Is quantum computing more dangerous than artificial intelligence?
Due to the power and revolutionary applications of this technology, quantum computing projects are likely to have become part of the defense research of many countries.
Today’s artificial intelligence is as self-aware as a paperclip. Despite the hype - such as a Google engineer's bizarre claim that his company's AI system has "come alive" and Tesla CEO Elon Musk's tweet predicting that computers will possess human intelligence by 2029 - But the technology still isn't capable of simple, everyday tasks. This includes driving a vehicle, especially when encountering unexpected situations that require even the tiniest bit of human intuition or thinking.
The sensationalism surrounding artificial intelligence is surprising considering that Musk himself has warned that if countries do not regulate it, artificial intelligence technology could become humanity’s “biggest existential threat.” Not surprising. But whether or not computers can achieve human-like intelligence, the world has summoned a different, equally destructive AI demon: precisely because today’s AI is nothing more than a crude, unintelligent system that uses algorithms and other technologies to process superhuman amounts of automated decision-making data, and its widespread use by relevant agencies and businesses to broadly obtain information, create deepfakes, and unleash autonomous lethal weapons has posed a danger to humanity.
And compounding the danger is the lack of any regulation of artificial intelligence. Instead, unaccountable technology conglomerates like Google and Meta have acted as judge and jury in all areas of artificial intelligence. They are silencing dissenting voices, including their own engineers who warn of dangers.
The world’s failure to contain the demons of artificial intelligence—or, rather, the crude technology masquerading as artificial intelligence—should serve as a profound warning. There's an even more powerful emerging technology that has the potential to wreak havoc, especially if it's combined with artificial intelligence: quantum computing. We urgently need to understand the potential impact of this technology, regulate it, and prevent it from falling into the wrong hands before it’s too late. The world must not repeat the mistake of refusing to regulate artificial intelligence.
Although still in its infancy, quantum computing operates on a very different basis than today’s semiconductor-based computers. If the various projects underway around the world are successful, these machines will be so powerful that they can complete tasks in seconds that would take traditional computers millions of years.
Semiconductors represent information as a series of ones and zeros – that’s why we call it digital technology. Quantum computers, on the other hand, use a computing unit called a qubit. By adding a counterintuitive property to quantum physics called superposition, a qubit can hold the values of 1 and 0 simultaneously. If you think this is confusing, you're right—it's difficult even for experienced engineers to master. Therefore, two qubits can represent the sequence 1-0, 1-1, 0-1 and 0-0, all in parallel and at the same time. This results in a significant increase in computing power, which increases exponentially with each additional qubit.
If quantum physics leaves the experimental stage and enters everyday applications, it will find many uses and change many aspects of life. With their ability to quickly process large amounts of data that would overwhelm any system today, quantum computers have the potential to enable better weather forecasting, financial analysis, logistics planning, space research and drug discovery. And some actors may well use them for nefarious purposes, compromising bank records, private communications and passwords on every digital computer in the world. Today's cryptography encodes data in large combinations of numbers that are impossible to crack in a reasonable amount of time using classical numerical techniques. But quantum computers - which exploit quantum mechanical phenomena such as superposition, entanglement and uncertainty - may be able to try combinations so quickly that they can break encryption by brute force almost instantaneously.
To be clear, quantum computing is still in its infancy—although we can only guess where exactly. Due to the huge potential and revolutionary applications of this technology, quantum computing projects are likely to already become part of the defense research of various countries. Such research is often shrouded in secrecy, and there is much talk and speculation about reaching milestones. France, Russia, Germany, the Netherlands, the UK, Canada and India are all known to be pursuing projects, while in the US, companies including IBM, Google, Intel and Microsoft are working on quantum computing, along with various startups, defense contractors and universities. .
Despite the lack of publicity, some basic applications have been credible demonstrated, including quantum sensors capable of detecting and measuring electromagnetic signals. One such sensor is used to accurately measure Earth's magnetic field from the International Space Station.
In another experiment, Dutch researchers sent quantum information through a rudimentary quantum communications network. Rather than using conventional optical fibers, the scientists used three small quantum processors to instantly transmit qubits from the transmitter to the receiver. These experiments have yet to show practical applications, but they could lay the foundation for a future quantum internet in which quantum data can be transmitted securely through a network of quantum computers at faster than the speed of light. Until now, this has only been possible in the realm of science fiction.
The U.S. Biden administration considered the risk of losing the quantum computing race so imminent and dire that it issued two presidential directives in May: One to place the National Quantum Initiative advisory board directly at the White House Under the authority, another directs government agencies to ensure that the United States leads in quantum computing while reducing the potential security risks that quantum computing poses to cryptographic systems.
The experiment also aims to combine quantum computing with artificial intelligence to transcend the limitations of traditional computers. Today, large machine learning models take months to train on digital computers because of the massive calculations that must be performed—OpenAI’s GPT-3, for example, has 175 billion parameters. When these models grow to trillions of parameters—a necessity for today’s dumb AIs to become smart—they will take longer to train. Quantum computers can greatly speed up this process while using less energy and space. In March 2020, Google launched TensorFlow Quantum, the first quantum artificial intelligence hybrid platform, taking the search for patterns and anomalies in large amounts of data to a new level. Combined with quantum computing, artificial intelligence could theoretically lead to more revolutionary results than critics have been warning about artificial intelligence perception.
Given the potential scope and capabilities of quantum technology, the mistakes of artificial intelligence must not be repeated—regulatory failures that introduced algorithmic bias into the world, exacerbated human biases, social media support of conspiracy theories, and suspicion of AI institutions attack. Democracy fueled by AI-generated fake news and social media posts. The danger lies in the ability of machines to make autonomous decisions, with flaws in computer code leading to unexpected and often harmful results. In 2021, the quantum community issued a call to action to urgently address these issues. Additionally, critical public and private intellectual property related to quantum technologies must be protected from theft and misuse.
In addition, national defense issues are also involved. In the world of security technology, the Holy Grail is a so-called quantum computer relevant to cryptanalysis—a system capable of breaking much of the public-key cryptography used by digital systems around the world, such as blockchains. It's a very dangerous capability in the hands of a hostile power.
Therefore, in addition to accelerating research, targeted controls on developers, users and exports should be implemented without delay. Patents, trade secrets, and related intellectual property rights should be rigorously protected—a return to the kind of technological control that was a major element of security policy during the Cold War. The revolutionary potential of quantum computing takes risk to a new level.
Finally, in order to avoid serious ethical problems with artificial intelligence and machine learning, countries need to develop control measures that are consistent with the power of technology and respect democratic values, human rights and fundamental freedoms. Governments must urgently start thinking about regulations, standards and responsible use, and learn from the way countries have handled or mishandled other revolutionary technologies, including artificial intelligence, nanotechnology, biotechnology, semiconductors and nuclear fission. Therefore, we must not make the same mistakes we made with artificial intelligence again and prepare now for tomorrow’s quantum age.
The above is the detailed content of Is quantum computing more dangerous than artificial intelligence?. For more information, please follow other related articles on the PHP Chinese website!

