A review of 24 outstanding RPA tools worth noting

Robotic process automation (RPA) can streamline business workflows by eliminating tedious manual tasks without requiring a complete redesign of legacy systems.
Even the modern workplace can be boring and repetitive. RPA serves as a suite of smart tools that deploy artificial intelligence and low-code options to streamline workflows and save time, while also adding safeguards against costly mistakes.
What is RPA?
RPA is a technology application controlled by business logic and structured inputs designed to automate business processes. Using RPA tools, businesses can configure software or artificial intelligence bots to capture and interpret applications used to process transactions, manipulate data, trigger responses, and communicate with other digital systems.
For some enterprises, RPA is a way to modernize and improve old software without replacing it. Most enterprises have business applications that work well, but require employees and users to run in the same mode all day long. RPA tools are designed to replace this tedious work, adding a new layer to automate repetitive tasks without having to redesign the application.
Benefits of RPA
RPA is also a relatively simple way to integrate artificial intelligence algorithms into legacy applications. Many RPA platforms offer computer vision and machine learning tools that can leverage legacy code. For example, optical character recognition can extract purchase orders from uploaded document images and trigger accounting software to process them. The ability to extract text and numbers from images can be of great help to businesses that require large amounts of documents, such as insurance or banking.
Perhaps the biggest benefit is how the RPA tool is "programmed" or "trained" - through this process, the RPA robot "learns" the user's clicks. This effort, sometimes called "process discovery," can use a clickstream to mimic what the user just did, similar to how you create spreadsheet macros.
However, RPA is not automatic. During the training process, manual intervention and adjustments are necessary. Sometimes you have to write code to handle features that are not possible with pre-configured bots, but you don't need to do a lot of that. Additionally, robots are getting smarter, making their training easier. AI programs can also help workers look for patterns that might speed up robots in the future.
Top RPA Tools
RPA tools have evolved into part of a larger ecosystem for planning and managing enterprise computing architecture. These systems can manage various APIs and services, while also helping with the flow of data through additional bots.
RPA tools have also begun to play the role of managing cloud platforms. While the first iteration is aimed at desktop users, features to aid back-end control are more common. The lines between RPA for the desktop and maintaining databases and services are increasingly blurred.
The RPA market offers a mix of new purpose-built tools and older tools that have been given added automation features. Some started as business process management (BPM) tools and were extended with new features. Some vendors market their tools as "workflow automation" or "workflow management." Others distinguish RPA from "business process automation," claiming that RPA includes more complex artificial intelligence and machine vision routines.
The following are the top RPA tools currently available:
1.Airslate
For document-centric tasks (such as PDF editing or generating electronic signatures for contracts), Airlate One of the key points. Bots for streamlined workflows are programmed using drag-and-drop Flow Creator. Pre-programmed resources include connections to major backends such as Salesforce, as well as a collection of templates for common processes.
•Key Features: Document Editing and Signature Tracking
•Key Use Cases: Contract and Agreement Processing
2.Appian
Appian acquired in 2020 Jidoka and changed the product name to Appian RPA while integrating it with its digital process automation suite. Jiodka is a Japanese term that translates to "humanized automation" and refers to how its software robots are trained to imitate humans interacting with standard systems (host terminals, networks, databases, etc.). Appian RPA's low-code integrated development environment (IDE) encourages the rapid creation of custom bots, with a dashboard tracking all operating bots and the ability to create on-screen videos to help debug bots deployed on the Appian cloud platform. This information is absorbed into what they call "data structures," which contain not only numbers and letters but also relationships between elements. Deep integration across desktop and mobile platforms brings their tools to the edge of any enterprise network.
•Key Features: Java-centric bot supports cross-platform usage
•Key Use Cases: Customer Management and Compliance Paperwork
3.Automation Anywhere
Automation Anywhere’s bot store provides the Automation 360 platform with a range of tools that can perform standard clicks and tracking, as well as the process of gluing together complex data files. Some bots extract information from spreadsheets, files, or web pages, and some store this information in databases for issue tracking, invoice processing, and more. Many bots rely on APIs, such as Microsoft Azure's image analysis API. One of the goals is to open access across the enterprise with easy-to-automate tools like AARI, which can transform any web application into an automated worker. They also offer a "community edition" that is free for small businesses with limited workflows and the cloud-based service saves businesses the hassle of installing and maintaining the RPA itself.
