 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 20 seconds warning, saved 127 children! Can AI predict the 6.8 magnitude earthquake in Luding, Sichuan?
20 seconds warning, saved 127 children! Can AI predict the 6.8 magnitude earthquake in Luding, Sichuan?
20 seconds warning, saved 127 children! Can AI predict the 6.8 magnitude earthquake in Luding, Sichuan?
The latest news is that the 6.8-magnitude earthquake in Luding, Sichuan has killed 29 people in Ganzi Prefecture and 17 people in Ya'an City. Another 16 people are missing and 50 people are injured.
I feel extremely heartbroken when I see this news...
In this summer’s super heat wave, Sichuan, as the main force in the West-East electricity transmission The great province has resisted all grievances for the people of the country.
This heroic city chose to carry its own weight: in order to continue supplying power to other brother provinces, it extinguished the street lights, turned off the air conditioner, and plunged itself into darkness.
Subsequently, Sichuan encountered an epidemic again, and cities such as Chengdu fell into silence.
Yesterday, Luding suffered another earthquake, and the number of casualties is still being counted.

Source: China Firefighting
20 seconds, save 127 children
In Hailuogou, the epicenter of the earthquake, two hotel buildings collapsed.

Source: Lizhi News
Mr. Xu, the hotel owner, said that he I still have lingering fears, "I have never seen such a violent earthquake" and "my hands are shaking now." There were many touching scenes during this earthquake. According to Red Star News, after receiving news of the earthquake, the Sichuan Provincial People's Hospital immediately organized an emergency rescue team to go to the rescue, and the National (Sichuan) Traditional Chinese Medicine Emergency Medical Rescue Team also rushed to Luding for rescue. The Provincial Orthopedic Hospital immediately formed an emergency team and headed to the epicenter to carry out rescue operations.
Who can go? I can! Really in tearsThe Office of the State Council Earthquake Relief Command and the Ministry of Emergency Management have launched the national earthquake emergency level three response and dispatched and deployed forward rescue.

Sichuan has urgently dispatched "large-scale high-altitude full-network emergency communication drones" to fly to the epicenter to perform public communication coverage tasks.

Source: Xiaoyang Video
Chengdu Fire Ground and Air Rescue Forces are also urgently gathering to rush to the epicenter to carry out joint reconnaissance and search and rescue missions. Search and rescue helicopters are constantly circling in the sky, never letting go of any possible opportunity!

Source: China Firefighting
At a moment when people across the country are worried, Jiupai News reported a gratifying news: After seeing the 20-second earthquake warning countdown message, teachers from a kindergarten in Ya'an immediately rushed to the class, woke up the sleeping children, and evacuated them one by one to a safe place. . The whole process took 1 minute and 57 seconds, and 127 children were successfully evacuated to a safe place.

Source: Jiupai News
Earthquake Early Warning This Key 20 In seconds, 127 children were saved.
earthquake early warning has made great contributions
As of press time, the earthquake has killed 65 people. In addition to being heartbroken, many people have raised this question: Why is it that even though technology is so advanced now, it is still impossible to prevent casualties through earthquake early warning? In fact, earthquake early warning has played a big role in this earthquake. At 12:52 on September 5, when a 6.8-magnitude earthquake occurred in Luding County, Ganzi Prefecture, Sichuan Province, many Chengdu citizens heard a countdown broadcast of "56, 55, 54..." on their mobile phones. Citizens immediately evacuated to safe areas.

