
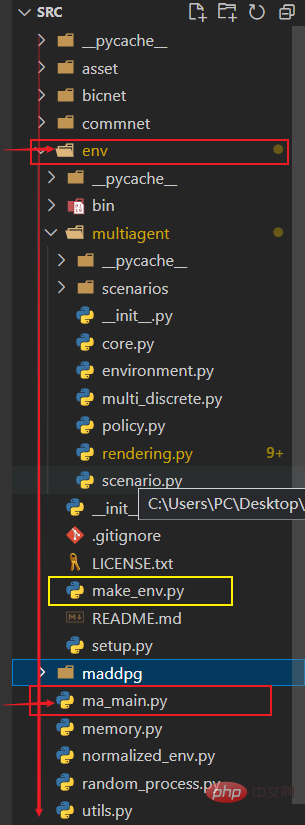
Direct import
For example, I want to import env package in ma_main.py The make_env.py file, thereby reading the functions
because at this time ma_main.py and env package are both in src is in the root directory, so you can directly import and continue to import
herefromand thenimportbecause## There is only one function in #make_env.py which is make_env(), so import this function directly and write the name directly when calling
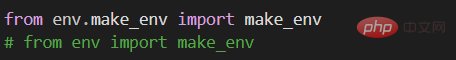
from env import make_env, then when calling the make_env() function in make_env.py, you must also use . Statement
PS: from env import make_env and import env.make_env are the same
not find the custom module.
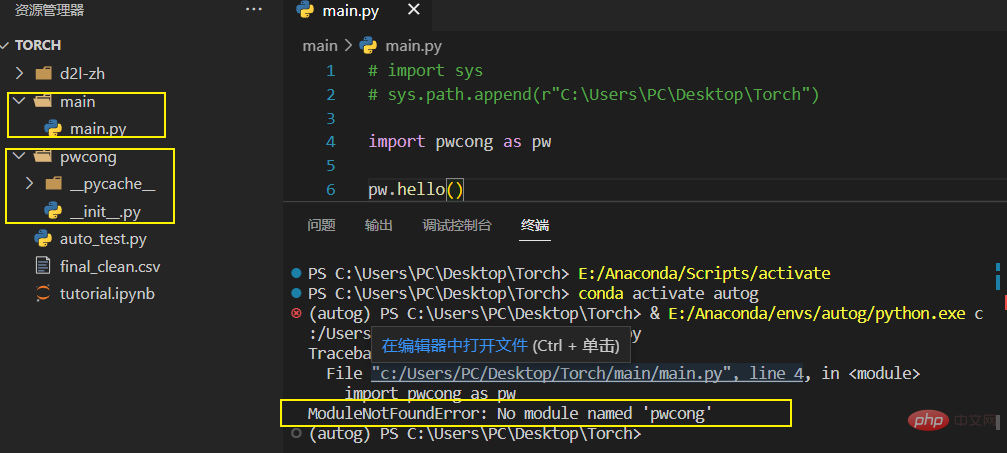
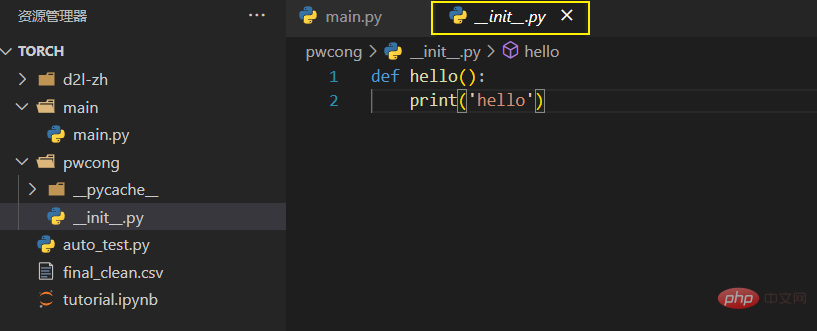
pwcong package in main.py Thus executing some methods of __init__.py
main.py is under ./Torch/main/, and pwcong Under ./Torch/
main.pyfilelist of paths searched by the python interpreter module does not include ./Torch
sys package that comes with python to import the path of the custom module , thereby manually adding the path list of the module search by the Python interpreter in main.py, and then the
import a module, the interpreter will find the module from a path list.