•Key Features: Center of Excellence (CoE) Manager tracks the performance of various bots in a centralized dashboard; BotInsight deeply tracks the performance of each bot
•Key Use Cases: In the enterprise Open Bot Development and Deployment in Scope
4.AutomationEdge
AutomationEdge’s bots provide “hyperautomation” capabilities through a blend of API interaction and artificial intelligence. The focus is on interaction with web pages, databases and Excel spreadsheets. Its conversational RPA brings natural language interfaces to many interactions. Many of the bots in the bot store are preconfigured for specific industries or business units, such as human resources or customer relations. AutomationEdge also offers a free version with limitations on time, steps, and coverage. Some AI-driven options like conversational RPA and intelligent document processing are not included.
•Key features: Pay-as-you-go billing simplifies adoption
•Key use cases: Chatbot management; document processing for front, middle and back offices
5.AWS Lambda
The Amazon cloud platform has many data processing options. Lambda functions are like the glue that connects services and automates work in your network. These functions can be as large or small as needed, and they can be triggered when new data arrives. Lambda functions are designed more to automate backend work and they are most efficient when using AWS services while being able to connect to any service that has additional work.
•Key Features: Automate backend data flow in the Amazon Cloud
•Key Use Cases: Fix issues and smooth data movement between services
6.Cyclone Robotics
The Cyclone toolset is growing to support low-code development. Its RPA Studio combines basic automation tools for building data pipelines with advanced artificial intelligence tools for OCR and computer vision. It also provides low-code options for integrating multiple tools into a cohesive automated workflow. Small and medium-sized businesses can also use the EasyPie service to run these tools in Cyclone's cloud platform.
•Key features: Has a wide range of plug-ins to connect major platforms and services for artificial intelligence
•Key use cases: A wide range of markets, including the mobile market
7.Datamatics
TruBot (Datamatics’ name for its separate program) was created using TruBot Designer, a tool that allows users to create and edit software. Most work is done by dragging and dropping components in the visual designer, and developers can also adjust system-generated code in the IDE. The robot can be coordinated with the TruBot Cockpit, a system that uses special tools to scan images and understand unstructured text, thus emphasizing text processing. The tool runs in the cloud, and some features can be installed on users' own computers, with a personal version for handling more personal tasks, something Datamatics calls "RPA democratization." Teams with heavy workloads can use TruCap, a template-free data ingestion tool.
•Key features: Integrated AI for OCR and language analysis; Mainframe integration; Desktop version
•Key use cases: Chatbot and call center support; Desktop automation
8 .EdgeVerve Systems
AssistEdge system helps users build data processing infrastructure by integrating with major data sources and tracking users to discover common working patterns. Call centers and customer help portals can use AssistEdge Engage to automate the repetitive tasks of coordinating multiple legacy systems. Where possible, EdgeVerve relies on artificial intelligence to provide scenario assistance and process incoming forms and other data. For example, the document processing system XtractEdge provides OCR to speed up form processing. The company also optimizes systems for industries such as supply chain management (TradeEdge) or banking. It provides migration from desktop to cloud solutions, as well as an open source version.
•Main Features: Open Source Edition; Tighter Integration with Artificial Intelligence on Scene and Vision Processing
•Main Use Cases: Supply Chain Management, Financial Transactions
9.Fortra Automate
Fortra’s (formerly HelpSystems) RPA tool handles everything from replying to queries to generating reports. Core desktop automation tools scrape data sources by simulating events in the Windows GUI and interact with web applications and local software. While managing business, people emphasize on using Microsoft Office tools to generate text and graphical reports. Larger jobs spanning multiple desktops can use Automate Plus and Automate Ultimate to increase scale. Document scanning is performed using automated smart capture, all with integrated security and auditing features.