Hot AI Tools

Undresser.AI Undress
AI-powered app for creating realistic nude photos

AI Clothes Remover
Online AI tool for removing clothes from photos.

Undress AI Tool
Undress images for free

Clothoff.io
AI clothes remover

AI Hentai Generator
Generate AI Hentai for free.

Hot Article

Hot Tools

Notepad++7.3.1
Easy-to-use and free code editor

SublimeText3 Chinese version
Chinese version, very easy to use

Zend Studio 13.0.1
Powerful PHP integrated development environment

Dreamweaver CS6
Visual web development tools

SublimeText3 Mac version
God-level code editing software (SublimeText3)

Hot Topics
 Bytedance Cutting launches SVIP super membership: 499 yuan for continuous annual subscription, providing a variety of AI functions
Jun 28, 2024 am 03:51 AM
Bytedance Cutting launches SVIP super membership: 499 yuan for continuous annual subscription, providing a variety of AI functions
Jun 28, 2024 am 03:51 AM
This site reported on June 27 that Jianying is a video editing software developed by FaceMeng Technology, a subsidiary of ByteDance. It relies on the Douyin platform and basically produces short video content for users of the platform. It is compatible with iOS, Android, and Windows. , MacOS and other operating systems. Jianying officially announced the upgrade of its membership system and launched a new SVIP, which includes a variety of AI black technologies, such as intelligent translation, intelligent highlighting, intelligent packaging, digital human synthesis, etc. In terms of price, the monthly fee for clipping SVIP is 79 yuan, the annual fee is 599 yuan (note on this site: equivalent to 49.9 yuan per month), the continuous monthly subscription is 59 yuan per month, and the continuous annual subscription is 499 yuan per year (equivalent to 41.6 yuan per month) . In addition, the cut official also stated that in order to improve the user experience, those who have subscribed to the original VIP
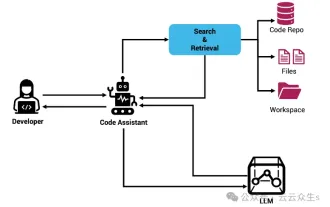 Context-augmented AI coding assistant using Rag and Sem-Rag
Jun 10, 2024 am 11:08 AM
Context-augmented AI coding assistant using Rag and Sem-Rag
Jun 10, 2024 am 11:08 AM
Improve developer productivity, efficiency, and accuracy by incorporating retrieval-enhanced generation and semantic memory into AI coding assistants. Translated from EnhancingAICodingAssistantswithContextUsingRAGandSEM-RAG, author JanakiramMSV. While basic AI programming assistants are naturally helpful, they often fail to provide the most relevant and correct code suggestions because they rely on a general understanding of the software language and the most common patterns of writing software. The code generated by these coding assistants is suitable for solving the problems they are responsible for solving, but often does not conform to the coding standards, conventions and styles of the individual teams. This often results in suggestions that need to be modified or refined in order for the code to be accepted into the application
 Seven Cool GenAI & LLM Technical Interview Questions
Jun 07, 2024 am 10:06 AM
Seven Cool GenAI & LLM Technical Interview Questions
Jun 07, 2024 am 10:06 AM
To learn more about AIGC, please visit: 51CTOAI.x Community https://www.51cto.com/aigc/Translator|Jingyan Reviewer|Chonglou is different from the traditional question bank that can be seen everywhere on the Internet. These questions It requires thinking outside the box. Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly important in the fields of data science, generative artificial intelligence (GenAI), and artificial intelligence. These complex algorithms enhance human skills and drive efficiency and innovation in many industries, becoming the key for companies to remain competitive. LLM has a wide range of applications. It can be used in fields such as natural language processing, text generation, speech recognition and recommendation systems. By learning from large amounts of data, LLM is able to generate text
 Can fine-tuning really allow LLM to learn new things: introducing new knowledge may make the model produce more hallucinations
Jun 11, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Can fine-tuning really allow LLM to learn new things: introducing new knowledge may make the model produce more hallucinations
Jun 11, 2024 pm 03:57 PM
Large Language Models (LLMs) are trained on huge text databases, where they acquire large amounts of real-world knowledge. This knowledge is embedded into their parameters and can then be used when needed. The knowledge of these models is "reified" at the end of training. At the end of pre-training, the model actually stops learning. Align or fine-tune the model to learn how to leverage this knowledge and respond more naturally to user questions. But sometimes model knowledge is not enough, and although the model can access external content through RAG, it is considered beneficial to adapt the model to new domains through fine-tuning. This fine-tuning is performed using input from human annotators or other LLM creations, where the model encounters additional real-world knowledge and integrates it
