How to use Java API?
1.API
1.1API Overview
What is API
API (Application Programming Interface): Application Programming Interface
The API
in java refers to the one provided in the JDK Java classes with various functions encapsulate the underlying implementation. We don't need to care about how these classes are implemented. We only need to learn how to use these classes. We can learn how to use these APIs through the help documentation.
1.2 Specific use of API help documentation
Open the help documentation

Find the input box in the Index tab
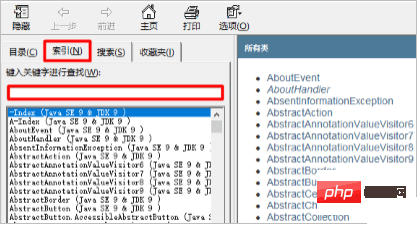
- ##Enter Random
# in the input box
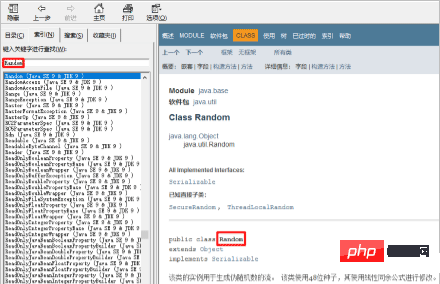 ##Look at which package the class is under
##Look at which package the class is under
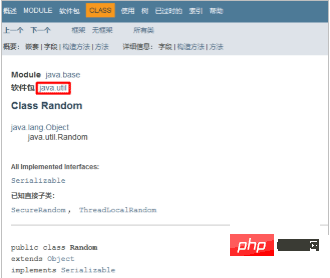
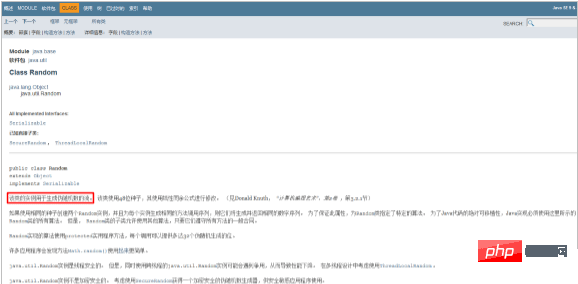
- Look at the description of the class
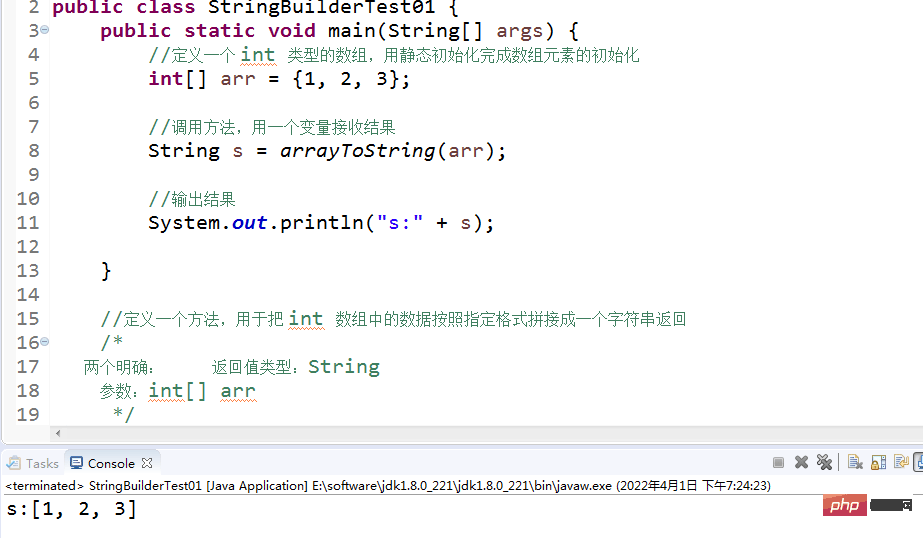
2.String class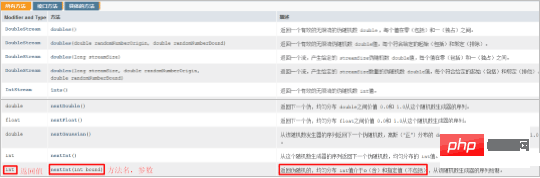
- Although String values are immutable, but they can be shared
- A string is effectively equivalent to a character array (char[]), but the underlying principle is a byte array (byte[] )
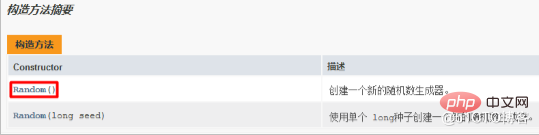
- 2.3Construction method of String class

- public class StringDemo01 { public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String();
System.out.println("s1:" s1);
// public String(char[] chs): Create a string object based on the contents of the character array
char[] chs = {'a', 'b', 'c'};
String s2 = new String (chs);
System.out.println("s2:" s2);
//public String(byte[] bys): Create a string object based on the contents of the byte array
byte[] bys = {97, 98, 99};
String s3 = new String(bys);
System.out.println("s3:" s3);
/ /String s = "abc"; Create a string object by direct assignment, the content is abc
String s4 = "abc";
System.out.println("s4:" s4);
}
}
The specific execution results are as follows:
