How to get the property value of an object field using Java reflection?
Java reflection gets the field attribute value
Reflection gets all the fields of the Java class, including all fields in the parent class. The fields of the class itself can be obtained directly through the method
getDeclaredFields() [get all modifier fields] or getFields() [get public modified fields], but there is no direct way to obtain the fields in the parent class. .
Need to recursively obtain all parent classes, then obtain their fields, and finally obtain all fields of the class.
If you want to get the field value, you need to set the field to be accessible: field.setAccessible(true); field is the Field class under the reflect package
Case
1. Parent class
package com.carl.study.springboot.bean;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.experimental.Accessors;
/**
* @author changez
* @desc
* @date 2019/3/10 11:30
*/
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)
public class BeanBasic {
private Integer id;
private Long createTime;
private Long updateTime;
}2. Subclass
package com.carl.study.springboot.bean;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.EqualsAndHashCode;
import lombok.ToString;
import lombok.experimental.Accessors;
/**
* @author changez
* @desc
* @date 2019/3/10 11:17
*/
@Data
@EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper = true)
@ToString(callSuper = true)
@Accessors(chain = true)
public class Student extends BeanBasic{
private String name;
private String address;
}3. Test class, get all fields of student class
package test.lombok;
import com.carl.study.springboot.bean.Student;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author changez
* @desc Java反射获取类的所有属性.
* @date 2019/3/10 11:41
*/
public class LombokTest {
@Test
public void getParentField(){
Student stu1 = new Student();
stu1.setName("student-name")
.setAddress("student1-address")
.setId(1)
.setCreateTime(20190310140423L)
.setUpdateTime(20190310140423L)
;
Class clazz = Student.class;
List<Field> allFields = new ArrayList<>(100);
// 获取当前对象的所有属性字段
// clazz.getFields():获取public修饰的字段
// clazz.getDeclaredFields(): 获取所有的字段包括private修饰的字段
allFields.addAll(Arrays.asList(clazz.getDeclaredFields()));
// 获取所有父类的字段, 父类中的字段需要逐级获取
Class clazzSuper = clazz.getSuperclass();
// 如果父类不是object,表明其继承的有其他类。 逐级获取所有父类的字段
while (clazzSuper != Object.class) {
allFields.addAll(Arrays.asList(clazzSuper.getDeclaredFields()));
clazzSuper = clazzSuper.getSuperclass();
}
allFields.stream().forEach(field -> {
// 设置字段可访问, 否则无法访问private修饰的变量值
field.setAccessible(true);
try {
// 获取字段名称
String fieldName = field.getName();
// 获取指定对象的当前字段的值
Object fieldVal = field.get(stu1);
System.out.println(fieldName+"="+fieldVal);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}4. Result output
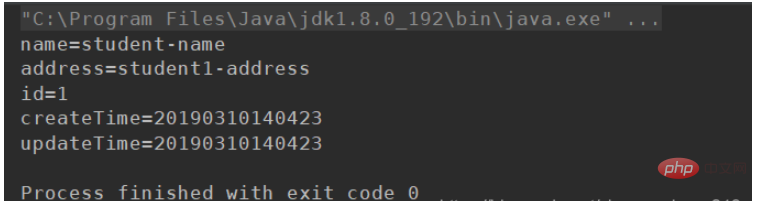
The reflection object obtains the properties and values into string
Description
Sometimes it is necessary to splice the passing objects in the form of kv. In this case, it is good to use reflection
Directly enter the code
public class FanSeVo {
private String name;
private String id;
//.......
// 如果是跟外部程序或者接口对接的话,下面还可以加2个属性,一个是相互约定的秘钥,一个//是排除秘钥之后对属性和值做凭借之后的MD5加密之后的值,可以做数据安全考虑,防止传输过程数据被篡改
}package com.ycj.my_all_demo.fanse;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.HashMap;
/**
* @author ycj
* @data 17:55
*/
public class FanSe {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FanSeVo fanSeVo = new FanSeVo("1", "2");
Field[] fields = fanSeVo.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>();
for (Field field : fields) {
field.setAccessible(true);
try {
// 把对象的属性做k,值做v
// 当然中间还可做其他的业务操作,比如跳过某些属性什么的
String name = field.getName();
String s = field.get(fanSeVo).toString();
map.put(name,s);
System.out.println();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 吧map数据转成str,kv的形式
String strByMap = getStrByMap(map);
System.out.println(strByMap);//name1id2
}
public static String getStrByMap(HashMap<String, String> map){
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
map.forEach((k,v)->{str.append(k).append(v);});
return str.toString();
}
}The above is the detailed content of How to get the property value of an object field using Java reflection?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1386
1386
 52
52
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.




