
Getting the bean object is also called object assembly, which is to take the object out and put it somewhere In classes, it is sometimes called object injection.
There are three ways to implement object assembly (object injection):
Attribute injection
Construction method Injection
Setter Injection
We first create the following packages and classes:
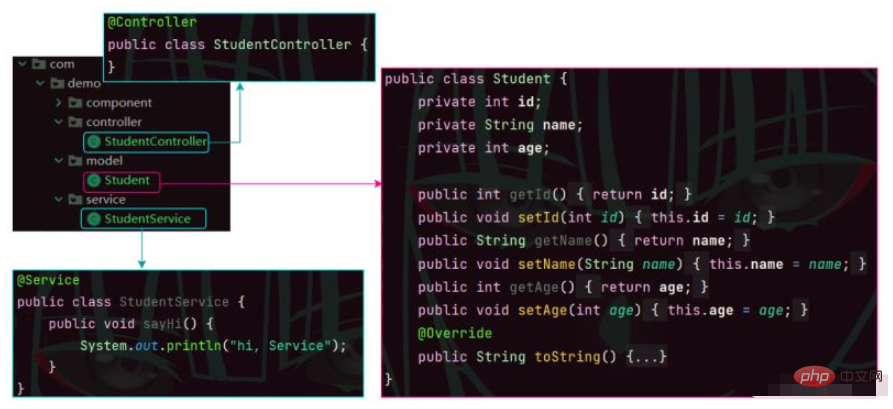
Attribute injection is implemented using @Autowired, and the Service class is injected into the Controller class.
@Controller
public class StudentController {
// 1.使用属性注入的方式获取 Bean
@Autowired
private StudentService studentService;
public void sayHi() {
// 调用 service 方法
studentService.sayHi();
}
}Advantages:
Simple to implement and easy to use.
Disadvantages:
Functionality Problem: Unable to inject immutable (final) objects.

final objects (immutable) in Java Either assign the value directly or assign the value in the constructor, so when using attributes to inject a final object, it does not comply with the usage specifications of final in Java, so the injection cannot be successful.
Universality issue: Can only be adapted to IoC containers.
Design principle issue: Easier Violates the single design principle. (For objects that are classes)
Single design principle:
For class level
For method level
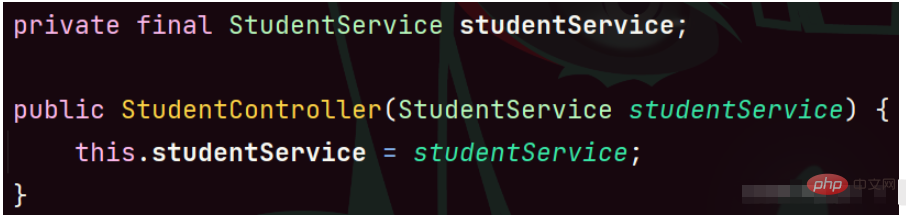
Since Spring 4.x, Spring official It is recommended to use the form of constructor injection.
@Controller
public class StudentController {
// 2.构造方法注入
private StudentService studentService;
// @Autowired 可省略
@Autowired
public StudentController(StudentService studentService) {
this.studentService = studentService;
}
public void sayHi() {
// 调用 service 方法
studentService.sayHi();
}
}# Note
#@Autowired Can be omitted.
But if there are multiple constructors in the class, you need to add @Autowired to clearly specify which constructor to use, otherwise the program An error will be reported.
Advantages:
Immutable objects can be injected.
The injected object will not be modified.
Added final modification symbol.
The construction method is only executed once as the class is loaded.
The injected object will be fully initialized. (Use Advantages brought by the construction method)
Better versatility.
Disadvantages:
Without attribute injection, the implementation is simple.
