 Backend Development
Backend Development
 Python Tutorial
Python Tutorial
 What is the principle of Python collection set implementation?
What is the principle of Python collection set implementation?
What is the principle of Python collection set implementation?
深入理解 Python 虚拟机:集合(set)的实现原理及源码剖析
数据结构介绍
typedef struct {
PyObject_HEAD
Py_ssize_t fill; /* Number active and dummy entries*/
Py_ssize_t used; /* Number active entries */
/* The table contains mask + 1 slots, and that's a power of 2.
* We store the mask instead of the size because the mask is more
* frequently needed.
*/
Py_ssize_t mask;
/* The table points to a fixed-size smalltable for small tables
* or to additional malloc'ed memory for bigger tables.
* The table pointer is never NULL which saves us from repeated
* runtime null-tests.
*/
setentry *table;
Py_hash_t hash; /* Only used by frozenset objects */
Py_ssize_t finger; /* Search finger for pop() */
setentry smalltable[PySet_MINSIZE]; // #define PySet_MINSIZE 8
PyObject *weakreflist; /* List of weak references */
} PySetObject;
typedef struct {
PyObject *key;
Py_hash_t hash; /* Cached hash code of the key */
} setentry;
static PyObject _dummy_struct;
#define dummy (&_dummy_struct)上面的数据结果用图示如下图所示:
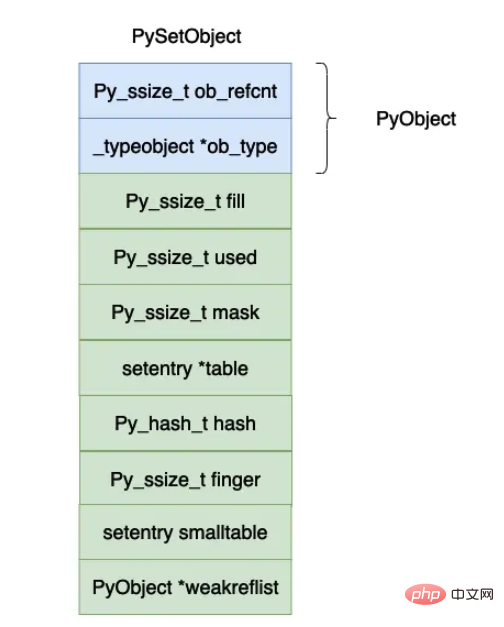
上面各个字段的含义如下所示:
dummy entries :如果在哈希表当中的数组原来有一个数据,如果我们删除这个 entry 的时候,对应的位置就会被赋值成 dummy,与 dummy 有关的定义在上面的代码当中已经给出,dummy 对象的哈希值等于 -1。
明白 dummy 的含义之后,fill 和 used 这两个字段的含义就比较容易理解了,used 就是数组当中真实有效的对象的个数,fill 还需要加上 dummy 对象的个数。
mask,数组的长度等于 2n2^n2n,mask 的值等于 2n−12^n - 12n−1 。
table,实际保存 entry 对象的数组。
hash,这个值对 frozenset 有用,保存计算出来的哈希值。如果你的数组很大的话,计算哈希值其实也是一个比较大的开销,因此可以将计算出来的哈希值保存下来,以便下一次求的时候可以将哈希值直接返回,这也印证了在 python 当中为什么只有 immutable 对象才能够放入到集合和字典当中,因为哈希值计算一次保存下来了,如果再加入对象对象的哈希值也会变化,这样做就会发生错误了。
finger,主要是用于记录下一个开始寻找被删除对象的下标。
smalltable,默认的小数组,cpython 设置的一半的集合对象不会超过这个大小(8),因此在申请一个集合对象的时候直接就申请了这个小数组的内存大小。
weakrelist,这个字段主要和垃圾回收有关,这里暂时不进行详细说明。
创建集合对象
首先先了解一下创建一个集合对象的过程,和前面其他的对象是一样的,首先先申请内存空间,然后进行相关的初始化操作。
这个函数有两个参数,使用第一个参数申请内存空间,然后后面一个参数如果不为 NULL 而且是一个可迭代对象的话,就将这里面的对象加入到集合当中。
static PyObject *
make_new_set(PyTypeObject *type, PyObject *iterable)
{
PySetObject *so = NULL;
/* create PySetObject structure */
so = (PySetObject *)type->tp_alloc(type, 0);
if (so == NULL)
return NULL;
// 集合当中目前没有任何对象,因此 fill 和 used 都是 0
so->fill = 0;
so->used = 0;
// 初始化哈希表当中的数组长度为 PySet_MINSIZE 因此 mask = PySet_MINSIZE - 1
so->mask = PySet_MINSIZE - 1;
// 让 table 指向存储 entry 的数组
so->table = so->smalltable;
// 将哈希值设置成 -1 表示还没有进行计算
so->hash = -1;
so->finger = 0;
so->weakreflist = NULL;
// 如果 iterable 不等于 NULL 则需要将它指向的对象当中所有的元素加入到集合当中
if (iterable != NULL) {
// 调用函数 set_update_internal 将对象 iterable 当中的元素加入到集合当中
if (set_update_internal(so, iterable)) {
Py_DECREF(so);
return NULL;
}
}
return (PyObject *)so;
}往集合当中加入数据
首先我们先大致理清楚往集合当中插入数据的流程:
首先根据对象的哈希值,计算需要将对象放在哪个位置,也就是对应数组的下标。
查看对应下标的位置是否存在对象,如果不存在对象则将数据保存在对应下标的位置。
如果对应的位置存在对象,则查看是否和当前要插入的对象相等,则返回。
如果不相等,则使用类似于线性探测的方式去寻找下一个要插入的位置(具体的实现可以查看相关代码,具体的操作为线性探测法 + 开放地址法)。
static PyObject *
set_add(PySetObject *so, PyObject *key)
{
if (set_add_key(so, key))
return NULL;
Py_RETURN_NONE;
}
static int
set_add_key(PySetObject *so, PyObject *key)
{
setentry entry;
Py_hash_t hash;
// 这里就查看一下是否是字符串,如果是字符串直接拿到哈希值
if (!PyUnicode_CheckExact(key) ||
(hash = ((PyASCIIObject *) key)->hash) == -1) {
// 如果不是字符串则需要调用对象自己的哈希函数求得对应的哈希值
hash = PyObject_Hash(key);
if (hash == -1)
return -1;
}
// 创建一个 entry 对象将这个对象加入到哈希表当中
entry.key = key;
entry.hash = hash;
return set_add_entry(so, &entry);
}
static int
set_add_entry(PySetObject *so, setentry *entry)
{
Py_ssize_t n_used;
PyObject *key = entry->key;
Py_hash_t hash = entry->hash;
