 Technology peripherals
Technology peripherals
 AI
AI
 How to evaluate the reliability of the theoretical foundation of machine learning?
How to evaluate the reliability of the theoretical foundation of machine learning?
How to evaluate the reliability of the theoretical foundation of machine learning?
In the field of machine learning, some models are very effective, but we are not entirely sure why. In contrast, some relatively well-understood research areas have limited applicability in practice. This article explores progress in various subfields based on the utility and theoretical understanding of machine learning.
The experimental utility here is a comprehensive consideration that takes into account the breadth of applicability of a method, the ease of implementation, and the most important factor, reality usefulness in the world. Some methods are not only highly practical, but also have a wide range of applications; while some methods, although very powerful, are limited to specific areas. Methods that are reliable, predictable, and free of major flaws are considered to have higher utility.
The so-called theoretical understanding is to consider the interpretability of the model method, that is, what is the relationship between input and output, how to obtain the expected results, what is the internal mechanism of this method, and consider the method involved Depth and completeness of documentation.
Methods with a low degree of theoretical understanding usually use heuristic methods or a large number of trial and error methods in implementation; methods with a high degree of theoretical understanding often have formulaic implementations, with strong theoretical foundations and predictable results. Simpler methods, such as linear regression, have lower theoretical upper bounds, while more complex methods, such as deep learning, have higher theoretical upper bounds. When it comes to the depth and completeness of the literature within a field, the field is evaluated against the theoretical upper bounds of the field's assumptions, which relies in part on intuition.
We can construct the utility matrix into four quadrants, with the intersection of the axes representing a hypothetical reference domain with average understanding and average utility. This approach allows us to interpret fields in a qualitative way according to the quadrant in which they are located. As shown in the figure below, fields in a given quadrant may have some or all of the characteristics of that quadrant.
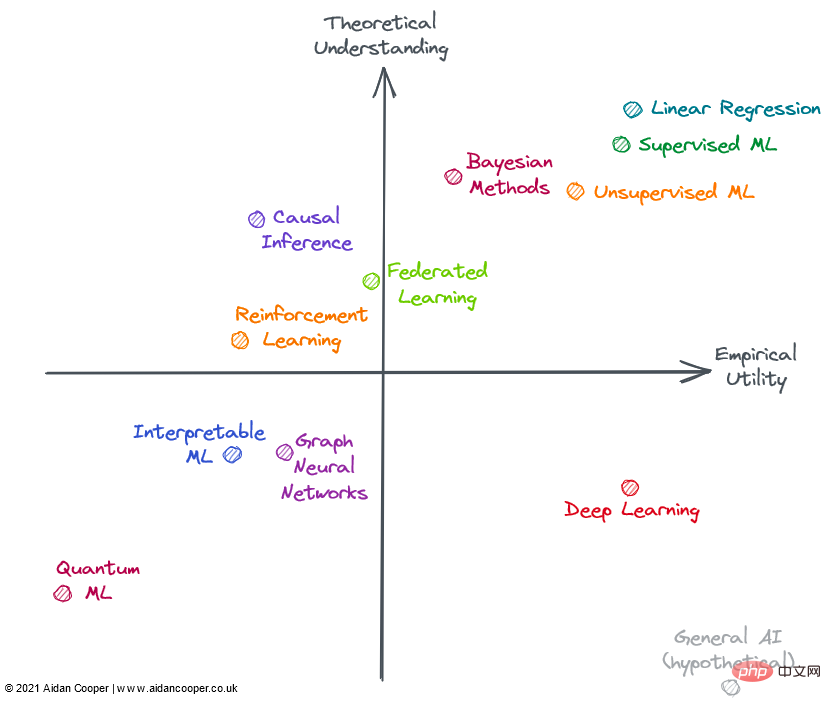
In general, we expect utility and understanding to be loosely related, such that methods with a high degree of theoretical understanding are more useful than methods with a low degree of theoretical understanding. This means that most fields should be in the lower left quadrant or the upper right quadrant. The areas away from the lower left-upper right diagonal represent exceptions. Typically, practical utility should lag behind theory because it takes time to translate nascent research theory into practical applications. Therefore, this diagonal should be above the origin, not directly through it.
