 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 Refresh your knowledge! I use these six bad habits that slow down my Python programs all the time!
Refresh your knowledge! I use these six bad habits that slow down my Python programs all the time!
Refresh your knowledge! I use these six bad habits that slow down my Python programs all the time!
In this article, I summarized 6 cases of Python writing methods.
1. Don’t import the root module
When using Python, one thing we cannot avoid is importing modules, whether they are built-in modules or third-party modules. Sometimes, we may only need one or a few functions or objects from the module. In this case we should try to import only the functions or objects we need instead of importing the root module.
This is a simple example. Suppose we need to calculate the square root of some numbers in a program.
Slower Example
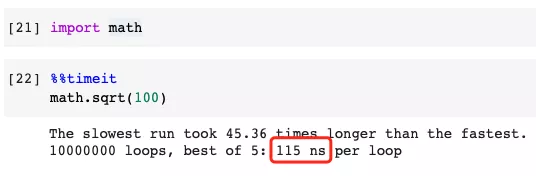
#In the bad example, we import the math module and use math.sqrt() to access the function. Of course, there's nothing wrong with it, but if we could import the sqrt() function, the performance would be better.
Faster Example

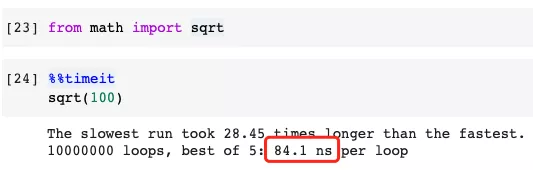
2. Avoid using dot/dot chains
Using dot is very intuitive. Access properties or functions of an object in Python. Most of the time, no problem. However, if we could avoid using dots or even linking dots, the performance would actually be better.
The example below shows appending numbers to a list and then removing them.
Slower example

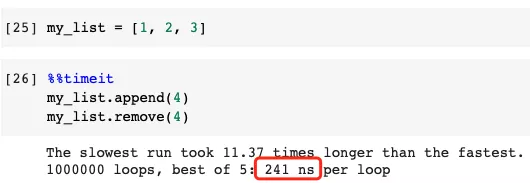
Faster example

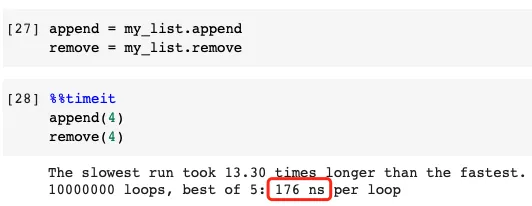
If you don't believe this actually does the same thing, we can verify it.

I can expect many Python developers to jump out and say that the technique in this example is a bit ridiculous. In fact, even myself, I rarely write code like the one above. However, it's nice to know that we can program it this way and even make it faster.
If we want to append to a list and remove items from it millions of times, we should probably consider using this trick. That's why we need to balance performance and readability of our code.
3. Do not use connection strings
Strings are immutable in Python. Therefore, when we use " " to concatenate multiple strings into one long string, each substring is operated individually.
Slower example
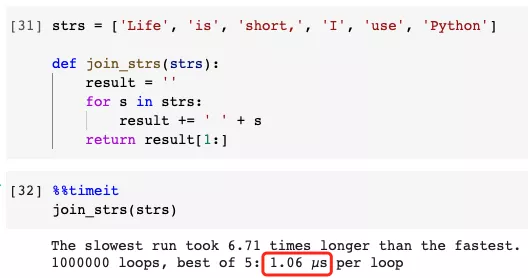
Specifically, for each substring, it needs to request a memory address and then combine it with that memory address The raw strings are concatenated, which becomes an overhead.
Faster example