 To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
To provide a new scientific and complex question answering benchmark and evaluation system for large models, UNSW, Argonne, University of Chicago and other institutions jointly launched the SciQAG framework
Jul 25, 2024 am 06:42 AM
Editor |ScienceAI Question Answering (QA) data set plays a vital role in promoting natural language processing (NLP) research. High-quality QA data sets can not only be used to fine-tune models, but also effectively evaluate the capabilities of large language models (LLM), especially the ability to understand and reason about scientific knowledge. Although there are currently many scientific QA data sets covering medicine, chemistry, biology and other fields, these data sets still have some shortcomings. First, the data form is relatively simple, most of which are multiple-choice questions. They are easy to evaluate, but limit the model's answer selection range and cannot fully test the model's ability to answer scientific questions. In contrast, open-ended Q&A
 SOTA performance, Xiamen multi-modal protein-ligand affinity prediction AI method, combines molecular surface information for the first time
Jul 17, 2024 pm 06:37 PM
SOTA performance, Xiamen multi-modal protein-ligand affinity prediction AI method, combines molecular surface information for the first time
Jul 17, 2024 pm 06:37 PM
Editor | KX In the field of drug research and development, accurately and effectively predicting the binding affinity of proteins and ligands is crucial for drug screening and optimization. However, current studies do not take into account the important role of molecular surface information in protein-ligand interactions. Based on this, researchers from Xiamen University proposed a novel multi-modal feature extraction (MFE) framework, which for the first time combines information on protein surface, 3D structure and sequence, and uses a cross-attention mechanism to compare different modalities. feature alignment. Experimental results demonstrate that this method achieves state-of-the-art performance in predicting protein-ligand binding affinities. Furthermore, ablation studies demonstrate the effectiveness and necessity of protein surface information and multimodal feature alignment within this framework. Related research begins with "S
 Improved detection algorithm: for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:33 PM
Improved detection algorithm: for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images
Jun 06, 2024 pm 12:33 PM
01 Outlook Summary Currently, it is difficult to achieve an appropriate balance between detection efficiency and detection results. We have developed an enhanced YOLOv5 algorithm for target detection in high-resolution optical remote sensing images, using multi-layer feature pyramids, multi-detection head strategies and hybrid attention modules to improve the effect of the target detection network in optical remote sensing images. According to the SIMD data set, the mAP of the new algorithm is 2.2% better than YOLOv5 and 8.48% better than YOLOX, achieving a better balance between detection results and speed. 02 Background & Motivation With the rapid development of remote sensing technology, high-resolution optical remote sensing images have been used to describe many objects on the earth’s surface, including aircraft, cars, buildings, etc. Object detection in the interpretation of remote sensing images
 Five schools of machine learning you don't know about
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Five schools of machine learning you don't know about
Jun 05, 2024 pm 08:51 PM
Machine learning is an important branch of artificial intelligence that gives computers the ability to learn from data and improve their capabilities without being explicitly programmed. Machine learning has a wide range of applications in various fields, from image recognition and natural language processing to recommendation systems and fraud detection, and it is changing the way we live. There are many different methods and theories in the field of machine learning, among which the five most influential methods are called the "Five Schools of Machine Learning". The five major schools are the symbolic school, the connectionist school, the evolutionary school, the Bayesian school and the analogy school. 1. Symbolism, also known as symbolism, emphasizes the use of symbols for logical reasoning and expression of knowledge. This school of thought believes that learning is a process of reverse deduction, through existing






