 Java
Java
 javaTutorial
javaTutorial
 What is the database and cache data consistency scheme for Java concurrent programming?
What is the database and cache data consistency scheme for Java concurrent programming?
What is the database and cache data consistency scheme for Java concurrent programming?
1. Preface
In distributed concurrent systems, database and cache data consistency is a challenging technical difficulty. Assuming there is a complete industrial-grade distributed transaction solution, then the consistency of database and cache data will be easily solved. In fact, distributed transactions are currently immature.
2. Different voices
In the database and cache data consistency solution, there are various voices.
Operate the database first and then cache or cache first and then the database
Should the cache be updated or deleted
1. Sequence of operations
In a concurrent system, in the dual-write scenario of the database and cache, in order to pursue greater concurrency, the operations on the database and cache will obviously not be performed simultaneously. The former operation is successful and the latter is performed in an asynchronous manner.
As a mature industrial-grade data storage solution, relational database has a complete transaction processing mechanism. Once the data is placed on the disk, regardless of hardware failure, it can be responsibly said that the data will not be lost.
The so-called cache is nothing more than data stored in memory. Once the service is restarted, all cached data will be lost. Since it is called caching, be prepared for the loss of cached data at all times. Although Redis has a persistence mechanism, can it guarantee 100% persistence? Redis asynchronously persists data to disk. The cache is a cache, and the database is a database. They are two different things. Using a cache as a database is extremely dangerous.
From the perspective of data security, the database is operated first, and then the cache is operated asynchronously to respond to user requests.
2. Attitude when dealing with cache
Whether the cache is updated or deleted corresponds to the lazy style and the full style. From the perspective of thread safety practices, deleting the cache operation is relatively difficult. If query performance is satisfied under the premise of deleting the cache, then deleting the cache is preferred.
Although updating the cache can improve query efficiency, the concurrent dirty data caused by threads is more troublesome to process. The preface introduces other message middleware such as MQ, so it is not recommended unless necessary.
3. Thread concurrency analysis
The key to understanding the problems caused by thread concurrency is to first understand system interrupts. When the operating system is scheduling tasks, interrupts occur at any time. This is caused by thread data inconsistency. the origin. Taking 4- and 8-thread CPUs as an example, up to 8 threads can be processed at the same time. However, the operating system manages far more than 8 threads, so the threads proceed in a seemingly parallel manner.
Querying data
1. Non-concurrent environment
In a non-concurrent environment, there is nothing wrong with using the following method to query data: first query the cache, if the cached data does not exist, Query the database, update the cache, and return the results.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 |
|
If there is a serious flaw in a high-concurrency environment: when the cache fails, a large number of query requests pour in, all hitting the DB in an instant. The database connection resources may be exhausted, and the client responds with a 500 error. In severe cases, the database may be under too much pressure and the service may be shut down.
2. Concurrent environment
Therefore, in a concurrent environment, the above code needs to be modified and distributed locks are used. When a large number of requests pour in, the thread that obtains the lock has the opportunity to access the database to query data, and the remaining threads are blocked. When the data is queried and the cache is updated, the lock is released. The waiting thread rechecks the cache and finds that the data can be obtained, and responds directly to the cached data.
Distributed locks are mentioned here, so should we use table locks or row locks? Use distributed row locks to increase concurrency; use a secondary check mechanism to ensure that threads waiting to obtain locks can quickly return results
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
|
Update data
1. Non-concurrent environment
In a non-concurrent environment, the following code may cause data inconsistency (data is overwritten). Although using database-level optimistic locking can solve the problem of data being overwritten, invalid update traffic will still flow to the database.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
|
2. Concurrent environment
The use of database optimistic locking in the above analysis can solve the problem of data being overwritten in concurrent updates. However, when the same row of records is modified, the version number changes. Subsequent Concurrent requests flowing to the database are invalid traffic. The primary strategy to reduce database pressure is to intercept invalid traffic before the database.
Using distributed locks can ensure that concurrent traffic accesses the database in an orderly manner. Considering that optimistic locking has been used at the database level, the second and subsequent threads that obtain the lock operate the database as invalid traffic.
The thread adopts a timeout exit strategy when acquiring the lock. The thread waiting for the lock will timeout and exit quickly, respond to user requests quickly, and retry the update data operation.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 |
|
Dependent environment
The above code uses a tool class that encapsulates the lock.
1 2 3 4 5 |
|
LockOptionalPerform subsequent operations based on the status of the lock.
4. Database first, then cache
Data consistency
1. Problem description
Next, we will discuss whether there is concurrency in updating the database first and then deleting the cache. question.
(1) The cache just expired
(2) Request A to query the database and get an old value
(3) Request B to write the new value into the database
(4) Request B to delete Cache
(5) Request A to write the found old value into cache
The key to the above concurrency problem is that step 5 occurs after steps 3 and 4. It can be seen from the uncertain factors of operating system interruption that this situation may occur.
2. Solution
From the actual situation, writing data to Redis takes far less time than writing data to the database. Although the probability of occurrence is low, it will still happen. .
