 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 How to use inheritance, constructor methods, overriding and overloading methods in JAVA?
How to use inheritance, constructor methods, overriding and overloading methods in JAVA?
How to use inheritance, constructor methods, overriding and overloading methods in JAVA?

Constructor method
The constructor method of the class is a special method, this method name It must be consistent with the class name. The construction cannot have a return value, does not use void, and cannot be called directly. It is automatically called when the class object is instantiated, and can be called when new. General constructors are used for initialization when instantiating class objects. If a class does not have a constructor written, the system automatically adds a no-argument constructor to this class during compilation. If the declaring class has written a constructor, the system will no longer add a parameterless constructor. It is recommended that after writing the constructor, it is best to write a parameterless constructor.
No-parameter construction
To put it bluntly, it is a construction method without parameters
If you don’t understand the concept, it will be clear with an example .
Declare a class A
public class A {
}Create a constructor method A() in class A, and print out a sentence
The constructor must be the same as the class name
public class A {
public A(){
System.out.println("构造方法A()");
}}Create a new test class and nuw an object of class A in the class
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new A();
}}Execute the main method and try it
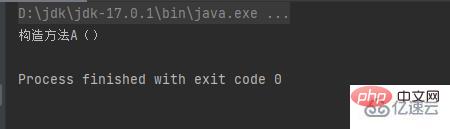
The construction method is equivalent to the method that is automatically used in the new object
Construction with parameters
Construction with parameters is Constructor with parameters
Declare a constructor with parameters in class A and pass in two String type parameters, a and b
public class A {
public A() {
}
public A(String a, String b) {
System.out.println(a + b);
}}New one in the test class Pass in the parameters when object a
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new A("aaa", "bbb");
}}Execute the main method
Note
There is no constructor When , there is a parameterless construct hidden in the class. But when you create a parameterized constructor, the hidden parameterless constructor disappears. Then the new object can only take parameters in the future. Therefore, when building a parameterized constructor, you must create a parameterless constructor and put it there.
Inheritance of classes
In the Java language, a class class has a single inheritance and multiple implementation interfaces. Interface interface is multiple inheritance.
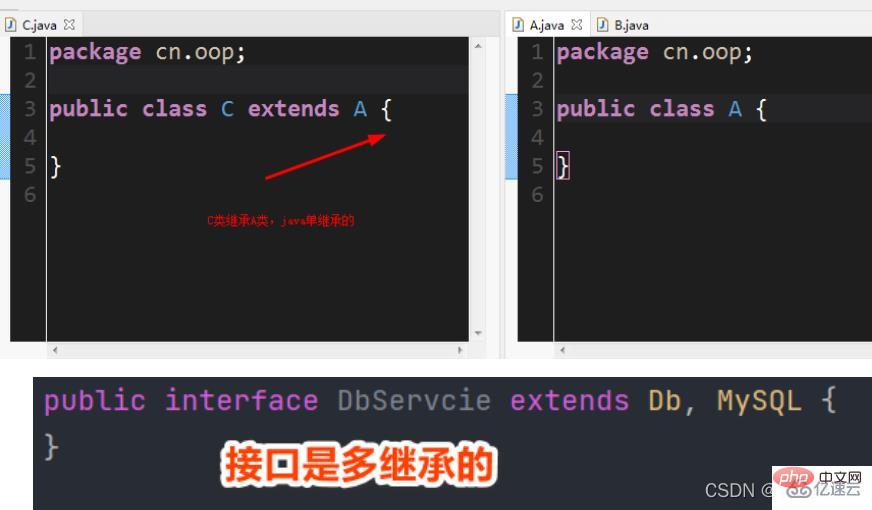
Why should we inherit? Because the subclass wants to add new features based on the parent class.
Subclasses inherit the methods and attributes of the parent class.
The following is an example analysis:
The parent class is a person, and the subclass is an experienced driver.
Human characteristics include: two hands, two eyes, two feet, the ability to eat and drink
The old driver has inherited the characteristics of humans, and has the added function of being able to drive.
The code is as follows:
This is a human being with the following attributes and functions.
public class Ren {
public final String shou = "两只手";
public final String jiao = "两只脚";
public final String yan = "两只眼";
public void chi() {
System.out.println("会吃");
}
public void he() {
System.out.println("会喝");
}}This is the veteran class, which inherits from humans. And there is an additional function that can drive
public class Siji extends Ren {
public void kai() {
System.out.println("会开车");
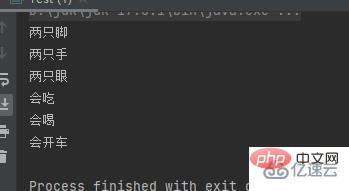
}}Test: Create the output attribute of the old driver object and call the method.
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Siji b = new Siji();
System.out.println(b.jiao);
System.out.println(b.shou);
System.out.println(b.yan);
b.chi();
b.he();
b.kai();
}}
Method rewriting, overloading
Rewriting Override: The method name, return type, and formal parameters are all the same. If this is the case, it must be an inheritance relationship.
Overloading: Methods with the same method name, return type, number of formal parameters, and different types do not necessarily have to be inheritance relationships. They can be in the same class, such as constructor method overloading
Rewrite
Because the subclass is not satisfied with the method of the parent class and wants to change it, this is how the subclass overrides the method of the parent class.
For example, a person can eat and drink, but an experienced driver doesn’t like the feature of eating and wants to change it to eat shit.
The code is as follows:
Old driver rewrites the human chi() method
The method name must be the same
public class Siji extends Ren {
public void kai() {
System.out.println("会开车");
}
public void chi() {
System.out.println("会吃屎");
}}Now rewrite the running test class
Overloading
Construction with parameters and construction without parameters are method overloading. In a class, there are Two methods with the same name, but their return value types, parameter types, and number of parameters are different.
Only one of the return value type, parameter type, and number of parameters of the two methods is different. But their method names are the same, so the two methods are overloaded.
The above is the detailed content of How to use inheritance, constructor methods, overriding and overloading methods in JAVA?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to Square Root in Java. Here we discuss how Square Root works in Java with example and its code implementation respectively.
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Armstrong Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to the Armstrong Number in Java. Here we discuss an introduction to Armstrong's number in java along with some of the code.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is







