How to connect Python to Mysql to implement a book lending system
Table structure of database
We need three tables here, a user table, a book table and a borrowing table. Note that our database is named bbs (book borrow system)
1. User table
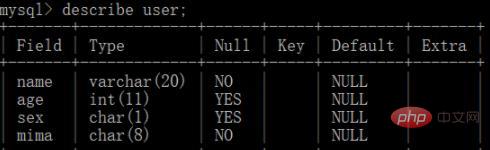
2. Book table
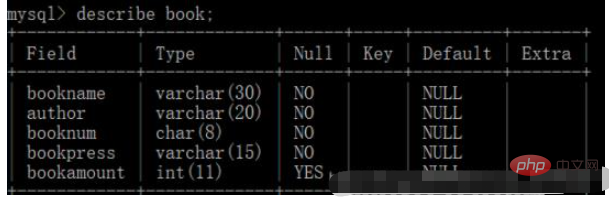
bookname: book title
author: author
booknum: book number
bookpress: publisher
bookamoun: Number of books
3. Borrowing table
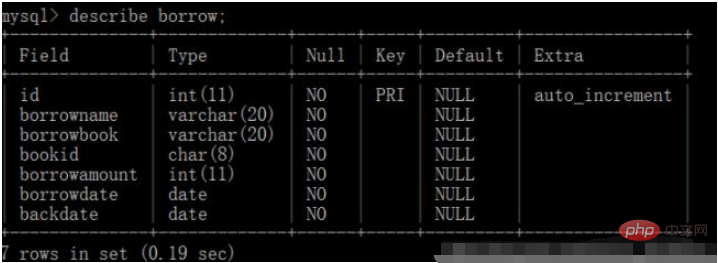
##id:borrowing numberPython program 1. Main program: book lending system.pyborrowname:borrower
borrowbook: Borrowing book
bookid: Book number is the same as the book list booknum
borrowamoun: Borrowing quantity
borrowdate: Borrowing date
borrowback: Returning date
# _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
import pymysql
import db_event
import book_manage
while True:
print("欢迎使用图书借阅系统\
[1]登陆 [2]注册 [3]退出")
choice = int(input("请输入您要进行的操作(数字):"))
if choice == 1:
name = input("请输入用户名:")
login_status=db_event.user_login(name)
if login_status==1:
book_manage.manage(name)
else:
print("登陆失败")
continue
elif choice==2:
create_user = db_event.user_create()
print("用户创建成功,您创建的用户信息如下:/n\
姓名:%s 年龄:%d 性别:%s 密码:%s" % (create_user[0], create_user[1], create_user[2], create_user[3]))
elif choice==3:
exit()
else:
print("无效操作!")
continueimport db_event
def manage(name):
while True:
print("欢迎进入图书系统\n\
[1]查询图书 [2] 借阅图书 [3]捐赠图书 [4]归还图书 [5]退出")
num = int(input('输入您的选择:'))
if num == 1:
db_event.book_select()
elif num == 2 :
chos=int(input("请选择[1]借阅 [2]续借 [3]查询借阅信息 [4]退出"))
if chos==1:
db_event.book_borrow(name)
elif chos==2:
db_event.borrow_again()
elif chos==3:
db_event.borrow_info_select(name)
elif chos==4:
continue
else:
print("无效操作")
elif num == 3 :
db_event.book_juanzeng()
elif num == 4 :
db_event.book_back()
elif num == 5 :
break
else:
print("无效输入!")# _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
import pymysql
import random
import string
def user_login(name):
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "ljz", "redhat", "bbs")
cursor = db.cursor()
sql = "SELECT name,mima FROM user WHERE name='%s'" %(name)
cursor.execute(sql)
results = cursor.fetchall()
if results:
res=results[0]
for i in range(3):
mima = input("请输入密码:")
if mima == res[1]:
print("登陆成功!")
login_status = 1
break
else:
login_status=0
print("密码输入不正确!请重新输入")
# print(login_status)
if login_status == 1 :
return login_status
else:
print("您已输入错误密码三次,无法登陆图书借阅系统,欢迎下次使用!")
login_status = 0
return login_status
else:
login_status = 0
print("您输入的用户不存在!")