•Key Features: Integration with Microsoft Desktop Applications
•Key Use Cases: Claims Processing, Service Industries
10. IBM Automation
IBM for Automation Low-level tasks provide a wide range of options, which are divided into separate products and bundled with IBM Automation. For example, IBM's CloudPak for business automation provides a low-code studio for testing and developing automation strategies. Artificial intelligence tools provide optical character recognition for documents. Watson Assistant provides services to customers through integrated bots. Teams can use process mining tools to iterate workflows and explore hypothesized strategies. All software can be deployed on-premises or in IBM's cloud.
•Main features: Extensive experience with enterprise workflows, integrated with many mainframes
•Main use cases: Data capture, scientific process management; business decision-making automation, customer care
11. Kofax
ImageTech Systems developed Kofax, a suite of bots for document processing and workflow automation. Its design studio offers an IDE that converts code written in Java, Python or other programming languages into instructions for the robot. Some users want to use their automation process discovery code to track existing workflows and generate bots. The code can also be broken down into smaller KapowKapplets tools to handle centralized transactions locally. All behavior is tracked via standard analytics and reported via a dashboard so that robot malfunctions can be observed.
•Key features: Integration with enterprise content management tools; Micro-application platform that simplifies deployment
•Key use cases: Managing content collections; Data pipeline integration
12.Laiye
Laiye is another platform emerging from the Chinese market, targeting retail groups and other groups with a wide range of customer needs. Automation Creator is a drag-and-drop IDE for converting workflows into bots that can be deployed and tracked using tools like Creativity Center.
•Key features: AI chatbots and cloud-native bots
•Key use cases: Job execution system provides general support for document-centric tasks
13. Microsoft Power
The Power Automate tool from Microsoft is part of the company's Power platform for creating applications, virtual agents and business intelligence reports. Desktop tools focus on automating common Windows 10 (or higher) operations, and cloud computing tools handle server-side tasks. The user-friendly interface allows everyone to track their workflow and convert it into automated, editable routines. Power Advisor tracks statistics about performance to locate bottlenecks and other issues. Microsoft is integrating some of its artificial intelligence into Microsoft Power. Users can build new automation scripts in natural language by describing what should happen. AI Builder can also create and deploy models that make predictions and even decisions, relieving even more work for users.
•Key features: Desktop-focused Windows 10 or 11 platform or Azure
•Key use cases: Broad, enterprise-wide licensing; AI integration
14. MuleSoft RPA (formerly Servicetrace)
Salesforce’s Mulesoft RPA tool, once known as Servicetrace, is now part of the workplace automation and enterprise architecture platform. RPA tools use artificial intelligence and machine learning to help decode documents and collect data automatically. Automation can be scripted with the drag-and-drop RPA Builder or automatically collected via the RPA Recorder, which monitors users to capture repetitive tasks. When deployed using Robot Manager, the vertical scaling of the system enhances parallel operations, enabling multiple robots to run simultaneously.
• Key features: AI-based OCR and a good editor; recent merger will strengthen integration with API-based workflows
• Key use cases: Banks, utilities and Other industries with large compliance-driven jobs
14. NICE
NICE bots are designed to be supervised assistants or, if they are competent enough, to serve as unsupervised back-office tools. The goal is "journey orchestration" so that customers or employees are helped at every step of the digital pipeline. One of the assistants, NEVA, is promoted as a friendly assistant and "workforce multiplier" for solving customer service problems. Scene Composer for Live Designer tracks how clicks and keystrokes interact with web pages. Data from other sources can be collected through connectors to standard back office sources such as SAP, Siebel and .net servers. Its CXexchange offers hundreds of extensions and proxies that accelerate integrations. Its open cloud platform CXone helps support this growth globally.
•Key Features: Desktop Assistant and Server-Side Backend Integration
•Key Use Cases: Call Center Automation: Customer Service Tools; Accelerate workflows by creating bots that learn by assisting humans first, and then Achieve complete autonomy in the backend
15. Nintex
The RPA tool from Kryon is now part of Nintex Data Automation, creating a complete platform for management processes and business workflows. Process discovery helps find jobs that need automation and convert them into bots that can be deployed and tracked. For document-intensive processes that may require signatures, Nintex’s collection of RPA bots focuses on integrating with Office 365, Salesforce and Adobe tools to automate the process of creating documents and signing them in digital legal pipelines. Results can run in the cloud or on-premises.
