch(obj.hobby, (newValue, oldValue) => {
// obj.hobby = { eat: '面条' }
console.log('对 reactive 自身的修改不会触发监听')
})
return { obj }
},
}
</script>
Be careful not to modify reactive itself , the modification itself does not trigger
- 2.1 Monitor a ref Data
<template>
<p>{{ age }}</p>
<button @click="age++">click</button>
</template>
<script>
import { watch, ref } from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
setup() {
const age = ref(18)
// 监听 ref 数据 age,会触发后面的回调,不需要 .value
watch(age, (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log(newValue, oldValue)
})
return { age }
},
}
</script>- 2.2 Monitor multiple ref data
You can monitor changes in age and num at the same time in the form of an array.
<template>
<p>age: {{ age }} num: {{ num }}</p>
<button @click="handleClick">click</button>
</template>
<script>
import { watch, ref } from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
setup() {
const age = ref(18)
const num = ref(0)
const handleClick = () => {
age.value++
num.value++
}
// 数组里面是 ref 数据
watch([age, num], (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log(newValue, oldValue)
})
return { age, num, handleClick }
},
}
</script>
Trigger the listening attribute immediately:
{
immediate: true,
}<template>
<p>{{ age }}</p>
<button @click="handleClick">click</button>
</template>
<script>
import { watch, ref } from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
setup() {
const age = ref(18)
const handleClick = () => {
age.value++
}
watch(
age,
(newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log(newValue, oldValue) // 18 undefined
},
{
immediate: true,
}
)
return { age, handleClick }
},
}
</script>
Turn on Deep monitoring of ref data
? 问题:修改 ref 对象里面的数据并不会触发监听,说明 ref 并不是默认开启 deep 的。见下
<template>
<p>{{ obj.hobby.eat }}</p>
<button @click="obj.hobby.eat = '面条'">修改 obj.hobby.eat</button>
</template>
<script>
import { watch, ref } from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
setup() {
const obj = ref({
hobby: {
eat: '西瓜',
},
})
// 注意:ref 监听对象,默认监听的是这个对象地址的变化
watch(obj, (newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log(newValue === oldValue)
})
return { obj }
},
}
</script>
Faced with such a situation where the watch is not triggered, we have three solutions:
- Solution 1: Of course, directly modify the entire object It will definitely be monitored (note that the modification of obj in the template is equivalent to modifying obj.value).
-`{{ obj.hobby.eat }}
`
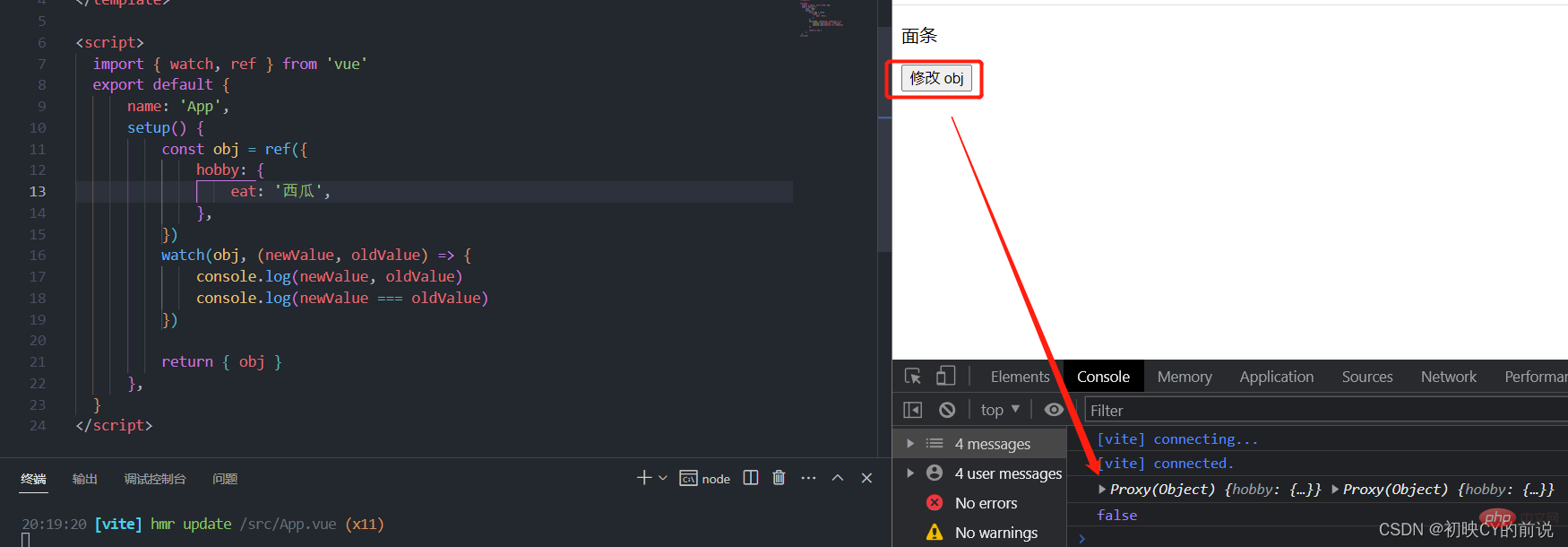
- ##Solution 2 : Enable deep monitoring of ref data.
