Guide to using the os and sys modules in Python
一、os模块
os.getcwd() 获取当前的工作目录
os.chdir(‘绝对路径/相对于当前工作目录的路径’) 改变工作目录,相当于shell的cd命令,例如Windows平台下os.chdir(r’D:\PythonScripts\test\c’),用r对\进行转义,第一层级必须使用双斜线,其他层级可以单斜线也可以双斜线,在linux和unix平台下用/分割
os.curdir 返回当前路径 .
os.pardir 返回当前路径的上一层路径,即 ..
os.mkdir('dir') 生成单级目录
os.makedirs(r'dir1\dir2') 创建递归目录,不加绝对路径表示在当前工作目录下创建
os.rmdir('dir') 删除单级空目录,如果目录不为空无法删除
os.removedirsr('dir1\dir2') 若目录为空则删除,并递归到上一层目录,若上一层为空也删除,以此类推
os.listdir(dir) 列出指定目录下的所有一级文件和目录,并以列表形式打印
os.remove('file') 删除一个文件
os.rename('oldname','newname') 重命名文件或目录
os.listdir('dir')以列表形式列出dir目录下所有的文件和目录
os.stat('file'/'dir') 获取文件/目录的大小,链接数,创建时间,上一次修改、访问时间等信息
os.sep 获取当前环境的分隔符
os.linesep 获取当前环境的换行符,windows下为/r/n,linux下为/n
os.pathsep 获取当前环境分割文件路径的字符串,windows下为;,linux下为:
os.name 获取当前使用平台,windows为nt,linux为posix
os.environ 获取系统环境变量
os.system(shell command) 运行shell命令,返回执行状态码,执行结果显示到屏幕
os.path.abspath(path) 返回绝对路径
os.path.split(path) 将path分割成目录和文件名的两个元素的元组
os.path.dirame(path) 返回path的目录,相当于os.path.split(path)的第一个元素
os.path.basename(path) 返回path最后的文件名,如果path以/或\结尾则返回空值,即os.path.split(path)的第二个元素
os.path.exists(path) 如果path存在则返回True,否则返回False
os.path.isabs(path) 如果path是绝对路径则返回True,否则返回False
os.path.isfile(path) 如果path是一个存在的文件则返回True,否则返回False
os.path.isdir(path) 如果path是一个存在的目录则返回True,否则返回False
os.path.join(path2[,path3[,path4…]]) 将多个路径组合后返回,第一个绝对路径之前的参数将被忽略
os.path.getatime(path) 获取path所指向的文件或者目录的最后访问时间
os.path.getmtime(path) 获取path所指向的文件或者目录的最后修改时间
二、os模块中的os.walk()函数
os.walk(‘path’)函数对于每个目录返回一个三元组,(dirpath, dirnames, filenames),
第一个是路径,第二个是路径下面的目录,第三个是路径下面的文件
如果加参数topdown=False则表示自下而上进行遍历,默认为topdown=True即自上而下进行遍历
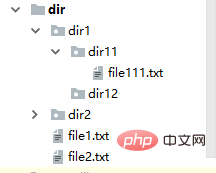
#对于上述结构,os.walk()的结果为
['dir', ['dir1', 'dir2'], ['file1.txt', 'file2.txt']]
['dir\\dir1', ['dir11', 'dir12'], []]
['dir\\dir1\\dir11', [], ['file111.txt']]
['dir\\dir1\\dir12', [], []]
['dir\\dir2', ['dir21'], ['file21.txt']]
['dir\\dir2\\dir21', [], []]
#可通过如下脚本验证
import sys
l=[]
for root,dirs,files in os.walk('dir'):
l.append(root)
l.append(dirs)
l.append(files)
print(l)
l=[]结果分析
1.先以给定的目录作为根目录进行遍历,读取根目录的文件夹和文件
2.以根目录下子目录为新的根目录进行遍历,读取其下面的文件夹和文件
3.再以2中得到的子目录为根目录进行遍历,读取其下面的文件夹和文件
4.重复3,直至所有子目录下面没有子目录和文件
三、sys模块
sys.path 获取python PATH环境变量的值
sys.version 获取python解释器的版本
sys.exit(n) 在程序执行过程中退出程序,正常退出为exit(0)
sys.argv 返回的结果为一个列表且各元素都为字符串,第一个元素为当前执行文件的名称,后面的元素为执行文件时传入的参数,以空格分隔各参数,如果只有空格表示没有参数。
[root@oldboy test]# cat argv.py
import sys
print(sys.argv)
[root@oldboy test]# python argv.py
['argv.py']
[root@oldboy test]# python argv.py 11 '22' [33,44] 'True' {1:'a'}#文件执行时传入的参数不能为元组,否则会报错
['argv.py', '11', '22', '[33,44]', 'True', '{1:a}']sys.stdout.write(‘str’) 向屏幕输出,不换行,相当于print,但是print(‘str’)是换行输出
sys.stdout.flush( ) 将缓存输出到屏幕
例如通过#逐步打印进度条
import time,sys
for i in range(20):
sys.stdout.write('#') #打印一个#,不换行
time.sleep(0.1) #睡0.1秒再输出下一个#
sys.stdout.flush() #将缓存中的#输出到屏幕,没有这一行系统会等到输出完毕再将缓存中的20个#输出到屏幕
print('')解析文件执行时输入的参数:optparse模块
import optparse
class ArgvHandle():
def __init__(self):
self.op = optparse.OptionParser()
self.op.add_option('-s','--server',dest = 'server')
#,前面为文件执行时的输入,dest表示参数名。如果文件执行时带有-s或者--server,则形成参数名称为dest指定名称、参数值为-s或者--server后面紧跟着的内容
self.op.add_option('-P','--port',dest = 'port')
self.op.add_option('-u','--username',dest = 'username')
self.op.add_option('-p','--passwort',dest = 'password')
#学习中遇到问题没人解答?小编创建了一个Python学习交流群:725638078
option,args = self.op.parse_args()
print(type(option),type(args))
print(option,args)
print(option.server,option.port,option.username,option.password)#通过.取参数名对应的值
test = ArgvHandle()随意输入参数执行结果如下

可知op.parse_args()是将文件执行python mani.py后面的参数分割成两部分,一部分类似字典的形式(实际是一个对象),一部分是一个列表。
如果匹配到add_option定义的参数形式,则将后面紧跟着的输入作为参数的值;未匹配到add_option定义的参数形式的其余输入被整理到一个列表中。
The above is the detailed content of Guide to using the os and sys modules in Python. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
Is the vscode extension malicious?
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:57 PM