assert(so->fill <= so->mask); /* at least one empty slot */
n_used = so->used;
Py_INCREF(key);
// 调用函数 set_insert_key 将对象插入到数组当中
if (set_insert_key(so, key, hash)) {
Py_DECREF(key);
return -1;
}
// 这里就是哈希表的核心的扩容机制
if (!(so->used > n_used && so->fill*3 >= (so->mask+1)*2))
return 0;
// 这是扩容大小的逻辑
return set_table_resize(so, so->used>50000 ? so->used*2 : so->used*4);
}
static int
set_insert_key(PySetObject *so, PyObject *key, Py_hash_t hash)
{
setentry *entry;
// set_lookkey 这个函数便是插入的核心的逻辑的实现对应的实现函数在下方
entry = set_lookkey(so, key, hash);
if (entry == NULL)
return -1;
if (entry->key == NULL) {
/* UNUSED */
entry->key = key;
entry->hash = hash;
so->fill++;
so->used++;
} else if (entry->key == dummy) {
/* DUMMY */
entry->key = key;
entry->hash = hash;
so->used++;
} else {
/* ACTIVE */
Py_DECREF(key);
}
return 0;
}
// 下面的代码就是在执行我们在前面所谈到的逻辑,直到找到相同的 key 或者空位置才退出 while 循环
static setentry *
set_lookkey(PySetObject *so, PyObject *key, Py_hash_t hash)
{
setentry *table = so->table;
setentry *freeslot = NULL;
setentry *entry;
size_t perturb = hash;
size_t mask = so->mask;
size_t i = (size_t)hash & mask; /* Unsigned for defined overflow behavior */
size_t j;
int cmp;
entry = &table[i];
if (entry->key == NULL)
return entry;
while (1) {
if (entry->hash == hash) {
PyObject *startkey = entry->key;
/* startkey cannot be a dummy because the dummy hash field is -1 */
assert(startkey != dummy);
if (startkey == key)
return entry;
if (PyUnicode_CheckExact(startkey)
&& PyUnicode_CheckExact(key)
&& unicode_eq(startkey, key))
return entry;
Py_INCREF(startkey);
// returning -1 for error, 0 for false, 1 for true
cmp = PyObject_RichCompareBool(startkey, key, Py_EQ);
Py_DECREF(startkey);
if (cmp < 0) /* unlikely */
return NULL;
if (table != so->table || entry->key != startkey) /* unlikely */
return set_lookkey(so, key, hash);
if (cmp > 0) /* likely */
return entry;
mask = so->mask; /* help avoid a register spill */
}
if (entry->hash == -1 && freeslot == NULL)
freeslot = entry;
if (i + LINEAR_PROBES <= mask) {
for (j = 0 ; j < LINEAR_PROBES ; j++) {
entry++;
if (entry->key == NULL)
goto found_null;
if (entry->hash == hash) {
PyObject *startkey = entry->key;
assert(startkey != dummy);
if (startkey == key)
return entry;
if (PyUnicode_CheckExact(startkey)
&& PyUnicode_CheckExact(key)
&& unicode_eq(startkey, key))
return entry;
Py_INCREF(startkey);
// returning -1 for error, 0 for false, 1 for true
cmp = PyObject_RichCompareBool(startkey, key, Py_EQ);
Py_DECREF(startkey);
if (cmp < 0)
return NULL;
if (table != so->table || entry->key != startkey)
return set_lookkey(so, key, hash);
if (cmp > 0)
return entry;
mask = so->mask;
}
if (entry->hash == -1 && freeslot == NULL)
freeslot = entry;
}
}
perturb >>= PERTURB_SHIFT; // #define PERTURB_SHIFT 5
i = (i * 5 + 1 + perturb) & mask;
entry = &table[i];
if (entry->key == NULL)
goto found_null;
}
found_null:
return freeslot == NULL ? entry : freeslot;
}哈希表数组扩容
在 cpython 当中对于给哈希表数组扩容的操作,很多情况下都是用下面这行代码,从下面的代码来看对应扩容后数组的大小并不简单,当你的哈希表当中的元素个数大于 50000 时,新数组的大小是原数组的两倍,而如果你哈希表当中的元素个数小于等于 50000,那么久扩大为原来长度的四倍,这个主要是怕后面如果继续扩大四倍的话,可能会浪费很多内存空间。
set_table_resize(so, so->used>50000 ? so->used*2 : so->used*4);
首先需要了解一下扩容机制,当哈希表需要扩容的时候,主要有以下两个步骤:
创建新的数组,用于存储哈希表的键。
遍历原来的哈希表,将原来哈希表当中的数据加入到新的申请的数组当中。
这里需要注意的是因为数组的长度发生了变化,但是 key 的哈希值却没有发生变化,因此在新的数组当中数据对应的下标位置也会发生变化,因此需重新将所有的对象重新进行一次插入操作,下面的整个操作相对来说比较简单,这里不再进行说明了。
static int
set_table_resize(PySetObject *so, Py_ssize_t minused)
{
Py_ssize_t newsize;
setentry *oldtable, *newtable, *entry;
Py_ssize_t oldfill = so->fill;
Py_ssize_t oldused = so->used;
int is_oldtable_malloced;
setentry small_copy[PySet_MINSIZE];
assert(minused >= 0);