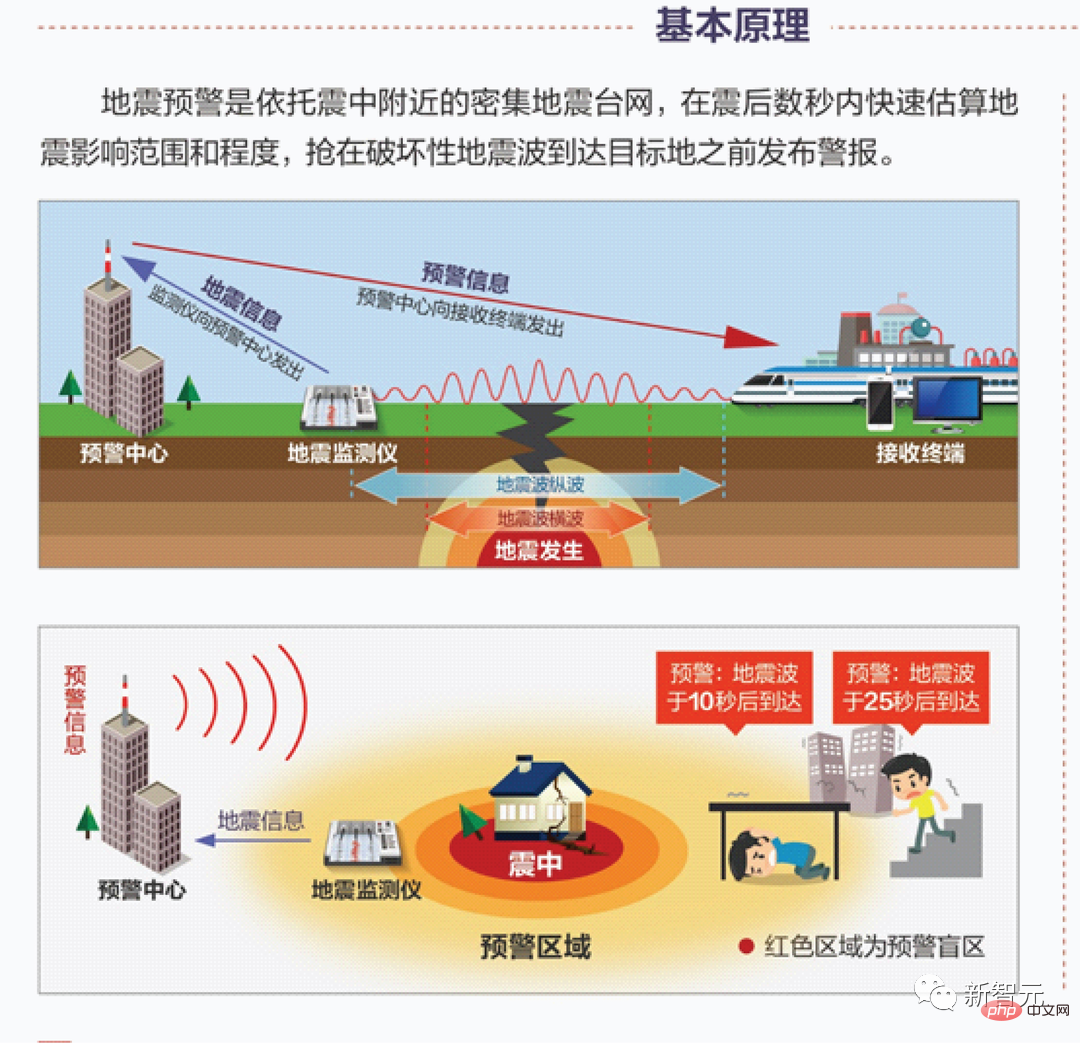
This earthquake early warning countdown, known as the "big speaker", comes from the "earthquake early warning" system independently developed by our country. After the Luding earthquake in Sichuan Province, earthquake warnings were issued in Chengdu, Ganzi, Luzhou, Ya'an and other places in Sichuan Province, including many people's TVs, mobile phones and other terminal devices. In short, earthquake early warning is to use the characteristic that electromagnetic waves (about 300,000 kilometers/second) are faster than seismic waves (about 4 kilometers/second) after an earthquake occurs to send out warnings that seismic waves are about to arrive in areas where the seismic waves have not yet arrived.
Source: Sichuan Provincial People’s Government official website
What are the earthquake early warnings? How important? Research shows that: if the warning time is 10 seconds, casualties are reduced by 39%; if the warning time is 20 seconds, casualties are reduced by 63%. The Wenchuan earthquake that year killed nearly 70,000 people, which caused us too much pain... If we had such an early warning system at that time, the death toll could be reduced by at least 30%.