2.4 The difference between the two ways of creating string objects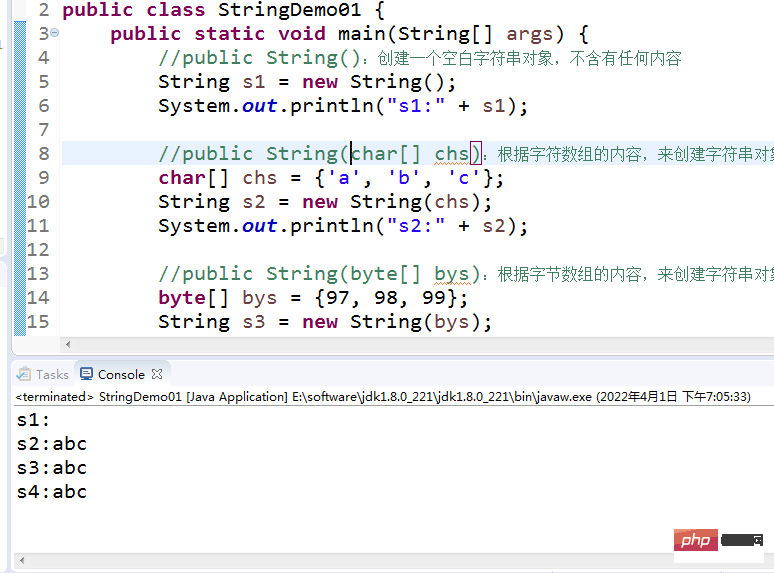
- String objects created through new, each time new will apply for a memory space, although the content is the same, the address value is different
- A string given in "" mode, as long as the character sequence is the same (order and case), no matter how many times it appears in the program code , the JVM will only create a String object and maintain it in the string pool
- Compare reference data types: Compare object address values
- 2.5.2 The role of the equals method
- public boolean equals(String s) Compares whether the contents of two strings are the same and distinguishes the size
public class StringDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Constructor method to get the object
char[] chs = {'a' , 'b', 'c'};
String s1 = new String(chs);
String s2 = new String(chs);
//Get the object by direct assignment
String s3 = "abc";
String s4 = "abc";
//Compare whether the string object addresses are the same
System.out.println(s1 == s2);
System.out.println(s1 == s3);
System.out.println(s3 == s4);
System.out.println("--------");
//Compare whether the string contents are the same
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));
System.out.println(s1.equals(s3));
System.out.println(s3.equals(s4));
}
}
The specific execution results are as follows:
<br>
Copy after loginCopy after login
/*<br>
Ideas:
1: Known username and password, definition Two strings can be represented
2: Enter the user name and password to log in with the keyboard, and use Scanner to implement
3: Compare the user name and password entered with the keyboard with the known user name and password, and give Corresponding tips. To compare the contents of strings, use the equals() method to implement
4: Use a loop to achieve multiple opportunities. The number of times here is clear. Use a for loop to implement it, and when the login is successful, use break to end the loop
*/