(1) Increase the cache expiration time
#Increase the cache expiration time to allow dirty data to exist within a certain time range until the next concurrent update occurs, Dirty data may occur. Dirty data exists periodically.
(2) Updates and queries share a row lock
Updates and queries share a row distributed lock, and the above problems no longer exist exist. When the read request acquires the lock, the write request is in a blocked state (timeout will fail and returns quickly), ensuring that step 5 is performed before step 3.
(3) Delayed cache deletion
Use RabbitMQ to delay cache deletion to remove the impact of step 5. Using an asynchronous method has almost no impact on performance.
Special cases
The database has a transaction mechanism to ensure the success of the operation; a single Redis instruction is atomic, but then combined it does not have atomic characteristics. Specifically, the database operation is successful, and then the application It hung up abnormally, resulting in the Redis cache not being deleted. This problem occurs when the Redis service network connection times out.
If a cache expiration time is set, dirty data will always exist before the cache expires. If the expiration time is not set, dirty data will exist until the next time the data is modified. (The database data has changed and the cache has not been updated)
Solution
Before operating the database, write a delayed cache deletion message to RabbitMQ, then perform the database operation and perform the cache deletion operation . Regardless of whether the code-level cache is successfully deleted, MQ deletes the cache as a guaranteed operation.
The above is the detailed content of What is the database and cache data consistency scheme for Java concurrent programming?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 1377
1377
 52
52
 Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
Java Spring Interview Questions
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:29 PM
In this article, we have kept the most asked Java Spring Interview Questions with their detailed answers. So that you can crack the interview.
 Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Break or return from Java 8 stream forEach?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:09 PM
Java 8 introduces the Stream API, providing a powerful and expressive way to process data collections. However, a common question when using Stream is: How to break or return from a forEach operation? Traditional loops allow for early interruption or return, but Stream's forEach method does not directly support this method. This article will explain the reasons and explore alternative methods for implementing premature termination in Stream processing systems. Further reading: Java Stream API improvements Understand Stream forEach The forEach method is a terminal operation that performs one operation on each element in the Stream. Its design intention is
 TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
TimeStamp to Date in Java
Aug 30, 2024 pm 04:28 PM
Guide to TimeStamp to Date in Java. Here we also discuss the introduction and how to convert timestamp to date in java along with examples.
 Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Create the Future: Java Programming for Absolute Beginners
Oct 13, 2024 pm 01:32 PM
Java is a popular programming language that can be learned by both beginners and experienced developers. This tutorial starts with basic concepts and progresses through advanced topics. After installing the Java Development Kit, you can practice programming by creating a simple "Hello, World!" program. After you understand the code, use the command prompt to compile and run the program, and "Hello, World!" will be output on the console. Learning Java starts your programming journey, and as your mastery deepens, you can create more complex applications.
 Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Java Program to Find the Volume of Capsule
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:37 AM
Capsules are three-dimensional geometric figures, composed of a cylinder and a hemisphere at both ends. The volume of the capsule can be calculated by adding the volume of the cylinder and the volume of the hemisphere at both ends. This tutorial will discuss how to calculate the volume of a given capsule in Java using different methods. Capsule volume formula The formula for capsule volume is as follows: Capsule volume = Cylindrical volume Volume Two hemisphere volume in, r: The radius of the hemisphere. h: The height of the cylinder (excluding the hemisphere). Example 1 enter Radius = 5 units Height = 10 units Output Volume = 1570.8 cubic units explain Calculate volume using formula: Volume = π × r2 × h (4
 How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
How to Run Your First Spring Boot Application in Spring Tool Suite?
Feb 07, 2025 pm 12:11 PM
Spring Boot simplifies the creation of robust, scalable, and production-ready Java applications, revolutionizing Java development. Its "convention over configuration" approach, inherent to the Spring ecosystem, minimizes manual setup, allo
 Java Made Simple: A Beginner's Guide to Programming Power
Oct 11, 2024 pm 06:30 PM
Java Made Simple: A Beginner's Guide to Programming Power
Oct 11, 2024 pm 06:30 PM
Java Made Simple: A Beginner's Guide to Programming Power Introduction Java is a powerful programming language used in everything from mobile applications to enterprise-level systems. For beginners, Java's syntax is simple and easy to understand, making it an ideal choice for learning programming. Basic Syntax Java uses a class-based object-oriented programming paradigm. Classes are templates that organize related data and behavior together. Here is a simple Java class example: publicclassPerson{privateStringname;privateintage;
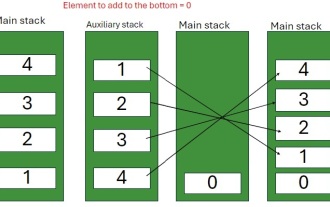 Java Program to insert an element at the Bottom of a Stack
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:59 AM
Java Program to insert an element at the Bottom of a Stack
Feb 07, 2025 am 11:59 AM
A stack is a data structure that follows the LIFO (Last In, First Out) principle. In other words, The last element we add to a stack is the first one to be removed. When we add (or push) elements to a stack, they are placed on top; i.e. above all the