Machine Learning Fields in 2022
Not all fields in the above picture are completely included in machine learning (ML), but they can all be applied in the context of ML or are closely related to it . Many of the areas evaluated overlap and cannot be clearly described: advanced methods in reinforcement learning, federated learning, and graph ML are often based on deep learning. Therefore, I consider non-deep learning aspects of their theoretical and practical utility.
Upper right quadrant: high understanding, high utility
Linear regression is a simple, easy to understand and efficient method. Although often underestimated and ignored. , but its breadth of use and thorough theoretical basis put it in the upper right corner of the figure.
Traditional machine learning has developed into a field of high theoretical understanding and practicality. Complex ML algorithms, such as gradient boosted decision trees (GBDT), have been shown to often outperform linear regression in some complex prediction tasks. This is certainly the case with big data problems. Arguably, there are still gaps in the theoretical understanding of over-parameterized models, but implementing machine learning is a delicate methodological process, and when done well, models can run reliably within the industry.
However, the extra complexity and flexibility does lead to some errors, which is why I put machine learning to the left of linear regression. In general, supervised machine learning is more sophisticated and impactful than its unsupervised counterpart, but both methods effectively solve different problem spaces.
Bayesian methods have a cult following of practitioners who tout its superiority over more popular classical statistical methods. Bayesian models are particularly useful in certain situations: point estimates alone are not enough and estimates of uncertainty are important; when data are limited or highly missing; and when you understand the data-generating process that you want to explicitly include in the model hour. The usefulness of Bayesian models is limited by the fact that for many problems point estimates are good enough and people simply default to non-Bayesian methods. What's more, there are ways to quantify uncertainty in traditional ML (they're just rarely used). Often it is easier to simply apply ML algorithms to the data without having to consider the data generation mechanism and priors. Bayesian models are also computationally expensive and would have greater utility if theoretical advances resulted in better sampling and approximation methods.
Lower Right Quadrant: Low Understanding, High Utility
Contrary to progress in most fields, deep learning has achieved some stunning successes, even though the theoretical aspects have proven fundamentally difficult to make progress on. Deep learning embodies many of the characteristics of a little-known approach: models are unstable, difficult to build reliably, configure based on weak heuristics, and produce unpredictable results. Questionable practices like random seed "tweaking" are common, and the mechanics of the working model are difficult to explain. However, deep learning continues to advance and reach superhuman performance levels in areas such as computer vision and natural language processing, opening up a world of otherwise incomprehensible tasks, such as autonomous driving.
Hypothetically, general AI will occupy the lower right corner because, by definition, superintelligence is beyond human understanding and can be used to solve any problem. Currently, it is included only as a thought experiment.
