Java distributed Kafka message queue instance analysis
Introduction
Apache Kafka is a distributed publish-subscribe messaging system. The definition of kafka on the kafka official website is: a distributed publish-subscribe messaging system. It was originally developed by LinkedIn, which was contributed to the Apache Foundation in 2010 and became a top open source project. Kafka is a fast, scalable, and inherently distributed, partitioned, and replicable commit log service.
Note: Kafka does not follow the JMS specification (), it only provides publish and subscribe communication methods.
Kafka core related names
Broker: Kafka node, a Kafka node is a broker, multiple brokers can form a Kafka cluster
Topic: A type of message. The directory where the message is stored is the topic. For example, page view logs, click logs, etc. can exist in the form of topics. The Kafka cluster can be responsible for the distribution of multiple topics at the same time.
massage: The most basic delivery object in Kafka.
Partition: The physical grouping of topics. A topic can be divided into multiple partitions, and each partition is an ordered queue. Partitioning is implemented in Kafka, and a broker represents a region.
Segment: Partition is physically composed of multiple segments. Each segment stores message information.
Producer: Producer, produces messages and sends them. Go to topic
- ##Consumer: consumer, subscribe to topic and consume messages, consumer consumes as a thread
- Consumer Group: consumer group, A Consumer Group contains multiple consumers
- Offset: offset, understood as the index position of the message in the message partition
- Install jdk1.8 environment on each server
- Install Zookeeper cluster environment
- Install kafka cluster environment
- Run environment test
tar -zxvf kafka_2.11 -1.0.0.tgz3. Modify kafka’s configuration file config/server.propertiesConfiguration file modification content:
- zookeeper connection address:
zookeeper.connect=192.168.1.19:2181
- The listening ip is changed to the local ip
listeners=PLAINTEXT:// 192.168.1.19:9092
- #kafka’s brokerid, each broker’s id is different
broker.id=0
./kafka-server-start.sh -daemon config/server.properties
./kafka-topics.sh --create --zookeeper localhost: 2181 --replication-factor 1 --partitions 3 --topic kaico
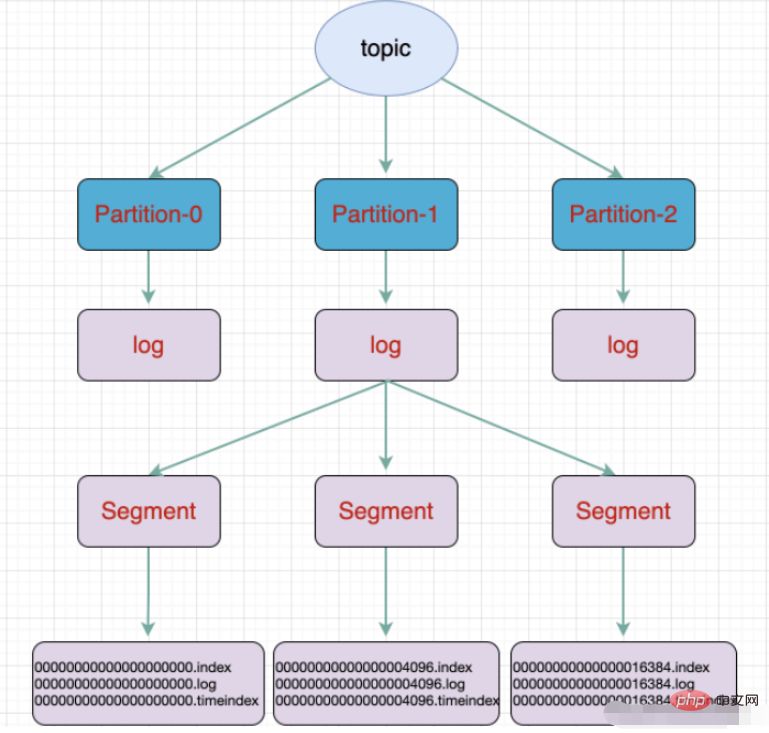
- ##a partition Divided into multiple segments
- .log log file
- .index offset index file
- .timeindex timestamp index file
- Other files (partition.metadata, leader-epoch-checkpoint)
- Springboot integration kafka
maven dependency
<dependencies>
<!-- springBoot集成kafka -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-kafka</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- SpringBoot整合Web组件 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>yml configuration
# kafka
spring:
kafka:
# kafka服务器地址(可以多个)
# bootstrap-servers: 192.168.212.164:9092,192.168.212.167:9092,192.168.212.168:9092
bootstrap-servers: www.kaicostudy.com:9092,www.kaicostudy.com:9093,www.kaicostudy.com:9094
consumer:
# 指定一个默认的组名
group-id: kafkaGroup1
# earliest:当各分区下有已提交的offset时,从提交的offset开始消费;无提交的offset时,从头开始消费
# latest:当各分区下有已提交的offset时,从提交的offset开始消费;无提交的offset时,消费新产生的该分区下的数据
# none:topic各分区都存在已提交的offset时,从offset后开始消费;只要有一个分区不存在已提交的offset,则抛出异常
auto-offset-reset: earliest
# key/value的反序列化
key-deserializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer
value-deserializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer
producer:
# key/value的序列化
key-serializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
value-serializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
# 批量抓取
batch-size: 65536
# 缓存容量
buffer-memory: 524288
# 服务器地址
bootstrap-servers: www.kaicostudy.com:9092,www.kaicostudy.com:9093,www.kaicostudy.com:9094producer
@RestController
public class KafkaController {
/**
* 注入kafkaTemplate
*/
@Autowired
private KafkaTemplate<String, String> kafkaTemplate;
/**
* 发送消息的方法
*
* @param key
* 推送数据的key
* @param data
* 推送数据的data
*/
private void send(String key, String data) {
// topic 名称 key data 消息数据
kafkaTemplate.send("kaico", key, data);
}
// test 主题 1 my_test 3
@RequestMapping("/kafka")
public String testKafka() {
int iMax = 6;
for (int i = 1; i < iMax; i++) {
send("key" + i, "data" + i);
}
return "success";
}
}consumer
@Component
public class TopicKaicoConsumer {
/**
* 消费者使用日志打印消息
*/
@KafkaListener(topics = "kaico") //监听的主题
public void receive(ConsumerRecord<?, ?> consumer) {
System.out.println("topic名称:" + consumer.topic() + ",key:" +
consumer.key() + "," +
"分区位置:" + consumer.partition()
+ ", 下标" + consumer.offset());
//输出key对应的value的值
System.out.println(consumer.value());
}
}The above is the detailed content of Java distributed Kafka message queue instance analysis. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.




