
This library management system uses the IDEA development tool to realize
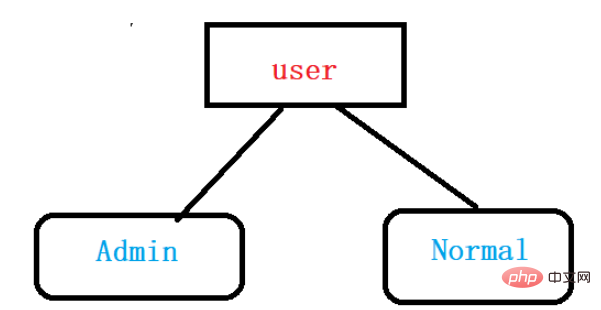
There are two identities for access to the library system:
1. Administrator identity:
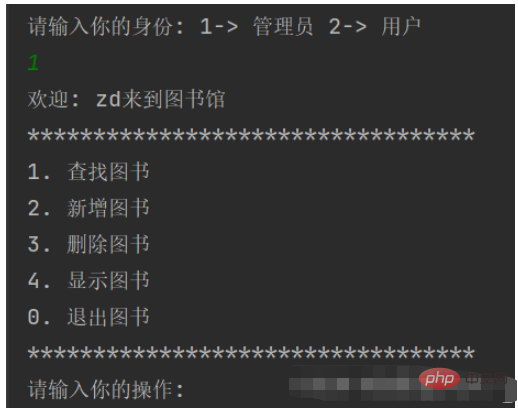
2. Ordinary user identity:
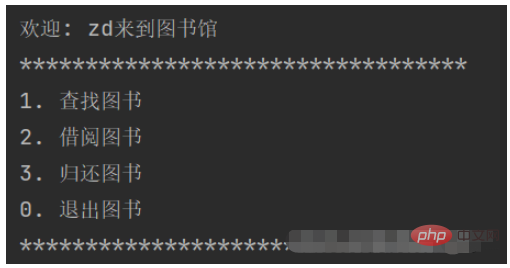
us There are three packages in total, namely book, operations, and user implementation.
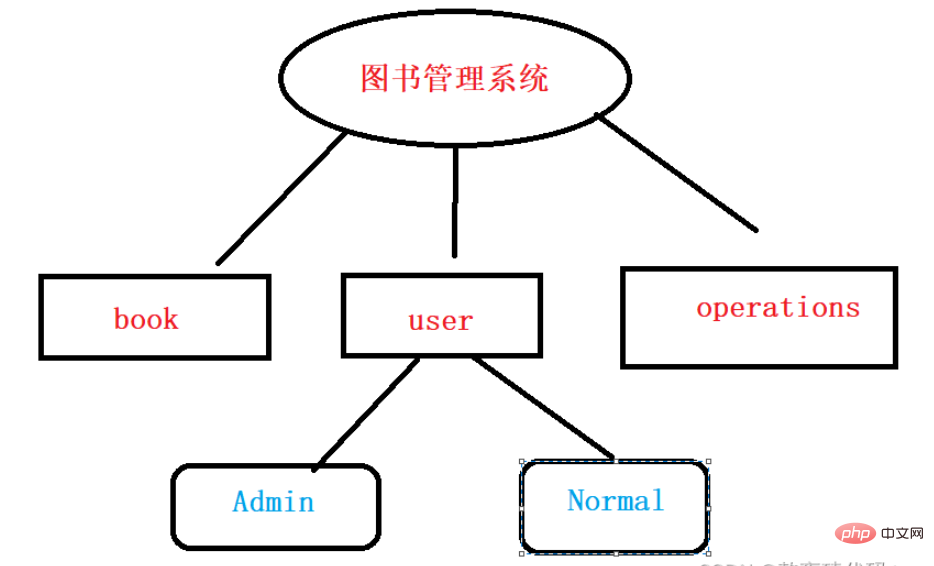
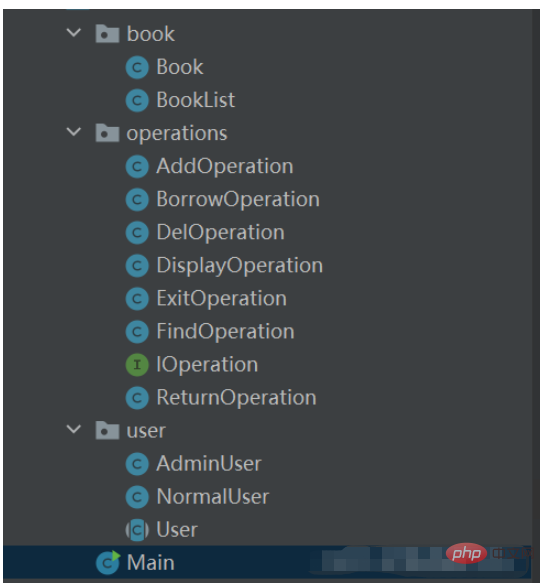
import book.BookList;
import user.AdminUser;
import user.NormalUser;
import user.User;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.先初始化图书库,以及初始化:
BookList bookList = new BookList();
//2.登录
User user = login();//向上转型,User接受管理员或者用户对象
//3.打印菜单,进行具体操作
while(true) {
int choice = user.menu();
user.doOperation(choice,bookList);
}
}
} public static User login() {
System.out.println("请输入你的姓名: ");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String userName = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入你的身份: 1-> 管理员 2-> 用户");
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
if(choice == 1) {
return new AdminUser(userName);
}else {
return new NormalUser(userName);
}
}
package user;
import book.BookList;
import operations.IOperation;
public abstract class User {
protected String name;
IOperation[] iOperations;
public User(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public abstract int menu();
public void doOperation(int choice, BookList bookList) {
iOperations[choice].work(bookList);
}
}package user;
import operations.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AdminUser extends User{
public AdminUser(String name) {
super(name);
this.iOperations = new IOperation[]{
new ExitOperation(),
new FindOperation(),
new AddOperation(),
new DelOperation(),
new DisplayOperation()
};
}
public int menu() {
System.out.println("欢迎: "+name+"来到图书馆");
System.out.println("**********************************");
System.out.println("1. 查找图书");
System.out.println("2. 新增图书");
System.out.println("3. 删除图书");
System.out.println("4. 显示图书");
System.out.println("0. 退出图书");
System.out.println("**********************************");
System.out.println("请输入你的操作: ");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
return choice;
}
}package user;
import operations.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class NormalUser extends User{
public NormalUser(String name) {
super(name);
this.iOperations = new IOperation[]{
new ExitOperation(),
new FindOperation(),
new BorrowOperation(),
new ReturnOperation()
};
}
public int menu() {
System.out.println("欢迎: "+name+"来到图书馆");
System.out.println("**********************************");
System.out.println("1. 查找图书");
System.out.println("2. 借阅图书");
System.out.println("3. 归还图书");