return login_status
db.close()
#判断是否登陆成功,1为成功,0为不成功
# login_status=user_login()
# if login_status==1:
# print("ok")
# else:
# print("no")
#关闭数据库连接
# curcor.close()
# db.close()
def user_create():
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "ljz", "redhat", "bbs")
cursor = db.cursor()
name=input("请输入姓名:")
age=int(input("请输入年龄:"))
sex=input("请输入性别[M]男 [W]女 :")
mima=input("为您的用户设置一个8位数密码:")
sql = "INSERT INTO user VALUES('%s',%s,'%s','%s')" %(name,age,sex,mima)
cursor.execute(sql)
db.commit()
sql1="SELECT * FROM user WHERE name='%s'" %(name)
cursor.execute(sql1)
results=cursor.fetchone()
return results
db.close()
#create_user=user_create()
#print("用户创建成功,您创建的用户信息如下:/n\
# 姓名:%s 年龄:%d 性别:%s 密码:%s" %(create_user[0],create_user[1],create_user[2],create_user[3]))
def book_info_select(x,y):
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "ljz", "redhat", "bbs")
cursor = db.cursor()
sql = "SELECT * FROM book WHERE %s='%s'" %(x,y)
cursor.execute(sql)
results=cursor.fetchone()
if results:
print("书名:%s 作者:%s 书籍编号:%s 出版社:%s 剩余数量:%d " %(results[0],results[1],results[2],results[3],results[4]))
else:
print("没有您所要查询的图书")
db.close()
def book_select():
a = int(input("输入您要查询的图书关键信息\
[1]书名 [2]作者 [3]书籍号 [4]出版社"))
b=""
if a == 1 :
b="bookname"
name=input("请输入要查询的书名:")
book_info_select(b,name)
elif a == 2 :
b="author"
auth=input("请输入作者名:")
book_info_select(b,auth)
elif a == 3 :
b="booknum"
num=input("请输入书籍编号")
book_info_select(b,num)
elif a == 4 :
b="bookpress"
press=input("请输入出版社:")
book_info_select(b,press)
else:
print("输入有误")
book_select()
def gen_code(len=8):
code_str = string.ascii_letters + string.digits
return ''.join(random.sample(code_str, len))
def book_add(name,auth,press,amount):
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "ljz", "redhat", "bbs")
cursor = db.cursor()
num=gen_code()
sql = "INSERT INTO book VALUES('%s','%s','%s','%s',%s)" %(name,auth,num,press,amount)
sql1 = "SELECT booknum FROM book"
cursor.execute(sql1)
res = cursor.fetchall()
list=[]
for i in res :
list.append(i)
try:
while True:
if num in list:
gen_code()
else:
cursor.execute(sql)
db.commit()
print("图书捐赠成功,谢谢您!")
break
except:
print("输入图书数目错误!")
db.rollback()
db.close()
def book_update_add(name,auth,press,amount):
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "ljz", "redhat", "bbs")
cursor = db.cursor()
sql="UPDATE book SET bookamount=bookamount+%s WHERE bookname='%s' AND author='%s' AND bookpress='%s'" %(amount,name,auth,press)
try:
cursor.execute(sql)
db.commit()
print("图书捐赠成功,谢谢您!")
except:
print("输入图书数目错误!")
db.rollback()
db.close()
def book_juanzeng():
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "ljz", "redhat", "bbs")
cursor = db.cursor()
name=input("请输入您要捐赠的图书书名:")
auth=input("请输入您要捐赠的图书作者:")
press=input("请输入您要捐赠的图书的出版社:")
amount = int(input("输入您要捐赠的数目:"))
sql = "SELECT * FROM book WHERE bookname='%s'AND author='%s' AND bookpress='%s'" %(name,auth,press)
cursor.execute(sql)
results=cursor.fetchone()
if results:
book_update_add(name,auth,press,amount)
else:
book_add(name,auth,press,amount)
db.close()
def book_if_borrow(booknum,amount):
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "ljz", "redhat", "bbs")
cursor = db.cursor()
sql = "SELECT bookamount FROM book WHERE booknum='%s'" %(booknum)
cursor.execute(sql)
res = cursor.fetchall()
if res:
if res[0][0] >= amount :
#编号为booknum的书的数量还有,可以借
return True
else:
print("您所需要的编号为%s的书籍当前图书馆只有%d本,不满足您的需求" %(booknum,res[0][0]))
return False
else:
print("查无此书,请确认您的书籍编号!")