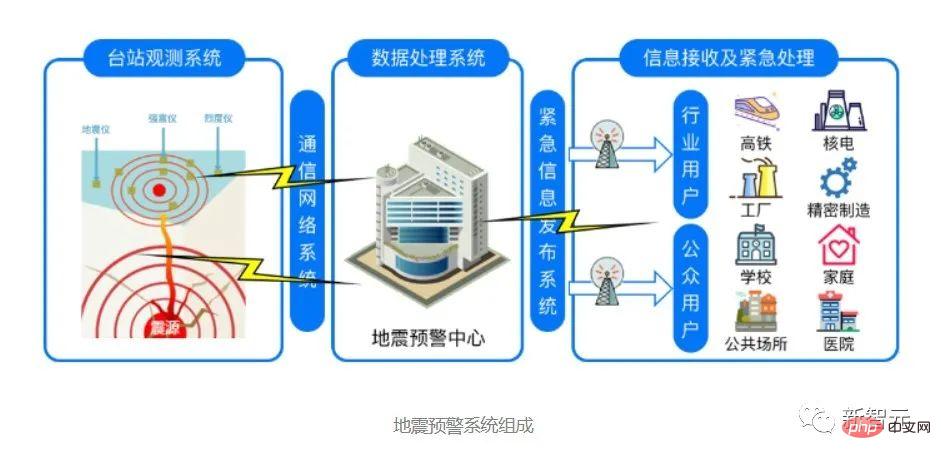
After the Wenchuan earthquake, my country increased its investment in disaster early warning in areas prone to earthquakes. As an earthquake-prone area, Sichuan Province began pilot installation of an early warning system in Chengdu in 2012. By the end of 2020, the early warning system can cover the entire province of Sichuan. The "earthquake early warning" system that played a big role this time is the mainland earthquake early warning network jointly built by the Chengdu High-tech Disaster Reduction Institute and the China Earthquake Administration. Seismic waves are divided into longitudinal waves and transverse waves. The former propagates fast and has little destructive power, while the latter propagates slowly and has high destructive power. The basic principle of earthquake early warning is to use the time difference between the two to issue an alarm.
After receiving the seismic longitudinal waves, the seismic observation instruments closer to the earthquake source will estimate the seismic parameters and their effects in real time and continuously, and send signals to the possible disaster areas where the seismic shear waves have not yet reached, a few seconds in advance. An alarm message is sent out within tens of seconds. According to an interview with Wang Dun, director of the institute, in Science and Technology Daily, after an earthquake early warning network is established using seismic sensors, once an earthquake occurs, the earthquake early warning system will use the characteristics of electromagnetic wave transmission speed to be much faster than seismic waves, and deploy it through reading and analysis. Recorded data from earthquake monitoring stations in various places are transmitted in real time to quickly determine the location and approximate magnitude of the earthquake, and then fully automatically issue early warnings to users who have not yet been affected, from seconds to tens of seconds in advance.
##Source: China Science and Technology Network
Due to earthquake waves affecting different areas The time is different, and the location of the terminal equipment that receives the earthquake early warning message is also inconsistent, so the early warning countdown time will also be different. Wang Tun said that after the 6.8-magnitude earthquake occurred in Luding County, the early warning network issued an early warning in 5 seconds when the 6.8-magnitude earthquake occurred in Luding, 7 seconds in advance to Kangding City, 20 seconds in advance to Ya'an City, and 20 seconds in advance to Chengdu City. 50 seconds advance warning.
my country’s earthquake early warning achievements, developed since the Wenchuan aftershock area, are already at the leading level in the world. Currently, the second-generation mainland earthquake early warning network is widely used in Sichuan. The second-generation earthquake early warning technology has comprehensively upgraded the front-end early warning stations, mid-end transmission response channels, and terminal processing systems based on distributed processing. It further optimizes the algorithm through the cloud computing operation center and can use 5G communication technology to improve system response. speed. However, all we can do now is to issue early warnings quickly after an earthquake occurs.
Predicting earthquakes that have not yet occurred is still an unsolvable problem for the whole world. Earthquake forecasting refers to predicting the time, location, and magnitude of possible future earthquakes based on monitoring data before an earthquake occurs. According to Director Wang Tun’s introduction:
What we do is earthquake early warning, not earthquake prediction. Imminent earthquake prediction is still a problem in the world. Earthquake early warning can only reduce casualties, but cannot prevent them.
Because it can only provide early warning but cannot predict, casualties cannot be avoided.