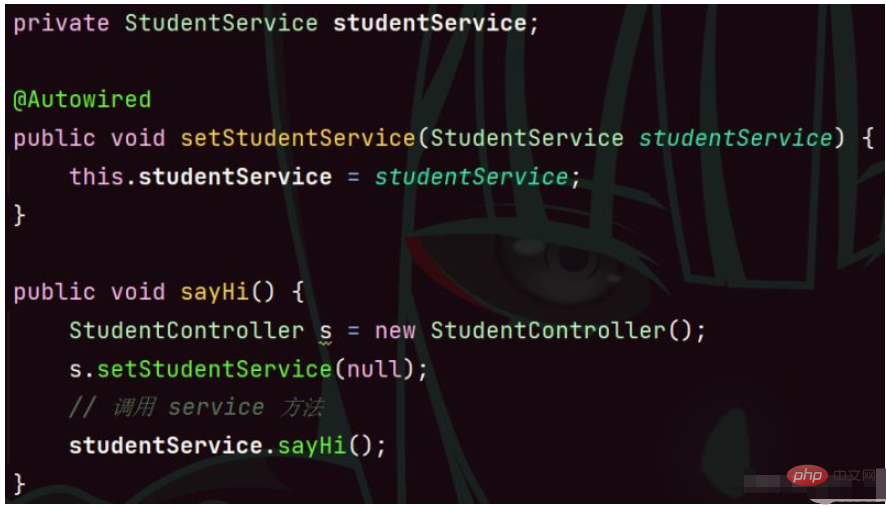
Setter Injection is similar to the Setter method implementation of the attribute, except that it needs to be added when setting the set method. @Autowired Annotation.
@Controller
public class StudentController {
// 3.setter 注入
private StudentService studentService;
@Autowired
public void setStudentService(StudentService studentService) {
this.studentService = studentService;
}
public void sayHi() {
// 调用 service 方法
studentService.sayHi();
}
}Advantages:
is more in line with a single design principle. (Method level for objects)
Disadvantages:
Cannot inject immutable objects (final modified objects).
set The method is a normal set method and can be called repeatedly, with the risk of being modified.
Summary: In daily development, using attribute injection to achieve simpler reading of beans is still the mainstream implementation method.@Resource Keyword
When performing class injection, in addition to using the @Autowired keyword, we can also use @Resource for injection.@Autowired Differences from @ResourceSame points: both are used to implement dependency injection.Differences:@Controller public class StudentController { @Resource private StudentService studentService; public void sayHi() { // 调用 service 方法 studentService.sayHi(); } }Copy after login
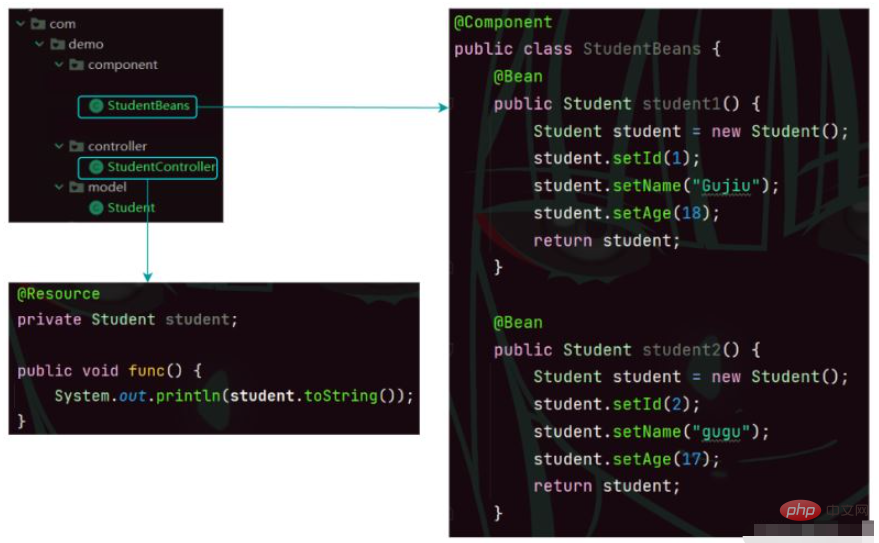
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
StudentController studentController =
applicationContext.getBean("studentController", StudentController.class);
studentController.func();
}
}@Resource(name="student1") to define.
@Qualifier to annotate the name.
# 使⽤ @Resource(name="student1") 定义.
@Controller
public class StudentController {
@Resource(name = "student2")
private Student student;
public void func() {
System.out.println(student.toString());
}
}# 使⽤ @Qualifier 注解定义名称.
@Controller
public class StudentController {
@Resource
@Qualifier("student2")
private Student student;
public void func() {
System.out.println(student.toString());
}
}# 如果我们想用 @Autowired 可以写成:
@Autowired private Student student1; // 存在有耦合性问题
The above is the detailed content of What is Spring's simple way to read and store objects in Java?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!