/* Find the smallest table size > minused. */
/* XXX speed-up with intrinsics */
for (newsize = PySet_MINSIZE;
newsize <= minused && newsize > 0;
newsize <<= 1)
;
if (newsize <= 0) {
PyErr_NoMemory();
return -1;
}
/* Get space for a new table. */
oldtable = so->table;
assert(oldtable != NULL);
is_oldtable_malloced = oldtable != so->smalltable;
if (newsize == PySet_MINSIZE) {
/* A large table is shrinking, or we can't get any smaller. */
newtable = so->smalltable;
if (newtable == oldtable) {
if (so->fill == so->used) {
/* No dummies, so no point doing anything. */
return 0;
}
/* We're not going to resize it, but rebuild the
table anyway to purge old dummy entries.
Subtle: This is *necessary* if fill==size,
as set_lookkey needs at least one virgin slot to
terminate failing searches. If fill < size, it's
merely desirable, as dummies slow searches. */
assert(so->fill > so->used);
memcpy(small_copy, oldtable, sizeof(small_copy));
oldtable = small_copy;
}
}
else {
newtable = PyMem_NEW(setentry, newsize);
if (newtable == NULL) {
PyErr_NoMemory();
return -1;
}
}
/* Make the set empty, using the new table. */
assert(newtable != oldtable);
memset(newtable, 0, sizeof(setentry) * newsize);
so->fill = 0;
so->used = 0;
so->mask = newsize - 1;
so->table = newtable;
/* Copy the data over; this is refcount-neutral for active entries;
dummy entries aren't copied over, of course */
if (oldfill == oldused) {
for (entry = oldtable; oldused > 0; entry++) {
if (entry->key != NULL) {
oldused--;
set_insert_clean(so, entry->key, entry->hash);
}
}
} else {
for (entry = oldtable; oldused > 0; entry++) {
if (entry->key != NULL && entry->key != dummy) {
oldused--;
set_insert_clean(so, entry->key, entry->hash);
}
}
}
if (is_oldtable_malloced)
PyMem_DEL(oldtable);
return 0;
}
static void
set_insert_clean(PySetObject *so, PyObject *key, Py_hash_t hash)
{
setentry *table = so->table;
setentry *entry;
size_t perturb = hash;
size_t mask = (size_t)so->mask;
size_t i = (size_t)hash & mask;
size_t j;
// #define LINEAR_PROBES 9
while (1) {
entry = &table[i];
if (entry->key == NULL)
goto found_null;
if (i + LINEAR_PROBES <= mask) {
for (j = 0; j < LINEAR_PROBES; j++) {
entry++;
if (entry->key == NULL)
goto found_null;
}
}
perturb >>= PERTURB_SHIFT;
i = (i * 5 + 1 + perturb) & mask;
}
found_null:
entry->key = key;
entry->hash = hash;
so->fill++;
so->used++;
}从集合当中删除元素 pop
从集合当中删除元素的代码如下所示:
static PyObject *
set_pop(PySetObject *so)
{
/* Make sure the search finger is in bounds */
Py_ssize_t i = so->finger & so->mask;
setentry *entry;
PyObject *key;
assert (PyAnySet_Check(so));
if (so->used == 0) {
PyErr_SetString(PyExc_KeyError, "pop from an empty set");
return NULL;
}
while ((entry = &so->table[i])->key == NULL || entry->key==dummy) {
i++;
if (i > so->mask)
i = 0;
}
key = entry->key;
entry->key = dummy;
entry->hash = -1;
so->used--;
so->finger = i + 1; /* next place to start */
return key;
}上面的代码相对来说也比较清晰,从 finger 开始寻找存在的元素,并且删除他。我们在前面提到过,当一个元素被删除之后他会被赋值成 dummy 而且哈希值为 -1 。
The above is the detailed content of What is the principle of Python collection set implementation?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1378
1378
 52
52
 The 2-Hour Python Plan: A Realistic Approach
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:04 AM
The 2-Hour Python Plan: A Realistic Approach
Apr 11, 2025 am 12:04 AM
You can learn basic programming concepts and skills of Python within 2 hours. 1. Learn variables and data types, 2. Master control flow (conditional statements and loops), 3. Understand the definition and use of functions, 4. Quickly get started with Python programming through simple examples and code snippets.