watch(
obj,
(newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log(newValue, oldValue)
console.log(newValue === oldValue)
},
{
deep: true,
}
)Just add a sentence, so there is no screenshot
- Solution 3: You can also achieve the same effect by monitoring ref.value.
Because if the object is wrapped inside ref, it is actually implemented with reactive, which can be proved through the isReactive method.<template> <p>{{ obj.hobby.eat }}</p> <button @click="obj.hobby.eat = '面条'">修改 obj</button> </template> <script> import { watch, ref } from 'vue' export default { name: 'App', setup() { const obj = ref({ hobby: { eat: '西瓜', }, }) watch(obj.value, (newValue, oldValue) => { console.log(newValue, oldValue) console.log(newValue === oldValue) }) return { obj } }, } </script>Copy after login
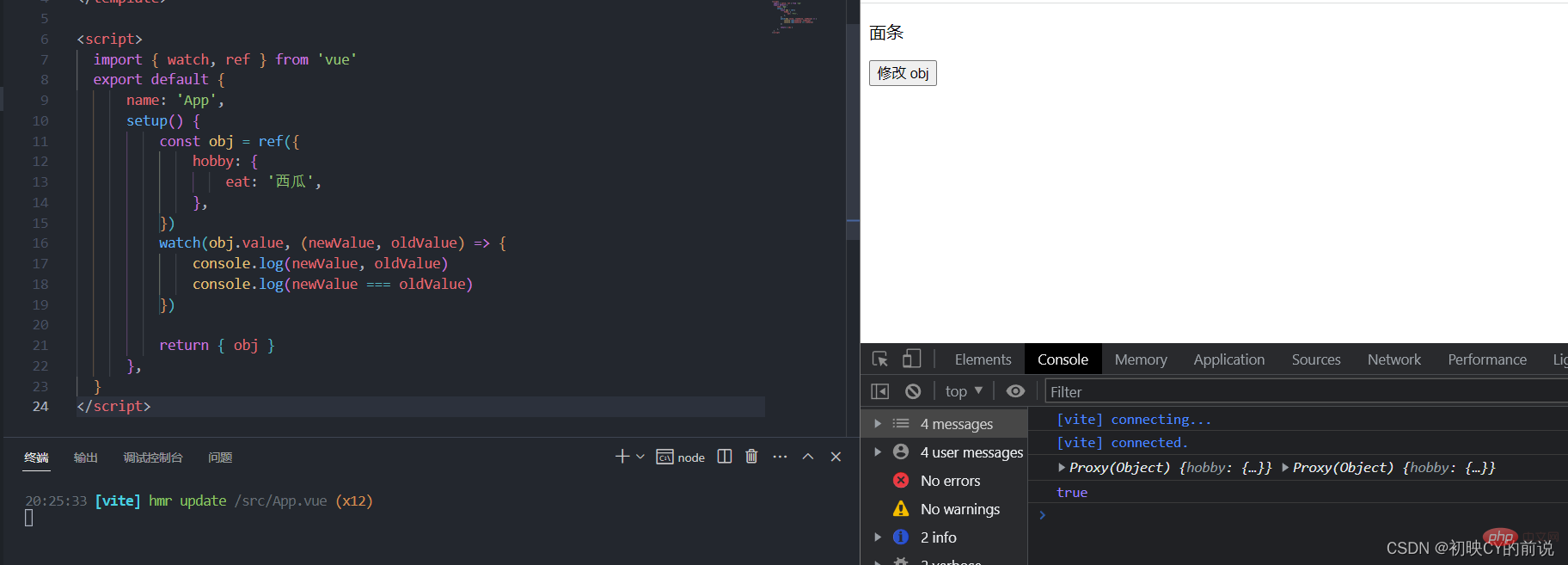
- Monitoring common data
- Monitoring a common attribute value in the responsive object must be done by returning the function (if returned It is an object/responsive object, and deep monitoring needs to be turned on to modify the internal data).