System.out.println("0. 退出图书");
System.out.println("**********************************");
System.out.println("请输入你的操作: ");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
return choice;
}
}package book;
public class Book {
private String name;//书名
private String author;//作者
private int price;//价格
private String type;//书的类型
private boolean isBorrowed;//书默认未借出
public Book(String name, String author, int price, String type) {
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.price = price;
this.type = type;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
public boolean isBorrowed() {
return isBorrowed;
}
public void setBorrowed(boolean borrowed) {
isBorrowed = borrowed;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", author='" + author + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
", type='" + type + '\'' +
","+ ((isBorrowed == true) ? "该书已借出" : "该书未借出" )+
'}';
}
}package book;
public class BookList {
public Book[] books = new Book[100];
public int usedSize;//用来存当前共有多少本书
/**
* 事先通过代码块
*
* 事先存进去三本书
*/
{
books[0] = new Book("java","高斯林",95,"IT");
books[1] = new Book("C++","姚琳",93,"IT");
books[2] = new Book("python","马瑟斯",80,"IT");
this.usedSize = 3;
}
public Book getPos(int pos) {
//获取某一位置的书
return books[pos];
}
public void setBooks(Book book,int pos) {
//存储一本书 到指定位置
books[pos] = book;
}
public int getUsedSize() {
return usedSize;
}
public void setUsedSize(int usedSize) {
this.usedSize = usedSize;
}
}package operations;
import book.BookList;
public interface IOperation {
void work(BookList bookList);
}package operations;
import book.Book;
import book.BookList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AddOperation implements IOperation{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("新增图书! ");
System.out.println("请输入要新增的图书的名字: ");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入要新增的图书的作者: ");
String author = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("请输入要新增的图书的价格: ");
int price = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入要新增的图书的类型: ");
String type = scanner.nextLine();
Book book = new Book(name,author,price,type);
//1.获取当前书存放的位置
int curSize = bookList.getUsedSize();
//2.把书放在指定位置
bookList.setBooks(book,curSize);
//3.更新书的个数
bookList.setUsedSize(curSize+1);
}
}package operations;
import book.Book;
import book.BookList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class BorrowOperation implements IOperation{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("借阅图书! ");
System.out.println("请输入要借阅的图书的名字: ");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = scanner.nextLine();
for (int i = 0; i < bookList.getUsedSize(); i++) {
Book book = bookList.getPos(i);
if(name.equals(book.getName())) {
if(book.isBorrowed()) {