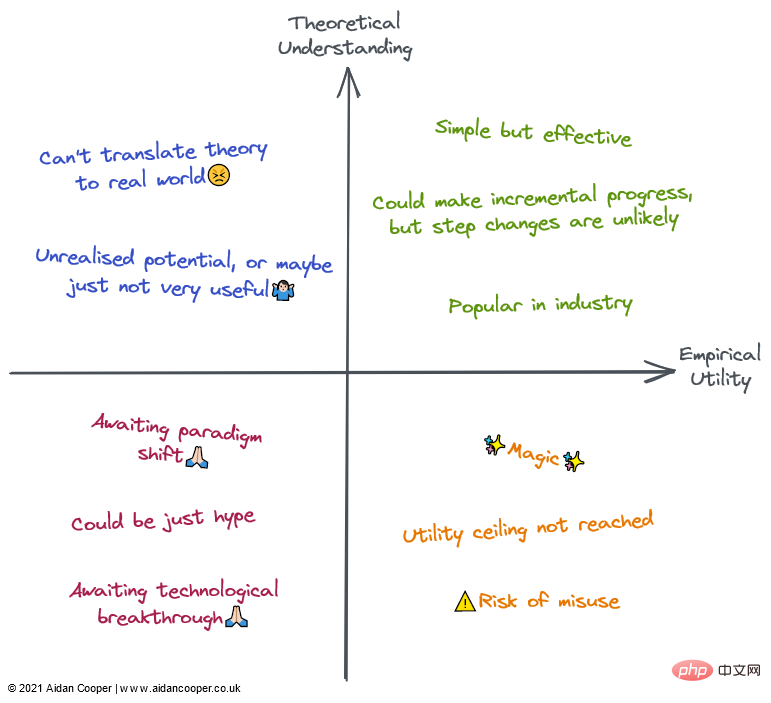
Qualitative description of each quadrant. Fields can be described by some or all of the descriptions in their corresponding regions
Upper left quadrant: high understanding, low utility
Most forms of causal inference are not machine learning, but sometimes they are, and Always interested in predictive models. Causality can be divided into randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and more sophisticated methods of causal inference, which attempt to measure causal relationships from observational data. RCTs are simple in theory and give rigorous results, but are often expensive and impractical—if not impossible—to conduct in the real world and therefore have limited utility. Causal inference methods essentially imitate RCTs without doing anything, which makes them much easier to perform, but there are a number of limitations and pitfalls that can invalidate the results. Overall, causality remains a frustrating pursuit, where current methods are often inadequate for the questions we want to ask, unless these questions can be explored through randomized controlled trials, or they fit neatly into some framework (e.g., as an accidental result of a "natural experiment").
Federated learning (FL) is a cool concept that has received little attention - probably because its most compelling applications require distribution to a large number of smartphone devices, so FL has only two players To really research: Apple and Google. Other use cases for FL exist, such as pooling proprietary data sets, but there are political and logistical challenges in coordinating these initiatives, limiting their utility in practice. Still, for what sounds like a fancy concept (roughly summarized as: "Put the model into the data, rather than the data into the model"), FL works and has applications in areas such as keyboard text prediction and personalized news recommendations. Tangible success stories. The basic theory and technology behind FL appear to be sufficient for wider application of FL.
Reinforcement learning (RL) has reached unprecedented levels of capability in games such as chess, Go, poker, and DotA. But outside of video games and simulation environments, reinforcement learning has yet to translate convincingly into real-world applications. Robotics was supposed to be the next frontier in RL, but that didn't happen - reality seemed more challenging than the highly constrained toy environment. That said, RL's achievements so far are encouraging, and someone who really likes chess might argue that its utility should be even higher. I'd like to see RL realize some of its potential practical applications before placing it on the right side of the matrix.
Lower left quadrant: low understanding, low utility
Graph neural network (GNN) is now a very popular field in machine learning, and has achieved gratifying results in many fields. But for many of these examples, it's unclear whether GNNs are better than alternatives that use more traditional structured data paired with deep learning architectures. Problems where the data are naturally graph-structured, such as molecules in cheminformatics, appear to have more compelling GNN results (although these are generally inferior to non-graph related methods). More than in most fields, there appears to be a large gap between open source tools for training GNNs at scale and in-house tools used in industry, which limits the feasibility of large GNNs outside these walled gardens. The complexity and breadth of the field suggests a high theoretical upper limit, so there should be room for GNNs to mature and convincingly demonstrate advantages for certain tasks, which will lead to greater utility. GNNs could also benefit from technological advances, as graphs currently do not fit naturally on existing computing hardware.
Interpretable Machine Learning (IML) is an important and promising field that continues to receive attention. Technologies like SHAP and LIME have become really useful tools for interrogating ML models. However, due to limited adoption, the utility of existing approaches has not yet been fully realized—robust best practices and implementation guidelines have yet to be established. However, the current main weakness of IML is that it does not address the causal question that we are really interested in. IML explains how models make predictions, but does not explain how the underlying data are causally related to them (although it is often misinterpreted like this). Before major theoretical advances, legitimate uses of IML were mostly limited to model debugging/monitoring and hypothesis generation.