•Key features: Tight integration with mainstream desktop tools
•Key use case: Document-led compliance pipeline
16. NTT-AT WinActor
NTT-AT's WinActor saves Windows users time by automating the most common steps. It integrates with major Microsoft tools to build complex workflows by recording user actions. These are converted into scenes that users can trigger when new events occur, such as receiving an email. For example, a new request for information can be converted into a qualified lead for a sales database with just a click of the keyboard. A variety of supplementary libraries extend the tool to handle specific tasks, such as creating PDF versions.
•Key features: Extensive integration with Microsoft tools
•Key use cases: Email processing and database integration; spreadsheet automation
17. Pega
Pega by Pegasystems offers a variety of tools to accelerate enterprise integration and processing, including AI classifiers, chatbots, DevOps enablement tools, and RPA. Creating the right automation can start with Pega's AI-powered workforce intelligence tool, a desktop-mounted bot that tracks how people work. This investigation will reveal bottlenecks where poor back-end processing can be automated now and in the future. Pega hopes to provide "self-healing" and "self-learning" applications that can use artificial intelligence and other statistics to identify new opportunities for better automation. Pega supports common use cases such as coordinating financial transactions and new customers. The company also offers low-code options for BPM.
•Key Features: Fully integrated with an enterprise tool suite for development, deployment, and automated data processing
•Key Use Cases: Compliance and Integration
18. Rocketbot
Processing documents with a python-based bot on a Linux, Mac or Windows desktop computer is Rocketbot's main focus. Text can be extracted using Rocketbot Telescope, and the backup data then entered using a robot trained using Rocketbot Studio’s drag-and-drop editor. Rocketbot Orquestador will manage them, running them as needed while compiling statistics.
•Main features: Python-based bots
•Main use cases: document processing and data extraction
19.Samsung SDS Brity RPA
Samsung SDS Brity RPA is divided into three parts. Designers provide drag-and-drop flow diagrams for desktop and enterprise backend legacy services through a variety of connectors. Bots will schedule and run various jobs at preset times, or respond to events, restart virtual machines, and simulate all events that may be generated by humans. Larger, more independent jobs can be separated out and run on the Bot processor. Samsung has also integrated a wide variety of AI routines (ML, NLP, vision and analytics) and is expanding to offer collaboration software for teams.
•Key features: Designed to improve industrial and enterprise business processes through automation
•Key use cases: Save time and improve quality for enterprise-driven tasks
20.SAP
SAP now offers robotic process automation options to streamline many workflow operations of its software. SAP's tools can observe current teams to mimic their actions. Once completed, users can adjust the process in a drag-and-drop low-code IDE. The results are deployed into the SAP environment and run as attended or unattended bots. Teams looking to leverage the work of others can turn to the SAP RPA store to download bots to perform common tasks, such as opening Excel spreadsheets and finding orders to identify and classify.
•Key Features: Integration with SAP stack
•Key Use Case: Automate SAP traced and driven business processes
21.SS&C Blue Prism
SS&C Blue Prism, one of the first RPA companies founded in 2012, promotes "intelligent automation" to integrate more artificial intelligence into processes to simplify scalable and adaptive processes. The focus is on using artificial intelligence and machine learning to "create a journey" for an enterprise's data, as the data is passed through a series of bots that make automated decisions, often through complex machine learning algorithms. In the beginning, a series of operations are strung together, but then each operation generates statistics that can be used to train and improve the choices made. The company also maintains a digital exchange platform, and third-party plug-ins can be purchased to extend features by establishing connections with traditional databases (such as MySQL), large providers (such as AWS), and social media (such as Twitter).
•Key features: Significant investments in artificial intelligence, including machine vision and sentiment analysis to classify and respond to all information
•Key use cases: Building complete document and message processing chains
22.UiPath
UiPath provides a complete collection of tools for discovering workflows through process mining and task analysis and turning them into autonomous processes that can be edited and adjusted. These bots are controlled by Orchestrator, which triggers them in response to events while tracking behavior, generating reports, and controlling access where required for compliance. UiPath is expanding into artificial intelligence and emphasizing machine vision tools that can extract information from images or screenshots. These usually focus on OCR, converting letters and numbers into a form that machines can understand.