Earthquake prediction is still a world problemWhy is it so difficult to predict the next major earthquake? Let's start with a simple question: Where will the next big earthquake happen?
Research shows that larger faults often cause larger earthquakes. In theory, if all the faults were mapped, we should be able to put limits on the strongest earthquakes a given region could experience. However, estimating fault size and the corresponding energy released is not always straightforward. Faults often exhibit complex geometries, which complicates modeling of fault regions. Additionally, faults can rupture simultaneously: During New Zealand's 2016 Kaikōura earthquake, 13 different faults ruptured simultaneously. Furthermore, the magnitude of an earthquake does not necessarily correlate positively with its destructive power. Depending on where they occur, moderate-magnitude earthquakes can be more damaging than "large" earthquakes. For example, the 1994 Northridge magnitude 6.7 earthquake in California caused significant property damage and loss of life, while the 2018 Fiji magnitude 8.2 earthquake, which was 178 times stronger, did not cause any damage. Now, let’s look at this more complex question: When will the next big earthquake happen? Predicting time is the most difficult challenge in earthquake prediction. There are two theories that explain why predictions about time are flawed. The first theory is called the elastic rebound theory, which states that the earth's crust bends and deforms under intense pressure until it eventually breaks under the strain. Slip along a fracture (i.e., an earthquake) causes the rocks on either side to rebound to a less deformed state and release stored energy, allowing the process of accumulated strain to begin again. The second theory, known as signature earthquakes, describes the faults produced by the most studied earthquakes that appear to have distinct segments. In the intervals between earthquakes, these plates rupture repeatedly, accumulating the same amount of strain and thus producing earthquakes of similar magnitude. Assuming that these two theories have always existed, we can based on 1) The position of the maximum unstressed strain, 2) The time since the last earthquake, and precise knowledge of fault zones to predict when the next earthquake will occur. It can be seen that due to various complex factors in reality, it is difficult for us to predict the time when an earthquake will occur. So, what will happen if artificial intelligence technology is used? Theoretically, in earthquake prediction data, there are many patterns and signals that humans cannot see but that artificial intelligence can clearly detect. In 2018, researchers from Google and Harvard University demonstrated in a paper published in Nature How to predict aftershock locations using deep learning. The model looked for patterns in a database of more than 131,000 "mainshock-aftershock" events, and then tested its predictions on a database of 30,000 pairs of similar events. The results showed that the deep learning network was more reliable than a model known at the time as "Coulomb rupture stress change." ##Paper address: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-018-0438-y However, one year after the article was published, data scientist Rajiv Shah discovered when analyzing the results: the accuracy of the neural network was a bit ridiculously high. In subsequent recurrences, a very serious problem emerged - the data used to train and test the model overlapped (data leak). The short answer is that the model already knows the answers to the test during training. And this means that the test results have almost no practical significance. However, Nature ignored the researcher's questions and suggestions in the end... Despite this, scientists have not given up exploring this field, and various related studies are emerging one after another. At the 2021 Annual Meeting of the Seismological Society of America (SSA), a research team from Stanford University proposed a new method for real-time analysis of seismic signals - DeepShake, and later published In Seismological Research Letters. The training data for the model comes from earthquake records in California in 2019. The test results show that DeepShake can issue an alarm between 7 and 13 seconds before the arrival of high-intensity ground shaking. Compared with traditional earthquake early warning, DeepShake can directly issue early warning based on the characteristics of ground motion, eliminating some intermediate steps used by existing systems. The researchers say DeepShake demonstrates the potential of machine learning models to improve the speed and accuracy of earthquake warning systems. Paper link: https://doi.org/10.1785/02202101412022, Researchers from the Institute of Geology and Geophysics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Stanford University proposed a new method in a paper published in Science Advances that greatly improves the detection capabilities of earthquake monitoring networks located in urban areas. UrbanDenoiser Algorithm By filtering out background seismic noise, it improves overall signal quality and recovers signals that may have previously been too weak to record. Applications to Phalanx data and seismic sequences in urban areas show that UrbanDenoiser can improve signal quality and recover signals at signal-to-noise ratios as low as ~0dB. Paper link: https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.abl3564 What can be expected is that with the continuous improvement of computing power and the continuous improvement of data, AI will also have further development in the field of earthquake prediction. Finally, let us pray silently that more people affected by the disaster can be rescued. God bless Sichuan and God bless China. 