Quantum Machine Learning (QML) is well outside my wheelhouse, but currently seems to be a hypothetical exercise in waiting patiently for viable quantum computers to become available. Until then, QML sat insignificantly in the lower left corner.
Incremental Progress, Technological Leap and Paradigm Shift
There are three main mechanisms through which the field traverses the theoretical understanding and empirical utility matrix (Figure 2).
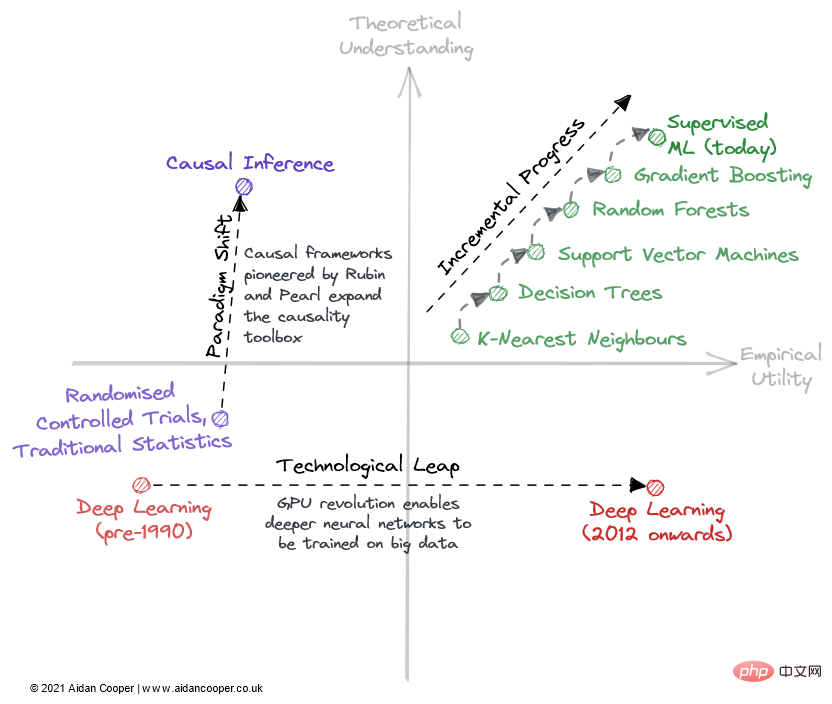
Illustrative example of the way fields can be traversed through a matrix.
Progressive progression is a slow and steady progression that moves up the inch field on the right side of the matrix. A good example of this is supervised machine learning over the past few decades, during which time increasingly effective predictive algorithms have been refined and adopted, giving us the powerful toolbox we enjoy today. Incremental progress is the status quo in all mature fields, except for periods of more dramatic movement due to technological leaps and paradigm shifts.
As a result of technological leaps, some fields have seen step changes in scientific progress. The field of *deep learning* was not unraveled by its theoretical foundations, which were discovered more than 20 years before the deep learning boom of the 2010s - it was parallel processing powered by consumer GPUs that fueled its renaissance. Technological leaps usually appear as jumps to the right along the empirical utility axis. However, not all technology-led advancements are leaps and bounds. Today's deep learning is characterized by incremental progress achieved by training larger and larger models using more computing power and increasingly specialized hardware.
The ultimate mechanism of scientific progress within this framework is paradigm shift. As Thomas Kuhn noted in his book The Structure of Scientific Revolutions, paradigm shifts represent important changes in the basic concepts and experimental practices of scientific disciplines. The causal framework pioneered by Donald Rubin and Judea Pearl is one such example, elevating the field of causality from randomized controlled trials and traditional statistical analysis to a more powerful mathematical discipline in the form of causal inference. Paradigm shifts often manifest as an upward movement in understanding, which may follow or be accompanied by an increase in utility.
