How machine learning can make agriculture more sustainable
In an era of rapid climate change, achieving agricultural sustainability is critical to ensuring the health and well-being of the planet.
With limited resources and a growing population, traditional farming methods are no longer able to support a sustainable food system.
Fortunately, current technological advances in machine learning offer a promising path toward more sustainable agricultural practices. By leveraging computer vision and predictive analytics, farmers can reduce water usage, control pests with fewer resources, and optimize fertilizer use to reduce negative environmental impacts. This article explores the environmental benefits of using machine learning in agriculture and how it can help achieve more sustainable farming.
Challenges facing agriculture today
One of the major challenges facing agriculture today is the ever-increasing demand for food to feed a growing population. According to the International Monetary Fund, the population will reach 9.7 billion by 2050. With agricultural land reaching its limits, there is an urgent need to find new, more efficient ways to produce food while protecting the environment. Climate change is also a major threat, with extreme weather conditions such as floods, droughts and storms causing widespread damage to crops and livestock. Also, natural resources such as water and soil fertility are dwindling, and unsustainable farming practices exacerbate this challenge.
How machine learning can help agriculture
- Reduce water consumption
Traditional agriculture often consumes too much water, which is harmful to the environment Had a devastating impact. Decades of over-irrigation in California's Central Valley, for example, led to dangerous levels of salt accumulation in the soil and made it impossible to grow crops in some areas. In other parts of the world, such as India and China, farmers over-extract groundwater that is not replenished fast enough, leading to water shortages and soil degradation.
In addition to depleting natural resources such as water and soil, excessive water use also has economic consequences. Farmers are often forced to pay exorbitant fees for irrigation systems or use inefficient methods that require large amounts of water but produce low yields.
With machine learning-enabled remote sensing technology, farmers can monitor soil levels or set up automated sensors to detect when crops need extra water. These strategies can help improve water use efficiency, reduce overall farming costs, and ensure natural resources are not wasted. Additionally, machine learning can be used to detect drought-resistant crops and find optimal planting patterns based on soil type and climate conditions. All these measures contribute to making agricultural production more sustainable in the long term.
- Optimizing Pesticide Use
Pests are a major problem faced by most farmers as they can cause considerable damage to crops and significantly reduce yields. Traditional solutions to this problem involve the use of pesticides, which have a negative impact on the environment and are also considered unsustainable.
Machine learning offers another solution that allows farmers to better monitor and control pests with fewer resources. By leveraging computer vision and predictive analytics, farmers can automatically detect pests and monitor crops in real time. This enables an effective, targeted approach to pest control and greatly reduces reliance on pesticides. Additionally, machine learning algorithms can be used to monitor water levels and soil conditions, allowing farmers to accurately determine when pests are most likely to appear and take preventive measures.
- Optimizing Fertilizer Usage
While the use of synthetic fertilizers in agriculture is very beneficial for crop yields, it is harmful to the environment. Typically, most farmers apply fertilizer to the entire field, that is, over-fertilizing in areas where the soil already has a high nutrient content. This often results in nutrients spilling into the nearest rivers, lakes and oceans, causing excessive algae blooms. This, in turn, greatly reduces the oxygen content in the water and can lead to the death of fish and other aquatic life.
Additionally, fertilizers often cause soil acidification, which can have a negative impact on biodiversity. What’s even scarier is that the production of synthetic fertilizers is also responsible for 2.1% of annual CO2 emissions, according to a recent study by Greenpeace Research Labs.
Machine learning can help mitigate the negative environmental impacts associated with these practices. By using precision farming technologies such as automated data collection and analysis, farmers can monitor soil conditions in real time and apply fertilizer in optimal amounts only where needed. This helps reduce nutrient spillage into rivers and lakes, promoting healthier aquatic ecosystems and protecting biodiversity.