<template>
<p>{{ obj.hobby.eat }}</p>
<button @click="obj.hobby.eat = '面条'">修改 obj</button>
</template>
<script>
import { watch, reactive } from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
setup() {
const obj = reactive({
hobby: {
eat: '西瓜',
},
})
// 把 obj.hobby 作为普通值去进行监听,只能监听到 obj.hobby 自身的变化
/* watch(
() => obj.hobby,
(newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log(newValue, oldValue)
console.log(newValue === oldValue)
}
) */
// 如果开启了深度监听,则能监听到 obj.hobby 和内部数据的所有变化
/* watch(
() => obj.hobby,
(newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log(newValue, oldValue)
console.log(newValue === oldValue)
},
{
deep: true,
}
) */
// 能监听影响到 obj.hobby.eat 变化的操作,例如 obj.hobby = { eat: '面条' } 或 obj.hobby.eat = '面条',如果是 reactive 直接对 obj 的修改则不会被监听到(ref 可以)
watch(
() => obj.hobby.eat,
(newValue, oldValue) => {
console.log(newValue, oldValue)
console.log(newValue === oldValue)
}
)
return { obj }
},
}
</script>2. computed
Function: The computed function is used to define computed properties. The above basic concepts are the same as vue2 Yes, you can move on to the definitions of these two knowledge points in vue2:[vue2] Usage of calculation and listening.
<template>
<p>firstName: {{ person.firstName }}</p>
<p>lastName: {{ person.lastName }}</p>
<input type="text" v-model="person.fullName" />
</template>
<script>
import { computed, reactive } from 'vue'
export default {
name: 'App',
setup() {
const person = reactive({
firstName: '初',
lastName: '映',
})
// 也可以传入对象,目前和上面等价
person.fullName = computed({
get() {
return person.firstName + '*' + person.lastName
},
set(value) {
console.log(value,'value');//为上述get的返回值
const newArr = value.split('*')
person.firstName = newArr[0]
person.lastName = newArr[1]
},
})
return {
person,
}
},
}
</script>
vuejs introductory tutorial, Basic programming video)
The above is the detailed content of Let's talk about how to use watch and computed in vue3. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
How to use bootstrap in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:33 PM
Using Bootstrap in Vue.js is divided into five steps: Install Bootstrap. Import Bootstrap in main.js. Use the Bootstrap component directly in the template. Optional: Custom style. Optional: Use plug-ins.
 How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
How to add functions to buttons for vue
Apr 08, 2025 am 08:51 AM
You can add a function to the Vue button by binding the button in the HTML template to a method. Define the method and write function logic in the Vue instance.
 How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
How to reference js file with vue.js
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
There are three ways to refer to JS files in Vue.js: directly specify the path using the <script> tag;; dynamic import using the mounted() lifecycle hook; and importing through the Vuex state management library.
 How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
How to use watch in vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:36 PM
The watch option in Vue.js allows developers to listen for changes in specific data. When the data changes, watch triggers a callback function to perform update views or other tasks. Its configuration options include immediate, which specifies whether to execute a callback immediately, and deep, which specifies whether to recursively listen to changes to objects or arrays.
 What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
What does vue multi-page development mean?
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:57 PM
Vue multi-page development is a way to build applications using the Vue.js framework, where the application is divided into separate pages: Code Maintenance: Splitting the application into multiple pages can make the code easier to manage and maintain. Modularity: Each page can be used as a separate module for easy reuse and replacement. Simple routing: Navigation between pages can be managed through simple routing configuration. SEO Optimization: Each page has its own URL, which helps SEO.
 How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
How to return to previous page by vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:30 PM
Vue.js has four methods to return to the previous page: $router.go(-1)$router.back() uses <router-link to="/" component window.history.back(), and the method selection depends on the scene.
 How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
How to use vue traversal
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:48 PM
There are three common methods for Vue.js to traverse arrays and objects: the v-for directive is used to traverse each element and render templates; the v-bind directive can be used with v-for to dynamically set attribute values for each element; and the .map method can convert array elements into new arrays.
 How to query the version of vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:24 PM
How to query the version of vue
Apr 07, 2025 pm 11:24 PM
You can query the Vue version by using Vue Devtools to view the Vue tab in the browser's console. Use npm to run the "npm list -g vue" command. Find the Vue item in the "dependencies" object of the package.json file. For Vue CLI projects, run the "vue --version" command. Check the version information in the <script> tag in the HTML file that refers to the Vue file.