However, paradigm transformation can traverse the matrix in any direction. When neural networks (and subsequently deep neural networks) established themselves as a separate paradigm from traditional ML, this initially corresponded to a decline in practicality and understanding. Many emerging fields branch off from more established areas of research in this way.
The Scientific Revolution of Prediction and Deep Learning
To summarize, here are some speculative predictions of what I think may happen in the future (Table 1). Fields in the upper right quadrant are omitted because they are too mature to see significant progress.
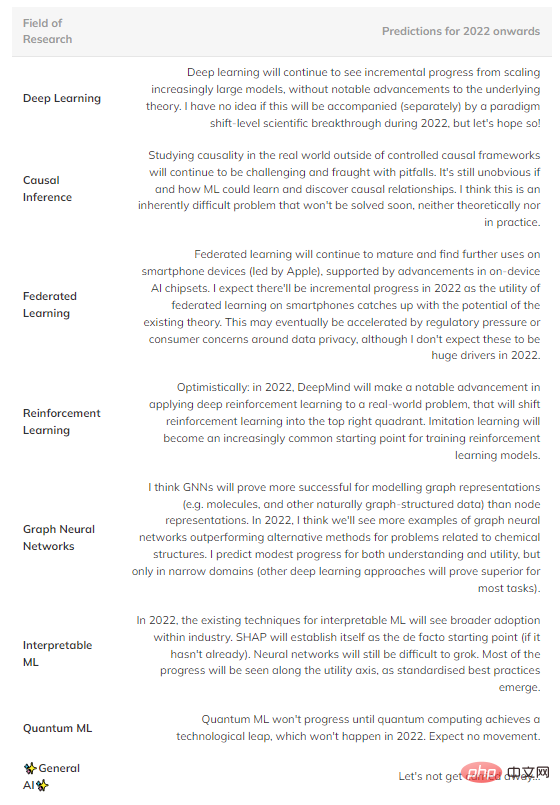
Table 1: Forecast of future progress in several major fields of machine learning.
A more important observation than how individual fields develop, however, is the general trend toward empiricism and an increasing willingness to acknowledge comprehensive theoretical understanding.
From historical experience, generally theories (hypotheses) appear first, and then ideas are formulated. But deep learning has ushered in a new scientific process that subverts this. That is, methods are expected to demonstrate state-of-the-art performance before anyone focuses on theory. Empirical results are king, theory is optional.
This has led to systematic widespread gaming in machine learning research of getting the latest state-of-the-art by simply modifying existing methods and relying on randomness to surpass the baseline, rather than meaningfully advancing theory in the field. Results. But maybe that’s the price we pay for this new wave of machine learning boom.
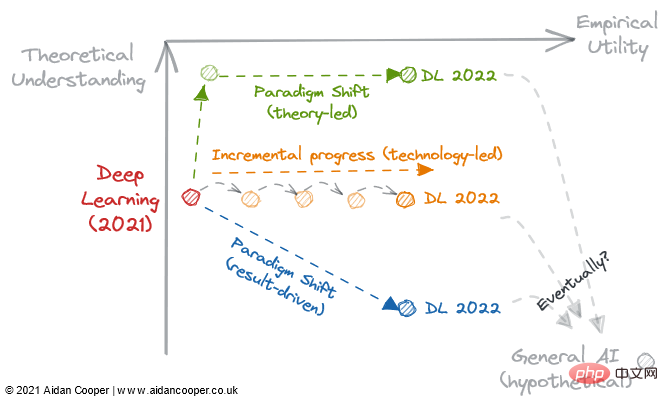
Figure 3: 3 potential trajectories for deep learning development in 2022.
Whether deep learning irreversibly becomes a results-oriented process and relegates theoretical understanding to optionality, 2022 may be the turning point. We should consider the following questions:
Will theoretical breakthroughs allow our understanding to catch up with practicality and transform deep learning into a more structured discipline like traditional machine learning?