•Key features: Open environment allows integration of VB.Net, C#, Python and Java code
•Key use cases: Integration with full legacy stack solutions; transaction processing
23.WorkFusion
WorkFusion’s digital employees all have their own special concerns. For example, Tara is a top OFAC/AML expert focused on making transactions risk-free. Casey is a customer relations expert obsessed with creating better, faster customer experiences. Enterprises can take them and create a customized version that can deploy OCR and some artificial intelligence to their specific tasks. Digital workers are deployed with Workforce Enterprise and can operate autonomously or as a human assistant.
•Key Features: Digital workers adapted for common roles in RPA and workforce automation
•Key use cases: Email and customer interaction; task routing
24. Open source
While community versions with limited features are common, large enterprises often sell proprietary tools. Open source processes are less common, but by putting a few open source projects together, users can often accomplish many simple tasks. You may need to do more work yourself to train these tools, usually typing code in an editor. Still, they're an interesting option.
•Key features: Full open source code access; no vendor lock-in
•Key use cases: Web integration; data collection; testing and validation
The above is the detailed content of A review of 24 outstanding RPA tools worth noting. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Bytedance Cutting launches SVIP super membership: 499 yuan for continuous annual subscription, providing a variety of AI functions
Jun 28, 2024 am 03:51 AM
Bytedance Cutting launches SVIP super membership: 499 yuan for continuous annual subscription, providing a variety of AI functions
Jun 28, 2024 am 03:51 AM
This site reported on June 27 that Jianying is a video editing software developed by FaceMeng Technology, a subsidiary of ByteDance. It relies on the Douyin platform and basically produces short video content for users of the platform. It is compatible with iOS, Android, and Windows. , MacOS and other operating systems. Jianying officially announced the upgrade of its membership system and launched a new SVIP, which includes a variety of AI black technologies, such as intelligent translation, intelligent highlighting, intelligent packaging, digital human synthesis, etc. In terms of price, the monthly fee for clipping SVIP is 79 yuan, the annual fee is 599 yuan (note on this site: equivalent to 49.9 yuan per month), the continuous monthly subscription is 59 yuan per month, and the continuous annual subscription is 499 yuan per year (equivalent to 41.6 yuan per month) . In addition, the cut official also stated that in order to improve the user experience, those who have subscribed to the original VIP
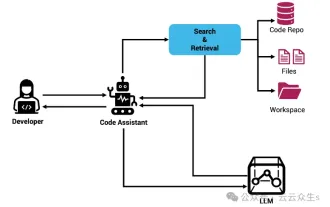 Context-augmented AI coding assistant using Rag and Sem-Rag
Jun 10, 2024 am 11:08 AM
Context-augmented AI coding assistant using Rag and Sem-Rag
Jun 10, 2024 am 11:08 AM
Improve developer productivity, efficiency, and accuracy by incorporating retrieval-enhanced generation and semantic memory into AI coding assistants. Translated from EnhancingAICodingAssistantswithContextUsingRAGandSEM-RAG, author JanakiramMSV. While basic AI programming assistants are naturally helpful, they often fail to provide the most relevant and correct code suggestions because they rely on a general understanding of the software language and the most common patterns of writing software. The code generated by these coding assistants is suitable for solving the problems they are responsible for solving, but often does not conform to the coding standards, conventions and styles of the individual teams. This often results in suggestions that need to be modified or refined in order for the code to be accepted into the application
 Seven Cool GenAI & LLM Technical Interview Questions
Jun 07, 2024 am 10:06 AM
Seven Cool GenAI & LLM Technical Interview Questions
Jun 07, 2024 am 10:06 AM
To learn more about AIGC, please visit: 51CTOAI.x Community https://www.51cto.com/aigc/Translator|Jingyan Reviewer|Chonglou is different from the traditional question bank that can be seen everywhere on the Internet. These questions It requires thinking outside the box. Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly important in the fields of data science, generative artificial intelligence (GenAI), and artificial intelligence. These complex algorithms enhance human skills and drive efficiency and innovation in many industries, becoming the key for companies to remain competitive. LLM has a wide range of applications. It can be used in fields such as natural language processing, text generation, speech recognition and recommendation systems. By learning from large amounts of data, LLM is able to generate text
 Can fine-tuning really allow LLM to learn new things: introducing new knowledge may make the model produce more hallucinations
Jun 11, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Can fine-tuning really allow LLM to learn new things: introducing new knowledge may make the model produce more hallucinations