return False
db.close()
def book_borrow_after(amount,booknum):
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "ljz", "redhat", "bbs")
cursor = db.cursor()
sql = "UPDATE book SET bookamount=bookamount-%s WHERE booknum='%s'" %(amount,booknum)
cursor.execute(sql)
db.commit()
db.close()
def borrow_add(name,booknum,amount):
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "ljz", "redhat", "bbs")
cursor = db.cursor()
days = int(input("请输入您选择借阅的天数(不可超过365天):"))
sql = "INSERT INTO borrow VALUES(NULL,'%s',(SELECT bookname FROM book WHERE booknum='%s'),'%s',%s,CURDATE(),DATE_ADD(CURDATE(),INTERVAL %s DAY))" %(name,booknum,booknum,amount,days)
cursor.execute(sql)
db.commit()
def select_after_borrow(booknum,name):
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "ljz", "redhat", "bbs")
cursor = db.cursor()
sql2 = "SELECT * FROM borrow WHERE bookid='%s' AND borrowname='%s'" % (booknum, name)
cursor.execute(sql2)
return cursor.fetchall()
def book_borrow(name):
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "ljz", "redhat", "bbs")
cursor = db.cursor()
booknum=input("请输入您要借阅的图书编号:")
amount=int(input("请输入您要借阅的书籍个数:"))
sql1 = "SELECT * FROM book WHERE booknum='%s'" % (booknum)
cursor.execute(sql1)
result = cursor.fetchone()
res = book_if_borrow(booknum,amount)
if res:
print("您要借阅的书籍书名:%s 作者:%s 书籍编号:%s 出版社: %s 当前剩余:%d本 借后剩余:%d本" %(result[0],result[1],result[2],result[3],result[4],result[4]-amount))
book_borrow_after(amount,booknum)
#db.commit()
borrow_add(name,booknum,amount)
info=select_after_borrow(booknum,name)
print("以下是您的借阅图书信息,注意借阅号,这将是您还书的凭证!\n\
借阅号:%d 借阅人:%s 借阅图书:%s 图书编号:%s 借阅数量:%d 借阅日期:%s 归还日期:%s" %(info[-1][0],info[-1][1],info[-1][2],info[-1][3],info[-1][4],info[-1][5],info[-1][6]))
print("借阅成功")
while True:
a=int(input("请输入您选择:[1]继续借阅 [2]退出"))
if a == 1:
book_borrow(name)
break
elif a == 2 :
break
else:
print("无效操作")
else:
print("借阅失败")
while True:
a=int(input("请输入您选择:[1]继续借阅 [2]退出"))
if a == 1:
book_borrow(name)
break
elif a == 2 :
break
else:
print("无效操作")
db.close()
def back_if_over(id):
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "ljz", "redhat", "bbs")
cursor = db.cursor()
sql = "SELECT * FROM borrow WHERE backdate >= CURDATE() AND id = %s" %(id)
cursor.execute(sql)
res=cursor.fetchall()
if res:
return True
else:
return False
db.close()
def book_back_update(id):
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "ljz", "redhat", "bbs")
cursor = db.cursor()
sql = "UPDATE book SET bookamount=bookamount+(SELECT borrowamount FROM borrow WHERE id = %s) WHERE booknum=(SELECT bookid FROM borrow WHERE id = %s)" %(id,id)
cursor.execute(sql)
db.commit()
db.close()
def borrow_back_update(id):
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "ljz", "redhat", "bbs")
cursor = db.cursor()
sql = "DELETE FROM borrow WHERE id=%s" %(id)
cursor.execute(sql)
db.commit()
db.close()
def book_back():
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "ljz", "redhat", "bbs")
cursor = db.cursor()
while True:
id = int(input("请输入您的借阅号:"))
sql1 = "SELECT * FROM borrow WHERE id=%s" %(id)
cursor.execute(sql1)
info =cursor.fetchone()
if info:
print("以下是您的借阅图书信息,注意借阅号,这将是您还书的凭证!\n\
借阅号:%d 借阅人:%s 借阅图书:%s 图书编号:%s 借阅数量:%d 借阅日期:%s 归还日期:%s" % (info[0], info[1], info[2], info[3], info[4], info[5], info[6]))
choice=int(input("请确认您的归还借书信息:[1]确认 [2]返回 [3]退出"))
if choice == 1 :
#判断是否逾期:
if back_if_over(id):
book_back_update(id)
borrow_back_update(id)
print("还书成功")
break
else:
print("您已逾期,请联系管理员!")
break
elif choice == 2:
continue
elif choice == 3 :
break
else:
print("无效输入")
else:
print("请输入正确的借阅号")
def borrow_info_again(id,day):
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "ljz", "redhat", "bbs")
cursor = db.cursor()
sql1 = "SELECT * FROM borrow WHERE id=%s" % (id)
cursor.execute(sql1)
info = cursor.fetchone()
print("以下是您的借阅图书信息:\n\
借阅号:%d 借阅人:%s 续借天数:%d 借阅图书:%s 图书编号:%s 借阅数量:%d 初始借阅日期:%s 归还日期:%s" %(info[0], info[1],day,info[2], info[3], info[4], info[5], info[6]))
db.close()
def borrow_update_again(id):
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "ljz", "redhat", "bbs")
cursor = db.cursor()
a=int(input("请输入您的续借天数(不超过31天):"))
if a > 31 :
print("您的借阅天数已超过系统权限,如要借阅,请联系管理员!")