However, when we use the join() function, the function knows all the substrings in advance, and the memory address is allocated The length is suitable for the final concatenated string. Therefore, there is no overhead of allocating memory for each substring.
It is strongly recommended to use the join() function whenever possible. However, sometimes we may just want to concatenate two strings. Or, just for convenience, we want to use " ". In these cases, using " " will result in better readability and less code length.
4. Do not use temporary variables for value exchange
Many algorithms require the value exchange of two variables. In most other programming languages, this is usually done by introducing a temporary variable, as shown below.
Slower example
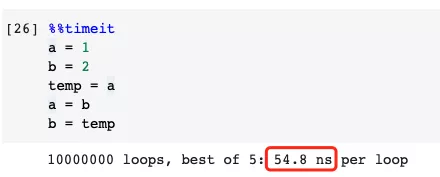
Faster example
But, in Python, we don’t have to use the temp variable. Python has a built-in syntax to implement this value exchange, as shown below.
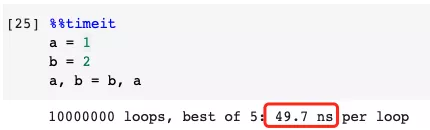
5. Use If-Condition to short-circuit
"Short-circuit" evaluation exists in many programming languages, and the same is true for Python. Basically, it refers to the behavior of certain Boolean operators where the second argument is executed or evaluated only if the first argument is not sufficient to determine the value of the entire expression.
Let's demonstrate this in an example. Suppose we have a list as follows.
my_dict = [
{
'name': 'Alice',
'age': 28
},
{
'name': 'Bob',
'age': 23
},
{
'name': 'Chris',
'age': 33
},
{
'name': 'Chelsea',
'age': 2
},
{
'name': 'Carol',
'age': 24
}
]
Our job is to filter the list and find all people whose names start with "C" and whose age is 30 years or older.
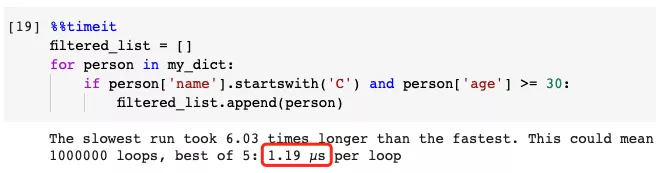
Slower example
There are two conditions that need to be met at the same time:
- Name starts with "C"
- Age ≥ 30 Therefore , we can write the following code.
Faster Example
There is nothing wrong with the code in the previous example. However, in this particular fictional example, only "Chris" is over 30 years old.
If we first write the condition for checking names, then three names (Chris, Chelsea and Carol) are met. The second condition regarding age is then checked again for all 3 individuals.
However, because of short-circuit evaluation, if we write the age condition first, only Chris's age is above 30, and it will be checked again whether his name starts with "C".
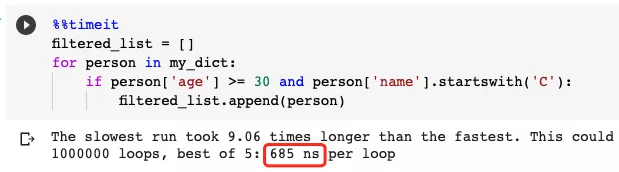
In this case it's almost 100% faster.
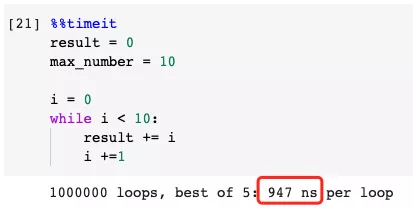
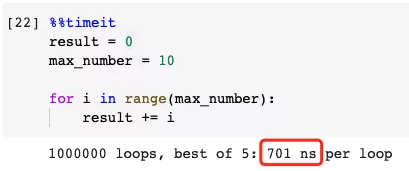
6. Don’t use While Loop if you can use For Loop
Python uses a lot of C to improve performance, that is, CPython. In terms of loop statements, a For-Loop in Python has relatively fewer steps, more of which are run as C code than a While-Loop.
So, while we can use For-Loop in Python, we should not use while loop. This is not only because For-Loop is more elegant in Python, but also performs better.
Slower example
Faster example
The above is the detailed content of Refresh your knowledge! I use these six bad habits that slow down my Python programs all the time!. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.
 How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
In VS Code, you can run the program in the terminal through the following steps: Prepare the code and open the integrated terminal to ensure that the code directory is consistent with the terminal working directory. Select the run command according to the programming language (such as Python's python your_file_name.py) to check whether it runs successfully and resolve errors. Use the debugger to improve debugging efficiency.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VS Code extensions pose malicious risks, such as hiding malicious code, exploiting vulnerabilities, and masturbating as legitimate extensions. Methods to identify malicious extensions include: checking publishers, reading comments, checking code, and installing with caution. Security measures also include: security awareness, good habits, regular updates and antivirus software.
 What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
What is vscode What is vscode for?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:45 PM
VS Code is the full name Visual Studio Code, which is a free and open source cross-platform code editor and development environment developed by Microsoft. It supports a wide range of programming languages and provides syntax highlighting, code automatic completion, code snippets and smart prompts to improve development efficiency. Through a rich extension ecosystem, users can add extensions to specific needs and languages, such as debuggers, code formatting tools, and Git integrations. VS Code also includes an intuitive debugger that helps quickly find and resolve bugs in your code.
 Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in automation, scripting, and task management. 1) Automation: File backup is realized through standard libraries such as os and shutil. 2) Script writing: Use the psutil library to monitor system resources. 3) Task management: Use the schedule library to schedule tasks. Python's ease of use and rich library support makes it the preferred tool in these areas.
 Can visual studio code run python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
Can visual studio code run python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:00 PM
VS Code not only can run Python, but also provides powerful functions, including: automatically identifying Python files after installing Python extensions, providing functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Relying on the installed Python environment, extensions act as bridge connection editing and Python environment. The debugging functions include setting breakpoints, step-by-step debugging, viewing variable values, and improving debugging efficiency. The integrated terminal supports running complex commands such as unit testing and package management. Supports extended configuration and enhances features such as code formatting, analysis and version control.
 Can vs code run python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
Can vs code run python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:21 PM
Yes, VS Code can run Python code. To run Python efficiently in VS Code, complete the following steps: Install the Python interpreter and configure environment variables. Install the Python extension in VS Code. Run Python code in VS Code's terminal via the command line. Use VS Code's debugging capabilities and code formatting to improve development efficiency. Adopt good programming habits and use performance analysis tools to optimize code performance.