Jun 11, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Large Language Models (LLMs) are trained on huge text databases, where they acquire large amounts of real-world knowledge. This knowledge is embedded into their parameters and can then be used when needed. The knowledge of these models is "reified" at the end of training. At the end of pre-training, the model actually stops learning. Align or fine-tune the model to learn how to leverage this knowledge and respond more naturally to user questions. But sometimes model knowledge is not enough, and although the model can access external content through RAG, it is considered beneficial to adapt the model to new domains through fine-tuning. This fine-tuning is performed using input from human annotators or other LLM creations, where the model encounters additional real-world knowledge and integrates it
 To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
Editor |ScienceAI Question Answering (QA) data set plays a vital role in promoting natural language processing (NLP) research. High-quality QA data sets can not only be used to fine-tune models, but also effectively evaluate the capabilities of large language models (LLM), especially the ability to understand and reason about scientific knowledge. Although there are currently many scientific QA data sets covering medicine, chemistry, biology and other fields, these data sets still have some shortcomings. First, the data form is relatively simple, most of which are multiple-choice questions. They are easy to evaluate, but limit the model's answer selection range and cannot fully test the model's ability to answer scientific questions. In contrast, open-ended Q&A
 SOTA performance, Xiamen multi-modal protein-ligand affinity prediction AI method, combines molecular surface information for the first time
Jul 17, 2024 pm 06:37 PM
SOTA performance, Xiamen multi-modal protein-ligand affinity prediction AI method, combines molecular surface information for the first time
Jul 17, 2024 pm 06:37 PM
Editor | KX In the field of drug research and development, accurately and effectively predicting the binding affinity of proteins and ligands is crucial for drug screening and optimization. However, current studies do not take into account the important role of molecular surface information in protein-ligand interactions. Based on this, researchers from Xiamen University proposed a novel multi-modal feature extraction (MFE) framework, which for the first time combines information on protein surface, 3D structure and sequence, and uses a cross-attention mechanism to compare different modalities. feature alignment. Experimental results demonstrate that this method achieves state-of-the-art performance in predicting protein-ligand binding affinities. Furthermore, ablation studies demonstrate the effectiveness and necessity of protein surface information and multimodal feature alignment within this framework. Related research begins with "S
 Five schools of machine learning you don't know about
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Five schools of machine learning you don't know about
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Machine learning is an important branch of artificial intelligence that gives computers the ability to learn from data and improve their capabilities without being explicitly programmed. Machine learning has a wide range of applications in various fields, from image recognition and natural language processing to recommendation systems and fraud detection, and it is changing the way we live. There are many different methods and theories in the field of machine learning, among which the five most influential methods are called the "Five Schools of Machine Learning". The five major schools are the symbolic school, the connectionist school, the evolutionary school, the Bayesian school and the analogy school. 1. Symbolism, also known as symbolism, emphasizes the use of symbols for logical reasoning and expression of knowledge. This school of thought believes that learning is a process of reverse deduction, through existing
 SK Hynix will display new AI-related products on August 6: 12-layer HBM3E, 321-high NAND, etc.
Aug 01, 2024 pm 09:40 PM
SK Hynix will display new AI-related products on August 6: 12-layer HBM3E, 321-high NAND, etc.
Aug 01, 2024 pm 09:40 PM
According to news from this site on August 1, SK Hynix released a blog post today (August 1), announcing that it will attend the Global Semiconductor Memory Summit FMS2024 to be held in Santa Clara, California, USA from August 6 to 8, showcasing many new technologies. generation product. Introduction to the Future Memory and Storage Summit (FutureMemoryandStorage), formerly the Flash Memory Summit (FlashMemorySummit) mainly for NAND suppliers, in the context of increasing attention to artificial intelligence technology, this year was renamed the Future Memory and Storage Summit (FutureMemoryandStorage) to invite DRAM and storage vendors and many more players. New product SK hynix launched last year