Is the existing deep learning literature sufficient to allow utility to increase indefinitely, simply by scaling to larger and larger models?
Or will an empirical breakthrough lead us further down the rabbit hole, into a new paradigm that enhances utility, even though we know less about it?
Do any of these routes lead to general artificial intelligence? Only time will tell.
The above is the detailed content of How to evaluate the reliability of the theoretical foundation of machine learning?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

Video Face Swap
Swap faces in any video effortlessly with our completely free AI face swap tool!

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1387
1387
 52
52
 Bytedance Cutting launches SVIP super membership: 499 yuan for continuous annual subscription, providing a variety of AI functions
Jun 28, 2024 am 03:51 AM
Bytedance Cutting launches SVIP super membership: 499 yuan for continuous annual subscription, providing a variety of AI functions
Jun 28, 2024 am 03:51 AM
This site reported on June 27 that Jianying is a video editing software developed by FaceMeng Technology, a subsidiary of ByteDance. It relies on the Douyin platform and basically produces short video content for users of the platform. It is compatible with iOS, Android, and Windows. , MacOS and other operating systems. Jianying officially announced the upgrade of its membership system and launched a new SVIP, which includes a variety of AI black technologies, such as intelligent translation, intelligent highlighting, intelligent packaging, digital human synthesis, etc. In terms of price, the monthly fee for clipping SVIP is 79 yuan, the annual fee is 599 yuan (note on this site: equivalent to 49.9 yuan per month), the continuous monthly subscription is 59 yuan per month, and the continuous annual subscription is 499 yuan per year (equivalent to 41.6 yuan per month) . In addition, the cut official also stated that in order to improve the user experience, those who have subscribed to the original VIP
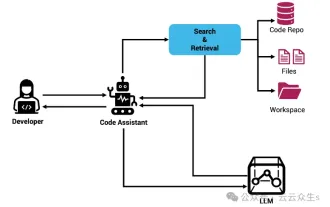 Context-augmented AI coding assistant using Rag and Sem-Rag
Jun 10, 2024 am 11:08 AM
Context-augmented AI coding assistant using Rag and Sem-Rag
Jun 10, 2024 am 11:08 AM
Improve developer productivity, efficiency, and accuracy by incorporating retrieval-enhanced generation and semantic memory into AI coding assistants. Translated from EnhancingAICodingAssistantswithContextUsingRAGandSEM-RAG, author JanakiramMSV. While basic AI programming assistants are naturally helpful, they often fail to provide the most relevant and correct code suggestions because they rely on a general understanding of the software language and the most common patterns of writing software. The code generated by these coding assistants is suitable for solving the problems they are responsible for solving, but often does not conform to the coding standards, conventions and styles of the individual teams. This often results in suggestions that need to be modified or refined in order for the code to be accepted into the application
 Can fine-tuning really allow LLM to learn new things: introducing new knowledge may make the model produce more hallucinations
Jun 11, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Can fine-tuning really allow LLM to learn new things: introducing new knowledge may make the model produce more hallucinations
Jun 11, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Large Language Models (LLMs) are trained on huge text databases, where they acquire large amounts of real-world knowledge. This knowledge is embedded into their parameters and can then be used when needed. The knowledge of these models is "reified" at the end of training. At the end of pre-training, the model actually stops learning. Align or fine-tune the model to learn how to leverage this knowledge and respond more naturally to user questions. But sometimes model knowledge is not enough, and although the model can access external content through RAG, it is considered beneficial to adapt the model to new domains through fine-tuning. This fine-tuning is performed using input from human annotators or other LLM creations, where the model encounters additional real-world knowledge and integrates it
 Seven Cool GenAI & LLM Technical Interview Questions
Jun 07, 2024 am 10:06 AM
Seven Cool GenAI & LLM Technical Interview Questions
Jun 07, 2024 am 10:06 AM
