java web instance analysis
Text
In actual work projects, cache has become a key component of high-concurrency and high-performance architecture. So why can Redis be used as a cache? First of all, there are two main characteristics of caching:
Being in memory/CPU with good access performance in a layered system,
Cache data Saturated, with a good data elimination mechanism
Because Redis naturally has these two characteristics, Redis is based on memory operations, and it has a complete data elimination mechanism, which is very suitable as a cache component. .
Among them, based on memory operation, the capacity can be 32-96GB, and the average operation time is 100ns, and the operation efficiency is high. Moreover, there are many data elimination mechanisms. After Redis 4.0, there are 8 types, which makes Redis applicable to many scenarios as a cache.
So why does Redis cache need a data elimination mechanism? What are the 8 data elimination mechanisms?
Data elimination mechanism
The Redis cache is implemented based on memory, so its cache capacity is limited. When the cache is full, how should Redis handle it?
Redis When the cache is full, Redis needs a cache data elimination mechanism to select and delete some data through certain elimination rules so that the cache service can be used again. So what elimination strategies does Redis use to delete data?
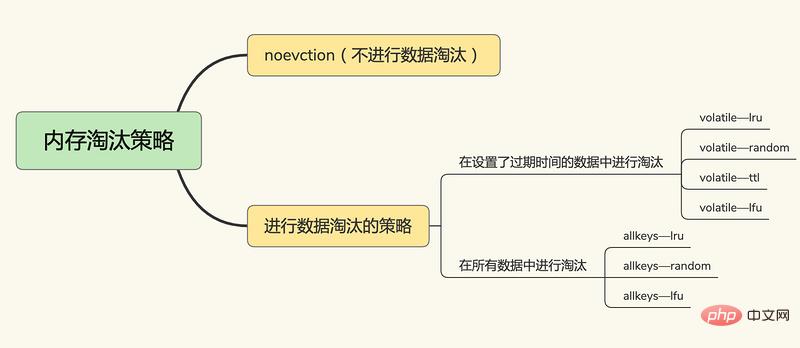
After Redis 4.0, there are 6 2 Redis cache elimination strategies, including three major categories:
No data elimination
noeviction, no data elimination is performed. When the cache is full, Redis does not provide services and directly returns an error.
In the key-value pair that sets the expiration time,
volatile-random, in the key that sets the expiration time Randomly delete
volatile-ttl from the value pairs. The key-value pairs that set the expiration time will be deleted based on the expiration time. The earlier the expiration date, the earlier it will be deleted.
volatile-lru, based on the LRU (Least Recently Used) algorithm to filter key-value pairs with an expiration time, and filter data based on the least recently used principle
volatile-lfu uses the LFU (Least Frequently Used) algorithm to select the key-value pairs with expiration time set, and filter the data by using the key-value pairs with the least frequency.
Among all key-value pairs,
allkeys-random, randomly selected from all key-value pairs And delete the data
allkeys-lru, use the LRU algorithm to filter in all data
- ##allkeys-lfu, use the LFU algorithm to filter in all data Filter
##Note: LRU (Least Recently Used) algorithm, LRU maintains a two-way linked list. The head and tail of the linked list represent the MRU end and the LRU end respectively, representing the most recently used data and the most recently least commonly used data respectively. When the LRU algorithm is actually implemented, it is necessary to use a linked list to manage all cached data, which will bring additional space overhead. Moreover, when data is accessed, the data needs to be moved to the MRU on the linked list. If a large amount of data is accessed, many linked list move operations will occur, which will be very time-consuming and reduce Redis cache performance.
Among them, LRU and LFU are implemented based on the lru and refcount attributes of redisObject, the object structure of Redis:
typedef struct redisObject {
unsigned type:4;
unsigned encoding:4;
// 对象最后一次被访问的时间
unsigned lru:LRU_BITS; /* LRU time (relative to global lru_clock) or
* LFU data (least significant 8 bits frequency
// 引用计数 * and most significant 16 bits access time). */
int refcount;
void *ptr;
} robj;Redis’ LRU will use redisObject’s lru to record the last access time , randomly select the number configured with the parameter maxmemory-samples as a candidate set, and select the data with the smallest lru attribute value among them to eliminate them.
In actual projects, how to choose the data elimination mechanism?
- Prioritize the allkeys-lru algorithm to keep the most recently accessed data in the cache to improve application access performance.
- The top data uses the volatile-lru algorithm. The top data does not set a cache expiration time. Other data sets an expiration time and is filtered based on LRU rules.
- After understanding the Redis cache elimination mechanism, let’s see how many modes Redis has as a cache?
Redis cache mode
Redis cache mode can be divided into read-only cache and read-write cache based on whether to receive write requests:
Read-only cache: only handles read operations, all All update operations are performed in the database, so there is no risk of data loss.