Machine Learning Saves Agriculture
Clearly, machine learning has the potential to revolutionize agriculture and make it more sustainable. By leveraging automated technologies like computer vision and predictive analytics, farmers can increase crop yields while conserving natural resources. This helps reduce the negative environmental impact of traditional farming practices, including the use of water, pesticides and fertilizers.
As machine learning technology becomes more advanced and mainstream, there is no doubt that these methods will become a staple in the agricultural industry. Ultimately, with the help of modern technology, we can ensure better management of the Earth's natural resources and create a more sustainable future for future generations.
The above is the detailed content of How machine learning can make agriculture more sustainable. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1382
1382
 52
52
 Bytedance Cutting launches SVIP super membership: 499 yuan for continuous annual subscription, providing a variety of AI functions
Jun 28, 2024 am 03:51 AM
Bytedance Cutting launches SVIP super membership: 499 yuan for continuous annual subscription, providing a variety of AI functions
Jun 28, 2024 am 03:51 AM
This site reported on June 27 that Jianying is a video editing software developed by FaceMeng Technology, a subsidiary of ByteDance. It relies on the Douyin platform and basically produces short video content for users of the platform. It is compatible with iOS, Android, and Windows. , MacOS and other operating systems. Jianying officially announced the upgrade of its membership system and launched a new SVIP, which includes a variety of AI black technologies, such as intelligent translation, intelligent highlighting, intelligent packaging, digital human synthesis, etc. In terms of price, the monthly fee for clipping SVIP is 79 yuan, the annual fee is 599 yuan (note on this site: equivalent to 49.9 yuan per month), the continuous monthly subscription is 59 yuan per month, and the continuous annual subscription is 499 yuan per year (equivalent to 41.6 yuan per month) . In addition, the cut official also stated that in order to improve the user experience, those who have subscribed to the original VIP
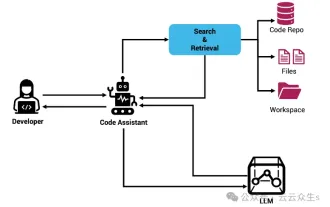 Context-augmented AI coding assistant using Rag and Sem-Rag
Jun 10, 2024 am 11:08 AM
Context-augmented AI coding assistant using Rag and Sem-Rag
Jun 10, 2024 am 11:08 AM
Improve developer productivity, efficiency, and accuracy by incorporating retrieval-enhanced generation and semantic memory into AI coding assistants. Translated from EnhancingAICodingAssistantswithContextUsingRAGandSEM-RAG, author JanakiramMSV. While basic AI programming assistants are naturally helpful, they often fail to provide the most relevant and correct code suggestions because they rely on a general understanding of the software language and the most common patterns of writing software. The code generated by these coding assistants is suitable for solving the problems they are responsible for solving, but often does not conform to the coding standards, conventions and styles of the individual teams. This often results in suggestions that need to be modified or refined in order for the code to be accepted into the application
 Can fine-tuning really allow LLM to learn new things: introducing new knowledge may make the model produce more hallucinations
Jun 11, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Can fine-tuning really allow LLM to learn new things: introducing new knowledge may make the model produce more hallucinations
Jun 11, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Large Language Models (LLMs) are trained on huge text databases, where they acquire large amounts of real-world knowledge. This knowledge is embedded into their parameters and can then be used when needed. The knowledge of these models is "reified" at the end of training. At the end of pre-training, the model actually stops learning. Align or fine-tune the model to learn how to leverage this knowledge and respond more naturally to user questions. But sometimes model knowledge is not enough, and although the model can access external content through RAG, it is considered beneficial to adapt the model to new domains through fine-tuning. This fine-tuning is performed using input from human annotators or other LLM creations, where the model encounters additional real-world knowledge and integrates it
 Seven Cool GenAI & LLM Technical Interview Questions
Jun 07, 2024 am 10:06 AM
Seven Cool GenAI & LLM Technical Interview Questions
Jun 07, 2024 am 10:06 AM