 How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
How to read redis queue
Apr 10, 2025 pm 10:12 PM
To read a queue from Redis, you need to get the queue name, read the elements using the LPOP command, and process the empty queue. The specific steps are as follows: Get the queue name: name it with the prefix of "queue:" such as "queue:my-queue". Use the LPOP command: Eject the element from the head of the queue and return its value, such as LPOP queue:my-queue. Processing empty queues: If the queue is empty, LPOP returns nil, and you can check whether the queue exists before reading the element.
 How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
How to start the server with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 08:12 PM
The steps to start a Redis server include: Install Redis according to the operating system. Start the Redis service via redis-server (Linux/macOS) or redis-server.exe (Windows). Use the redis-cli ping (Linux/macOS) or redis-cli.exe ping (Windows) command to check the service status. Use a Redis client, such as redis-cli, Python, or Node.js, to access the server.
 How to read data from redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:30 PM
How to read data from redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:30 PM
To read data from Redis, you can follow these steps: 1. Connect to the Redis server; 2. Use get(key) to get the value of the key; 3. If you need string values, decode the binary value; 4. Use exists(key) to check whether the key exists; 5. Use mget(keys) to get multiple values; 6. Use type(key) to get the data type; 7. Redis has other read commands, such as: getting all keys in a matching pattern, using cursors to iterate the keys, and sorting the key values.
 Python vs. C : Applications and Use Cases Compared
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python vs. C : Applications and Use Cases Compared
Apr 12, 2025 am 12:01 AM
Python is suitable for data science, web development and automation tasks, while C is suitable for system programming, game development and embedded systems. Python is known for its simplicity and powerful ecosystem, while C is known for its high performance and underlying control capabilities.
 What types of files are composed of oracle databases?
Apr 11, 2025 pm 03:03 PM
What types of files are composed of oracle databases?
Apr 11, 2025 pm 03:03 PM
Oracle database file structure includes: data file: storing actual data. Control file: Record database structure information. Redo log files: record transaction operations to ensure data consistency. Parameter file: Contains database running parameters to optimize performance. Archive log file: Backup redo log file for disaster recovery.
 How to find keys with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 05:45 PM
How to find keys with redis
Apr 10, 2025 pm 05:45 PM
There are several ways to find keys in Redis: Use the SCAN command to iterate over all keys by pattern or condition. Use GUI tools such as Redis Explorer to visualize the database and filter keys by name or schema. Write external scripts to query keys using the Redis client library. Subscribe to keyspace notifications to receive alerts when key changes.
 How to obtain redis login permission
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:18 PM
How to obtain redis login permission
Apr 10, 2025 pm 07:18 PM
To obtain Redis login permission, you need to perform the following steps: 1. Create a username and password; 2. Allow remote connections; 3. Restart the Redis server; 4. Connect using the Redis CLI or programming language.