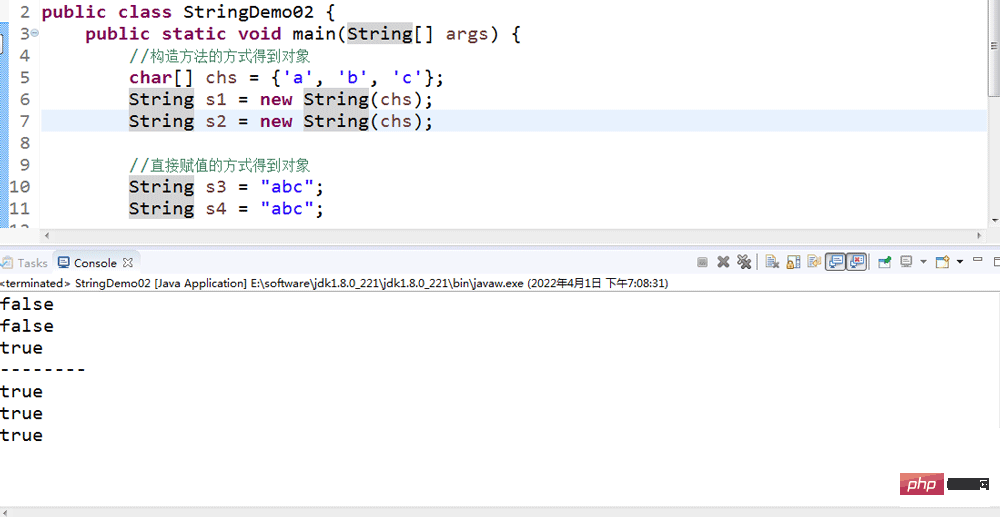
public class StringTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//If the username and password are known, just define two string representations
String username = "itheima";
String password = "czbk";
//Use a loop to achieve multiple opportunities. The number of times here is clear. Use a for loop to implement it. When the login is successful, use break to end the loop
for (int i=0; i
//Enter the username and password to log in with the keyboard, use Scanner to implement
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please enter the user name:");
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.println("Please enter the password:");
String pwd = sc.nextLine();
//Compare the user name and password entered by the keyboard with the known user name and password, and give corresponding prompts. String content comparison is implemented using the equals() method
if (name.equals(username) && pwd.equals(password)) {
System.out.println("Login successful");
break;
} else {
if(2-i == 0) {
System.out.println("Your account is locked, please contact the administrator");
} else {
//2,1,0
//i,0,1,2
System.out.println("Login failed, you still have" (2 - i) "second chances") ;
}
}
}
}
}
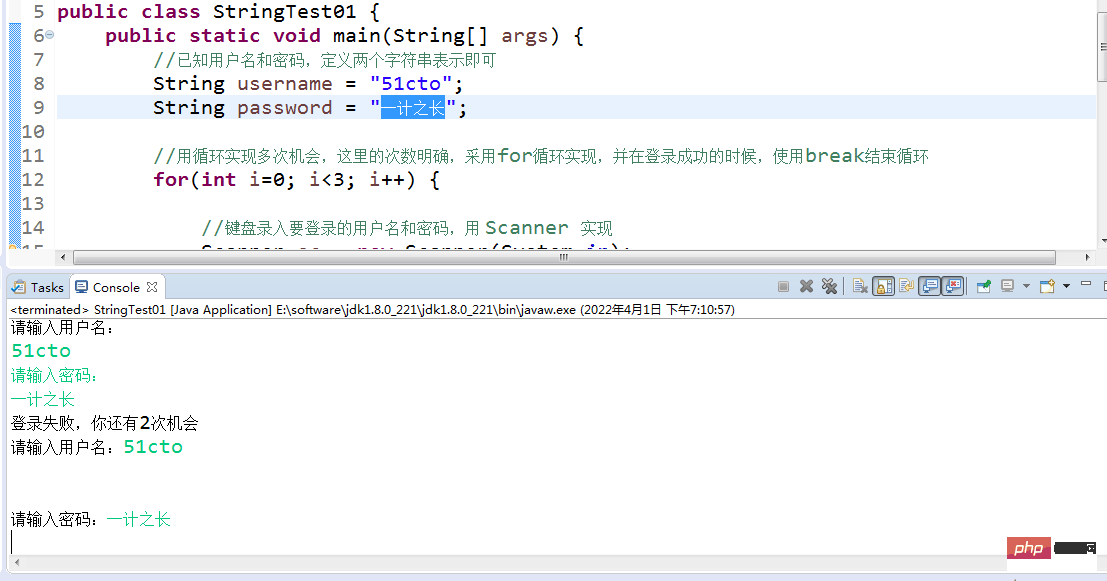
| Method name | Description |
| public boolean equals(Object anObject) | Compare the contents of strings, strictly case-sensitive (username and password) |
| public char charAt(int index) | Returns the char value at the specified index |
| public int length() | Return the length of this string |
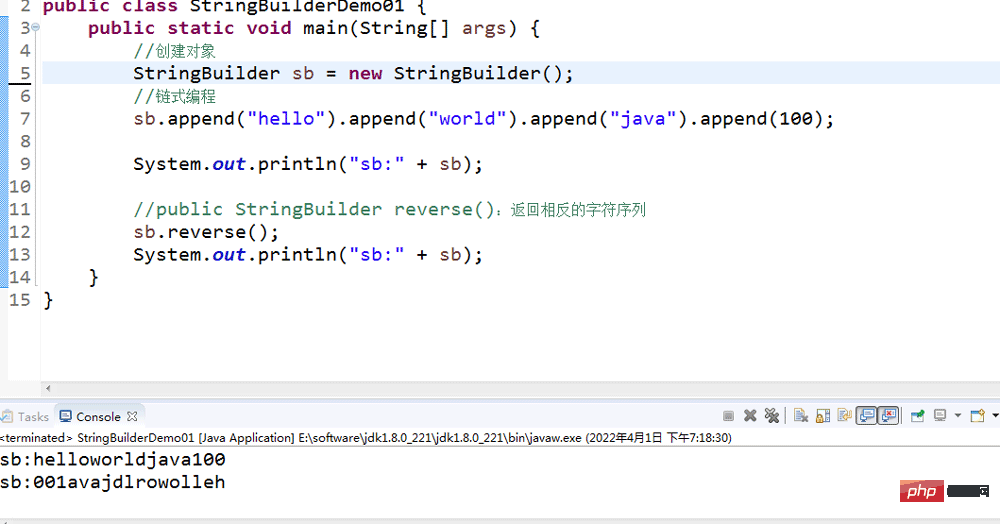
3.1 Overview of StringBuilder class
StringBuilder is a variable string class. We can think of it as a container. The variable here means that the content in the StringBuilder object is variable
3.2 The difference between the StringBuilder class and the String class
- String class: the content is immutable