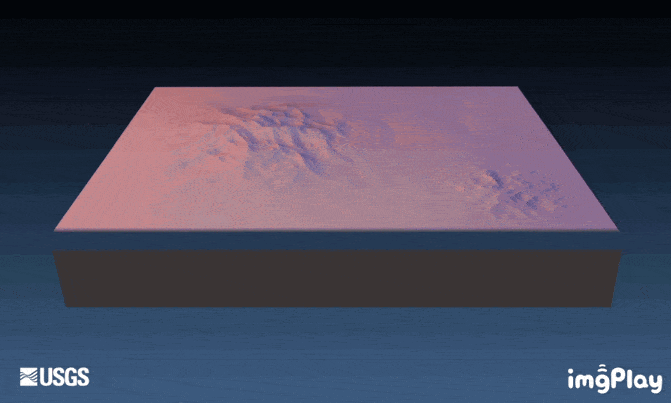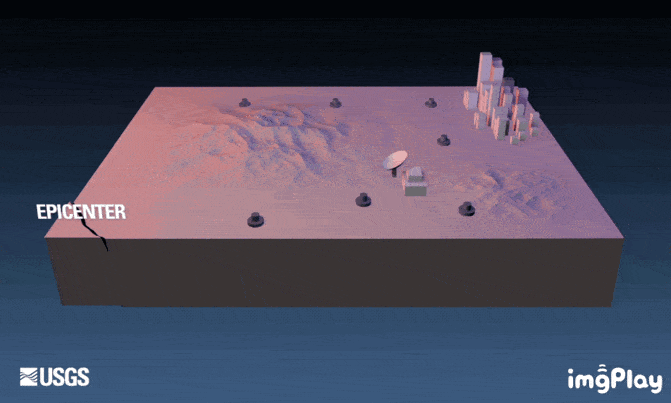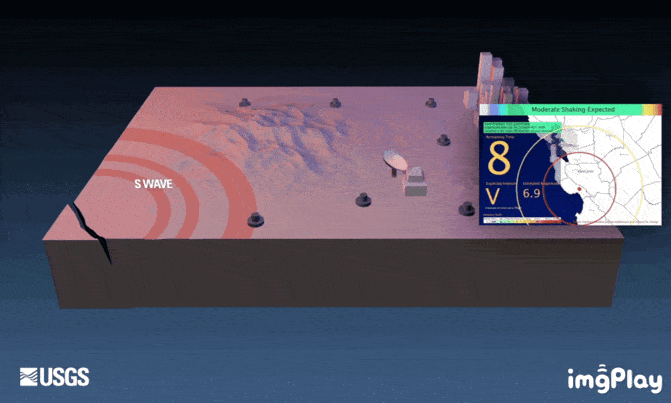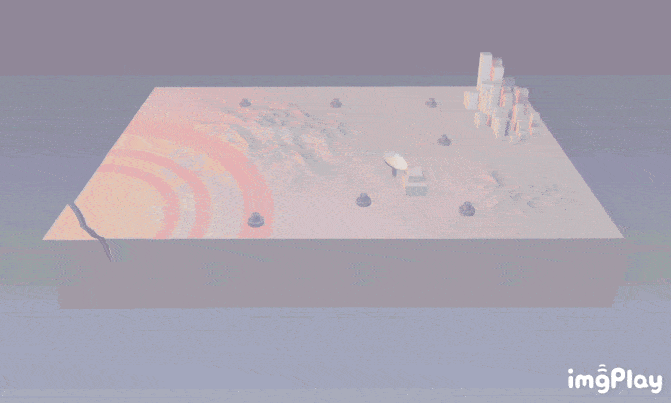
Is it feasible to use AI to predict earthquakes?


The above is the detailed content of 20 seconds warning, saved 127 children! Can AI predict the 6.8 magnitude earthquake in Luding, Sichuan?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 How to solve SQL parsing problem? Use greenlion/php-sql-parser!
Apr 17, 2025 pm 09:15 PM
How to solve SQL parsing problem? Use greenlion/php-sql-parser!