default path for the Python interpreter installation , as well as any paths specified in the environment variable PYTHONPATH .
sys.path.append() function to add a new path to this path list so that the interpreter can find you specified module.
import statement.
not affect the namespace , but just tells the interpreter where to find the module to be imported.
custom module is located through the sys.path.append(path) function
main.py to manually define the python interpreter path of the file
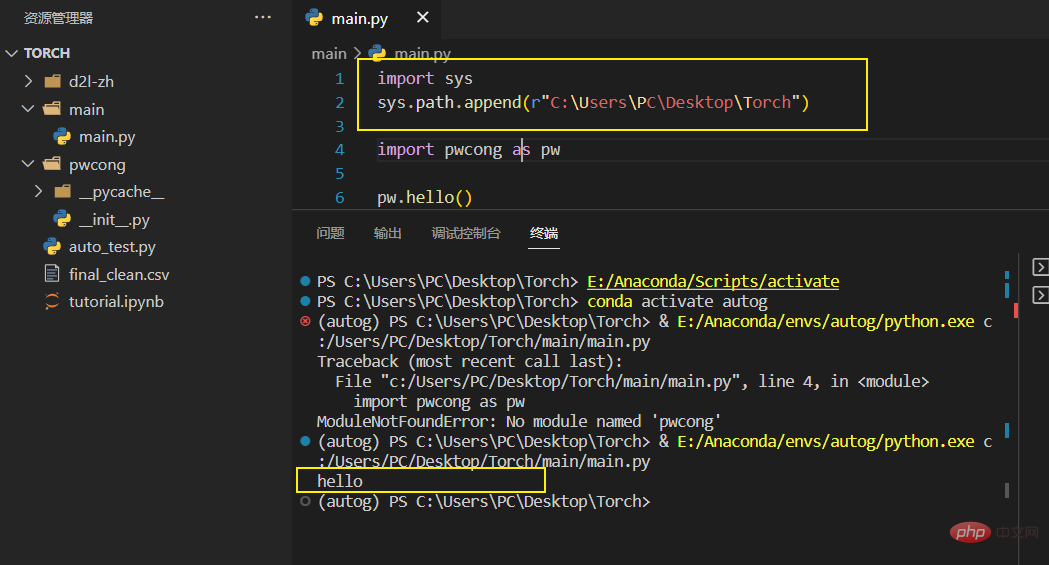
import sys sys.path.append(r"C:\Users\PC\Desktop\Torch") # 要加上地址生命符r, 并且要是绝对路径
, print hello
 Add the path searched by the interpreter module through sys.path.append, and then execute it through the module name Function
Add the path searched by the interpreter module through sys.path.append, and then execute it through the module name Function
 A module must have a
A module must have a
fileIn Python,
requires To be considered a package, it must contain an __init__.py file. This file can be an empty file, or contain some package initialization code. A directory without a
file is just a directory, and other py files cannot import the functions
The file may contain:
: __init__.pyThe file may contain declarations of variables, classes, and functions
: The init.py file can contain initialization code that will be executed when the package is imported. This can be used to perform certain necessary operations, such as configuring a package or ensuring that a package's dependencies are installed.
: The init.py file can contain code that imports other modules. This can be used to add submodules to a package's namespace so that users can access them.
In Python, a namespace is a dictionary containing variable and function names, used to record the name and value of each identifier (identifier). Each namespace in the Python interpreter is a dictionary object whose variables and functions can be accessed through the dictionary's key-value pairs.
There are three namespaces in Python:
Built-in namespace: Contains the variables and functions built into the Python interpreter. These variables and functions It can be used directly in the program without importing any modules, such as: print() function, len() function, etc.
Global namespace: Created when the module is defined, it contains variables and functions defined in the module file. These variables and functions can be used anywhere in the module.
Local namespace: Created when a function is called, it contains variables and functions defined in the function. These variables and functions can only be used inside functions.
The role of namespace is to avoid variable or function name conflicts between different namespaces and to better manage variables and functions in the program. In Python, variables in the global and non-local namespaces can be accessed and modified by using the global and nonlocal keywords.
The above is the detailed content of What are the ways to import python packages?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