- StringBuilder class: the content is mutable Change
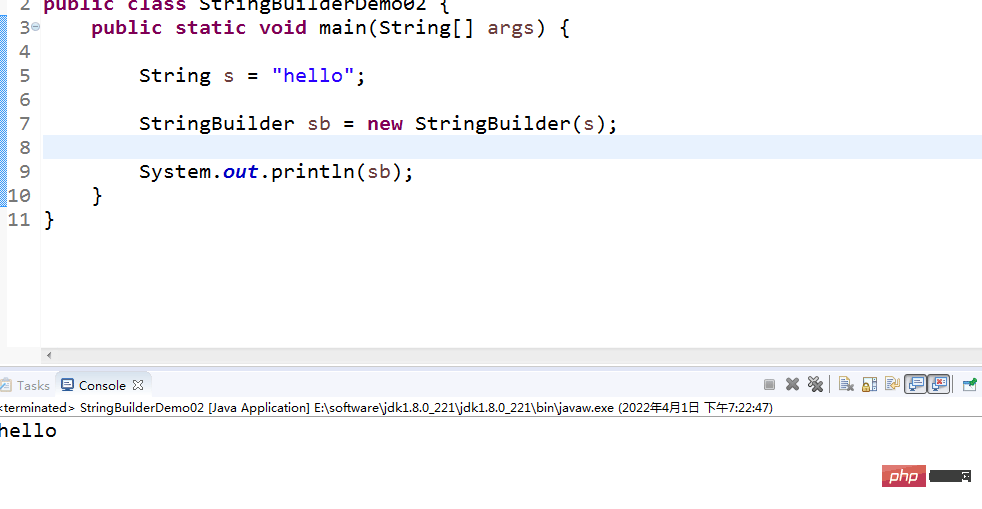
- 3.3Construction method of StringBuilder class
- Commonly used construction methods
| Description |
| ##Method name | Description |
public StringBuilder append (any type) |
Add data and return the object itself |
public StringBuilder reverse() |
Returns the reverse character sequence |
public int length() |
Returns the length, the actual stored value |
public String toString() |
You can convert StringBuilder into String through toString() |
The above is the detailed content of How to use Java API?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1376
1376
 52
52
 Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Square Root in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:26 PM
Guide to Square Root in Java. Here we discuss how Square Root works in Java with example and its code implementation respectively.
 Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Perfect Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Perfect Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check Perfect number in Java?, examples with code implementation.
 Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Random Number Generator in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:27 PM
Guide to Random Number Generator in Java. Here we discuss Functions in Java with examples and two different Generators with ther examples.
 Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Weka in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Weka in Java. Here we discuss the Introduction, how to use weka java, the type of platform, and advantages with examples.
 Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Smith Number in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to Smith Number in Java. Here we discuss the Definition, How to check smith number in Java? example with code implementation.
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.