
In Linux, the full name of mv is move, which means "move" in Chinese. Its main function is to move files or folders. It can also be used to modify the name. The syntax "mv [option] source file or directory target file or directory"; when the second parameter type (target) in the mv command is a file, the function of "renaming" the source file or directory is implemented.

#The operating environment of this tutorial: linux7.3 system, Dell G3 computer.
In Linux, the full name of the mv command is move, which means "move" in Chinese. Its main function is to move files or folders, similar to the cut function under Windows, and it can also be used to modify the name.
Linux mv command
The mv command is a file management command under the Linux operating system. The mv command mainly has three major functions, as follows:
Rename the file
Move the file
Move the directory
mv command format
mv [选项] 源文件或目录 目标文件或目录
The parameters are as follows:
-i: When moving files to a specified directory, If a file with the same name exists, the user is asked whether to overwrite it.
-f: When moving a file to a specified directory, if a file with the same name exists, the existing file with the same name will be overwritten without any prompt.
#-b: When moving a file to a specified directory, if a file with the same name exists, create a backup for it before overwriting it.
#-u: When moving a file to a specified directory, the move operation will only be performed when the source file is newer than the target file, or the target file does not exist.
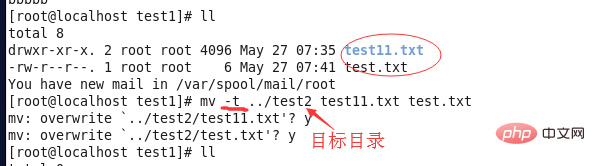
-t: When moving multiple files to a specified directory, use the -t parameter. At this time, the directory is first and the files are last.
Example
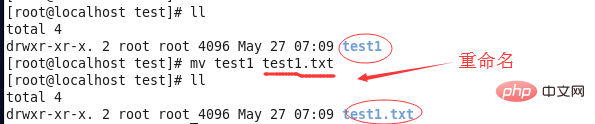
①When the second parameter type (target) in the mv command is a file, implement ** re- Function to name** source files or directories.
Note: There can only be one source file or directory here, because if there are multiple, there will be naming conflicts.
② When the second parameter type (target) in the mv command is a directory, the function of moving source files and directories is implemented.
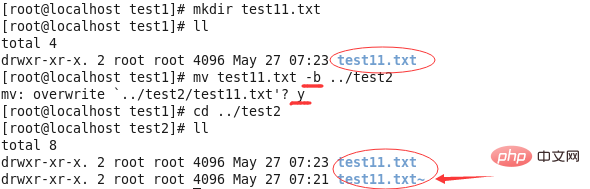
③mv -b: Back up the file before overwriting it.

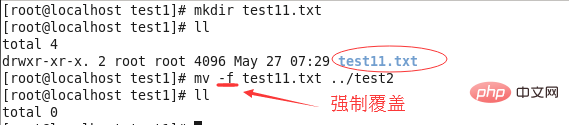
④mv -f (force): When overwriting a file, overwrite the existing file directly without asking.
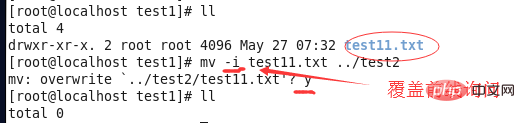
⑤mv -i: Before overwriting the file, you will be asked whether to overwrite it.
⑥mv -u: The target file can only be overwritten when the source file is the latest update.
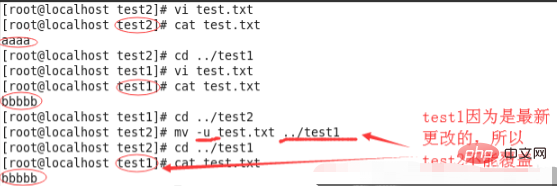
⑦mv -t: This method is suitable when multiple source files need to be moved. At this time, the target directory is first and the source files are last.
Related recommendations: "Linux Video Tutorial"
The above is the detailed content of What does linux mv mean?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!