To learn more about AIGC, please visit: 51CTOAI.x Community https://www.51cto.com/aigc/Translator|Jingyan Reviewer|Chonglou is different from the traditional question bank that can be seen everywhere on the Internet. These questions It requires thinking outside the box. Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly important in the fields of data science, generative artificial intelligence (GenAI), and artificial intelligence. These complex algorithms enhance human skills and drive efficiency and innovation in many industries, becoming the key for companies to remain competitive. LLM has a wide range of applications. It can be used in fields such as natural language processing, text generation, speech recognition and recommendation systems. By learning from large amounts of data, LLM is able to generate text
 Five schools of machine learning you don't know about
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Five schools of machine learning you don't know about
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Machine learning is an important branch of artificial intelligence that gives computers the ability to learn from data and improve their capabilities without being explicitly programmed. Machine learning has a wide range of applications in various fields, from image recognition and natural language processing to recommendation systems and fraud detection, and it is changing the way we live. There are many different methods and theories in the field of machine learning, among which the five most influential methods are called the "Five Schools of Machine Learning". The five major schools are the symbolic school, the connectionist school, the evolutionary school, the Bayesian school and the analogy school. 1. Symbolism, also known as symbolism, emphasizes the use of symbols for logical reasoning and expression of knowledge. This school of thought believes that learning is a process of reverse deduction, through existing
 To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
Editor |ScienceAI Question Answering (QA) data set plays a vital role in promoting natural language processing (NLP) research. High-quality QA data sets can not only be used to fine-tune models, but also effectively evaluate the capabilities of large language models (LLM), especially the ability to understand and reason about scientific knowledge. Although there are currently many scientific QA data sets covering medicine, chemistry, biology and other fields, these data sets still have some shortcomings. First, the data form is relatively simple, most of which are multiple-choice questions. They are easy to evaluate, but limit the model's answer selection range and cannot fully test the model's ability to answer scientific questions. In contrast, open-ended Q&A
 SOTA performance, Xiamen multi-modal protein-ligand affinity prediction AI method, combines molecular surface information for the first time
Jul 17, 2024 pm 06:37 PM
SOTA performance, Xiamen multi-modal protein-ligand affinity prediction AI method, combines molecular surface information for the first time
Jul 17, 2024 pm 06:37 PM
Editor | KX In the field of drug research and development, accurately and effectively predicting the binding affinity of proteins and ligands is crucial for drug screening and optimization. However, current studies do not take into account the important role of molecular surface information in protein-ligand interactions. Based on this, researchers from Xiamen University proposed a novel multi-modal feature extraction (MFE) framework, which for the first time combines information on protein surface, 3D structure and sequence, and uses a cross-attention mechanism to compare different modalities. feature alignment. Experimental results demonstrate that this method achieves state-of-the-art performance in predicting protein-ligand binding affinities. Furthermore, ablation studies demonstrate the effectiveness and necessity of protein surface information and multimodal feature alignment within this framework. Related research begins with "S
 SK Hynix will display new AI-related products on August 6: 12-layer HBM3E, 321-high NAND, etc.
Aug 01, 2024 pm 09:40 PM
SK Hynix will display new AI-related products on August 6: 12-layer HBM3E, 321-high NAND, etc.
Aug 01, 2024 pm 09:40 PM
According to news from this site on August 1, SK Hynix released a blog post today (August 1), announcing that it will attend the Global Semiconductor Memory Summit FMS2024 to be held in Santa Clara, California, USA from August 6 to 8, showcasing many new technologies. generation product. Introduction to the Future Memory and Storage Summit (FutureMemoryandStorage), formerly the Flash Memory Summit (FlashMemorySummit) mainly for NAND suppliers, in the context of increasing attention to artificial intelligence technology, this year was renamed the Future Memory and Storage Summit (FutureMemoryandStorage) to invite DRAM and storage vendors and many more players. New product SK hynix launched last year