VS Code extensions pose malicious risks, such as hiding malicious code, exploiting vulnerabilities, and masturbating as legitimate extensions. Methods to identify malicious extensions include: checking publishers, reading comments, checking code, and installing with caution. Security measures also include: security awareness, good habits, regular updates and antivirus software.
 How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
How to run programs in terminal vscode
Apr 15, 2025 pm 06:42 PM
In VS Code, you can run the program in the terminal through the following steps: Prepare the code and open the integrated terminal to ensure that the code directory is consistent with the terminal working directory. Select the run command according to the programming language (such as Python's python your_file_name.py) to check whether it runs successfully and resolve errors. Use the debugger to improve debugging efficiency.
 Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
Can vs code run in Windows 8
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:24 PM
VS Code can run on Windows 8, but the experience may not be great. First make sure the system has been updated to the latest patch, then download the VS Code installation package that matches the system architecture and install it as prompted. After installation, be aware that some extensions may be incompatible with Windows 8 and need to look for alternative extensions or use newer Windows systems in a virtual machine. Install the necessary extensions to check whether they work properly. Although VS Code is feasible on Windows 8, it is recommended to upgrade to a newer Windows system for a better development experience and security.
 Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
Can visual studio code be used in python
Apr 15, 2025 pm 08:18 PM
VS Code can be used to write Python and provides many features that make it an ideal tool for developing Python applications. It allows users to: install Python extensions to get functions such as code completion, syntax highlighting, and debugging. Use the debugger to track code step by step, find and fix errors. Integrate Git for version control. Use code formatting tools to maintain code consistency. Use the Linting tool to spot potential problems ahead of time.
 Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
Choosing Between PHP and Python: A Guide
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:24 AM
PHP is suitable for web development and rapid prototyping, and Python is suitable for data science and machine learning. 1.PHP is used for dynamic web development, with simple syntax and suitable for rapid development. 2. Python has concise syntax, is suitable for multiple fields, and has a strong library ecosystem.
 Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
Can vscode be used for mac
Apr 15, 2025 pm 07:36 PM
VS Code is available on Mac. It has powerful extensions, Git integration, terminal and debugger, and also offers a wealth of setup options. However, for particularly large projects or highly professional development, VS Code may have performance or functional limitations.
 Golang vs. Python: Concurrency and Multithreading
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Golang vs. Python: Concurrency and Multithreading
Apr 17, 2025 am 12:20 AM
Golang is more suitable for high concurrency tasks, while Python has more advantages in flexibility. 1.Golang efficiently handles concurrency through goroutine and channel. 2. Python relies on threading and asyncio, which is affected by GIL, but provides multiple concurrency methods. The choice should be based on specific needs.
 PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP and Python: Different Paradigms Explained
Apr 18, 2025 am 12:26 AM
PHP is mainly procedural programming, but also supports object-oriented programming (OOP); Python supports a variety of paradigms, including OOP, functional and procedural programming. PHP is suitable for web development, and Python is suitable for a variety of applications such as data analysis and machine learning.