To learn more about AIGC, please visit: 51CTOAI.x Community https://www.51cto.com/aigc/Translator|Jingyan Reviewer|Chonglou is different from the traditional question bank that can be seen everywhere on the Internet. These questions It requires thinking outside the box. Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly important in the fields of data science, generative artificial intelligence (GenAI), and artificial intelligence. These complex algorithms enhance human skills and drive efficiency and innovation in many industries, becoming the key for companies to remain competitive. LLM has a wide range of applications. It can be used in fields such as natural language processing, text generation, speech recognition and recommendation systems. By learning from large amounts of data, LLM is able to generate text
 Five schools of machine learning you don't know about
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Five schools of machine learning you don't know about
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Machine learning is an important branch of artificial intelligence that gives computers the ability to learn from data and improve their capabilities without being explicitly programmed. Machine learning has a wide range of applications in various fields, from image recognition and natural language processing to recommendation systems and fraud detection, and it is changing the way we live. There are many different methods and theories in the field of machine learning, among which the five most influential methods are called the "Five Schools of Machine Learning". The five major schools are the symbolic school, the connectionist school, the evolutionary school, the Bayesian school and the analogy school. 1. Symbolism, also known as symbolism, emphasizes the use of symbols for logical reasoning and expression of knowledge. This school of thought believes that learning is a process of reverse deduction, through existing
 To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
Editor |ScienceAI Question Answering (QA) data set plays a vital role in promoting natural language processing (NLP) research. High-quality QA data sets can not only be used to fine-tune models, but also effectively evaluate the capabilities of large language models (LLM), especially the ability to understand and reason about scientific knowledge. Although there are currently many scientific QA data sets covering medicine, chemistry, biology and other fields, these data sets still have some shortcomings. First, the data form is relatively simple, most of which are multiple-choice questions. They are easy to evaluate, but limit the model's answer selection range and cannot fully test the model's ability to answer scientific questions. In contrast, open-ended Q&A
 SOTA performance, Xiamen multi-modal protein-ligand affinity prediction AI method, combines molecular surface information for the first time
Jul 17, 2024 pm 06:37 PM
SOTA performance, Xiamen multi-modal protein-ligand affinity prediction AI method, combines molecular surface information for the first time
Jul 17, 2024 pm 06:37 PM
Editor | KX In the field of drug research and development, accurately and effectively predicting the binding affinity of proteins and ligands is crucial for drug screening and optimization. However, current studies do not take into account the important role of molecular surface information in protein-ligand interactions. Based on this, researchers from Xiamen University proposed a novel multi-modal feature extraction (MFE) framework, which for the first time combines information on protein surface, 3D structure and sequence, and uses a cross-attention mechanism to compare different modalities. feature alignment. Experimental results demonstrate that this method achieves state-of-the-art performance in predicting protein-ligand binding affinities. Furthermore, ablation studies demonstrate the effectiveness and necessity of protein surface information and multimodal feature alignment within this framework. Related research begins with "S
 SK Hynix will display new AI-related products on August 6: 12-layer HBM3E, 321-high NAND, etc.
Aug 01, 2024 pm 09:40 PM
SK Hynix will display new AI-related products on August 6: 12-layer HBM3E, 321-high NAND, etc.
Aug 01, 2024 pm 09:40 PM
According to news from this site on August 1, SK Hynix released a blog post today (August 1), announcing that it will attend the Global Semiconductor Memory Summit FMS2024 to be held in Santa Clara, California, USA from August 6 to 8, showcasing many new technologies. generation product. Introduction to the Future Memory and Storage Summit (FutureMemoryandStorage), formerly the Flash Memory Summit (FlashMemorySummit) mainly for NAND suppliers, in the context of increasing attention to artificial intelligence technology, this year was renamed the Future Memory and Storage Summit (FutureMemoryandStorage) to invite DRAM and storage vendors and many more players. New product SK hynix launched last year