System.out.println("该书已经被借出! ");
}else {
book.setBorrowed(true);
System.out.println("借阅图书成功! ");
return;
}
}
}
System.out.println("没有你要借阅的书! ");
}
}package operations;
import book.Book;
import book.BookList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class DelOperation implements IOperation{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("删除图书! ");
System.out.println("请输入要删除的图书: ");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = scanner.nextLine();
//查找图书是否有此图书,记录下标
int index = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < bookList.getUsedSize(); i++) {
Book book = bookList.getPos(i);
if(name.equals(book.getName())) {
index = i;
break;
}
}
if(index == -1) {
System.out.println("没有 "+name+"这本书!");
return;
}
for (int i = index; i < bookList.getUsedSize()-1; i++) {
Book book = bookList.getPos(i+1);
bookList.setBooks(book,i);
}
//删除的书,要置空
bookList.setBooks(null, bookList.getUsedSize()-1);
bookList.setUsedSize(bookList.getUsedSize()-1);
}
}package operations;
import book.Book;
import book.BookList;
public class DisplayOperation implements IOperation{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("显示图书! ");
for (int i = 0; i < bookList.getUsedSize(); i++) {
Book book = bookList.getPos(i);
System.out.println(book);
}
}
}package operations;
import book.BookList;
public class ExitOperation implements IOperation{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("退出系统! ");
System.exit(0);
}
}package operations;
import book.Book;
import book.BookList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class FindOperation implements IOperation{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
//查找图书
System.out.println("查找图书! ");
System.out.println("请输入要查找的图书: ");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = scanner.nextLine();
for (int i = 0; i < bookList.getUsedSize(); i++) {
Book book = bookList.getPos(i);
if(name.equals(book.getName())) {
System.out.println("找到了! ");
System.out.println(book);
return;
}
}
System.out.println("没有这本书! ");
}
}package operations;
import book.Book;
import book.BookList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ReturnOperation implements IOperation{
@Override
public void work(BookList bookList) {
System.out.println("归还图书! ");
System.out.println("请输入要归还的图书的名字: ");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = scanner.nextLine();
for (int i = 0; i < bookList.getUsedSize(); i++) {
Book book = bookList.getPos(i);
if(name.equals(book.getName())) {
book.setBorrowed(false);
System.out.println("归还图书成功! ");
return;
}
}
System.out.println("没有你要归还的书! ");
}
}The above is the detailed content of How to implement a library management system using Java code. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