- Cache Aside mode
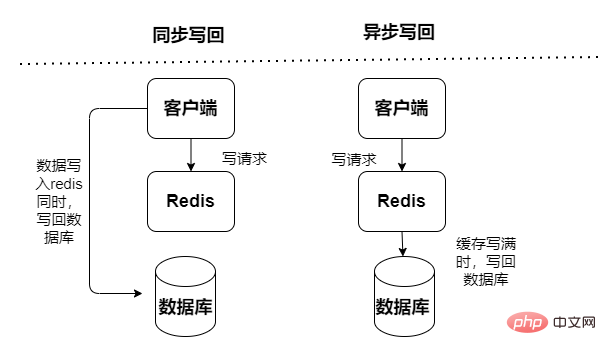
##Read and write cache, read and write operations are performed in the cache, appear Downtime failure will lead to data loss. Cache write-back data to the database is divided into two types: synchronous and asynchronous: 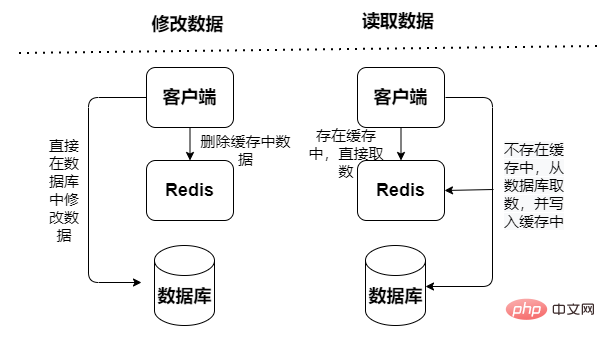
- Write-Through mode
- Asynchronous: There is a risk of data loss, its focus To provide low latency access
Write-Behind Mode
Cache Aside Mode
Query The data is first read from the cache. If it does not exist in the cache, the data is read from the database. After the data is obtained, it is updated into the cache. However, when updating data, the data in the database will be updated first. Then invalidate the cached data.
Moreover, the Cache Aside mode will have concurrency risks: the read operation will not hit the cache, and then the database will be queried to fetch the data. The data has been queried but has not been put into the cache. At the same time, an update write operation will invalidate the cache. , and then the read operation loads the query data into the cache, resulting in cached dirty data.
Read/Write-Throug mode
Both query data and update data directly access the cache service, the cache service updates the data to the database synchronously. The probability of dirty data is low, but it relies heavily on cache and has greater requirements for the stability of the cache service. However, synchronous updates will lead to poor performance.
Write Behind mode
Both query data and update data access the cache service directly, but the cache service uses an asynchronous way to update the data to the database (through asynchronous tasks) Speed It is fast and the efficiency will be very high, but the consistency of the data is relatively poor, there may be data loss, and the implementation logic is also relatively complex.
In actual project development, the cache mode is selected according to the actual business scenario requirements. After understanding the above, why do we need to use redis cache in our application?
Using Redis cache in applications can improve system performance and concurrency, mainly reflected in
High performance: based on memory query, KV structure, simple logical operation
High concurrency: Mysql can only support about 2,000 requests per second, and Redis can easily exceed 1W per second. Allowing more than 80% of queries to go through the cache and less than 20% of the queries to go through the database can greatly improve the system throughput
Although using Redis cache can greatly improve the performance of the system, using Without caching, some problems will arise, such as bidirectional inconsistency between the cache and the database, cache avalanche, etc. How to solve these problems?
Common problems with using cache
When using cache, there will be some problems, mainly reflected in:
The cache is inconsistent with the double write of the database
Cache avalanche: Redis cache cannot handle a large number of application requests, and the transfer to the database layer causes a surge in pressure on the database layer;
Cache penetration: access The data does not exist in the Redis cache and the database, causing a large number of accesses to penetrate the cache and transfer directly to the database, causing a surge in pressure on the database layer;
Cache breakdown: the cache cannot handle high-frequency hot spots Data, resulting in direct high-frequency access to the database, resulting in a surge in pressure on the database layer;
The cache is inconsistent with the database data
Read-only cache (Cache Aside mode)
For read-only cache (Cache Aside mode), read operations all occur in the cache, and data inconsistency only occurs in delete operations (new The operation will not happen, because new additions will only be processed in the database). When a deletion operation occurs, the cache will mark the data as invalid and update the database. Therefore, during the process of updating the database and deleting cached values, regardless of the execution order of the two operations, as long as one operation fails, data inconsistency will occur.
The above is the detailed content of java web instance analysis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to Square Root in Java. Here we discuss how Square Root works in Java with example and its code implementation respectively.
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to the Armstrong Number in Java. Here we discuss an introduction to Armstrong's number in java along with some of the code.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is