else:
sql="UPDATE borrow SET backdate=DATE_ADD(backdate,INTERVAL %s DAY) WHERE id=%s" %(a,id)
cursor.execute(sql)
db.commit()
db.close()
return a
def borrow_again():
id=int(input("输入您的借阅号:"))
if back_if_over(id):
day=borrow_update_again(id)
borrow_info_again(id,day)
print("续借成功")
else:
print("您已逾期,请先联系管理员再进行操作,谢谢!")
def borrow_info_select(name):
db = pymysql.connect("localhost", "ljz", "redhat", "bbs")
cursor = db.cursor()
sql = "SELECT * FROM borrow WHERE borrowname='%s'" %(name)
cursor.execute(sql)
res=cursor.fetchall()
if res:
for i in range(len(res)):
print("以下是您的第%d条借阅图书信息:\n\
借阅号:%d 借阅人:%s 借阅图书:%s 图书编号:%s 借阅数量:%d 借阅日期:%s 归还日期:%s" % (i+1,res[i][0], res[i][1], res[i][2], res[i][3], res[i][4], res[i][5], res[i][6]))
else:
print("您没有借阅图书")
db.close()The above is the detailed content of How to connect Python to Mysql to implement a book lending system. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python: Automation, Scripting, and Task Management
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:14 AM
Python excels in automation, scripting, and task management. 1) Automation: File backup is realized through standard libraries such as os and shutil. 2) Script writing: Use the psutil library to monitor system resources. 3) Task management: Use the schedule library to schedule tasks. Python's ease of use and rich library support makes it the preferred tool in these areas.
 Golang vs. Python: Concurrency and Multithreading
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Golang vs. Python: Concurrency and Multithreading
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Golang is more suitable for high concurrency tasks, while Python has more advantages in flexibility. 1.Golang efficiently handles concurrency through goroutine and channel. 2. Python relies on threading and asyncio, which is affected by GIL, but provides multiple concurrency methods. The choice should be based on specific needs.
 Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python vs. JavaScript: The Learning Curve and Ease of Use
Apr 16, 2025 am 12:12 AM
Python is more suitable for beginners, with a smooth learning curve and concise syntax; JavaScript is suitable for front-end development, with a steep learning curve and flexible syntax. 1. Python syntax is intuitive and suitable for data science and back-end development. 2. JavaScript is flexible and widely used in front-end and server-side programming.
 Golang vs. Python: Key Differences and Similarities
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Golang vs. Python: Key Differences and Similarities
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:15 AM
Golang and Python each have their own advantages: Golang is suitable for high performance and concurrent programming, while Python is suitable for data science and web development. Golang is known for its concurrency model and efficient performance, while Python is known for its concise syntax and rich library ecosystem.
 MySQL's Role: Databases in Web Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
MySQL's Role: Databases in Web Applications
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:23 AM
The main role of MySQL in web applications is to store and manage data. 1.MySQL efficiently processes user information, product catalogs, transaction records and other data. 2. Through SQL query, developers can extract information from the database to generate dynamic content. 3.MySQL works based on the client-server model to ensure acceptable query speed.
 How to use VSCode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
How to use VSCode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:21 PM
Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is a cross-platform, open source and free code editor developed by Microsoft. It is known for its lightweight, scalability and support for a wide range of programming languages. To install VSCode, please visit the official website to download and run the installer. When using VSCode, you can create new projects, edit code, debug code, navigate projects, expand VSCode, and manage settings. VSCode is available for Windows, macOS, and Linux, supports multiple programming languages and provides various extensions through Marketplace. Its advantages include lightweight, scalability, extensive language support, rich features and version
 Which one is better, vscode or visual studio
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:36 PM
Which one is better, vscode or visual studio
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:36 PM
Depending on the specific needs and project size, choose the most suitable IDE: large projects (especially C#, C) and complex debugging: Visual Studio, which provides powerful debugging capabilities and perfect support for large projects. Small projects, rapid prototyping, low configuration machines: VS Code, lightweight, fast startup speed, low resource utilization, and extremely high scalability. Ultimately, by trying and experiencing VS Code and Visual Studio, you can find the best solution for you. You can even consider using both for the best results.
 What is the difference between vscode and pycharm
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
What is the difference between vscode and pycharm
Apr 15, 2025 pm 11:54 PM
The main differences between VS Code and PyCharm are: 1. Extensibility: VS Code is highly scalable and has a rich plug-in market, while PyCharm has wider functions by default; 2. Price: VS Code is free and open source, and PyCharm is paid for professional version; 3. User interface: VS Code is modern and friendly, and PyCharm is more complex; 4. Code navigation: VS Code is suitable for small projects, and PyCharm is more suitable for large projects; 5. Debugging: VS Code is basic, and PyCharm is more powerful; 6. Code refactoring: VS Code is basic, and PyCharm is richer; 7. Code