Apr 17, 2025 pm 09:15 PM
When developing a project that requires parsing SQL statements, I encountered a tricky problem: how to efficiently parse MySQL's SQL statements and extract the key information. After trying many methods, I found that the greenlion/php-sql-parser library can perfectly solve my needs.
 How to solve the complexity of WordPress installation and update using Composer
Apr 17, 2025 pm 10:54 PM
How to solve the complexity of WordPress installation and update using Composer
Apr 17, 2025 pm 10:54 PM
When managing WordPress websites, you often encounter complex operations such as installation, update, and multi-site conversion. These operations are not only time-consuming, but also prone to errors, causing the website to be paralyzed. Combining the WP-CLI core command with Composer can greatly simplify these tasks, improve efficiency and reliability. This article will introduce how to use Composer to solve these problems and improve the convenience of WordPress management.
 How to solve complex BelongsToThrough relationship problem in Laravel? Use Composer!
Apr 17, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
How to solve complex BelongsToThrough relationship problem in Laravel? Use Composer!
Apr 17, 2025 pm 09:54 PM
In Laravel development, dealing with complex model relationships has always been a challenge, especially when it comes to multi-level BelongsToThrough relationships. Recently, I encountered this problem in a project dealing with a multi-level model relationship, where traditional HasManyThrough relationships fail to meet the needs, resulting in data queries becoming complex and inefficient. After some exploration, I found the library staudenmeir/belongs-to-through, which easily installed and solved my troubles through Composer.
 How to solve the complex problem of PHP geodata processing? Use Composer and GeoPHP!
Apr 17, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
How to solve the complex problem of PHP geodata processing? Use Composer and GeoPHP!
Apr 17, 2025 pm 08:30 PM
When developing a Geographic Information System (GIS), I encountered a difficult problem: how to efficiently handle various geographic data formats such as WKT, WKB, GeoJSON, etc. in PHP. I've tried multiple methods, but none of them can effectively solve the conversion and operational issues between these formats. Finally, I found the GeoPHP library, which easily integrates through Composer, and it completely solved my troubles.
 How to solve the problem of PHP project code coverage reporting? Using php-coveralls is OK!
Apr 17, 2025 pm 08:03 PM
How to solve the problem of PHP project code coverage reporting? Using php-coveralls is OK!
Apr 17, 2025 pm 08:03 PM
When developing PHP projects, ensuring code coverage is an important part of ensuring code quality. However, when I was using TravisCI for continuous integration, I encountered a problem: the test coverage report was not uploaded to the Coveralls platform, resulting in the inability to monitor and improve code coverage. After some exploration, I found the tool php-coveralls, which not only solved my problem, but also greatly simplified the configuration process.
 git software installation tutorial
Apr 17, 2025 pm 12:06 PM
git software installation tutorial
Apr 17, 2025 pm 12:06 PM
Git Software Installation Guide: Visit the official Git website to download the installer for Windows, MacOS, or Linux. Run the installer and follow the prompts. Configure Git: Set username, email, and select a text editor. For Windows users, configure the Git Bash environment.
 How to solve the problem of virtual columns in Laravel model? Use stancl/virtualcolumn!
Apr 17, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
How to solve the problem of virtual columns in Laravel model? Use stancl/virtualcolumn!
Apr 17, 2025 pm 09:48 PM
During Laravel development, it is often necessary to add virtual columns to the model to handle complex data logic. However, adding virtual columns directly into the model can lead to complexity of database migration and maintenance. After I encountered this problem in my project, I successfully solved this problem by using the stancl/virtualcolumn library. This library not only simplifies the management of virtual columns, but also improves the maintainability and efficiency of the code.
 Solve CSS prefix problem using Composer: Practice of padaliyajay/php-autoprefixer library
Apr 17, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
Solve CSS prefix problem using Composer: Practice of padaliyajay/php-autoprefixer library
Apr 17, 2025 pm 11:27 PM
I'm having a tricky problem when developing a front-end project: I need to manually add a browser prefix to the CSS properties to ensure compatibility. This is not only time consuming, but also error-prone. After some exploration, I discovered the padaliyajay/php-autoprefixer library, which easily solved my troubles with Composer.



