How to implement binary search in Java
Binary search
Overview
Binary search is also called binary search (Binary Search), which is a more efficient search method.
However, half search requires that the linear table must adopt a sequential storage structure, and the elements in the table must be arranged in order by keywords.
Merge sorting uses the idea of dichotomy. First, you need an array sorted from small to large. First compare the middle value. If it is larger than what you are looking for, search forward. Take the first half of the middle value and then find the middle value before comparing.
If it is smaller than what you are looking for, search backwards, take the half after the middle value and then take the middle value and compare.
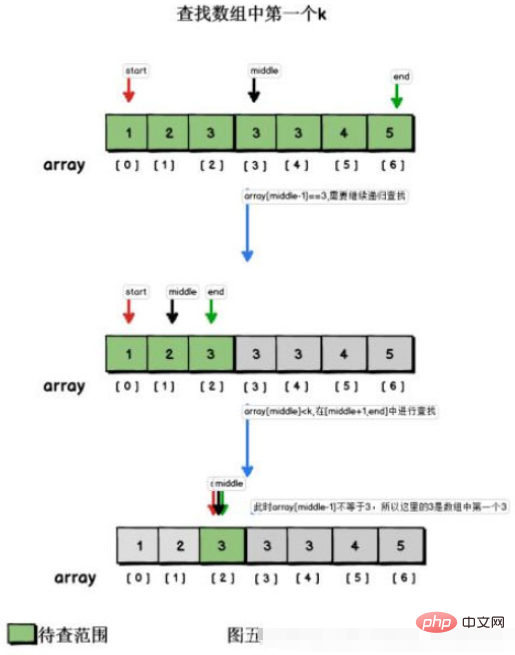
Recursive implementation
Here, I used the recursive method to implement.
First of all, you need to confirm the search range, that is, there is a left index and a right index. Each time, (left right)/2 is taken as the middle value, and the size of the element to be searched and the middle value are compared. If the middle value is larger , then search forward, that is, the recursion range is left, mid-1. Otherwise, search to the right, that is, the recursive range is mid 1, right. If they are equal, it is found.
But you need to continue to look before and after this index to see if there is an equal value, add it to the set, and finally return this set.
Recursive implementation code
package search;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class BinarySearch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {1,1,1,2,3,4,5,6,7};
List<Integer> integers = binarySearch(array, 0, array.length - 1, 1);
// for (Integer integer : integers) {
// System.out.print(integer+ " ");
// }
System.out.println(integers);
}
public static List<Integer> binarySearch(int[] array, int left, int right, int value){
//如果左索引大于右索引,则说明全部遍历完了,也没有找到相应的值,返回空集合即可
if (left>right){
return new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
//获取中间值的下标(二分)
int mid = (left+right)/2;
//如果要找的值比中间值小,则继续向左找
if (value < array[mid]){
return binarySearch(array, left, mid-1, value);
//要找的值比中间值小大,则向右找
}else if (value > array[mid]){
return binarySearch(array, mid+1, right, value);
//否则,说明相等,找到了
}else {
//找到一个,还需要向左右找找看有没有相同的值
List<Integer> resultList = new ArrayList();
//向左循环找,如果有,则加入到集合中
int temp = mid - 1;
while (temp>=0 && array[temp] == value){
resultList.add(temp);
temp -= 1;
}
//向右循环找,如果有,则加入到集合中
temp = mid + 1;
while (temp < array.length && array[temp] == value){
resultList.add(temp);
temp += 1;
}
//将一开始找到的那个索引页加入到集合中。
resultList.add(mid);
return resultList;
}
}
//以下这段代码来自百度百科,供大家参考。
public static int binarySearch(Integer[] srcArray, int des) {
//定义初始最小、最大索引
int start = 0;
int end = srcArray.length - 1;
//确保不会出现重复查找,越界
while (start <= end) {
//计算出中间索引值
int middle = (end + start)>>>1 ;//防止溢出
if (des == srcArray[middle]) {
return middle;
//判断下限
} else if (des < srcArray[middle]) {
end = middle - 1;
//判断上限
} else {
start = middle + 1;
}
}
//若没有,则返回-1
return -1;
}
}Loop implementation code (non-recursive)
package search;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Author: sshdg
* @Date: 2020/9/21 9:22
*/
public class BinarySearch3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] array = {1,1,1,1,1,2,3,4,5,6,7};
System.out.println(BinarySearch3.binarySearch(array, 7));
}
public static List<Integer> binarySearch(int[] array, int key){
List<Integer> resultList = new ArrayList<>();
int start = 0;
int end = array.length - 1;
while (start <= end){
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
int midValue = array[mid];
if (key > midValue){
//key比中间值大。向右找
start = mid + 1;
} else if (key < midValue){
//key比中间值小。向左找
end = mid - 1;
} else {
//否则就找到了
//先向左找有没有相同值
int temp = mid -1;
while (temp >= start && array[temp] == key){
resultList.add(temp);
temp -= 1;
}
//将一开始找到的加入结果集
resultList.add(mid);
//再向右找找有没有相同值
temp = mid + 1;
while (temp <= end && array[temp] == key){
resultList.add(temp);
temp += 1;
}
break;
}
}
return resultList;
}
}Binary search (recursive, loop)
public class BinarySearch {
/**
* @author JadeXu
* @// TODO: 2020/12/7 二分查找
* 思路:
* 1、获取数组的中间值,先获取下标,方便多次查找
* 奇数位的数组直接获取中间位,偶数位的数组获取中间的第一位或第二位都可,一般获取第一位(因为与奇数位获取中间值的方法一样)
* 2、获取查找的区间范围,start:区间开始的下标,end:区间结束的下标
* 3、判断查找的数和中间位的数是否相同
* 相同时,直接返回需要的数据,跳出方法
* 大于时,即数可能在中间值右边的区间内,此时start = mid+1,即mid往后移一位,就得到了中间值右边区间的开始下标
* 小于时,即数可能在中间值左边的区间内,此时end = mid-1,即mid往前移一位,就得到了中间值左边区间的结束下标
* 当一个区间里,开始下标小于等于结束下标时,该区间才是有效区间,才能继续查找。否则无效,返回找不到,跳出方法
*/
//循环
/**
* @param arr 已经升序好的int[]
* @param num 需要查找的数字
* @return 找到则返回下标,没找到则返回-1
*/
private static int binarySearchByCycle(int[] arr,int num) {
int start = 0;
int end = arr.length - 1;
while (start <= end){
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if(num == arr[mid]){
return mid;
}else if(num > arr[mid]){
start = mid + 1;
}else {
end = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
//递归
/**
* @param arr 已经升序好的int[]
* @param num 需要查找的数字
* @param start 区间开始下标
* @param end 区间结束下标
* @return 找到则返回下标,没找到则返回-1
*/
private static int binarySearchByRecursion(int[] arr,int num,int start,int end) {
int mid = (start + end) / 2;
if(num == arr[mid]){
return mid;
}else if(num > arr[mid]){
start = mid + 1;
}else {
end = mid - 1;
}
if(start <= end){
mid = binarySearchByRecursion(arr,num,start,end); //递归继续寻找
}else {
mid = -1;
}
return mid;
}
}The above is the detailed content of How to implement binary search in Java. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to Square Root in Java. Here we discuss how Square Root works in Java with example and its code implementation respectively.
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to the Armstrong Number in Java. Here we discuss an introduction to Armstrong's number in java along with some of the code.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is






